How Successful Is The Artificial Sphincter Surgery Is
The artificial sphincter surgery is quite successful. The patients who have undergone this surgery have shown great improvement in their condition. There are very few complications associated with this surgery and the patients are able to lead a normal life after the surgery.
Nearly 200000 Patients Have Had An Aus System Inserted
Urination occurs when muscles in the bladder tighten to facilitate the flow of urine out of the body through the urethra. Spinal nerves also play a role in controlling bladder muscles. If anything happens that disrupts the way nerves and muscles communicate in this area, it could result in urine leaks.
If common treatments such as medication and bladder training exercises are ineffective, a silicone cuff referred to as an artificial urinary sphincter may allow the urethra to be sufficiently sealed off at the point where it meets the bladder until urination is necessary.
Contact Us Today
How To Prepare For Surgery
Before you undergo surgery, we must make sure that your lab results, including your urine cultures, come back normal. If there are abnormalities or something from your medical history that potentially compromises your ability to receive anesthesia, you may need to visit your primary care provider or another specialist first. This is to ensure that your health is optimized for the best possible outcome.
If youve been cleared for surgery, you will need to shower with antibiotic soap for several days before your operation. This will be provided for you at our clinic.
You May Like: Azithromycin Urinary Tract Infection Dosage
Living With An Artificial Urinary Sphincter
The only time youll need to interact with the device is when you squeeze the pump to urinate.
Its important to go to all your scheduled follow-ups to make sure the device is functioning properly. AUS devices eventually need to be replaced, but they can last for many years.
AUS devices are compatible with MRIs, but its still a good idea to let healthcare professionals know ahead of time that you have one.
Other treatments for male urinary incontinence include:
Artificial Urinary Sphincter: Long
![[PDF] New Artificial Urinary Sphincter Devices in the Treatment of Male ...](https://www.urinaryhealthtalk.com/wp-content/uploads/pdf-new-artificial-urinary-sphincter-devices-in-the-treatment-of-male.png)
Drogo K. MontagueAcademic Editor: Received
Abstract
The published evidence concerning the safety, efficacy, and patient satisfaction for implantation of the current model of the artificial urinary sphincter in men with post prostatectomy urinary incontinence was the objective of this review. A Pub Med English language literature search from 1995 to 2011 was performed. A majority of men who undergo AUS implantation for post prostatectomy urinary incontinence achieve satisfactory results . Infection rates range from 0.46 to 7%, cuff erosion rates range from 3.8 to 10%, and urethral atrophy ranges from 9.6 to 11.4%. Kaplan-Meier 5 year projections for freedom from any reoperation were 50% for a small series and 79.4% for a larger series. Kaplan-Meier projections for freedom from mechanical failure were 79% at 5 years and 72% at 10 years. In another series 10 year projections for freedom from mechanical failure were 64%. Although the artificial urinary sphincter is the gold standard for the treatment of this disorder, most men will continue to need at least one pad per day for protection, and they are subject to a significant chance of future AUS revision or replacement.
1. Introduction
| AS 800 . |
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy
In a study of 54 men with mean follow-up of 7.2 years, 54% were socially continent . Mean pad score before AUS implantation was 2.75, and it decreased to 0.97 after AUS implantation .
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Self Care
Things To Keep In Mind
It’s important to tell your other health care providers that you have an artificial urinary sphincter. Implants are safe for getting an MRI, if needed. However, if youre having a dental procedure, youll likely need additional antibiotics. Or if you need a urinary catheter, a urologist or experienced physician will need to deactivate the cuff to prevent any damage.
What Is The Evidence Base For This Information
This leaflet includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association of Urological Surgeons, the Department of Health and evidence based sources it is, therefore, a reflection of best practice in the UK. It is intended to supplement any advice you may already have been given by your urologist or nurse specialist as well as the surgical team at Addenbrookes. Alternative treatments are outlined below and can be discussed in more detail with your urologist or specialist nurse.
