Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI.
A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service. They may be able to give antibiotics if they’re needed.
Is E Coli Contagious
When you hear the word contagious, you might immediately think of a cold or the flu illnesses you can get from breathing in bacteria or viruses lingering in the air of a sick persons cough or sneeze.
E. coli isnt an airborne illness. Its usually spread by eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water that contains illness-producing strains of E. coli.
E. coli can, however, be contagious and spread from person to person by the oral-fecal route. This means that harmful strains of E. coli are spread when people dont wash their hands thoroughly with soap and water after they use the bathroom or otherwise touch poop and they touch other people. People then get the invisible E. coli on their hands and swallow it when it is transferred from their hands to the food they eat or from putting their fingers in their mouth. E. coli spreads from person to person this way in settings such as day care centers and nursing homes.
Don’t Miss: How To Get A Urinary Tract Infection Male
Dna Extraction And Genome Sequencing
Liquid cultures of each strain were grown from freezer stock in LB at 37°C in a shaking incubator for 12 h. DNA was extracted from liquid culture using the Qiagen DNeasy UltraClean Microbial Kit following the manufacturers protocol. DNA concentration was quantified using the Qubit fluorometer. To confirm the MALDI-TOF classification, the 16S rRNA gene sequence was amplified using the 63f and 1387r primers and sequenced by Genewiz , using each primer individually for 2× coverage. The resulting sequences were manually trimmed and paired in Geneious v11.0.5 and queried against the NCBI 16S rRNA sequences database via blastn to confirm that they were E. coli. DNA libraries were constructed using the Nextera XT DNA Library preparation kit and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq platform using the MiSeq Reagent Kit v2 at Loyola University Chicagos Genomics Facility . Raw sequencing reads were deposited in NCBIs SRA database.
Treatments For Specific Populations

Treating Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should be screened for UTIs, since they are at high risk for UTIs and their complications. Antibiotics used for treating pregnant women with UTIs include amoxicillin, ampicillin, nitrofurantoin, and cephalosporins . Fosfomycin is not as effective as other antibiotics but is sometimes prescribed for pregnant women. In general, there is no consensus on which antibiotic is best for pregnant women although some types of antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines, should not be taken as they can cause harm to the fetus.
Pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria have an increased risk for acute pyelonephritis in their second or third trimester. They need screening and treatment for this condition. In such cases, they should be treated with a short course of antibiotics . For an uncomplicated UTI, pregnant women may need longer-term antibiotics .
Treating Children with UTIs
Children with UTIs are generally treated with TMP-SMX, cephalexin and other cephalosporins, or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid . These drugs are usually taken by mouth in either liquid or pill form. Doctors sometimes give them as a shot or IV. Children usually respond to treatment within a few days. Prompt treatment with antibiotics may help prevent renal scarring.
