Can I Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
You can usually prevent a urinary tract infection with lifestyle changes. These tips can include:
In some post-menopausal women, a healthcare provider may suggest an estrogen-containing vaginal cream. This may reduce the risk of developing a UTI by changing the pH of the vagina. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have recurrent UTIs and have already gone through menopause.
Over-the-counter supplements are also available for UTIs. These are sometimes recommended for people who have frequent UTIs as another way to prevent them. Talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplements and ask if these could be a good choice for you.
Are There Home Remedies For A Urinary Tract Infection
There are a variety of self-care measures and other treatments available for urinary tract infections.
- Use a hot-water bottle to ease the pain.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods, all of which irritate the bladder.
- There are some indications that cranberry juice can help fight a urinary tract infection.
Because the symptoms of a urinary tract infection mimic those of other conditions, someone should see a health care professional if a urinary tract infection is suspected. A urine test is needed to confirm an infection. Self-care is not recommended.
Urinary Tract Infections Or Utis: What To Know About Symptoms Treatment Prevention
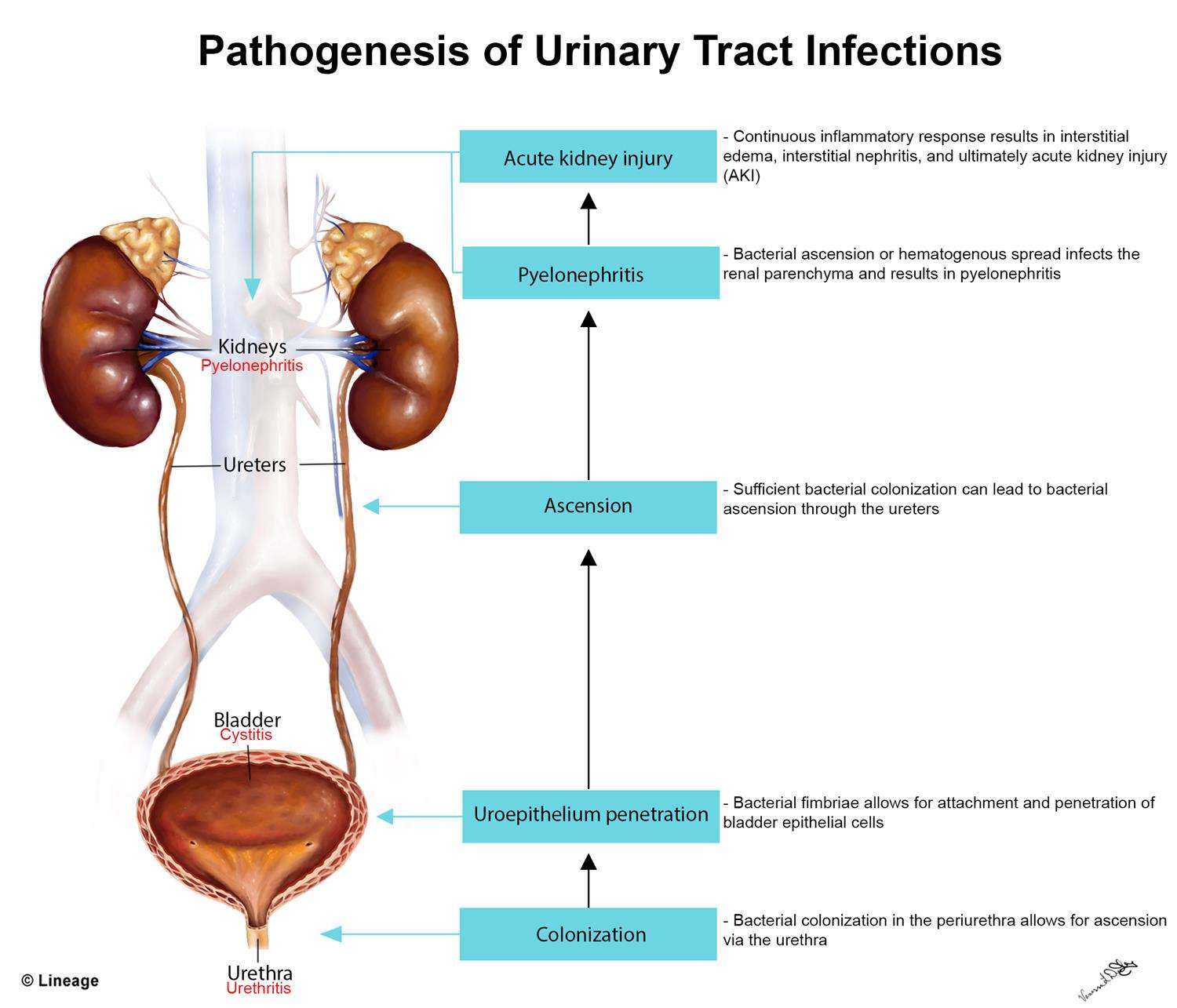
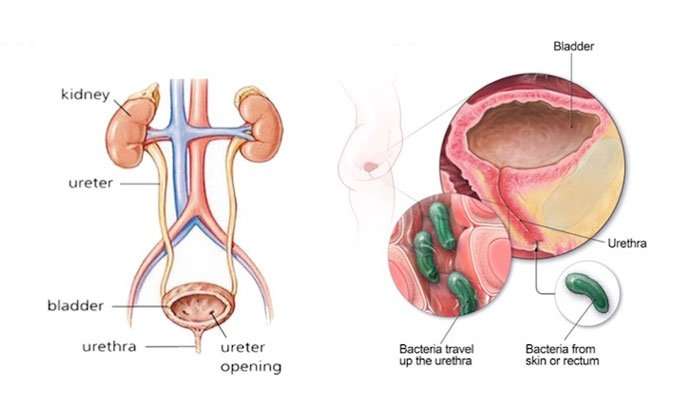
UTIs are caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, which consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. While any of these parts can become infected, most UTIs involve the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder and the urethra . A UTI that infects the bladder is called cystitis one that infects the urethra is called urethritis.
The majority of UTIs that affect the bladder and the urethra are caused by E. coli or other bacteria that are normally found in the digestive tract, which can travel from the anus to the urethra. UTIs that affect the urethra are also caused by sexually transmitted infections, including herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma. Most of the time, urinating flushes out lingering bacteria in the urethra before it causes problems, though your body isnt always able to do this.
