Whats The Difference Between A Yeast Infection And Bacterial Vaginosis
Both infections stem from too much bacteria in the vagina. Yeast infections are caused by an excess of candida fungus and symptoms include redness, itching and burning around the vulva, an unpleasant-smelling, thick white discharge, pain during intercourse and urination. Bacterial vaginosis results from the bacterial balance being out of whack. The symptoms also include redness, itching and pain but its discharge tends to be thin, white or yellowish in color. Visit Wake Womens Health to see what gynecological services are provided.
Can Hpv Be Prevented
A vaccine can keep you from getting it. Itâs best if youâre vaccinated before youâre sexually active so your immune system can be prepared to fight it off. The CDC recommends that girls and boys get vaccinated at age 11 or 12. Older kids should get the HPV vaccine up to age 26. If youâre older, are already having sex, and have gotten one type of HPV, the vaccine can protect you against other types. Adults through age 45 may also get the vaccine, but it may provide less benefit because of prior exposure to HPV in this age group. Pregnant women shouldnât get the vaccine, however.
What Stds Cause Frequent Urination
This is a question that many of us have had to ask ourselves and Google. Whether its early childhood programming or anxiety, whenever something is wrong down there, we jump to STDs. In some, this causes panic and embarrassment. This is largely because weve previously associated sexually transmitted diseases with dirty people and people who have unsafe sex. Well, all of those theories have been proved wrong by modern science. We now know that anyone can be at risk for an STD, even if youre only active with one person.
This article is going to look at the STDs that cause frequent urination and the symptoms of each disease. This is a key factor in narrowing down the possibilities. However, STDs are not the only cause of frequent urination. Here is a list of the possible causes:
- Bladder infection
- Urethritis
- Urinary tract infection
The items marked with a * are the only STDs on the list. As you can see, STDs are not the majority cause of frequent urination. In fact, the most frequent cause is a urinary tract infection. Of course, you dont want to read everything about all of these possible causes. Instead, lets focus on 5 causes of frequent urination:
Recommended Reading: Where Does A Urinary Tract Infection Hurt
Symptoms Of Hpv Infection
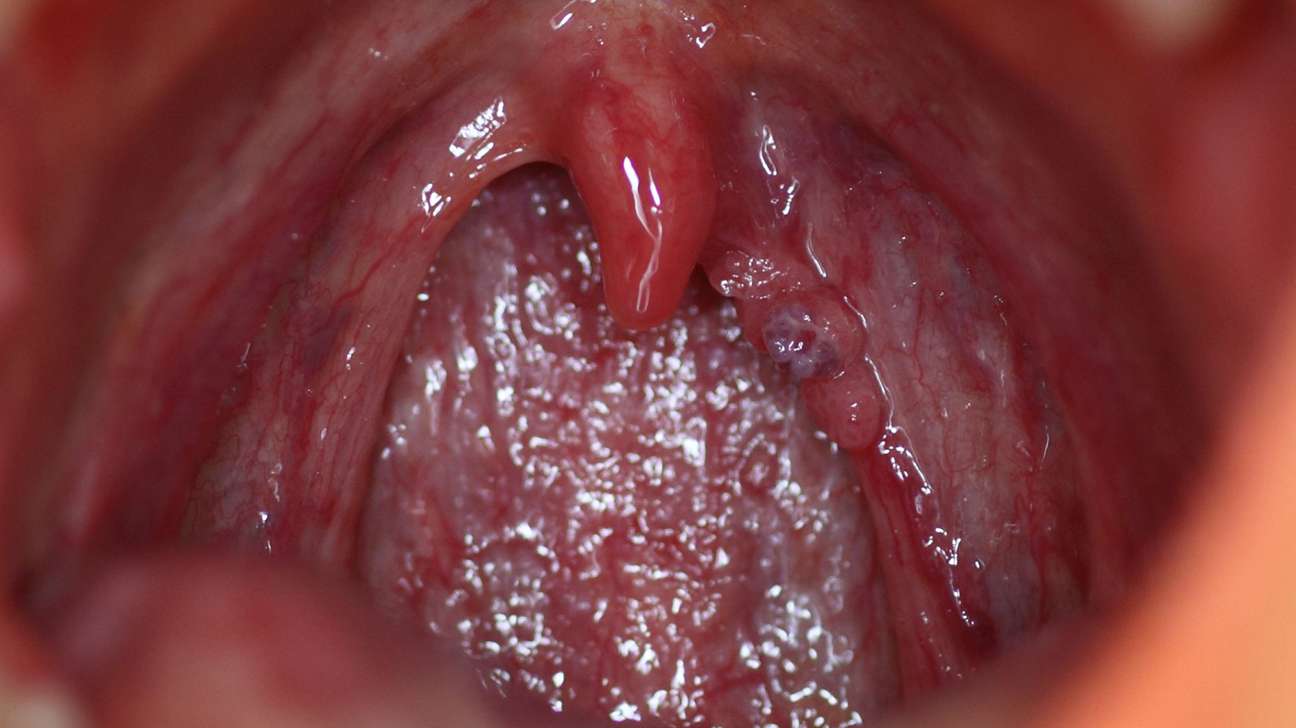
In men, warts usually occur on the penis, especially under the foreskin in uncircumcised men, or in the urethra. In women, genital warts occur on the vulva, vaginal wall, cervix, and skin around the vaginal area. Genital warts may develop in the area around and inside the anus, especially in people who engage in anal sex.
