Can Kidney Stones Affect Your Psa Count
Typically, no. While kidney infections or UTIs can cause an elevated PSA count, kidney stones generally do not. Kidney stones are formed in the kidneys and pass through the bladder and urethra. PSA is produced in the prostate. If you had a kidney stone that got caught in your urethra at the prostate, and caused further inflammation of the prostate, it could result in a spike in your PSA level.
Common Causes Of Elevated Psa
Prostatitis. This also means a prostate infection, which causes inflammation of the prostate gland. Prostatitis is the most common prostate condition in men younger than 50. It can usually be treated with antibiotics.
Age. As men age, their prostate naturally gets bigger. This happens regardless of any medical condition affecting the prostate gland.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia . BPH also means an enlarged prostate gland. This does not mean prostate cancer. BPH is the most common prostate condition men over 50 suffer from. It can often cause urination problems such as frequent urination or difficulty urinating.
Prostate Cancer. An elevated PSA could indicate prostate cancer. If you have an elevated PSA, your doctor will also do a digital rectal exam to see if there are any suspicious lumps present on the prostate gland. If the doctor suspects prostate cancer, a prostate biopsy will be recommended.
Its also important to monitor any changes in the PSA. If the PSA continues to rise, this may mean prostate cancer. If you continue to have an elevated PSA, but your biopsy is negative, your doctor will most likely recommend follow-up PSA tests and a follow-up biopsy within six months.
Urinary Tract Infection. A urinary tract infection can cause irritation and inflammation in the prostate gland, which can cause the PSA to go up. If you have a UTI, a doctor will prescribe antibiotics to treat it.
Related Coverage
What Is The Psa Test
Prostate-specific antigen, or PSA, is a protein produced by normal, as well as malignant, cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in a mans blood. For this test, a blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually reported as nanograms of PSA per milliliter of blood.
The blood level of PSA is often elevated in men with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 1986 to monitor the progression of prostate cancer in men who had already been diagnosed with the disease. In 1994, FDA approved the use of the PSA test in conjunction with a digital rectal exam to test asymptomatic men for prostate cancer. Men who report prostate symptoms often undergo PSA testing to help doctors determine the nature of the problem.
In addition to prostate cancer, a number of benign conditions can cause a mans PSA level to rise. The most frequent benign prostate conditions that cause an elevation in PSA level are prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia . There is no evidence that prostatitis or BPH leads to prostate cancer, but it is possible for a man to have one or both of these conditions and to develop prostate cancer as well.
Also Check: Are Urinary Tract Infections Contagious
What Can Falsely Lower Your Psa Level
There are also some conditions that can lower the PSA level, which could potentially lead to a normal PSA level reading even though cancer is present. Keep these in mind when getting your PSA level checked:
-
Medications, particularly testosterone-lowering medications used to treat BPH or male pattern baldness, like finasteride or dutasteride.
-
Obesity, which may be because of the way body fat can change hormone levels. And because theres a larger volume of blood in the body, which dilutes the PSA level.
Ways To Prevent Recurrence

When it comes to cancer recurrence, there are no guarantees. But there are things you can do to lower your risk and improve your overall health.
If you smoke, quit now. According to the Prostate Cancer Foundation, men who have a prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer and continue to smoke are twice as likely to have a recurrence. Men who quit smoking have a risk similar to those who never smoked. Smoking is also a risk factor for prostate cancer death.
Managing your weight may also help. Obesity is associated with more aggressive disease and death from prostate cancer. Whether you only have a few pounds or many pounds to lose, slow and steady weight loss can start today.
Even if your current weight is in a healthy zone, eating right can help keep you there. Here are a few tips to get started:
- Avoid or minimize saturated fats. They may
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Immediate Relief
High Result In Prostate Specific Antigen Test
Why Your Psa Is High
Elevated PSA levels dont necessarily mean that you have cancer. The PSA test is only one screening test that helps your doctor determine your prostate health. You might have high PSA levels due to a number of other conditions, including:
- Your age
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Prostatitis
- Urinary tract infection
- Recent urogenital medical procedure
If your PSA is already borderline high, even having a rectal exam or ejaculating could cause your levels to rise. Also, you could have a benign condition and prostate cancer at the same time.