Less often, UTIs involve the upper urinary tract, which includes the kidneys and the ureters . A UTI infection in the kidneys, called pyelonephritis or a kidney infection, most often begins in the bladder and moves up through the ureters to one or both kidneys. In certain cases, a kidney infection can lead to serious health problems.
Read Also: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Urinary S O Moderate Calorie
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically respond very well to treatment. A UTI can be uncomfortable before you start treatment, but once your healthcare provider identifies the type of bacteria and prescribes the right antibiotic medication, your symptoms should improve quickly. Its important to keep taking your medication for the entire amount of time your healthcare provider prescribed. If you have frequent UTIs or if your symptoms arent improving, your provider may test to see if its an antibiotic-resistant infection. These are more complicated infections to treat and may require intravenous antibiotics or alternative treatments.
Favorite Site For Urinary Health Podcasts
Podcasts arent just for politics, laughs, and murder mysteries. The American Urological Association has a fantastic one called, aptly, the Urology Care Podcast, which covers topics like sexual health myths, UTIs, prostate cancer, and more. Currently there are more than 140 episodes to listen to, ranging from about 4 minutes to 28 minutes long.
Also Check: Neurological Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Urine That Has A Strong Odor
Urine contains water and a small concentration of waste products. It typically has a subtle odor of its own. While urine odor may vary, it does not have a strong smell.
When there is an infection in the urinary tract, the urine may take on a foul-smelling odor. The main cause of the smell is bacterial overgrowth. Pus and/or blood from the infection may also contribute to the strong smell.
Bacteria can contaminate urine. This will result in a fishy and unpleasant odor. In some women, urine can come with a strong ammonia smell, or foul.
In addition, slightly sweet-smelling urine is often the first indication that UTI may be present.
