How Is A Uti Diagnosed
To find out whether you have a UTI, your doctor or nurse will test a clean sample of your urine. This means you will first wipe your genital area with a special wipe. Then you will collect your urine in midstream in a cup. Your doctor or nurse may then test your urine for bacteria to see whether you have a UTI, which can take a few days.
If you have had a UTI before, your doctor may order more tests to rule out other problems. These tests may include:
- A cystogram. This is a special type of x-ray of your urinary tract. These x-rays can show any problems, including swelling or kidney stones.
- A cystoscopic exam. The cystoscope is a small tube the doctor puts into the urethra to see inside of the urethra and bladder for any problems.
How Do You Diagnose And Treat A Uti
Most UTIs are diagnosed via a urine sample, collected mid-stream , according to the Mayo Clinic. This will likely be followed up with a lab culture of your urine in order to determine precisely which bacteria strain is behind the infection. This will allow your doctor to prescribe the right antibiotic able to fight that bacteria.
Cranberry juice and cranberry-based products have been touted as a natural means of healing UTIs. These methods have been extensively studied, and while there is some support for their effectiveness, overall, per the Mayo Clinic, the evidence is inconclusive. Most experts advise discussing with a doctor before embarking on using cranberry juice or tablets to heal a UTI.
Repeat UTIs or more severe infections may require imaging, or a cystoscopy, which allows a doctor to see inside the urethra and bladder. Severe UTIs may also require treatment with antibiotics via an IV.
Communication With The Patient
As mentioned earlier, recurrent UTI in women, rather than being just a sequence of isolated episodes that can be treated with appropriate antibiotic therapy, is often multifactorial. Thus, the most important step in treatment is identification of the causes leading to the problem. Clearly, communication between the female patient and her physician is paramount, but is not always easy because patients often underestimate their symptoms, or consider them too embarrassing to discuss with their doctor. However, when placed in a specialist setting, women will often appear more uninhibited and more willing to discuss their symptoms.
The use of urinary charts could prove useful even in unspecialized settings and help the practitioner to overcome the difficulties of imprecise reporting by patients. These can be presented to the patient and be taken home, in order to give the woman an opportunity to think about her problem in a more comfortable setting and answer questions sincerely and openly.
A subsequent evaluation some days later, together with the results of investigations will clarify whether the UTI can be adequately treated in general practice, or if there are complications requiring specialist referral. Either way, prescription of broad-spectrum therapy without attempting to identify the causative pathogen should be avoided. General symptoms are not reliable enough to enable diagnosis of UTI without culture and sensitivity analysis.98
Also Check: Treatment For Urinary Retention In Males
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women: Diagnosis And Management
CHARLES M. KODNER, MD, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, Kentucky
EMILY K. THOMAS GUPTON, DO, MPH, Primary Care Medical Center, Murray, Kentucky
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Sep 15 82:638-643.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are common in women and associated with considerable morbidity and health care use. The clinical features, diagnostic testing, and causative organisms are often similar to those of single cases of UTI, although there are additional treatment strategies and prevention measures to consider with recurrent UTIs.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
A urine culture with greater than 102 colony-forming units per mL is considered positive in patients who have symptoms of UTI.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
Continuous and postcoital antimicrobial prophylaxis have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the risk of recurrent UTIs. |
||
|
Cranberry products may reduce the incidence of recurrent symptomatic UTIs. |
||
|
Use of topical estrogen may reduce the incidence of recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women. |
||
|
Treatment of complicated UTIs should begin with broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, with adjustment of antimicrobial coverage guided by culture results. |
||
|
Prophylactic antimicrobial therapy to prevent recurrent UTIs is not recommended for patients with complicated UTIs. |
UTI = urinary tract infection.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
UTI = urinary tract infection.
