Latest Antibiotics For Utis
- Vabomere is a combination carbapenem antibiotic and beta-lactamase inhibitor. Vabomere was first approved in August of 2017.
- Vabomere is used for the treatment of adult patients with complicated urinary tract infections due to susceptible Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae species complex.
- Vabomere is given as an intravenous infusion every 8 hours. Dosage adjustments are required in patients with varying degrees of kidney impairment.
Zemdri
- Zemdri is an aminoglycoside antibacterial for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis. Zemdri was first approved in February of 2015.
- Zemdri is used against certain Enterobacteriaceae in patients who have limited or no alternative treatment options. Zemdri is an intravenous infusion, administered once daily.
See also: Treatment Options for UTIs
Recommendations For Uti Prevention
To prevent urinary tract infection, some research suggests that the following may be helpful:
- Increasing fluid intake: The doctor may recommend increased fluid intake to help flush bacteria out of the urinary system.
- Drinking cranberry juice: Drinking 8 ounces of cranberry juice a day may help prevent recurrent UTIs. People who take blood thinners such as warfarin or are prone to kidney stones should check with a physician before trying this approach.
- Proper hygiene: Regular bathing keeps the genital area bacteria free, and women should wipe front-to-back after using the bathroom so as to avoid introducing bacteria into the urethra.
Which Are The Different Types Of Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis can be classified into:.
- Acute pyelonephritis: Acute pyelonephritis most frequently occurs as a result of ascending movement of bacteria from a lower UTI . It is a more serious infection than a cystitis but it is usually well managed with the proper treatment. It can be a serious condition in elderly or immunocompromised people .
- Chronic pyelonephritis: It is a more serious infection often due to congenital urinary structural defects. The main possible complications are sepsis and kidney failure .
Pyelonephritis usually happens associated with vesicoureteral reflux where urine flows backward from the bladder. In these cases, there are usually recurrent acute pyelonephritis or chronic pyelonephritis.
You May Like: Acupuncture Points For Urinary Incontinence
Causes And Risk Factors Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, which consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. While any of these parts can become infected, most UTIs involve the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder and the urethra . A UTI that infects the bladder is called cystitis one that infects the urethra is called urethritis.
The majority of UTIs that affect the bladder and the urethra are caused by E. coli or other bacteria that are normally found in the digestive tract, which can travel from the anus to the urethra. UTIs that affect the urethra are also caused by sexually transmitted infections, including herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma. Most of the time, urinating flushes out lingering bacteria in the urethra before it causes problems, though your body isnt always able to do this.
Less often, UTIs involve the upper urinary tract, which includes the kidneys and the ureters . A UTI infection in the kidneys, called pyelonephritis or a kidney infection, most often begins in the bladder and moves up through the ureters to one or both kidneys. In certain cases, a kidney infection can lead to serious health problems.
What Is The Urinary Tract