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection And Alcohol
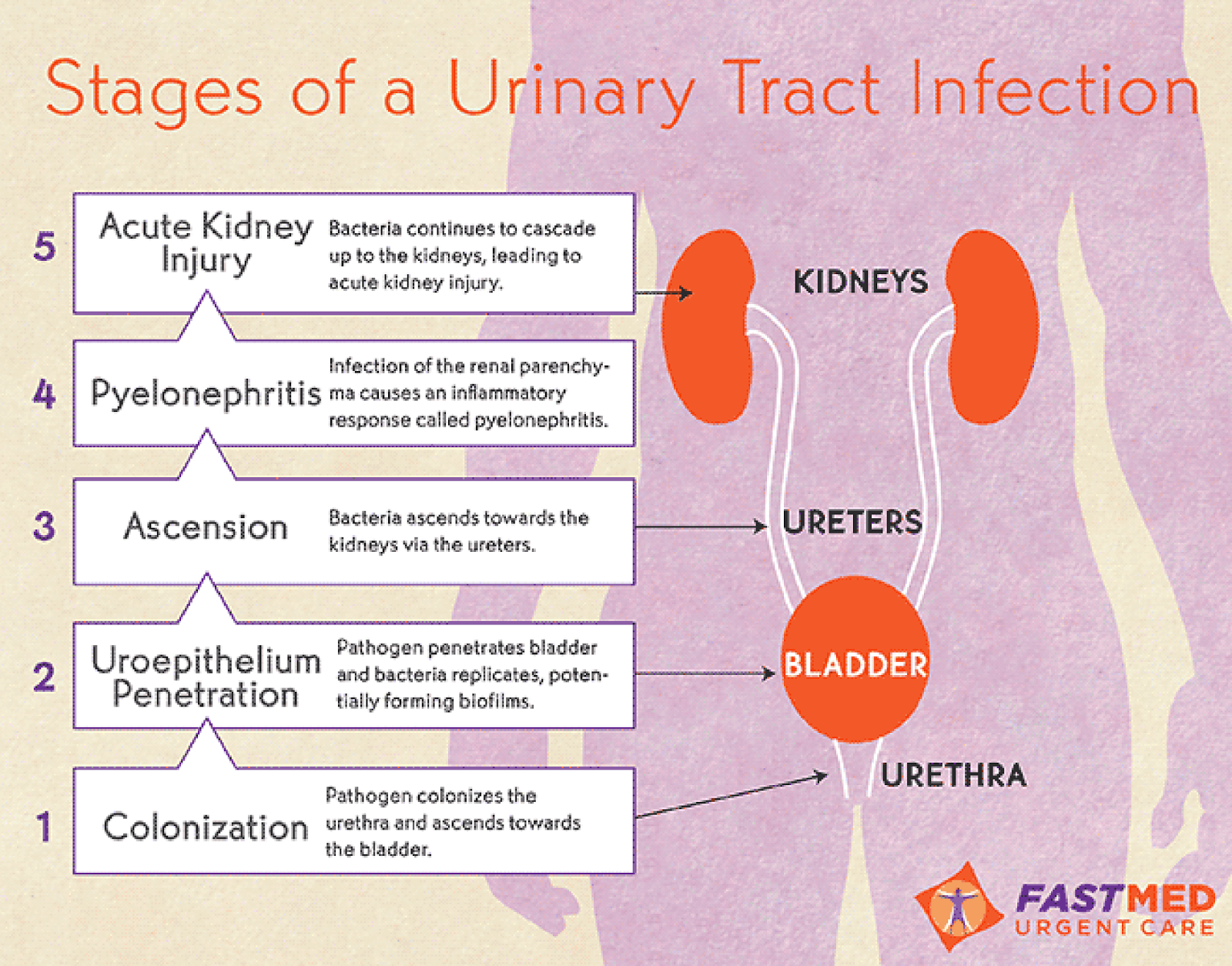
Types Of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections can occur anywhere within the urinary tract, which includes the:
- Urethra, the tube that passes urine out of the body from the bladder. Infection of the urethra is also known as urethritis
- Bladder, the organ that collects and stores urine. Infection of the bladder is also known as cystitis
- Ureters, the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
- Kidneys, the organs that filter blood, eliminating waste via the urine. Infection of one or both kidneys is also known as pyelonephritis
The majority of UTIs affect the bladder and/or the urethra. These are known as lower urinary tract infections.