Read Also: Hill’s Urinary Hairball Control
Elevated Psa Level Causes
Elevated PSA Level Causes
Prostate specific antigen is a protein that is produced by the prostate gland. Rising levels of PSA in the bloodstream can be an early sign of prostate problems, including prostate cancer. But there are also many non-cancerous reasons for elevated PSA levels. Infection, inflammation, and injury can all trigger a rise in PSA.
Possible causes for elevated PSA level include:
The likelihood of developing BPH increases as men age. According to the American Urological Association, BPH affects about half of men in their fifties and sixties and up to 90% of men over age eighty. The larger the prostate, the greater the chance a PSA elevation may be due to a benign condition like BPH and not prostate cancer.
In Men Over : Bph May Be The Cause Of High Psa
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is an enlargement of the prostate gland, but its not prostate cancer. “BPH means more cells, so that means more cells making PSA,” explains Dr. Castle.
BPH is the most common prostate problem in men over age 50. It may not need to be treated unless its causing frequent or difficult urination.
Your primary care doctor may be able to tell the difference between BPH and prostate cancer by doing a digital rectal exam, but commonly this will require evaluation by a urologist and further testing, such as a biopsy or imaging studies.
Also Check: What Causes Urinary Tract Infection In Women
What Happens If My Psa Comes Back High
Should your PSA level return higher than expected or above the normal physiologic range based on your age, the first step will likely be to draw a follow-up PSA. If the repeat PSA is lower, the initial elevation may have been temporary and associated with something other than prostate cancer. If the repeat PSA remains high, Dr. Kasraeian may recommend further studies, including an MRI, prostate biopsy, or another advanced diagnostic test to rule out prostate cancer. While all patients are monitored closely, patients who receive an elevated PSA result can expect to have PSAs drawn more frequently for a period of time.
Test Results And What They Mean
The National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health state:
- There is no specific normal or abnormal level of PSA in the blood. In the past, most doctors considered PSA levels of 4.0 ng/mL and lower as normal.
- However, more recent studies have shown that some men with PSA levels below 4.0 ng/mL have prostate cancer and that many men with higher levels do not have prostate cancer.
- Various factors can cause a man’s PSA level to fluctuate, ranging from having a urinary tract infection to taking medication to treat BHP.
- Although expert opinions vary, there is no clear consensus regarding the optimal PSA threshold for recommending a prostate biopsy for men of any racial or ethnic group.
- In general, the higher a man’s PSA level, the more likely it is that he has prostate cancer. Moreover, continuous rise in a man’s PSA level over time may also be a sign of prostate cancer.
Read Also: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Vs Azo Urinary Pain Relief
Other Reasons For An Elevated Psa Test
In addition to urinary tract infection and prostatitis, there are other reasons that can cause a high PSA level. These include:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia Benign prostatic hyperplasia, also known as BPH, is enlargement of the prostate caused by aging. An enlarged prostate can produce higher levels of PSA. There are treatments available for BPH.
- Medical procedures A prostate exam or digital rectal exam can result in inflammation of the prostate and increased PSA levels. A urinary catheter or urethral scope can also cause higher PSA levels. For accurate results, wait a few weeks after having a medical procedure done before having a PSA test.
- Age It is normal for PSA levels to gradually trend up with age. If the rise in your PSA level is slow, and consistent with your age, there is likely no concern.
- Cancer An elevated PSA level does not mean you have cancer but most men with prostate cancer do have an elevated PSA level. If you have an elevated PSA level your doctor may perform a digital rectal exam to check for lumps on the prostate. They will also likely order another PSA test to see if your level continues to rise. They may order imaging tests to check for cancer on the prostate. If you are receiving treatment for prostate cancer, your doctor will likely monitor your PSA level to help determine how effective treatment is. If PSA decreases, it can indicate that treatment is effective.
There Are Several Causes Of Elevated Psa Aside From Prostrate Cancer
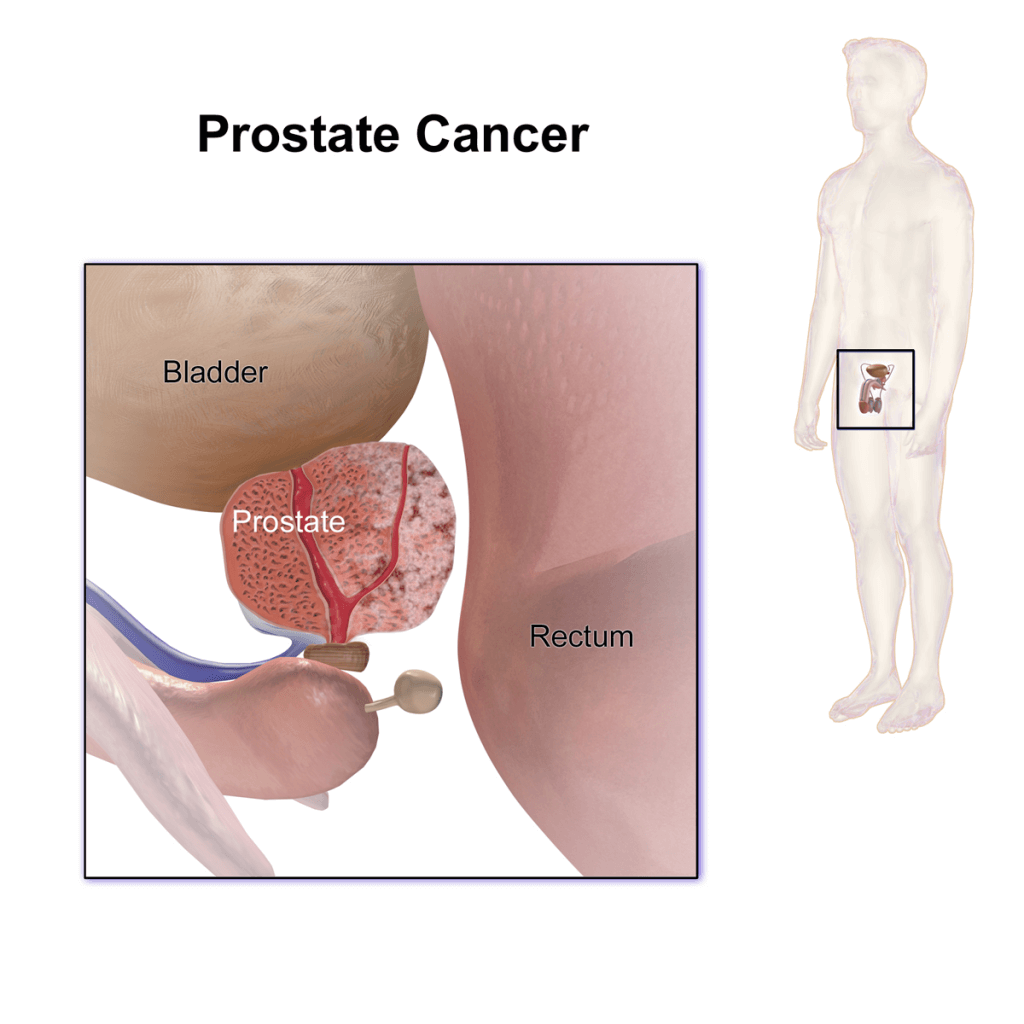
The PSA blood test is a screening tool used in the detection of prostate cancer. Sometimes, test results will indicate an elevation in PSA blood levels. Fortunately, this does not definitively mean a cancer diagnosis. Known causes of elevated PSA can range from simple activities such as cycling prior to the blood test, to an inflammation of the prostate. In fact, a number of benign medical issues can affect PSA numbers.
In general, PSA screening should begin as men reach their 50s. However, men who are at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer, such as African American men and those who have a history of prostate cancer in their family, should begin PSA testing by 40.
Don’t Miss: Male Urinary Tract Infection Over The Counter Treatment
Elevated Psa In Men May Signal Problems With The Prostate Gland
Prostate specific antigen is a glycoprotein produced by normal prostate tissue and is measured by obtaining a blood sample. Several factors can cause an elevated PSA in men, including prostate cancer. However, having an elevated PSA does not always mean a cancer diagnosis. The best recommendation is to be evaluated by a urologist to determine why PSA levels are high.
Several non-cancerous conditions can cause an increase of PSA in the blood. Even common factors such as ejaculating during intercourse or having digital rectal exam of the prostate can cause slight elevations of PSA for a short period of time. Other contributors can include:
- BPH or enlarged prostate
- Prostatitis an inflammation of the prostate / infection. Prostatitis can be bacterial or non-bacterial.
- Slow urinary stream
Leaders In Prostate Cancer Treatment
If the diagnosis is prostate cancer, youll find expert care from the team at the John Theurer Cancer Center at Hackensack University Medical Center. Our specialists provide you with the most advanced, proven, and effective treatment with the fewest possible side effects. Learn more about prostate cancer care at John Theurer Cancer Center
You May Like: D Mannose For Urinary Tract Health
Medical Procedures Can Cause Psa To Rise
“Anything that traumatically interferes with the architecture around the prostate gland can make PSA go up,” says Dr. Milner. “One of the most common causes of significantly high PSA from this type of trauma is the placing of a catheter into the bladder.”
Another cause is a prostate or bladder exam that involves passing a scope or taking a biopsy.
“Since it takes about two to three days for PSA to go down by half, you should wait two to three weeks after this type of trauma to do a PSA test,” Milner says.
Does Normalizing Psa After Successful Treatment Of Chronic Prostatitis With High Psa Value Exclude Prostatic Biopsy
Sherif Azab1, Ayman Osama2, Mona Rafaat3
1 Urology Department, Faculty of medicine, October 6 University, 2 Radiology Department, October 6 University 3 Clinical Pathology Department, National research Center, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to:
Objective: Evaluate male patients with diagnosed chronic prostatitis, elevated serum prostate-specific antigen to find out whether medical treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs can lower serum PSA, and consequently decrease the prostate cancer detection rate in patients with post-treatment PSA< 4 ng/mL.
Materials and methods: This prospective study evaluated 142 male patients aged 40-73 years whose presented with elevated serum PSA> 4 ng/mL and were consequently diagnosed with chronic prostatitis as expressed prostatic excretions examination revealed more than 10 white blood cells per high power field. The Patients underwent treatment with antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents for 6-weeks. Subsequently, all patients are Followed-up by serum PSA and performed transrectal ultrasonography-guided prostate biopsy within 2 months of treatment.
Chronic prostatitis is one of the causes that elevate serum PSA levels. Treatment of chronic prostatitis with elevated PSA by antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents can decrease the elevated PSA to the normal levels. Nevertheless, the opportunities of potential prostate cancer still exist in patients with a decreased PSA level even also if PSA< 2.5 ng/mL.
Read Also: Medtronic Interstim Therapy For Urinary Control
Should Everyone Be Screened With Psa
Screening is defined as looking for cancer before a person has symptoms. Prostate cancer is a complex disease it can develop into a fatal, painful disease, but it can also develop so slowly that it will never cause problems during the man’s lifetime. There are concerns regarding the mass use of PSA and over-detection of incidental, small volume and low-grade prostate cancer with little potential to cause harm to the patient. A prostate biopsy can cause harmful side effects such as bleeding and infection. Even if the prostate biopsy is negative, the PSA still has to be monitored regularly and this can cause psychological stress on the patient. Prostate cancer treatments, such as surgery and radiation therapy, may cause incontinence, erection problems and other complications. Therefore, the risks and benefits of diagnostic procedures and treatments must be taken into account when considering whether to have prostate cancer screening.
The Urology Society of Australia and New Zealand currently does not recommend the use of mass populationbased PSA screening as a public health policy, as published studies to date have not taken into account the cost effectiveness of screening, nor the full extent of overdetection and overtreatment.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A high PSA level has been linked to an increased chance of having prostate cancer.
PSA testing is an important tool for detecting prostate cancer, but it is not foolproof. Other conditions can cause a rise in PSA, including:
- A larger prostate
- Recent tests on your bladder or prostate
- Catheter tube recently placed into your bladder to drain urine
- Recent intercourse or ejaculation
Your provider will consider the following things when deciding on the next step:
- Your age
- If you had a PSA test in the past and how much and how fast your PSA level has changed
- If a prostate lump was found during your exam
- Other symptoms you may have
- Other risk factors for prostate cancer, such as ethnicity and family history
Men at high risk may need to have more tests. These may include:
- Repeating your PSA test, most often sometime within 3 months. You may receive treatment for a prostate infection first.
- A prostate biopsy will be done if the first PSA level is high, or if the level keeps rising when the PSA is measured again.
- A follow-up test called a free PSA . This measures the percentage of PSA in your blood that is not bound to other proteins. The lower the level of this test, the more likely it is that prostate cancer is present.
Other tests may also be done. The exact role of these tests in deciding on treatment is unclear.
- A urine test called PCA-3.
- An MRI of the prostate may help identify cancer in an area of the prostate that is hard to reach during a biopsy.
You May Like: Help For Female Urinary Incontinence