Warts cause no symptoms in many people but cause occasional burning pain, itching, or discomfort in some.
The warts usually appear 1 to 6 months after infection with HPV, beginning as tiny, soft, moist, pink or gray growths. They grow rapidly and become rough, irregular bumps, which sometimes grow out from the skin on narrow stalks. Their rough surfaces make them look like a small cauliflower. Warts often grow in clusters.
Warts may grow more rapidly and spread more widely in pregnant women and in people who have a weakened immune system, such as those who have HIV infection.
How Does Hpv Affect Pregnancy
HPV does not affect your chances of getting pregnant, but it may cause problems during pregnancy.
Some possible problems during pregnancy include:
- Cervical cell changes. Continue to get regular cervical cancer screening during and after pregnancy to help your doctor find any changes.
- Genital warts that bleed and grow. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause any genital warts that you had before getting pregnant or that you get during pregnancy to bleed and grow .
- Cesarean section. If genital warts block the birth canal, you may need to have a cesarean section .
- Health problems in the baby. A woman with genital HPV can very rarely pass it on to her baby. Babies and children may develop growths in their airways from HPV. This rare but potentially serious condition is called recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Urinary Tract Infection
You Dont Pee After Sex
The threat of getting a UTI shouldnt stop you from getting it on. But that doesnt mean resigning yourself to the afterburn.
One simple way to cut your risk: Head to the potty after youve finished your romp. Youll possibly flush out the bacteria that may have made their way into your urinary tract. Urinary Tract Infection. .
Can Hpv Be Treated
Theres no treatment for the virus itself. But most genital HPV infections go away with the help of a persons immune system.
Even though HPV itself cannot be treated, the cell changes caused by an HPV infection can. For example, genital warts can be treated. Pre-cancer cell changes caused by HPV can be found by Pap tests and treated. And head and neck, cervical, anal, and genital cancers can be treated, too.
Recommended Reading: Home Remedies For Urinary Urgency
You Wipe From Back To Front
Wiping from back to front can transport E. coli, the bacteria thats behind most UTIs, from the rectal region to the urethra. Moral of the story: Always wipe from front to back. Al-Badr A, et al. . Recurrent urinary tract infections management in women: A review.
How Is It Treated
Although genital HPV infections are very common,most show no signs and go away without treatmentwithin a few years. If HPV does not go away, treatmentsare different for low risk HPV and high-risk HPV:
- Low-Risk HPV Even when genitalwarts are treated, HPV infection may remain. Wartscan also come back after treatment. Over-the-countertreatments for other types of warts shouldnot be used. Treatments for genital warts include:
- Watch and wait to see if the warts stay the same, get bigger, or go away
- Medicines put directly on the warts
- Burning off the warts
- Cutting the warts out
- Using special lights or lasers to destroy the warts
- High-Risk HPV Pap tests can find pre-cancerchanges in the cervix and other abnormal cells.Removing the abnormal cells is the best way toprevent cervical cancer.
- Abnormal cells can be surgically removed withoutremoving the uterus or damaging the cervix. After,women can still have normal pregnancies.
Recommended Reading: Homeopet Feline Urinary Tract Infection Supplement 15 Ml
How To Feel Better
If your healthcare professional prescribes you antibiotics:
- Take antibiotics exactly as your healthcare professional tells you.
- Do not share your antibiotics with others.
- Do not save antibiotics for later. Talk to your healthcare professional about safely discarding leftover antibiotics.
Drink plenty of water or other fluids. Your healthcare professional might also recommend medicine to help lessen the pain or discomfort. Talk with your healthcare professional if you have any questions about your antibiotics.
Can Trichomoniasis Cause Epididymitis
4.1/5TrichomoniasisTrichomonascancauseepididymitisTrichomoniasis
Herein, can trichomoniasis cause urinary tract infection?
Trichomoniasis infection is caused by a parasitic protozoan . Only about 30 percent of all trichomoniasis cases have symptoms. Women are more likely than men to display symptoms. If symptoms are present, they usually mirror a urinary tract infection .