However, the infection can also travel up the urinary tract to reach the kidneys. In rare cases, the ureters may also become infected. These are called upper urinary tract infections. They are less common than lower tract infections and tend to be more severe.
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
Don’t Miss: Will Az Pack Help A Urinary Tract Infection
Burning Or Painful Urination
People with UTI often feel a burning sensation when they urinate. This symptom is one of the key signs that a person may have a urinary tract infection.
Burning urination or painful urination is medically known as dysuria. It can be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions.
A urinary tract infection makes the lining of the bladder and urethra become red and irritated.
In addition to the burning sensation, there is also an itchy or stinging feeling as the urine comes out. The pain can be felt at the start of urination or after urination.
Pain is often felt in the urethra. These are the tubes that carry urine to the bladder. The pain can also extend to the area around the genitals.
Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis
Your doctor will review your symptoms with you first and conduct a physical exam.
A urine sample is then taken to test for microbes. It is important to use a clean-catch sample for testing, which is done midstream rather than at the beginning. This helps to eliminate bacteria or yeast from your skin.
A large number of white blood cells in your urine indicate an infection, and a urine culture will help identify the specific microbe causing the infection.
Special testing is required if a viral infection is suspected, but they are rare causes of UTIs. Viral UTIs are more common in those with weakened immune systems or those who have had organ transplants.
If your doctor thinks you may have an upper tract infection, a blood count and culture is necessary to make sure the infection has not yet spread to your bloodstream through infected kidneys.
Some individuals have recurring UTIs, and these involve additional testing to identify possible abnormalities in the tract that could be the cause.
Don’t Miss: Why Am I Prone To Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary Tract Infection And Surgery
Surgery may be recommended in cases of recurrent UTIs. A need for surgery is common in men who have prostatitis. The inflamed prostate increases pressure on the bladder, which interferes with urine flow.
Often the same bacteria that cause prostatitis can also cause UTIs in men, so after antibiotic treatment is complete, surgery can be done to reduce the size of the prostate. Some surgeries that require the use of a catheter afterward can increase the risk for UTI.
Risk Factors In Women
Women are particularly susceptible to urinary tract infections because their urethra is shorter, meaning the infection can spread throughout the urinary tract more easily. Additionally, the anal and urinary openings of a woman are in closer proximity, increasing the risk of bacteria spreading between the two.
In addition to the above, women are also susceptible to the following risk factors for UTIs:
- Sexual intercourse can contribute to the spread of genital or anal bacteria, especially with a new sexual partner when the rate of sexual activity is typically higher. However, UTIs are not a sexually transmitted disease
- Spermicides and birth control methods which use spermicides can affect the natural balance of healthy bacteria within the vagina
- Antibiotics can also alter the natural bacterial balance within the vagina
- Diaphragms can place pressure on a womanââ¬â¢s urethra, resulting in the possibility of the bladder not emptying properly
- Pregnancy. As the uterus grows in pregnancy, it can put added weight on the bladder, leading to the possibility of the bladder not emptying properly
- Menopause can cause hormonal changes which affect the vaginaââ¬â¢s natural bacterial balance
Also Check: How To Cure A Urinary Tract Infection In A Woman
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the body’s liquid waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body removing waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Also Check: Hills Urinary Care C D Multicare
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease pain:
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day, especially during hot weather
It’s important to follow the instructions on the packet so you know how much paracetamol you or your child can take, and how often.
It may also help to avoid having sex until you feel better.
You cannot pass a UTI on to your partner, but sex may be uncomfortable.
Taking cystitis sachets or cranberry products has not been shown to help ease symptoms of UTIs.
Complications Of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are an extremely common condition, and most people recover quickly with antibiotic treatment. However, if left untreated the infection can spread throughout the urinary tract system, increasing in severity and causing complications.