You May Like: Is Azithromycin Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Risk Of Bias For Articles In The Meta
We assessed the risk of bias for articles eligible in the final meta-analysis, which was modified from the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale , including representativeness of the cohort, ascertainment of intervention, documentation that outcome of interest was not present at the start of the study, comparability of cohorts on the basis of the design or analysis, assessment of outcomes, follow-up long enough for outcomes to occur, and adequacy of follow-up of cohorts. After reviewing the full-text carefully, low risk of bias, high risk of bias, and unclear risk of bias were applied to each eligible article according to stated information. All the procedure was completed on RevMan 5.3 .
Artificial Urinary Sphincter Patient Reviews
If you are considering an artificial urinary sphincter to treat your incontinence, you may be wondering what others who have undergone the procedure think about it. In this blog post, well take a look at some AUS patient reviews to give you a better idea of what to expect.Overall, patients who have had an AUS implanted report high levels of satisfaction with the results. The majority of patients say that their incontinence symptoms are much improved or even completely resolved after having the device installed. Many also report that their quality of life has greatly increased as they no longer have to worry about leakage or embarrassing accidents.There are a few potential side effects associated with an AUS, but these are generally mild and temporary. The most common complaints include discomfort during urination and difficulty emptying the bladder completely. These side effects usually resolve within a few weeks as the body adjusts to the new device.If you are struggling with incontinence, an artificial urinary sphincter may be worth considering. The vast majority of patients who have one implanted report high levels of satisfaction with both the short- and long-term results.
Also Check: Does A Urinary Tract Infection Smell
Artificial Urinary Sphincter Risks
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks. The most significant is infection. Infection rates with implants are quite lowaround one percent. There are, however, certain conditions or events that do increase your risk of infection:
- spinal cord injury,
- chronic use of steroids such as prednisone, or
- undergoing a re-do surgery or in the setting of extensive scarring.
One of the great medical advances of artificial urinary sphincters is the use of a coating that holds in antibiotics to prevent bacteria from getting on the device. Our urologic surgeons use many meticulous techniques before and during surgery to minimize a patient’s risks of infection as much as possible.
What Is The Best Artificial Urinary Sphincter
The best artificial urinary sphincter is the one that is best suited to the individual patient. There are many different types and brands of artificial urinary sphincters, and the best type for each patient depends on several factors, including the severity of incontinence, the patients age and health, and personal preferences. Some patients may prefer a manual device that they can control themselves, while others may prefer an automated device that is implanted under the skin and activated by a remote control. Ultimately, the best artificial urinary sphincter for each patient is the one that provides the most effective incontinence relief with the fewest side effects.
Also Check: Is Urinary Tract Infection A Sexually Transmitted Disease
Scale Of The Problem In The Uk And Use Of Nhs Resources
Men undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer frequently report the troublesome symptom of stress urinary incontinence . Prevalence estimates vary widely between 5% and 57% depending on definition, timing of assessment after surgery, and population characteristics. The rate of recovery of continence plateaus at around 12 months after surgery. This was confirmed in a recent large HTA-funded RCT of pelvic-floor muscle training in patients who suffered incontinence 6 weeks after radical prostatectomy. Subsequently, 40% had persistent UI at 1 year, with half of these having severe UI needing containment which then did not improve further during the second 12 months up to 24 months after the original surgery .
This means that of the 6000 patients currently undergoing radical prostatectomy in the UK each year, 1200 will be using additional treatments for resultant stress incontinence beyond 12 months. UI has a major impact on quality of life, including profound loss of self-esteem together with restrictions on work, social interaction and personal relationships including sexual life. The utility value associated with a person with UI is 0.72 compared to 0.93 in a comparable age-matched population . This is particularly devastating for men undergoing radical prostatectomy since they were typically without any urinary problems prior to the surgery, are fit for their age, and have a long life expectancy having generally been cured of their prostate cancer.
