Early Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
The following are some of the early-stage bladder cancer symptoms you might experience:
1. Blood in the Urine
Blood in urine, often referred to as hematuria, is the most common symptom or sign of bladder cancer. With this symptom:
- You might have enough blood to change your urine color to pink, orange or, less often, dark red.
- Your urine color is sometimes normal, but a urine test , which the doctor performs during a general medical checkup or if you have other symptoms, can still detect small traces of blood.
- You may have blood one day and not the next, with your urine staying clear for weeks or maybe even months at a time.
Generally, the earlier stages of bladder cancer when the cancer is small and confined to your bladder only cause bleeding with either no pain or little pain.
It’s important to note that blood in your urine doesn’t necessarily indicate bladder cancer. The cause of blood may be due to another factor. In fact, many healthy individuals may have some unseen blood in their urine at some stage . And, for most individuals, the cause isn’t cancer.
In many situations, the cause is due to other things like benign tumors, medications or foods, infection, bladder or kidney stones or another benign kidney disease. Still, you should have your doctor check it out.
If you’re concerned about cancer, ask them about Cxbladder, a non-invasive genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer.
Bladder Cancer Symptoms In Men Vs Women
Many people assume that the symptoms of bladder cancer in men are different than those in women, but thats actually not the case. Men and women generally experience the same bladder cancer symptoms. However, because many signs of bladder cancer are easily mistaken for symptoms of other, less-serious conditions commonly experienced by females, women tend to be less likely than men to promptly seek professional care, leading to poorer outcomes.
For example, urinary tract infections can produce many of the same symptoms as bladder cancer, including blood in the urine, pain and a burning sensation while urinating, frequent urination and an urge to urinate even with an empty bladder. Although men can also develop UTIs, these infections are much more prevalent among women. In fact, according to the national Office on Womens Health, women develop UTIs up to 30 times more often than men do. The agency also reports that more than half of women will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime, and that approximately four in 10 women who develop a UTI will experience at least one more within the following six months.
How Does Bladder Cancer Spread
Bladder cancer usually begins in the cells of the bladder lining. In some cases, it may spread into surrounding bladder muscle. If the cancer penetrates this muscle, it can spread to other parts of the body, usually through the lymphatic system.
If bladder cancer spreads to other parts of the body, such as other organs, it’s known as metastatic bladder cancer.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Online
Transurethral Resection Of A Bladder Tumour
If abnormalities are found in your bladder during a cystoscopy, you should be offered an operation known as TURBT. This is so any abnormal areas of tissue can be removed and tested for cancer .
TURBT is carried out under general anaesthetic.
Sometimes, a sample of the muscle wall of your bladder is also taken to check whether the cancer has spread, but this may be a separate operation within 6 weeks of the first biopsy.
You should also be offered a dose of chemotherapy after the operation. This may help to prevent the bladder cancer returning if the removed cells are found to be cancerous.
See treating bladder cancer for more information about the TURBT procedure
How Can I Prevent Bladder Cancer
You may not be able to prevent bladder cancer, but it may be helpful to know the risk factors that may increase the chance youll develop bladder cancer. Bladder cancer risk factors may include:
- Smoking cigarettes: Cigarette smoking more than doubles the risk of developing bladder cancer. Smoking pipes and cigars or being exposed to second-hand smoke also increases that risk.
- Cancer treatments: Radiation therapy is the second-most common risk factor. People who have certain chemotherapy drugs may also develop an increased risk of bladder cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines , are at an increased risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infections: People who have frequent bladder infections, bladder stones or other urinary tract diseases may have an increased risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Past bladder cancer: People with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Don’t Miss: What To Drink To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection
Signs Of Urinary Tract Cancer
Urinary tract cancer is a cancer that forms in the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.Cancer can develop in the urine collection system, but this condition is often rare.
Urinary tract cancer is closely related to bladder cancer. Urinary lining cells are the same type with cells lining the bladder. People diagnosed with urinary cancer have a higher risk of bladder cancer, so doctors often recommend testing to look for signs of bladder cancer.
Urinary tract cancer is uncommon and most common in older people and people who have previously been treated for bladder cancer.
According to statistics, about 60% of urinary cancers detect the disease at the papillary stage 40% of the remaining cases are detected when the disease has turned into a late stage. Therefore, knowing how to recognize urinary cancer will make the process of finding and treating the disease easier.
Urinary tract cancer is uncommon and most common in the elderly.