Children with acute kidney infection are treated with various antibiotics including oral cefixime or a short course of an intravenous antibiotic . An oral antibiotic then follows the IV.
Read Also: Can Alkaline Water Cause Urinary Tract Infection
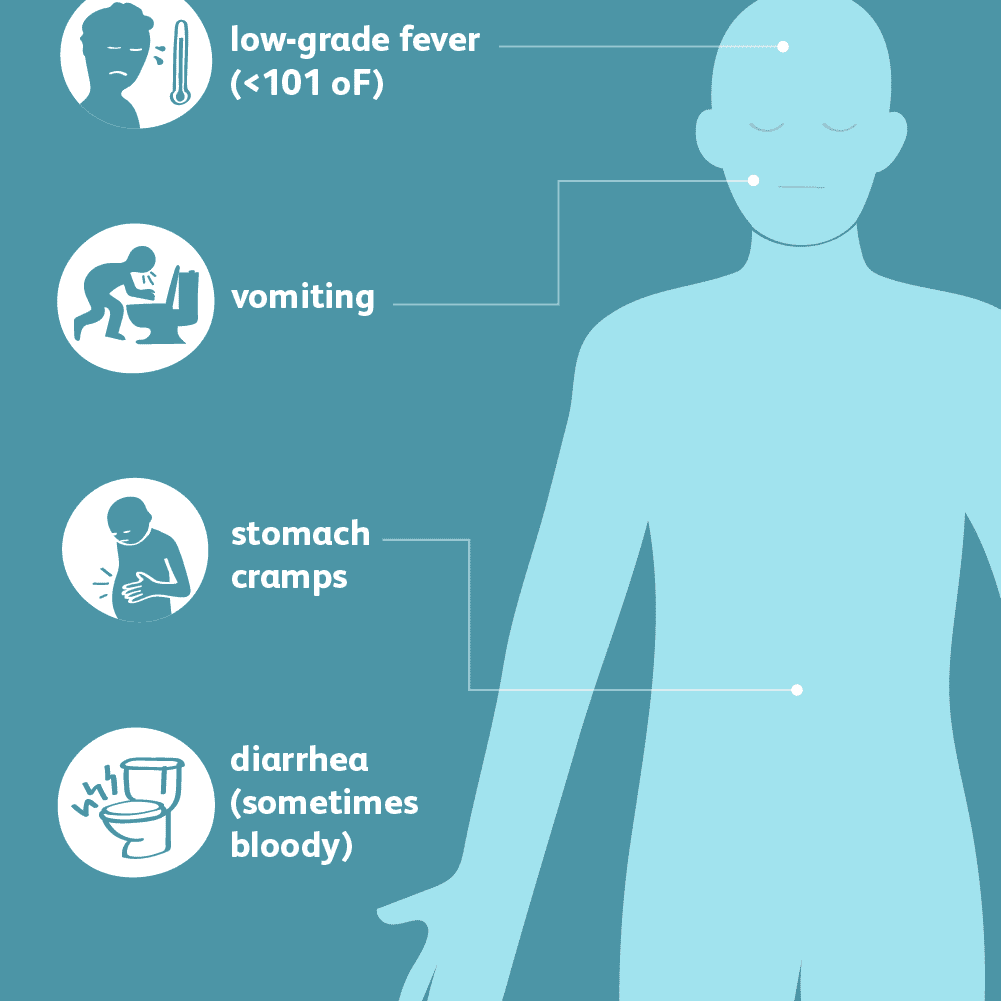
How Is An E Coli Infection Treated
Fortunately, most E. coli infections go away on their own. You can help yourself manage E. coli infection by drinking plenty of fluids to replace what youve lost through diarrhea and/or vomiting. Also, get as much rest as possible.
Antibiotics are usually not given for STEC O157 infection because they can make your illness worse and put you at risk for hemolytic uremic syndrome . Also, dont take any medicines to stop diarrhea , because it could keep the E. coli bacteria in your body and increase your chance of HUS.
You should start to feel better about five to seven days from the time you first developed symptoms.
Urinary Tract Infections In Boys
Urinary tract infections in boys are the result of bacteria getting into the bladder and staying there. UTIs are common in kids, especially girls and uncircumcised boys. E. Coli, responsible for over 75% of UTIs, doubles every 20 minutes in the bladder. That means if there are 100 bacteria of E. Coli in the bladder and you wait three hours to go to the bathroom, you will have over 50,000 bacteria in your bladder. The more bacteria in the bladder and the longer it stays there, the more likely you are to get a UTI.
There are many things that can be done to both treat urinary tract infections in boys and prevent them in the future.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Online
Upec Vaccine Development: Improving Uti Management Through Prevention
Although it appears that a prior UTI fails to elicit a protective host immune response and uropathogen heterogeneity complicates vaccine design, data from animal model studies offer encouragement for successful UPEC vaccine development . Immunization with UPEC antigens can stimulate a mucosal immune response that may be effective at preventing experimental UTI and increases in urinary and serum antibody titers correlate with reductions in bladder bacterial load and infection duration . With continued effort, these data provide encouragement that an effective UPEC vaccine can be developed.
How Is A Uti Diagnosed
To find out whether you have a UTI, your doctor or nurse will test a clean sample of your urine. This means you will first wipe your genital area with a special wipe. Then you will collect your urine in midstream in a cup. Your doctor or nurse may then test your urine for bacteria to see whether you have a UTI, which can take a few days.
If you have had a UTI before, your doctor may order more tests to rule out other problems. These tests may include:
- A cystogram. This is a special type of x-ray of your urinary tract. These x-rays can show any problems, including swelling or kidney stones.
- A cystoscopic exam. The cystoscope is a small tube the doctor puts into the urethra to see inside of the urethra and bladder for any problems.
You May Like: Hillâs Science Diet Adult Urinary & Hairball Control
Recommended Reading: What Foods Cause Urinary Tract Infections
Prevention Of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
Prevention of recurrent UTI has attracted much interest and was investigated by researchers. The European Association of Urology guideline suggests that the prevention of recurrent UTI should include the following in this order: behavioral modifications and avoidance of risk factors, nonantimicrobial measures, and antimicrobial prophylaxis . Due to the limited context, the current review mainly focuses on nonantimicrobial treatment of recurrent UTI.