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
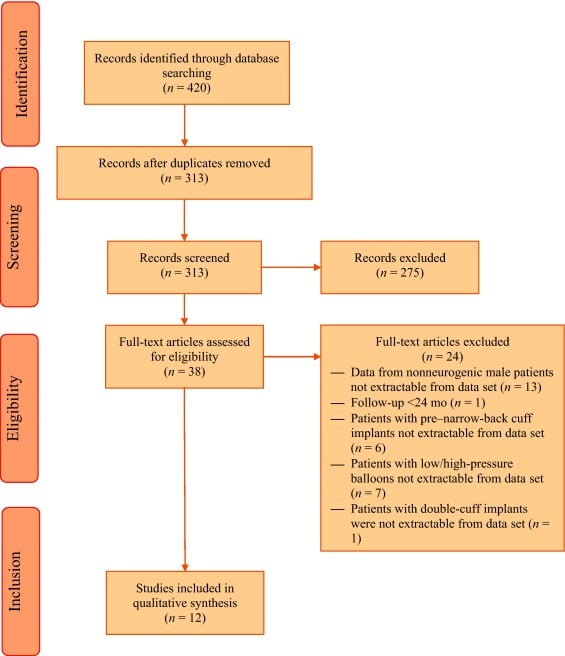
The articles were eligible if they contained the comparison of AUS and slings for the treatment of moderate male SUI in patients above 18 years old. As not all studies reported 24 h pad test results, we discussed and decided that the degree of moderate male SUI was defined as overall pad use 5 pad/d. The mean overall follow-up for both AUS and slings groups was required to be at least 12 months. Cohort study, case-controlled study, and randomized controlled study were all included. Reviews, guidelines, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses were excluded. Conference articles, editorial comments, protocols, and cases involved with pediatric patients were also excluded. The article language was restricted to English, and the articles with inadequate follow-up of < 12 months in either the AUS group or slings group were excluded.
Read Also: Royal Canin Urinary So Canned Food
Impact Of Radiation Therapy On Outcomes Of Artificial Urinary Sphincter: A Systematic Review And Meta
- 1Department of Pelvic Floor Comprehensive Diagnosis and Treatment Center, Huzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Huzhou, China
- 2Department of Endocrine, Huzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Huzhou, China
Background: To compare incontinence rates and complications in patients receiving artificial urinary sphincter with or without radiotherapy .
Methods: PubMed, Embase, ScienceDirect, CENTRAL, and Google Scholar databases were searched for studies comparing outcomes of AUS between patients with and without RT. Search limits were from 1st January 2002 to 15th September 2021.
Results: Eighteen studies were included. Meta-analysis revealed statistically significant reduced odds of the absence of incontinence in the RT group as compared to the no-RT group. We also noted statistically significant increased risk of revision surgery in the RT group . There was increased risk of infections and erosions in the RT group, but the difference was significant only for erosions. Meta-analysis revealed a statistically significant increased risk of explantation in patients with RT but there was no difference in the risk of urethral atrophy and mechanical failure between the two groups.
Systematic Review Registration:, identifier: NCT02612389.
How Long Does It Take To Recover From Artificial Sphincter Surgery
If you have had surgery to insert an artificial sphincter, you may be wondering how long it will take to recover. The good news is that most people make a full recovery within 6-8 weeks.During this time, it is important to follow your doctors instructions for care and rest. You may need to take pain medication and avoid strenuous activity. You should also expect some drainage from the surgery site.Most people can return to work and their normal activities within a few weeks. However, it is important to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard. If you experience any pain or other problems, be sure to contact your doctor right away.
Recommended Reading: Medicine For Male Urinary Tract Infection
List Of The Pros Of An Artificial Sphincter
1. You can return to normal activities almost immediately.Most men can return to doing most of their regular activities the day after they receive the surgery to implant their artificial sphincter. This advantage is possible even though a general anesthesia is used to place the device. You will need to wear a scrotal support for the first week after your surgery. If that support gets wet, then youâll need to replace it. After 4-6 weeks after the surgery, you can typically return to strenuous activities like riding a bicycle, playing golf, and lifting objects over 10 pounds.