How to identify signs of urinary tract cancer:
Usually, when you have urinary tract cancer, you will see symptoms like:
Talking To Your Doctor About Bladder Symptoms
When you meet with your doctor, its important to share all the symptoms youre experiencing and to be as specific as possible. Its a good idea to prepare for your appointment by writing a list of your symptoms and the questions you would like to ask.
When you create a list of your symptoms, try to include the following:
- All the symptoms you have experienced
- How often and at what time of day the symptoms occur
- How long the symptoms last
- If the symptoms seem to be getting better or worse
- If the symptoms interfere with your usual daily activities
- If anything relieves or worsens these issues
In addition to having a detailed list of symptoms to bring to your appointment, be ready to share information such as all of the medications you take , your habits and lifestyle , and any major life changes or stressors you may be experiencing.
Most importantly, be sure to answer your doctors questions openly and honestly, as this will help them to achieve a timely and accurate diagnosis.
Also Check: Medtronic Device For Urinary Incontinence
Don’t Miss: How Does A Urinary Tract Infection Feel Like
What Are The Signs Of These Types Of Tumors
The signs of urinary tract tumors depend on what area of the urinary system is affected. Tumors of the ureters, bladder, and urethra can cause hematuria , dysuria , difficulty urinating, and frequent urination. Recurrent and often unresolving secondary urinary tract infections are commonly associated with these types of tumors. If the tumor obstructs the ureter, preventing the flow of urine to the bladder, the kidney will swell with urine causing signs of abdominal pain. If the tumor obstructs the urethra, there may be lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, straining or the inability to urinate.
“The signs of urinary tract tumors depend on what area of the urinary system is affected.”
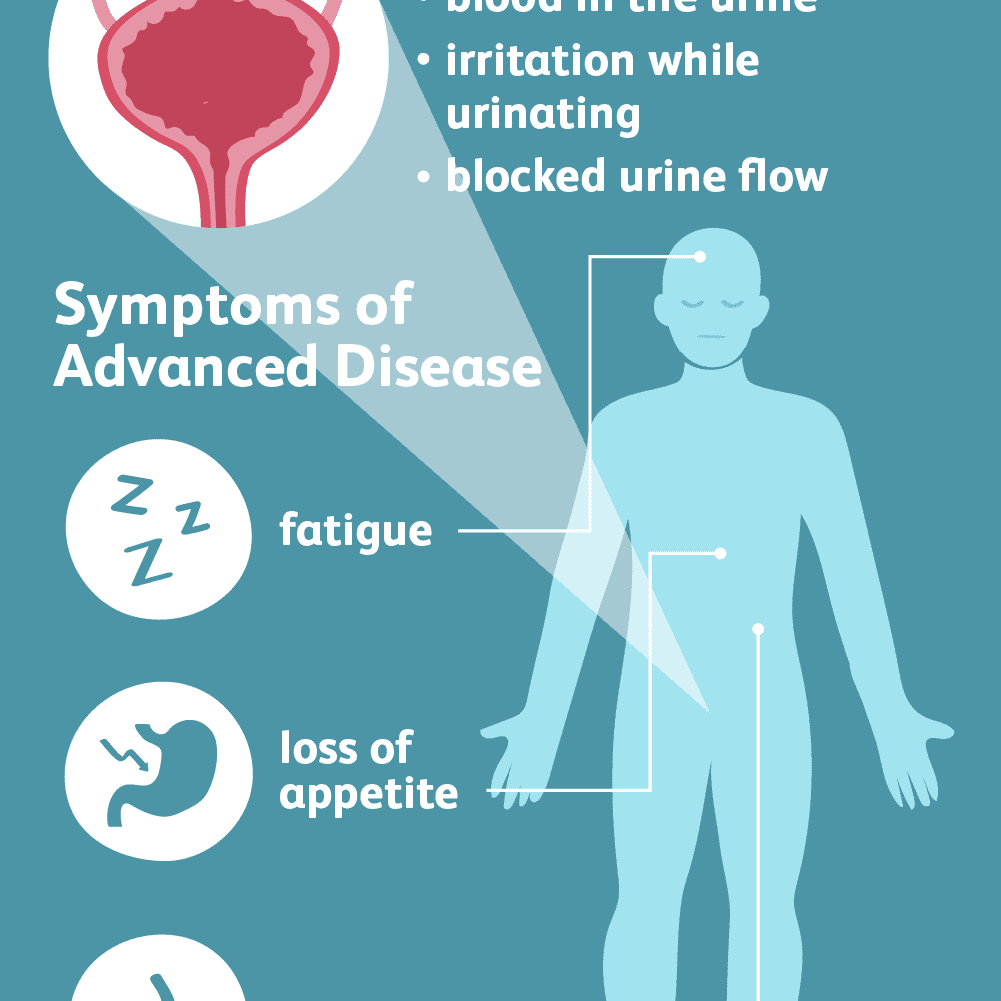
Tumors of the kidneys can cause abdominal pain, blood in the urine, or non-specific signs such as lack of appetite, nausea or vomiting, weight loss, fever, lethargy, and swelling of the abdomen. Occasionally kidney tumors can cause increased urination and drinking.