Beside above, does ejaculating hurt epididymitis? Signs of epididymitisA swollen, red or warm scrotum. Testicle pain and tenderness, usually on one side. A fever. Painful intercourse or ejaculation.
Besides, can HPV cause epididymitis?
The possible role of the male urogenital tract as a reservoir of HPV infection is not fully understood. We inferred from our previous observation of HPV-31 in epididymal tissue in a case of chronic epididymitis that HPV might be commonly present in cases of epididymitis caused by sexually transmitted pathogens.
Can trich cause testicle pain?
Men may be asymptomatic, or on occasion, they may present with symptoms including penile discharge, testicular pain, dysuria, urinary frequency, or cloudy urine. Trichomoniasis can cause urethritis in men and occasionally epididymitis or prostatitis.
Recommended Reading: To Treat Urinary Tract Infection
National Strategy On Hpv
In female, cervical cancer screening can prevent cervical cancer as part of the national strategy for HPV infections. The adaptation of screening programs has led to a decreased incidence of cervical cancers worldwide. Many epidemiologic studies have supported the effectiveness of cervical cancer screening on the incidence of invasive squamous cell carcinoma in regions, including the United States, Canada, and Europe . In the United States, NCI-designated cancer centers aimed to screen 93% of age-eligible females for cervical cancer to provide prompt follow-up and appropriate treatment of females who screen positive for high grade cervical precancerous lesions by 2020 .
In Korea, the Papanicolaou smear was introduced in 1988 in health examinations to employees and those insured by the National Health Insurance program. The Pap smear has played an essential role in reducing cervical cancer in Korea. The rate of Pap smears has increased from 33.5% in 1998 to 45.5% in 2009 in Korea . Since 2016, the National Cancer Screening Program provides free cervical cancer screening biennially to all Korean female over 20 years of age.
- CONFLICT OF INTEREST
-
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Who Should Get The Hpv Vaccine

The HPV vaccine series is recommended for girls and boys, at the age of 11 or 12, and the series can be started at age 9. It is important for males as well as females to get vaccinated, because both men and women can develop cancers of the mouth and throat, anal cancers, and genital warts. Women are also at risk for cervical cancer, and men for penile cancer. Vaccination can also reduce the spread of HPV that causes cancer to other people.
Children who start the vaccine series before age 15 need two doses to be protected. For young people who werent vaccinated within the age recommendations, HPV vaccination is recommended up to age 26. Those who receive their first dose at age 15 or older need three doses to be protected.
Read Also: How Can You Get A Urinary Tract Infection
Glomerular Syndromes Associated With Acute/subacute Viral Infections
This focus is on individual types of glomerular lesions seen with a variety of acute and subacute viral infections including cytomegalovirus , parvovirus, EpsteinBarr virus , hantavirus, and dengue. An accurate differential diagnosis in case of GN should rule out acute or chronic viral infections. Familiarity with the main renal syndromes associated with viral diseases is essential in order to begin accurate testing and therapeutic interventions .
Although any acute viral illness can lead to an immune complexproliferative glomerulonephritis , a select group of viral syndromes can induce glomerular injury: dengue, hantavirus, and non-HIV viruses associated with collapsing FSGS .
Dengue
Dengue is a worldwide infection with estimated 100 million new per year. It is classified into dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever, and dengue shock syndrome. GN in dengue results not only from immune complex deposition but also from direct viral entry into renal tissue . Treatment remains supportive in all categories of dengue.
Hantavirus
Hantaviruses are RNA viruses of the Bunyaviridae family which are associated with two major syndromes: hanta pulmonary syndrome and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, characterized by diffuse endothelial cell injury as a consequence of direct viral infection. Similar to dengue, no specific therapy is available for hantavirus infection but preventive strategies with widespread vaccination are undergoing clinical trials .
How Can You Avoid Hpv
- Get vaccinated against HPV.
- HPV vaccines can protect against 70% of cervical cancers.
- One type of HPV vaccine can protect against the low-risk HPV that causes 90% of genital warts.
- HPV vaccine is recommended for all females 9 to 26 years old.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends all 11-12 year old girls and boys get the HPV vaccine.
- Avoid sexual contact.
- Before anal sex
- Before oral sex
- Have sex with only one partner who does not have sex with others and does not have HPV.
- Know that other forms of birth control do not protect against HPV.
Condoms may not fully protect against HPV since HPV can infect areas not covered by a condom.
For more information, see Safer Sex.
Also Check: What Meds Treat Urinary Tract Infection
Cervix: Hpv And Cancer Symptoms
Depending on the type of HPV a female has, they will present with different symptoms.
If they have low risk HPV, warts may develop on the cervix, causing irritation and pain. In some people, these warts could cause bleeding.
High risk HPV usually presents with no initial symptoms. However, if the virus remains within the body for many years, infected cells can change and begin to divide uncontrollably. This would result in cancer.