2. It is a highly successful treatment for incontinence.Men receive this medical intervention more often than women because incontinence is a common problem after prostate removal or radiation therapy. It offers a success rate of 90% when installed correctly. Most men who have an artificial sphincter say that they are happy with it because the risks of leakage are minimal, especially during the day. Although there is a minor risk of failure at any time with this device, a majority of men can walk out of the hospital confident in what this technology provides.
The liquid in the cuff flows into the balloon, which then refills over time to restrict the urethra once again. If the leakage stops with placement, then you get to be in control of when and where you urinate.
Men and women can also have the artificial sphincter placed in their lower belly if those options are not reasonable for some reason.
Harm From Catheterisation In Patients With Implanted Artificial Urinary Sphincters
Through its core work to review patients safety events recorded on national systems, such as the National Reporting and Learning System , the new Learn from Patient Safety Events service , and other sources, the National Patient Safety Team identified a risk of harm from catheterisation in patients with implanted artificial urinary sphincters.
An artificial urinary sphincter is a surgically implanted device that is placed around the urethra or bladder neck, which is inflated to achieve continence or deflated to empty the bladder. The device is internally implanted and is not visible externally. If patients with an AUS require a catheter to be fitted, the cuff on the device must be deflated and the pump deactivated to avoid tissue damage, trauma, or infection.
The teams review of the NRLS identified three incidents, over a three-year period, describing a lack of awareness the patient had an AUS device prior to a catheter being fitted. This information was shared with the British Association of Urological Surgeons and the British Association of Urological Nurses. To help prevent further patients being harmed the association updated its guidance documents for catheter care and patient information leaflets. The issue was also added to a consensus document providing guidance to staff for long term catheter care.
Don’t Miss: Why Do You Keep Getting Urinary Tract Infections
Characteristics Of Included Studies
Five studies with a total of 509 patients were recruited. Two were in Korea, 1 in the USA, and the other countries were Canada and Italy. The included patients’ criteria varied slightly among studies. Four presented with moderate SUI and the other one included postprostatectomy incontinence with a mean pad use of 4.8 per day. Surgical success definition and other detailed information were illustrated in Table 1. We found that generally, all studies defined surgical success as daily pad use with 01 pad/d. One study included male patients according to the Male Stress Incontinence Grading System with moderate scores. There were various types of slings in studies, including AdVance, AdVanceXP, Augus, TiLOOP, and so on.
Table 1. Characteristics of included studies.
Evidence For Surgical Management For Men With Urinary Incontinence After Prostate Surgery
We have analysed long-term follow-up data from men approached for the Men After Prostate Surgery trial and found that around 70% of men still reported some urine leakage 4 to 6 years after a radical prostatectomy , and 39% after a transurethral resection of prostate . Of this cohort, 25% and 5% of men respectively were using pads, and 8% and 2% had leakage several times a day of a moderate or large amount of urine. A further 15 men had already had an AUS operation , and six a male sling . In addition to these, a further 5% and 3% of men were considering surgery for incontinence.
Also Check: How Can A Male Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
Two authors independently extracted the following data: author details, publication year, study type, study location, sample size, inclusion/exclusion criteria, age of the patients, percentage of diabetics, the severity of pre-operative incontinence , timing of RT, study outcomes and follow-up. Since residual urinary incontinence was variably measured amongst the included studies, we chose to compare the number of patients with no residual incontinence post AUS placement. Definitions of infection, erosion, explantation, urethral atrophy, and revision surgery were as per the included studies. Since erosions and explantations represent revision surgeries, for studies not reporting data of ârevision surgeryâper se, we included data of erosions/explantations in the meta-analysis for revision surgery.
The methodological quality of studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale . It was conducted by two authors independent of each other. Any disagreements were solved by a discussion. Studies were assessed for selection of study population, comparability, and outcomes, with each domain being awarded a maximum of four, two, and three points respectively. The maximum score which can be awarded was nine. Studies with nine points were considered to have a low risk of bias, seven to eight points were considered to have a moderate risk of bias and those with scores of six and below were with a high risk of bias.