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
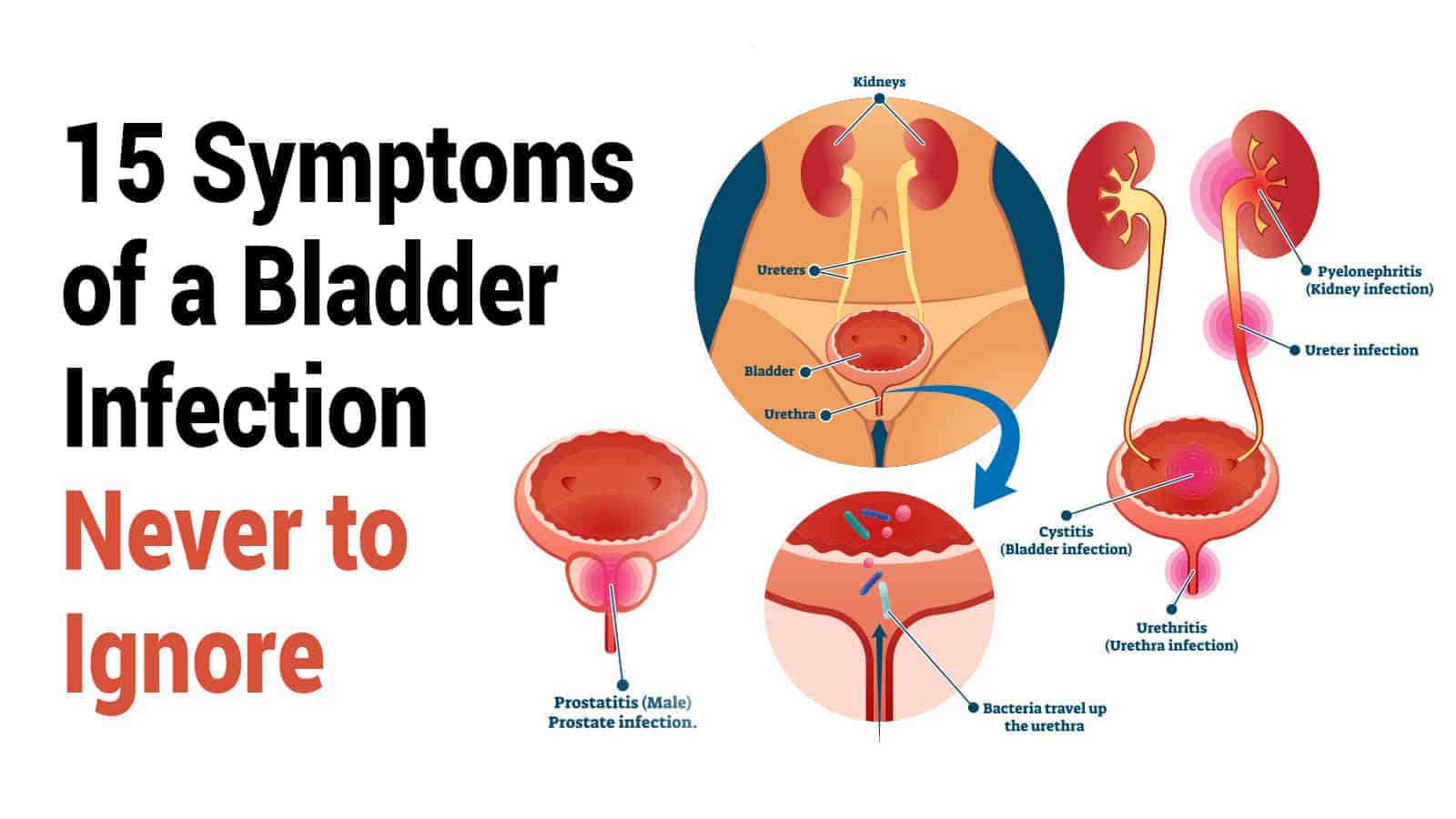
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
Recommended Reading: Can Being Overweight Cause Urinary Incontinence
Diagnosing A Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults
Vague, uncommon symptoms such as confusion make UTIs challenging to diagnose in many older adults. Once your doctor suspects a UTI, its easily confirmed with a simple urinalysis.
Your doctor may perform a urine culture to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection and the best antibiotic to treat it.
There are home UTI tests that check urine for nitrates and leukocytes. Both are often present in UTIs. Because bacteria are often in the urine of older adults to some degree, these tests arent always accurate. Call your doctor if you take a home test and get a positive result.
Antibiotics are the treatment of choice for UTIs in older adults and younger people. Your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin and nitrofurantoin .
More severe infections may require a broad-spectrum antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin .
You should start antibiotics as soon as possible and take them for the entire duration of treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Stopping treatment early, even if symptoms resolve, increases the risks of recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic overuse also increases your risk for antibiotic resistance. For this reason, your doctor will likely prescribe the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 7 days, and your infection should clear up in a few days.
Its important to drink plenty of water during treatment to help flush out the remaining bacteria.
Preventing Future Urinary Tract Infections
BATHING AND HYGIENE
To prevent future urinary tract infections, you should:
- Choose sanitary pads instead of tampons, which some doctors believe make infections more likely. Change your pad each time you use the bathroom.
- Do not douche or use feminine hygiene sprays or powders. As a general rule, do not use any product containing perfumes in the genital area.
- Take showers instead of baths. Avoid bath oils.
- Keep your genital area clean. Clean your genital and anal areas before and after sexual activity.
- Urinate before and after sexual activity. Drinking 2 glasses of water after sexual activity may help promote urination.
- Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom.
- Avoid tight-fitting pants. Wear cotton-cloth underwear and pantyhose, and change both at least once a day.
DIET
The following improvements to your diet may prevent future urinary tract infections:
- Drink plenty of fluids, 2 to 4 quarts each day.
- Do not drink fluids that irritate the bladder, such as alcohol and caffeine.
RECURRING INFECTIONS
Some women have repeated bladder infections. Your provider may suggest that you:
- Use vaginal estrogen cream if you have dryness caused by menopause.
- Take a single dose of an antibiotic after sexual contact.
- Take a cranberry supplement pill after sexual contact.
- Have a 3-day course of antibiotics at home to use if you develop an infection.
- Take a single, daily dose of an antibiotic to prevent infections.
Recommended Reading: What Can Cause Urinary Frequency
Can Utis Be Prevented
A few things can help prevent UTIs. After peeing, girls should wipe from front to back with toilet paper. After BMs, wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
Also, go to the bathroom when needed and don’t hold the pee in. Pee that stays in the bladder gives bacteria a good place to grow.
Keep the genital area clean and dry. Girls should change their tampons and pads regularly during their periods. Bubble baths can irritate the vaginal area, so girls should take showers or plain baths. Avoid long exposure to moisture in the genital area by not wearing nylon underwear or wet swimsuits. Wearing underwear with cotton crotches is also helpful. Skip using feminine hygiene sprays or douches, as these can irritate the urethra.
If you are sexually active, go to the bathroom both before and within 15 minutes after sex. After sex, gently wash the genital area to remove any bacteria. Avoid sexual positions that irritate or hurt the urethra or bladder. Couples who use lubrication during sex should use a water-soluble lubricant such as K-Y Jelly.
Finally, drinking lots of water each day keeps the bladder active and bacteria-free.
UTIs are uncomfortable and often painful, but they’re common and easily treated. The sooner you contact your doctor, the sooner you’ll be able to get rid of the problem.
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will use the following tests to diagnose a urinary tract infection:
- Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is used to determine the type of bacteria in your urine. This is an important test because it helps determine the appropriate treatment.
If your infection does not respond to treatment or if you keep getting infections over and over again, your doctor may use the following tests to examine your urinary tract for disease or injury:
- Ultrasound: In this test, sound waves create an image of the internal organs. This test is done on top of your skin, is painless and doesnt typically need any preparation.
- Cystoscopy: This test uses a special instrument fitted with a lens and a light source to see inside the bladder from the urethra.
- CT scan: Another imaging test, a CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes cross sections of the body . This test is much more precise than typical X-rays.
Recommended Reading: Causes Of Urinary Urgency In Males
Risk Factors For Urinary Tract Infections
And now a brief note about reproductive parts: Although people with penises do get UTIs, people with vaginas are more at risk. It all boils down to the anatomy, Minkin says.
Bacteria that cause UTIs often make their way from the back door to the front and then up the urethra to wreak havoc on the urinary system.
Because the male reproductive system has a longer urethra than the female reproductive system, the bacteria have farther to travel, which makes it more difficult for a UTI to develop.
But regardless of anatomy, once youve had one UTI, youre more likely to get another, especially if you have a vagina. Hickling DR, et al. . Management of recurrent urinary tract infections in healthy adult women.
What If The Infection Does Not Clear Up With Treatment
Most infections clear up with treatment. However, if an infection does not clear up, or if you have repeated infections, you may be given some special tests such as:
-
a type of x-ray called an intravenous pyleogram , which involves injecting a dye into a vein and taking pictures of your kidney and bladder
-
an ultrasound exam, which gives a picture of your kidneys and bladder using sound waves
-
a cytoscopic exam, which uses a hollow tube with special lenses to look inside the bladder.
Read Also: Common Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection
If You Have Trouble Emptying Your Bladder Completely This Is What You Can Do To Facilitate Bladder Emptying:
- When urinating, sit in a posture that relaxes the pelvic floor, leaning slightly forward with bent knees and feet resting on the ground or on a footstool
- When you have finished voiding, stand up and sit down again a few times. This may encourage urine to be voided that was left behind the first time.
Bacteria Identification Key To Therapy Selection
Studies analysing the typology of pathogens cau-sing urinary tract infections in non-diabetic patients quote Escherichia coli , Enterococcus sp. , Klebsiella sp. , Pseudomonas aeruginosa , Proteus sp. , and Staphylococcus sp. as the most prevalent bacteria . For diabetic patients, the most typical pathogens observed were Escherichia coli , Klebsiella spp , Staphylococcus spp , and Enterococcus spp . In pregnant women, urinary tract infections are usually caused by Escherichia coli , bacteria from the Staphylococcus genus , Proteus mirabilis , Enterococcus faecalis , and Klebsiella pneumoniae . In infants, the most common pathogens included Escherichia coli , Klebsiella , and Staphylococci .
Read Also: Fruits Good For Urinary Tract
Why Are Women And Older Adults More At Risk
E. coli or other bacteria cause UTIs, which are infections in your kidneys, bladder, ureters or urethra. Unfortunately, women are more likely to get them mainly because of their anatomy.
A womans urethra is shorter than a mans and closer to the anus. The urethra is also close to the vagina, which can collect bacteria during sex. So bacteria from both the anus and vagina have easy access to a womans urinary tract.
Post-menopausal women are also at higher risk because pH changes in the vagina make it more susceptible to infection.
Both men and women are more likely to get UTIs as they age. Certain medical conditions, such as bladder prolapse in women and enlarged prostate in men, cause incomplete bladder emptying in older adults. Urine that stays in your bladder too long can encourage bacteria to grow.
Some newer diabetic drugs can also promote sugar in the urine and create conditions ideal for a UTI, Dr. Vasavada adds.
Key Points About Urinary Tract Infections
- Urinary tract infections are a common health problem that affects millions of people each year. These infections can affect any part of the urinary tract.
- Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
- The most common symptoms of UTIs include changes in urination such as frequency, pain, or burning urine looks dark, cloudy, or red and smells bad back or side pain nausea/vomiting and fever.
- Antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Other treatments may include pain relievers, and drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Other things that can be done may help reduce the likelihood of developing UTIs.
Read Also: How To Heal Urinary Tract Infection Naturally
Can I Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
You can usually prevent a urinary tract infection with lifestyle changes. These tips can include:
In some post-menopausal women, a healthcare provider may suggest an estrogen-containing vaginal cream. This may reduce the risk of developing a UTI by changing the pH of the vagina. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have recurrent UTIs and have already gone through menopause.
Over-the-counter supplements are also available for UTIs. These are sometimes recommended for people who have frequent UTIs as another way to prevent them. Talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplements and ask if these could be a good choice for you.
From A Lower Uti To An Upper Uti
The most common type of UTI occurs in the lower urinary tract, infecting the urethra and bladder. Highly virulent strains, if left untreated, can spread further up to the ureters and the kidneys, in the upper urinary tract. Kidney infection symptoms in women are considerably worse than lower UTI symptoms, and may include back pain, nausea and fever. Kidney infections are potentially serious since they can cause damage to the kidneys and even kidney failure if left untreated. Eventually, they can also lead to urosepsis, an infection of the bloodstream that requires intensive care.
Read Also: Severe Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
How To Help Your Loved One Avoid Utis
Do you give the older adult in your life cranberry juice or probiotics to prevent a UTI? These products wont hurt them, but whether theyll help is unclear.
We dont have enough research to support their effectiveness in UTI prevention, although their medical benefits cant be ruled out completely, says Dr. Goldman.
Instead, he recommends these tried-and-true prevention strategies:
- Encourage sufficient fluid intake
- Promote genital and urinary hygiene
- Ask the doctor about low-dose vaginal cream for postmenopausal women
Dr. Goldman says researchers are also studying D-Mannose for UTI prevention. The supplement, which has few side effects, sticks to bladder receptors that normally attract the E. coli bacteria usually responsible for UTIs.
Researchers also believe D-Mannose may keep bad bacteria from colonizing the digestive tract, which can harbor the bacteria responsible for UTIs in women.
Following these tips should help your aging relative stay healthy, productive and out of the hospital.
Managing Urinary Tract Infections
If symptoms such as painful or overly frequent urination occur, as in the case of a urinary tract infection, consult your healthcare provider. Infections are easily treated with antibiotics but often tend to recur. To help prevent these infections, urinate before and after intercourse, be sure your bladder is not full for long periods, drink plenty of fluids, and keep your genital area clean. Douching is not thought to be effective in preventing infection. Currently, a vaccine is being developed which may help prevent recurrent bladder infections.
Verywell / Gary Ferster
For some women with recurrent urinary tract infections associated with menopause, low-dose antibiotics may be needed. A 2016 study also found that a supplement of hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, curcumin, and quercetin was effective in reducing the frequency of urinary tract infections in post-menopausal women, especially when combined with topical vaginal estrogen therapy .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get An E Coli Urinary Tract Infection