The presence of early cervical cancer or precancerous cells may not cause any symptoms. This is why it is important for females to undergo a Pap test every , depending on their age and other risk factors.
Some symptoms of advanced cervical cancer
- a cluster that looks like a cauliflower
- a scatter of bumps that are darker than unaffected skin
- growths that may be raised, flat, smooth, or rough
Warts are usually indicative of low risk HPV. A specific type of vulvar cancer may present as cauliflower-like growths, so a person should speak to a doctor if they see any unusual growths around the vulva.
Without treatment, high risk HVP may cause vaginal or vulvar cancer. Females may not experience any symptoms when they have precancerous cells or during the early stages of vaginal or vulvar cancer.
How often someone needs a Pap test depends on their age and other risk factors.
Some symptoms of vaginal cancer
can detect precancerous cells and HPV.
The National Cancer Institute list three types of screening tests:
A doctor may treat genital warts with:
Urinary Tract Infections They Can Be Prevented
What is a urinary tract infection?
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection in the urinary tract which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Any or all of these parts of the urinary tract can become infected. An infection that is not treated can permanently hurt the bladder and kidneys. It can even spread to the blood and cause a life threatening infection.
How does a UTI occur?
Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria. Normally the urinary tract does not have any bacteria in it. Bacteria that cause a UTI often spread from the rectum or vagina to the urethra and then to the bladder or kidneys. Urinary tract infections are more common in women because the urethra is short. This makes it easy for bacteria to move up to the bladder and kidneys. Sometimes bacteria spread from another part of the body through the bloodstream to the urinary tract.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
The symptoms of a UTI may include:
- urinating more often
- feeling an urgent need to urinate
- pain or discomfort when you urinate
- strong-smelling urine
- pain in the lower pelvis, stomach, lower back, or side
- urine that looks cloudy or reddish
- shaking chills
- change in amount of urine, either more or less
- pain during sex
How is a UTI diagnosed?
A sample of urine can be tested for bacteria at the Health Center or in your Primary Care Phyisican’s Office.
How is a UTI treated?
How can I take care of myself when I have a UTI?
How can I prevent a UTI?
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Go Away
When Can I Get The Hpv Vaccine
Experts recommend that most people get the HPV vaccine at age 11 or 12. The HPV vaccine works best when you get it before you have any type of sexual contact with someone else. The Food and Drug Administration approved the HPV vaccine for people ages 9 through 45.
There is not enough research to show whether the HPV vaccine is safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women. As a result, experts do not recommend the HPV vaccine for pregnant women. If you got an HPV vaccine shot while pregnant, wait until your pregnancy is over before getting any more HPV vaccine shots. You can also enroll in the HPV vaccine pregnancy registry by calling 1-800-986-8999. Talk to your doctor, nurse, or midwife about the HPV vaccine if you are breastfeeding and want to get the shots.
If you are 45 or younger and never had the HPV vaccine, or did not get all of the HPV shots, ask your doctor or nurse about getting vaccinated. When and how often you need HPV vaccine shots depends on your age and health history. Learn more about recommended doses of the HPV vaccine from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Find a clinic near you where you can get the HPV vaccine.
Can You Get A Uti From Condoms
Most condoms dont cause UTIs. In fact, by putting a barrier between you and your partner they may make it less likely that bacteria gets into the urethra.
There is some research, however, that shows condoms with spermicidal lube already on them can increase the chances of a UTI. If youre worried about UTIs, make sure to choose a condom without spermicide.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection In Children
Hpv : The Facts About The Infection And The Vaccine
HPV: Sexually Transmitted Infection
- What is HPV?Human papillomavirus is the most common sexually transmitted infection in the United States, with approximately 14 million cases diagnosed annually. There are more than 150 strains of HPV, over 40 of which can cause and genital warts . The types of HPV that can cause genital warts are not the same as the types that can cause cancers.
- What are the symptoms?Most people with HPV do not develop symptoms or health problems from it. In 90% of cases, the bodys immune system clears HPV naturally within two years.
- What are warts?
- Genital warts Usually appear as a small bump or group of bumps in the genital area. They can be small or large, raised or flat or shaped like a cauliflower. Warts can appear within weeks or months after sexual contact with an infected partner. If left untreated, genital warts might go away, remain unchanged or increase in size or number. They will not turn into cancer. For more information on symptoms and treatment for genital warts, .
- Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Is a condition in which warts grow in the throat. These growths can sometimes block the airway, causing a hoarse voice or trouble breathing.
HPV and Cancer
- Anal Cancer
- Sometimes there are no signs or symptoms.
- Anal bleeding, pain, itching or discharge
- Swollen lymph nodes in the anal or groin area
- Changes in bowel habits or the shape of your stool