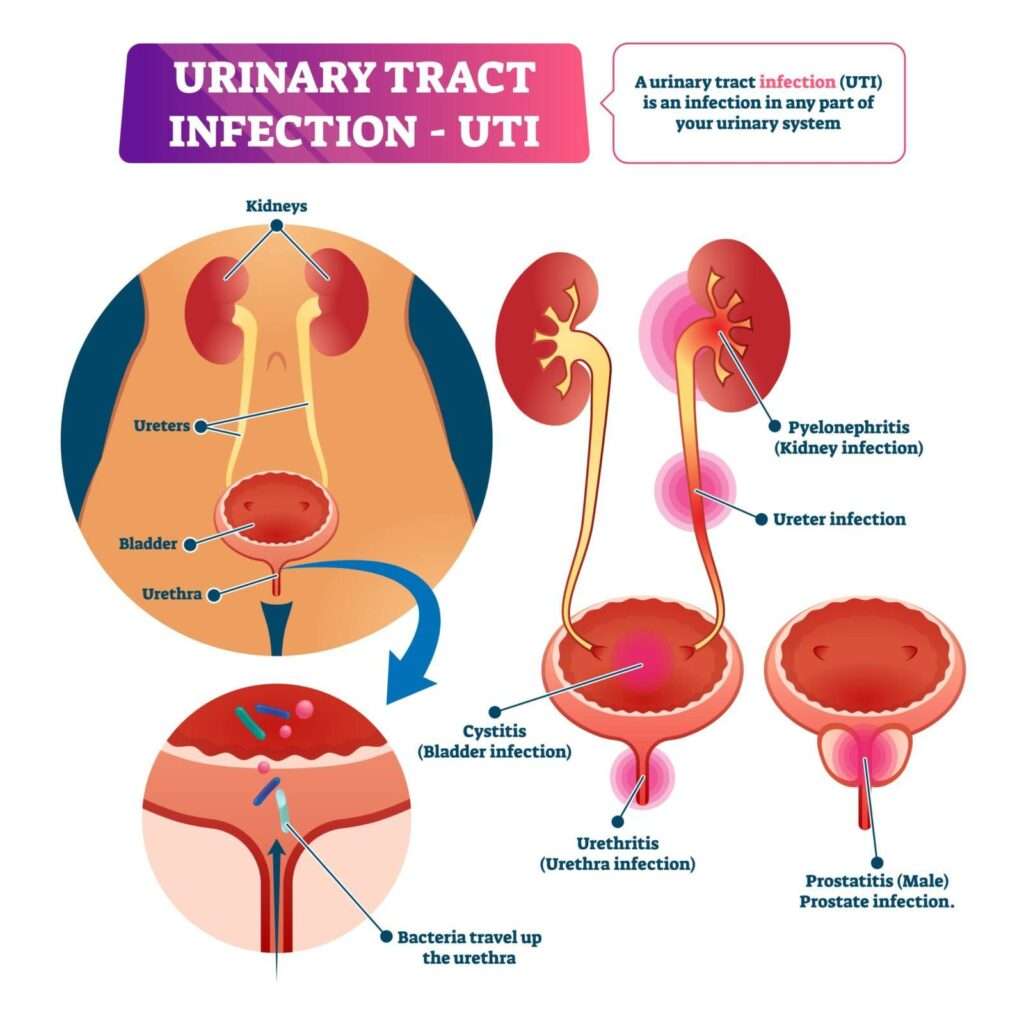
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the body’s liquid waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body removing waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
Recommended Reading: Exercises To Prevent Urinary Incontinence
How To Treat Urinary Tract Infection In Women
Doctors can treat lower and upper urinary tract infections with antibiotics. Lab tests can determine the best antibiotic for treatment. Most uncomplicated lower tract infections are treated with a three-day course of antibiotics, but women who are pregnant or have immunosuppressive diseases such as diabetes often need to take antibiotics for a longer period.
People with upper canal infections are usually treated with a 10-to-14-day course of antibiotics. People with serious upper tract infections may need to be treated in hospital with antibiotics given through a vein . This is especially true in cases where nausea, vomiting and fever increase the risk of dehydration and prevent the person from taking oral antibiotics.
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically respond very well to treatment. A UTI can be uncomfortable before you start treatment, but once your healthcare provider identifies the type of bacteria and prescribes the right antibiotic medication, your symptoms should improve quickly. Its important to keep taking your medication for the entire amount of time your healthcare provider prescribed. If you have frequent UTIs or if your symptoms arent improving, your provider may test to see if its an antibiotic-resistant infection. These are more complicated infections to treat and may require intravenous antibiotics or alternative treatments.
Read Also: What’s Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infection And Its Causes
It is any inflammation of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra, as these are the components of the human urinary system, which is responsible for purifying blood through the kidneys and then excreting waste and excess water in urine through the ureters and collecting it in the bladder and finally draining it out through the urethra.
Urinary tract infections are common in general, and anyone can get them regardless of their gender or age, but they affect women more commonly, especially after they reach the age of menopause, The reason for this is due to the shorter length of the urethra in women compared to men, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter it.
Urinary tract infection results from a bacterial infection that is naturally present in the human digestive system when it travels through the urethra to infect the rest of the urinary system.
There are factors that may increase the chance of a urinary tract infection, such as suffering from medical conditions that block the urethra, such as kidney stones, or using certain types of contraceptives such as condoms containing antiseptics, Or suffering from a deficiency in the bodys immunity resulting from either chemotherapy, HIV infection or others, and these factors also include prostate enlargement in men, or diabetes, or the use of urinary catheters.
About Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are common infections that can affect the bladder, the kidneys and the tubes connected to them.
Anyone can get them, but they’re particularly common in women. Some women experience them regularly .
UTIs can be painful and uncomfortable, but usually pass within a few days and can be easily treated with antibiotics.
This page is about UTIs in adults. There is a separate article about UTIs in children.