In some cases, the infection can reach the kidneys in the upper urinary tract, an infection known as pyelonephritis. Without medical intervention, this can lead to permanent kidney damage. Possible complications from untreated UTIs include:
- Formation of abscesses within or around the kidneys
- Swelling of the kidneys, also known as hydronephrosis
- , also known as blood poisoning
All of these complications are serious and require immediate medical attention.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Canine Urinary S O
Diagnosis Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnosis of a urinary tract infection usually begins with a consultation based on the symptoms and a physical examination. It is usual for a doctor to also ask about sexual history, medical history and any instances of previous UTIs.
A sample of urine might be requested in order to confirm a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Dipstick analysis may be done first to indicate the presence of bacteria in the urine. This quick test entails dipping a small chemical strip into a urine sample, then looking for certain color changes on the strip which may indicate abnormal levels of blood, sugar or bacteria in the urine. Looking at the urine sample under a microscope can usually confirm the diagnosis, as well as which bacteria has caused the infection.
If an upper urinary tract infection is suspected, a doctor may also recommend blood tests in order to check the infection hasnââ¬â¢t spread to the bloodstream.
People suffering from recurring or chronic urinary tract infections may be given additional tests to determine if there are any obstructions or abnormalities causing the repeat of the condition. Such tests can include:
- An ultrasound scan of the bladder and kidneys, which uses painless soundwaves to generate an image of the urinary tract
- A CT scan or MRI scan for a more detailed analysis of the urinary tract
- A cystoscopy, in which a small camera is inserted through the urethra to see inside the urethra and bladder
Causes And Risk Factors Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, which consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. While any of these parts can become infected, most UTIs involve the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder and the urethra . A UTI that infects the bladder is called cystitis one that infects the urethra is called urethritis.
The majority of UTIs that affect the bladder and the urethra are caused by E. coli or other bacteria that are normally found in the digestive tract, which can travel from the anus to the urethra. UTIs that affect the urethra are also caused by sexually transmitted infections, including herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma. Most of the time, urinating flushes out lingering bacteria in the urethra before it causes problems, though your body isnt always able to do this.
Less often, UTIs involve the upper urinary tract, which includes the kidneys and the ureters . A UTI infection in the kidneys, called pyelonephritis or a kidney infection, most often begins in the bladder and moves up through the ureters to one or both kidneys. In certain cases, a kidney infection can lead to serious health problems.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection In Babies
Related Conditions And Causes Of Uti
There are a number of health conditions that share some symptoms with urinary tract infections, including:
The following conditions may make you more susceptible to developing a UTI and increase the severity of symptoms:
Type 2 diabetes
And having a UTI can increase a man’s risk for benign prostatic hyperplasia .
Home Remedies For Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
In addition to antibiotics, many people seek natural, at-home remedies to help UTIs. A heating pad can relieve pressure and pain, and wearing loose cotton clothing is recommended. For those with recurrent UTIs, modifying certain habits may help: Choose fragrance-free personal care products to reduce the risk of irritation, and cut back on foods that can irritate the bladder caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, raw onions, citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and artificial sweeteners.
Don’t Miss: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Antibacterial Plus Urinary Pain Relief Tablets
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
As adherence has a key role at nearly every step of UTI pathogenesis, one attractive strategy for the development of antivirulence therapies, including vaccines, has been to target CUP pili. As a general rule, vaccination with whole pili has been ineffective at generating an antibody response that can protect against UTIs. However, adhesin-based vaccines have been shown to be effective at blocking hostpathogen interactions, thus preventing the establishment of disease. Experiments using mouse and cynomolgus monkey models of UTIs determined that immunization with PapDPapG or FimCFimH chaperoneadhesin complexes protected against UTIs. The effectiveness of the FimCFimH vaccine was shown to be due, in large part, to antibodies that block the function of FimH in bladder colonization. Furthermore, the anti-FimH antibodies did not seem to alter the E. coli niche in the gut microbiota. Modifications of this vaccine are currently under development, with the aim of inducing greater immune stimulation,. For example, one approach has been to fuse FimH to the flagellin FliC in order to induce a more substantial acute inflammatory response, which functions through TLR4 signalling via the MYD88 pathway. A Phase I clinical trial began in January 2014 to evaluate the efficacy of a FimCFimH vaccine using a synthetic analogue of monophosphoryl lipid A as the adjuvant.
Recommended Reading: Ways To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection