De Novo Or Increasing Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms During Covid
1Department of Urology, School of Medicine, Sakarya University, 54100 Sakarya, Turkey
22Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Sakarya University, 54100 Sakarya, Turkey
3Department of Infectious Diseases, School of Medicine, Sakarya University, 54100 Sakarya, Turkey
DOI:10.31083/j.jomh1808161Vol.18,Issue 8,August 2022 pp.1-6
31 August 2022
You May Like: Can Urinary Incontinence Be Cured
Urinary Tract Infections In Men
Men can get UTIs, particularly if they have trouble with urine flow. Older men who experience prostatitis are at a higher risk. If the bladder is not emptying properly, the build up ofurine makes it more difficult to cure the infection.
A small number of young men may get a UTI. In males, this is usually the result of a sexually transmitted disease.
Which Antibiotic Will Work Best
Your doctor will take a urine sample to confirm that you have a UTI. Then the lab will grow the germs in a dish for a couple of days to find out which type of bacteria you have. This is called a culture. Itâll tell your doctor what type of germs caused your infection. Theyâll likely prescribe one of the following antibiotics to treat it before the culture comes back:
Which medication and dose you get depends on whether your infection is complicated or uncomplicated.
âUncomplicatedâ means your urinary tract is normal. âComplicatedâ means you have a disease or problem with your urinary tract. You could have a narrowing of your ureters, which are the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder, a narrowing in the urethra which transports urine from the bladder out of the body, or, you might have a blockage like a kidney stone or an enlarged prostate . It’s also possible you have a urinary fistula or a bladder diverticulum.
To treat a complicated infection, your doctor might prescribe a higher dose of antibiotics. If your UTI is severe or the infection is in your kidneys, you might need to be treated in a hospital or doctor’s office with high-dose antibiotics you get through an IV.
Your doctor will also consider these factors when choosing an antibiotic:
- Are you over age 65?
- Are you allergic to any antibiotics?
- Have you had any side effects from antibiotics in the past?
Recommended Reading: What Causes Multiple Urinary Tract Infections
Unsaon Nako Malikayan Ang Usa Ka Laygay Nga Impeksyon Sa Urinary Tract
Kung dali ka sa nagbalikbalik nga UTI, siguroha nga:
- pag-ihi sa kanunay kung gikinahanglan
- pagpahid gikan sa atubangan ngadto sa likod human sa pagpangihi
- pag-inom ug daghang tubig aron matangtang ang bakterya sa imong sistema
- pag-inom og cranberry juice kada adlaw
- magsuot ug cotton underwear
- likayi ang hugot nga karsones
- likayi ang paggamit sa diaphragms ug spermicides alang sa pagpugong sa pagpanganak
- likayi ang pag-inom og mga likido nga makapalagot sa imong pantog
- paggamit og lubrication sa panahon sa pakighilawas, kon gikinahanglan
- likayi ang mga bubble bath
- hugasi kanunay ang yamis kung wala ka tuli
What Causes Chronic Urinary Tract Infections

- Bacteria entering the urethra during sexual intercourse
- Urinary tract problems
- Problems emptying the bladder completely due to blockage, muscle or nerve problems
- Kidney or bladder stones
- Altered estrogen levels during menopause
- Genetic predisposition
Women are at an increased risk of getting urinary tract infections if they:
- Have had a UTI before
- Have had several children
Also Check: Urinary Tract Medication For Cats
Why Should I Take The Full Dose
Antibiotics work well against UTIs. You might start to feel better after being on the medicine for just a few days.
But even so, keep taking your medicine. If you stop your antibiotics too soon, you wonât kill all the bacteria in your urinary tract.
These germs can become resistant to antibiotics. That means the meds will no longer kill these bugs in the future. So if you get another UTI, the medication you take might not treat it. Take the full course of your medicine to make sure all the bacteria are dead.
Chronic Urinary Tract Infections In Women
Urinary tract infections are painful and can disrupt your life. They are a very common problem, especially for women. Up to 60 percent of women will have at least one UTI during their lifetime.
But for some women, the infection doesnt go away with treatment. Or it disappears only to come back again soon. Our urogynecology specialists are experts at treating these complex, chronic urinary tract infections.
If you have chronic or recurrent UTIs, we can help you finally find relief.
Read Also: Do Urinary Tract Infections Make You Pee A Lot
Prevention Of Catheter Acquired Urinary Tract Infections
Guidelines
Several evidence-based guidelines provide recommendations for the development and maintenance of prevention programs for CA-UTI. Approaches to prevention include avoidance of catheter use, policies for catheter insertion and maintenance, catheter selection, surveillance of CA-UTI and catheter use, and recommendations for quality indicators.
Program implementation
The facility infection prevention and control program should incorporate measures to limit CA-UTI. Improved outcomes following implementation of these programs have been reported. The program for a given institution should be individualized to be relevant to local experience, population characteristics, and resources. An essential element of any program is leadership at the senior management level.
Avoidance of catheter use
The single most important intervention to prevent CA-UTI is to avoid use of an indwelling urinary catheter. There are only a limited number of accepted indications for catheter use:
-
Monitoring of hourly urine output in acutely ill patients.
-
Perioperative use for selected surgical procedures
-
Urologic surgery
-
Surgery on contiguous structures of the genitourinary tract
-
Large volume infusions or diuretics during surgery
-
Requirement for intraoperative monitoring of urine output
Management of acute urinary retention and urinary obstruction.
To facilitate healing of open pressure ulcers or skin grafts in selected patients with urinary incontinence.
Selection of urinary catheter
Urinary Tract Infections In Women
UTIs are common, particularly with increasing age. Women are more likely to get a UTI than men. Nearly 1 in 3 women will have a UTI needing treatment before the age of 24.
In women, the urethra is short and straight, making it easier for germs to travel into the bladder. For some women, UTIs relate to changes in their hormonal levels. Some are more likely to get an infection during certain times in their menstrual cycle, such as just before a period or during pregnancy.
In older women, the tissues of the urethra and bladder become thinner and drier with age as well as after menopause or a hysterectomy. This can be linked to increased UTIs.
During pregnancy, the drainage system from the kidney to the bladder widens so urine does not drain as quickly. This makes it easier to get a UTI. Sometimes germs can move from the bladder to the kidney causing a kidney infection. UTIs during pregnancy can result in increased blood pressure, so it is very important to have them treated as soon as possible.
Women are more at risk of repeated UTIs if they:
- use spermicide jelly or diaphragm for contraception
- have had a new sexual partner in the last year
- had their first UTI at or before 15 years of age
- have a family history of repeated UTIs, particularly their mother
- suffer from constipation
You May Like: Rusch Easy Tap Urinary Leg Bag
Statistics Around Frequent Utis
While the statistics around chronic urinary tract infections are hard to find, we do know that:
- 30-44% of females with an initial UTI will experience a second UTI. And with each UTI, the risk of another UTI increases.
- Frequent UTIs may be caused by multiple organisms simultaneously.
- A significant proportion of our quiz respondents have suffered 7+ UTIs, with a recurrence every 1-3 months.
- Our own data indicate that most females who experience recurrent UTIs do so despite standard antibiotic treatment.
- Testing and treatment guidelines for chronic urinary tract infections are inadequate or do not exist in most parts of the world. This means even when doctors want to help, they generally dont have the resources or guidance they need to be able to.
- One study found that 74% of females diagnosed with Interstitial Cystitis had previously been diagnosed with recurrent UTIs. Interstitial Cystitis is a painful set of urinary tract symptoms with no identified cause and no known cure.
- 93% of the females included in the above study had also received negative test results after having their urine cultured .
In short, a significant number of females move through escalating stages of diagnosis as antibiotic treatment fails to cure them and testing fails to find a cause.
The Need For Nonantibiotic Management
The armamentarium of effective antibiotics is rapidly diminishing, and the size of this problem cannot be overstated. Resistance to amoxicillin is now 100% among urinary isolates of E. coli in some countries in Africa, and high levels of resistance to many commonly prescribed antibiotics have been identified worldwide. Resistant strains of E. coli, such as ST131 , are associated with outbreaks of UTI, and the widespread emergence and spread of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae is a global public health threat,. Transmissible resistance in Enterobacteriaceae is now emerging against colistin with the potential to rapidly spread. This development means that our drug of last resort for treating infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria is failing, and infection with these multidrug-resistant strains might, therefore, be untreatable with currently available antibiotics.
Fig. 2: Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance by mobile genetic elements.
We are facing a future in which combination therapy for UTI treatment will be routine, as resistance rates to single agents rise to unacceptable levels worldwide and untreatable UTIs present a real concern. This problem is exacerbated by the overuse of antibiotics, both in humans and in veterinary medicine. To control this crisis in antimicrobial resistance, nonantibiotic approaches are crucial in providing a means of reducing symptoms without resorting to antibiotic use.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection How You Get It
Assessment And Diagnostic Findings
Results of various tests help confirm the diagnosis of UTI.
- Urine cultures. Urine cultures are useful in identifying the organism present and are the definitive diagnostic test for UTI.
- STD tests. Tests for STDs may be performed because there are UTIs transmitted sexually.
- CT scan. A CT scan may detect pyelonephritis or abscesses.
- Ultrasonography. Ultrasound is extremely sensitive for detecting obstruction, abscesses, tumors, and cysts.
Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis
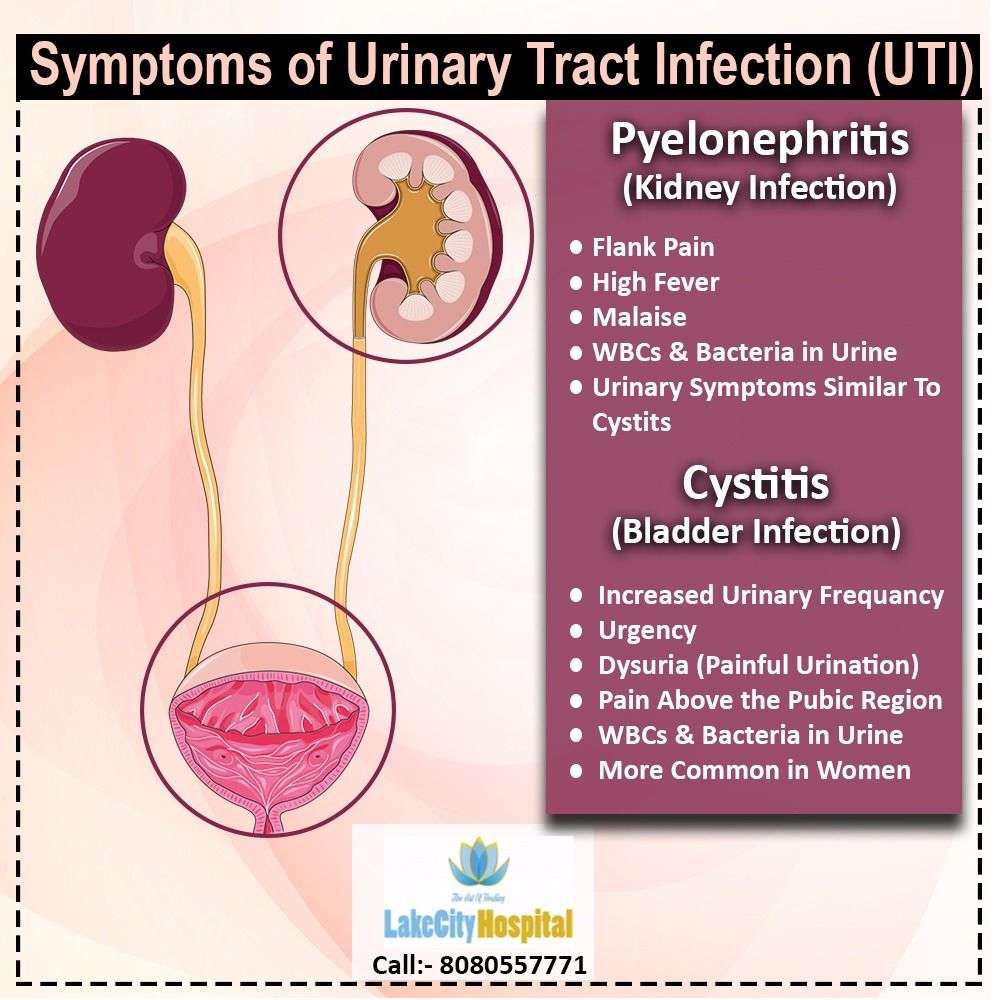
Your doctor will review your symptoms with you first and conduct a physical exam.
A urine sample is then taken to test for microbes. It is important to use a clean-catch sample for testing, which is done midstream rather than at the beginning. This helps to eliminate bacteria or yeast from your skin.
A large number of white blood cells in your urine indicate an infection, and a urine culture will help identify the specific microbe causing the infection.
Special testing is required if a viral infection is suspected, but they are rare causes of UTIs. Viral UTIs are more common in those with weakened immune systems or those who have had organ transplants.
If your doctor thinks you may have an upper tract infection, a blood count and culture is necessary to make sure the infection has not yet spread to your bloodstream through infected kidneys.
Some individuals have recurring UTIs, and these involve additional testing to identify possible abnormalities in the tract that could be the cause.
You May Like: Clear Tract Urinary Tract Formula
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection Treatments
Here are some treatments that are commonly used for successful treatment of chronic UTIs. Keep in mind that treatments employed will depend on the cause of the UTI:
- The primary treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics delivered over one week however, for chronic UTIs, if the patient takes low dose antibiotics long term or after sexual intercourse, it will help to prevent future UTIs.
- Along with prescribing antibiotics, the doctor may want to monitor the urinary system more closely using home urine tests. These are easy to do, and they are very effective at properly diagnosing the problem.
- Drinking cranberry juice and taking Vitamin C supplements can make your urine more acidic, which decreases the potential for bacteria growth while also keeping your heart and immune system healthy.
- If the chronic UTI occurs in combination with menopause, the patient may want to consider vaginal estrogen therapy in order to limit risk for future UTIs.
Consult your doctor before starting a treatment regimen. Chronic Urinary Tract Infections can be very painful, but with a little bit of time, the proper diagnosis, and patience, they can be a thing of the past.
What Causes Chronic Urinary Tract Infection
This is where the science gets a little more complicated.
Weve talked elsewhere about what causes UTIs. And above, we explained that recurrent UTIs can be attributed to a persistent bladder infection that is not properly eradicated by treatment.
A persistent bladder infection can last for years in the form of a chronic urinary tract infection. For many females, the cycle of acute and symptom-free periods is never broken, and some move on to be diagnosed with the conditions mentioned above, such as Interstitial Cystitis , or Painful Bladder Syndrome . More on that later.
Why has it been so difficult to detect and treat these infections?
There is a culprit here, so lets take a closer look. Behind the misdiagnosis of hundreds of thousands of people, are embedded chronic urinary tract infections that involve biofilms.
Donât Miss: Do You Get A Fever With A Urinary Tract Infection
Read Also: Opioid Induced Urinary Retention Treatment
Unsa Ang Mga Komplikasyon Sa Usa Ka Chronic Urinary Tract Infection
Ang mga tawo nga nag-antos sa laygay nga UTI mahimong makasinati og mga komplikasyon. Ang nagbalikbalik nga impeksyon sa urinary tract mahimog hinungdan sa:
- impeksyon sa kidney, sakit sa kidney, ug uban pang permanenteng kadaot sa kidney, labi na sa gagmay nga mga bata
- dugang nga risgo sa preterm nga pagpanganak o adunay ubos nga timbang nga mga bata
Utis And Hospital Stays
A hospital stay can put you at risk for a UTI, particularly if you need to use a catheter. This is a thin tube that’s inserted through the urethra to carry urine out of the body. Bacteria can enter through the catheter and reach the bladder. This is more often a problem for older adults who require prolonged hospital stays or who live in long-term care facilities.
Also Check: What Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics
Is Interstitial Cystitis Linked To Frequent Utis
We mentioned a study above, that found that 74% of survey respondents diagnosed with Interstitial Cystitis, had previously been diagnosed with recurrent UTI.
Research has also shown that a high percentage of females with Interstitial Cystitis may in fact have biofilms, IBCs, or both within their bladder, and that this is the cause of their ongoing infection and recurrent or continuous symptoms.
Interstitial Cystitis and associated conditions are considered to be incurable, however
Interstitial Cystitis is a diagnosis of exclusion. This means IC is diagnosed in the absence of any other obvious cause. If a cause for your UTI symptoms is not identified by testing, a diagnosis of IC may be given.
Check out our expert video series to learn more about the chronic UTI and IC connection.
How We Vet Brands And Products
Healthlineonly shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
- Evaluate ingredients and composition:Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims:Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand:Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
What is a chronic urinary tract infection?
Chronic urinary tract infections are infections of the urinary tract that either dont respond to treatment or keep recurring. They may either continue to affect your urinary tract despite getting the right treatment, or they may recur after treatment.
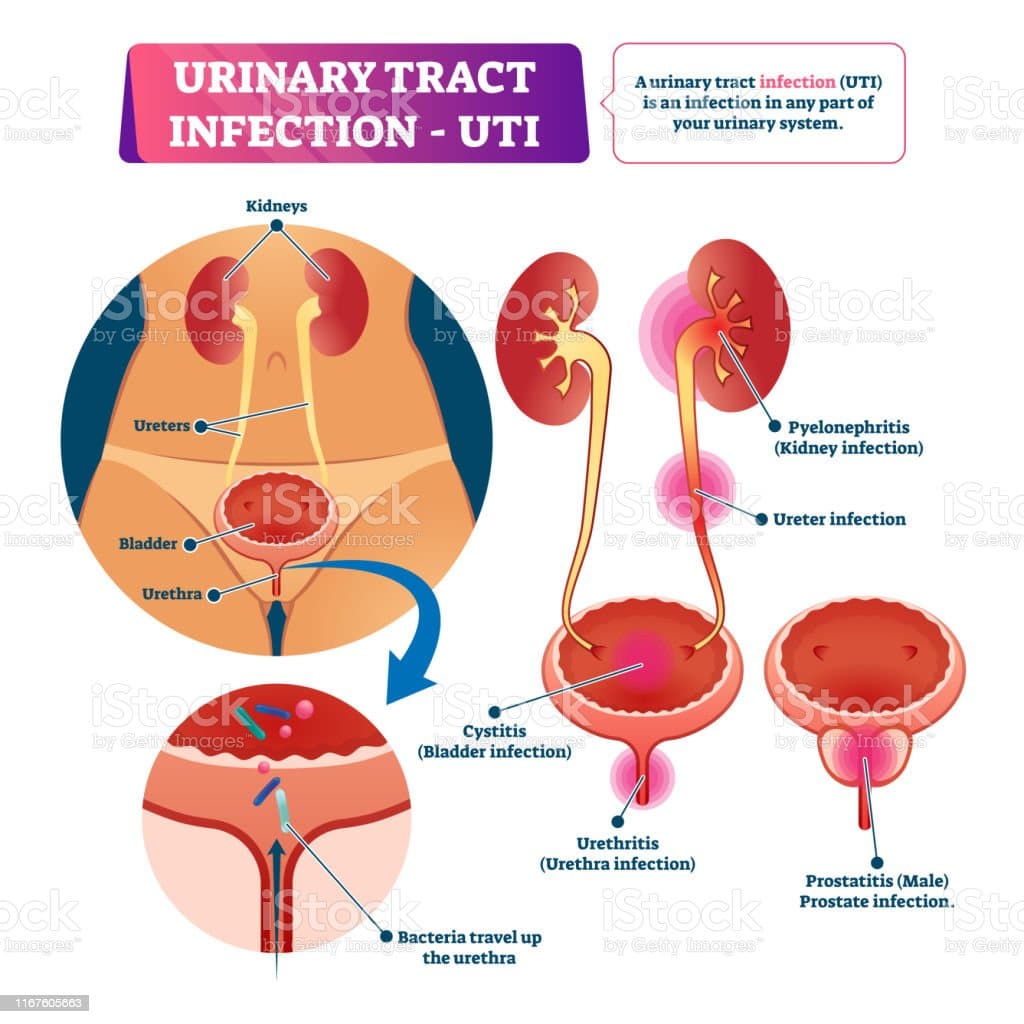
Your urinary tract is the pathway that makes up your urinary system. It includes the following:
- Your kidneys filter your blood and generate body waste in the form of urine.
- Your ureters are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Your bladder collects and stores urine.
- Your urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body.
A UTI can affect any part of your urinary system. When an infection only affects your bladder, its usually a minor illness that can be easily treated. However, if it spreads to your kidneys, you may suffer from serious health consequences, and may even need to be hospitalized.
Although UTIs can happen to anyone at any age, theyre more prevalent in women. In fact, the
You May Like: Royal Canin Urinary So Hp
So How Big Is The Problem
Its a massive problem. Up to 1.7 million women in the UK suffer from chronic lower urinary tract symptoms. A recent study found and other research suggests a similar number of men could be affected. A growing body of international research suggests that many people suffering from long-term urinary problems may have undiagnosed bacterial infections.
Yet the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines do not recognise the existence of chronic UTI and when tests results are negative and short courses of antibiotics fail to work many specialists seem unwilling to accept that chronic urinary symptoms can be caused by bacteria.
Patients are routinely dismissed as anxious and offered counselling and psychiatric referrals. Sufferers are forced to live in agony and lack quality of life, without ever finding effective treatment or anyone to diagnose and understand their condition. Stuck in a chronic UTI loop.
How Is It Investigated
If you have recurrent UTIs, then some of the ways that we investigate this are:
-
Enhanced Urine Testing We will take a urine sample to test for bacteria and white blood cells. We may also send your urine for specialised urine tests such as broth cultures and polymerase chain reaction to look for more unusual bacteria
-
Imaging It may be necessary to do ultrasounds to check on your kidneys and bladder emptying, special X-ray studies to see if there is an obstruction or stones in the urinary tract. We may also look into your bladder by passing a special scope through the opening into your bladder. This exam is called a cystoscopy.
-
Functional tests We may use a test called urodynamics to check how your bladder responds when it is filling up and how well coordinated your bladder and urethra are when you try to pass urine. Problems in these aspects of your bladder function may contribute to bladder symptoms and / or increase your susceptibility to UTIs.
Recommended Reading: Exercise To Strengthen Urinary Bladder