How Are Utis Diagnosed
Only a health care provider can treat urinary tract infections. The first thing a doctor will do is confirm that a person has a UTI by taking a clean-catch urine specimen. At the doctor’s office, you’ll be asked to clean your genital area with disposable wipes and then pee into a sterile cup.
The sample may be used for a urinalysis or a urine culture . Knowing what bacteria are causing the infection can help your doctor choose the best treatment.
You May Like: Can Turmeric Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Treatment For Kidney Infections
People with uncomplicated kidney infections may be treated at home with oral antibiotics. Ciprofloxacin or another fluoroquinolone is typically given but other antibiotics, such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole , may be used. People with moderate-to-severe acute kidney infection and those with severe symptoms or other complications may need to be hospitalized. In such cases, antibiotics are usually given intravenously for several days. Chronic pyelonephritis may require long-term antibiotic treatment.
Other Ways To Prevent Some Utis Coming Back
If you keep getting a bladder infection , there is some evidence it may be helpful to take:
- D-mannose a sugar you can buy as a powder or tablets to take every day
- cranberry products available as juice, tablets or capsules to take every day
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
If you’re taking warfarin, you should avoid cranberry products.
Page last reviewed: 22 March 2022 Next review due: 22 March 2025
You May Like: Benefits Of Cranberry Juice For Urinary Tract Infection
Can Urinary Tract Infections Be Prevented
These steps may help reduce the chance of getting UTIs:
- Drink plenty of water every day.
- Drink cranberry juice. Large amounts of vitamin C limit the growth of some bacteria by acidifying the urine. Vitamin C supplements have the same effect.
- Urinate when you feel the need. Do not wait.
- Take showers instead of tub baths.
- Clean the genital area before and after sex, and urinate shortly after sex.
- Women should not use feminine hygiene sprays or scented douches.
- Cotton underwear and loose fitting clothes help keep the area around the urethra dry. Tight clothes and nylon underwear trap moisture. This can help bacteria grow.
- Repeated bouts of urinary tract infections can be treated with small doses of regular antibiotics.
Please consult your health care provider with any questions or concerns you may have about UTIs.
Discover How Using Cranberry Pills For Kidney Stones Can Keep Your Urinary System In Great Shape
Substantive research shows taking cranberry pills for kidney stones can help in alleviating this debilitating and painful condition. Scientists believe that the active ingredients in these capsules are great for preventing and staving off urinary tract infections since it prevents the solidification of urine to form kidney stones. In effect, it has the opposite effect that typically culminates in the formation of kidney stones by stopping the deposition of oxalates.
You May Like: Can Intercourse Cause A Urinary Tract Infection
Phylogenetic Group And Vf Distribution Among Patient Groups And Clinical Syndromes
E. coli is commonly classified into four main phylogenetic groups namely A, B1, B2, and D as defined by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and multilocus sequence typing . Several studies have shown that E. coli pathogenic strains from extraintestinal infections mostly derive from group B2, and to a less extent group D . Most studies quote prevalence rates around 6365% for group B2 in pathogenic strains, and 1015% for group D . Commensal E. coli are mainly associated with phylogenetic groups A or B1, and are mainly devoid of virulence determinants . The overlapping associations of VFs and phylogeny with clinical virulence makes it difficult to understand which directly determines virulence. However, some studies in children showed that pyelonephritis isolates more often belonged to group B2, contained on average higher prevalences of individual VF genes, and consequently had higher VF scores than did cystitis or fecal isolates, suggesting that both VF repertoire and phylogenetic background play important roles in UTI pathogenesis.
You May Like: Kidney Stone In Urinary Tract
Small Molecules Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
Our detailed understanding of pilus assembly and pilusreceptor binding has opened the door to the development of two classes of small, rationally designed synthetic compounds to inhibit pili: mannosides, which inhibit pilus function and pilicides, which inhibit pilus assembly. Targeting CUP pilus function or assembly has therapeutic potential, as it should block UPEC colonization, invasion and biofilm formation, thus preventing disease30,31,120,121.