This page covers:
Recommended Reading: Function Of Kidney In Urinary System
How To Prevent Another Uti
While many women have heard they should drink cranberry juice for a UTI, drinking it wont cure a UTI. Likewise, home remedies are not cures, but they may help you feel better faster or prevent a future UTI. Some ways to prevent another UTI are:
- Empty your bladder every 2 to 3 hours. Avoid holding your urine for long periods of time.
- After a bowel movement, wipe your perineal area from front to back, using each tissue only once.
- Empty your bladder before and after sex.
- Wear all-cotton or cotton-crotch underwear and pantyhose.
- Change your underwear and pantyhose every day or whenever soiled.
- Avoid irritants such as bubble baths and perfumed vaginal cleaners or deodorants. While soaking in a bubble bath looks relaxing its not the best for your urinary tract.
- And, if you are past menopause and get frequent UTIs, vaginal estrogen may help to rejuvenate and protect genital tissue.
Uti Causes And Risk Factors
The most common cause of a UTI in the urethra is a sexually transmitted disease. Chlamydia and gonorrhea are two STDs that can cause a UTI. STDs are also the most common cause of UTIs in younger men.
Prostate problems can also cause UTIs. An enlarged prostate is common in older men and can block the flow of urine. This can increase the odds that bacteria will build up and cause a UTI.
Prostatitis, which is an infection of the prostate, shares many of the same symptoms as UTIs.
Diabetes and other medical issues that affect your immune system can also make you more likely to get a UTI.
Also Check: Probiotics For Women’s Urinary Health
Urinary Tract Infection And Surgery
Surgery may be recommended in cases of recurrent UTIs. A need for surgery is common in men who have prostatitis. The inflamed prostate increases pressure on the bladder, which interferes with urine flow.
Often the same bacteria that cause prostatitis can also cause UTIs in men, so after antibiotic treatment is complete, surgery can be done to reduce the size of the prostate. Some surgeries that require the use of a catheter afterward can increase the risk for UTI.
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI.
A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service. They may be able to give antibiotics if they’re needed.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Get Urinary Tract Infection
Check If Its A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Common Side Effects With Antibiotic Use
Each antibiotic is responsible for its own unique list of side effects, and the list is usually extensive. Be sure to discuss your individual antibiotic side effects with your healthcare provider. However, there are side effects that are common to most antibiotics, regardless of class or drug:
Related: Common Side Effects from Antibiotics, Allergies and Reactions
Recommended Reading: Best Probiotic For Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Recommended Treatment
The ultimate goal of acute pyelonephritis treatment is the control and remission of the infection. In addition, the treatment tries to reduce acute symptoms that usually persist more than 48 hours after the start of treatment.
The most common treatments used are:
- Antibiotics: They are used to fight against the bacterial infection. The most used ones are antibiotics such as TMP/SMX and ciprofloxacin. If the infection is severe or the risk of complications is high, they must be given by an intravenous injection. Antibiotics may be required for a long time.
- Analgesics- antipyretics: Drugs to fight against pain, fever and weakness.
- Intravenous fluids: To prevent dehydration and ensure that medication reach the kidneys quickly.
Chronic pyelonephritis may require high doses of antibiotics for as long as six months to clear the infection. Surgery is sometimes necessary if the patient has complications caused by obstructions, or to eradicate infection.
The treatment of any complication should be precise and effective. It may include hospitalization in an intensive care unit, cardiac monitoring and any other treatment. The underlying causes must be treated.
Urine cultures are repeated as part of the follow-up of patients with chronic pyelonephritis to ensure that bacterial infection is completely cleared.
How Can It Be Prevented
The treatment of cystitis, bladder infections and other UTI may prevent in many cases the development of pyelonephritis.
In addition, it is necessary the prevention of conditions that increase the risk, such as vesicoureteral reflux and obstructive uropathy.
Medically reviewed by our Medical staff on 18-02-2022
You May Like: Can Vitamins Cause Urinary Problems
Complications Of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are an extremely common condition, and most people recover quickly with antibiotic treatment. However, if left untreated the infection can spread throughout the urinary tract system, increasing in severity and causing complications.
In some cases, the infection can reach the kidneys in the upper urinary tract, an infection known as pyelonephritis. Without medical intervention, this can lead to permanent kidney damage. Possible complications from untreated UTIs include:
- Formation of abscesses within or around the kidneys
- Swelling of the kidneys, also known as hydronephrosis
- , also known as blood poisoning
All of these complications are serious and require immediate medical attention.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Canine Urinary S O
Are There Home Remedies For A Urinary Tract Infection
There are a variety of self-care measures and other treatments available for urinary tract infections.
- Use a hot-water bottle to ease the pain.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods, all of which irritate the bladder.
- There are some indications that cranberry juice can help fight a urinary tract infection.
Because the symptoms of a urinary tract infection mimic those of other conditions, someone should see a health care professional if a urinary tract infection is suspected. A urine test is needed to confirm an infection. Self-care is not recommended.
Also Check: Best Treatment For Urinary Retention
Which Department Should I Go To For Urinary Tract Infection In Women
A family doctor can treat most female urinary tract infections. For evaluation if you have a chronic kidney infection You should see a urologist, who specializes in urinary disorders, or a nephrologist, who specializes in kidney disorders. These doctors, who are specialized in their field, will identify the relevant problem, and apply the best treatment method for you.
What About Antibiotic Resistance
Resistance rates for antibiotics are always variable based on local patterns in the community and specific risk factors for patients, such as recent antibiotic use, hospital stay or travel. If you have taken an antibiotic in the last 3 months or traveled internationally, be sure to tell your doctor.
High rates of antibiotic resistance are being seen with both ampicillin and amoxicillin for cystitis , although amoxicillin/clavulanate may still be an option. Other oral treatments with reported increasing rates of resistance include sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and the fluoroquinolones. Resistance rates for the oral cephalosporins and amoxicillin/clavulanate are still usually less than 10 percent.
Always finish taking your entire course of antibiotic unless your doctor tells you to stop. Keep taking your antibiotic even if you feel better and you think you don’t need your antibiotic anymore.
If you stop your treatment early, your infection may return quickly and you can develop resistance to the antibiotic you were using previously. Your antibiotic may not work as well the next time you use it.
Recommended Reading: Apple Cider Vinegar For Urinary Tract Infection
Lower Tract Uti Symptoms:
- nausea
- vomiting
Sometimes a UTI can occur without causing obvious symptoms. For example, if your immune system is weakened, a UTI may not trigger your bodys infection-fighting response. Many of the symptoms you experience with a UTI are part of this response, including inflammation, pain and fever. Older adults who have a UTI may develop cognitive symptoms such as delirium.
Blood in the urine can indicate a serious health issue. Let your health care provider know right away if you see blood in your urine, with or without other UTI symptoms.
Treating Urinary Tract Infections
Your recommended treatment plan by your GP will depend on whether your infection is in the upper or lower urinary tract.
Both types of urinary tract infection can usually be treated at home using a course of antibiotics.
If an upper UTI is more serious or there is increased risk of complications, you may need hospital treatment.
Also Check: Walgreens Urinary Tract Infection Test Strips Instructions
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
Patients with three or more infections per year should be offered either continuous low-dose antibiotic prophylaxis, patient-initiated, or postcoital prophylaxis if the onset of infection is linked to sexual intercourse .7 Before a prophylactic regimen is chosen, a urine culture should be performed to determine the susceptibility of the pathogen. The duration of continuous prophylactic therapy is usually 6 months to a year. Unfortunately, within 6 months of discontinuing antibiotic prophylaxis, 40% to 60% of women develop a urinary tract infection, and prophylaxis must be resumed.20 Patient-initiated therapy at the onset of symptoms has been shown to be effective in young, healthy nonpregnant women.21 Short-course regimens have been advocated for patient-initiated therapy in compliant women with frequently recurring and symptomatic urinary tract infections. The major advantages of short-course therapy over continuous therapy are convenience and the avoidance of antibiotic toxicity symptomatic infections are not prevented, however. For postcoital prophylaxis, nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or fluoroquinolones taken within 2 hours after sexual intercourse have been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of recurrent cystitis.22, 23
Can I Treat A Uti Without Antibiotics
UTI treatment without antibiotics is NOT usually recommended. An early UTI, such as a bladder infection , can worsen over time, leading to a more severe kidney infection . However, a small study has suggested early, mild UTIs might clear up on their own. It’s always best to check with your doctor if you are having UTI symptoms.
Pregnant women should always see a doctor as soon as possible if they suspect they might have a UTI, as this can lead to a greater risk of delivering a low birth weight or premature infant.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Health Cranberry Pills