Mannosides, which are FimH receptor analogues, have been developed to bind FimH with high affinity and block FimH binding to mannosylated receptors35,121,123125. Mannosides are potent FimH antagonists that offer a promising therapeutic opportunity for the treatment and prevention of UTIs by interrupting key hostpathogen interactions123125. Studies in mouse models have demonstrated the potential of mannosides as novel therapeutic strategies against UTIs: mannosides are orally bioavailable they are potent and fast-acting therapeutics in treating and preventing UTIs they function by preventing bladder colonization and invasion they are effective against multidrug-resistant UPEC they potentiate antibiotic efficacy and they are effective against established UTIs and CAUTIs35,121,124,125.
Recommended Reading: Is Pineapple Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Sample Collection And In Vivo Rna Isolation
Fresh mid-stream urine was collected from consenting women with presumptive bacteriuria attending the University of Michigan Urology clinic. A diagnosis of presumptive bacteriuria was made based on symptoms of urgency and frequency and/or a history of previous UTI. Volumes collected ranged from 28 to 187 ml, with a median volume of 70 ml . Urine was collected from 34 women in order to obtain 10 E. coli-positive samples that were suitable for our study. Of these, two samples contained multiple E. coli strains and were not analyzed further. For the eight patients from whom single strains of E. coli were isolated and studied in this report, no patient was catheterized. Seven of eight patients reported a previous UTI. Two patients were taking one antibiotic however, each respective E. coli strain was resistant to that antibiotic.
Also Check: Cranberry D Mannose Urinary Tract Support
How Can I Prevent Or Avoid An E Coli Infection
The most important thing you can do to protect against E. coli infection is to wash your hands frequently. Always wash your hands thoroughly before and after cooking and after handling raw meat or poultry.
Wash your hands after using the restroom, changing diapers or after contact with animals.
If youve been infected with E. coli, scrub your hands vigorously with soap and clean under your fingernails where bacteria can get caught. Dry your hands with paper towels instead of cloth towels to avoid transferring bacteria.
You can also reduce your risk of an E. coli infection by following these food preparation and cooking tips.
When thawing meats:
- Dont defrost frozen meat unwrapped on the counter.
- Keep frozen meat in a separate plastic bag when thawing.
When prepping foods:
- Dont rinse meat before cooking. Its not necessary. Washing the meat could spread bacterial to nearby surfaces, utensils and other food.
- Use a plastic or ceramic cutting board to cut raw meat. These materials can be cleaned more easily and thoroughly than wooden cutting boards.
- Dont cross-contaminate a prepping surface. If you had raw meat or chicken on a prepping surface, such as a cutting board, wash it thoroughly with soap and hot water before putting another type of food on it. Better yet, use different cutting boards for the foods you are preparing.
- Rinse all raw fruits and vegetables under cold running water before eating them. Its ok to scrub firm produce but dont use detergent or soap.
Recommended Reading: What Are Some Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Acute And Chronic Prostatitis
In the 1800s, prostatitis was thought to be secondary to excessive alcohol consumption or physical or sexual activity. It was often associated with gonorrhea and could be fatal or lead to abscess formation. By the 1920s, most cases were attributed to microorganisms, and antibiotics combined with prostate massage were standard therapy after World War II. Although the role of bacteria was questioned in the 1950s, it was reemphasized in 1968 when Meares and Stamey described their “4-glass test.”
Acute prostatitis is caused by an acute infection of the entire prostate gland, resulting in fever and localized pain. Microscopically, neutrophilic infiltrates, diffuse edema, and microabscesses may be seen, which may coalesce into larger collections.
Chronic prostatitis may be caused by inflammatory or noninflammatory diseases. This condition may arise via dysfunctional voiding, intraprostatic reflux, chronic exposure to microorganisms, autoimmune mechanisms, irritative urinary metabolites, and as a variant of neuropathic pain. Chronic bacterial prostatitis often produces few or no symptoms related to the prostate, but it is probably the most common cause of relapsing UTI in men.
Chronic prostatitis has been subdivided by the National Institutes of Health into the following categories:
What Is The Long

Urinary tract infections are uncomfortable and painful. Most chronic UTIs will resolve with a prolonged course of antibiotics, but monitoring for further symptoms is important since the chronic UTIs usually recur. People with UTIs should monitor their bodies and seek immediate treatment with the onset of a new infection. Early treatment of infection decreases your risk for more serious, long-term complications.
If youre susceptible to recurring UTIs, make sure to:
- urinate as often as needed
- wipe front to back after urinating
Also Check: Artificial Urinary Sphincter Surgery Recovery