Because many urinary tract tumors will spread to other areas in the body , there may be signs elsewhere . Kidney pain can sometimes be difficult to distinguish from back pain.
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Healthcare providers and researchers dont know exactly why certain bladder cells mutate and become cancerous cells. Theyve identified many different risk factors that may increase your chance of developing bladder cancer, including:
- Cigarette smoke: Smoking cigarettes more than doubles your risk of developing bladder cancer. Smoking pipes and cigars and being exposed to second-hand smoke may also increase your risk.
- Radiation exposure: Radiation therapy to treat cancer may increase your risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Certain chemotherapy drugs may increase your risk.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Studies show that people who work with certain chemicals used in dyes, rubber, leather, paint, some textiles and hairdressing supplies may have an increased risk.
- Frequent bladder infections: People who have frequent bladder infections, bladder stones or other urinary tract infections may be at an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Chronic catheter use: People who have a chronic need for a catheter in their bladder may be at risk for squamous cell carcinoma.
Recommended Reading: Azo Pills For Urinary Tract Infection
Signs Of Bladder Cancer That Women Should Know
Even if you’re vigilant about getting routine GYN care, bladder cancer may not really be on your radar. After all, it’s far more common among men than women, and the majority of cases affect patients over age 65. But don’t let those stats keep you from learning to spot the symptoms. Many people mistakenly think bladder cancer is only a disease of older men, but there are more than 18,000 women who are diagnosed with this cancer every year in the United States.
And because women may not be on the lookout for early bladder cancer symptoms, the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network reports that women are more likely to be diagnosed with bladder cancer at an advanced stage. Knowing the symptoms can help you get diagnosed sooner, which can improve your prognosis.
Here are a few warning signs to watch for:
BLOOD IN YOUR URINE
This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer, and it’s an easy one for women to overlookespecially because it’s typically painless and you can go weeks or even months between occurrences. Many women ignore this symptom because they connect it with menstruation or menopause. Women who have microscopic blood in the urine without symptoms of urgency/frequency or pain, often do not have a UTI, and in fact, the blood in the urine may be due to cancer or other conditions.
UTI-LIKE SYMPTOMS
UNEXPLAINED PAIN
“SMOKING”
Can A Bacterial Infection Cause Cancer
More recently, infections with certain viruses, bacteria, and parasites have been recognized as risk factors for several types of cancer in humans. Worldwide, infections are linked to about 15% to 20% of cancers.
Can bacteria in urine be cancer?
Several investigators suggest that bacteria may play a role in inducing bladder cancer. Clinically, researchers have linked the development of infection, urinary stones and indwelling catheters with bladder cancer.
What causes cancer of the urinary tract?
Smoking is the single biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. This is because tobacco contains cancer-causing chemicals. If you smoke for many years, these chemicals pass into your bloodstream and are filtered by the kidneys into your urine.
Also Check: Otc Med For Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes This Cancer
The reason why a particular pet may develop this, or any tumor or cancer, is not straightforward. Very few tumors and cancers have a single known cause. Most seem to be caused by a complex mix of risk factors, some environmental and some genetic or hereditary.
Urinary tract tumors are most common in middle-aged to older animals. However, a rare form of primary kidney cancer called a nephroblastoma usually occurs in dogs less than 1 year of age and young cats. Its cause is related to genetic changes that occur early in life. In German Shepherds, a mutation of a specific gene is associated with renal carcinoma and the development of a nodular skin condition called dermatofibrosis.
Bladder tumors in dogs have been linked to being overweight and to exposure to certain insecticides. It has also been proposed that chronic bladder infections and inflammation may increase the risk of developing bladder cancers. Certain breeds of dogs are more likely to develop bladder tumors, including the Scottish Terrier.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
Bladder cancer is relatively rare, so you may not know as much as youd like about the condition. Here are some questions that may be helpful:
- What stage of bladder cancer do I have?
- What are possible treatments?
- What are treatment side effects?
- Will I need surgery?
- How will surgery affect my daily life?
- How often does bladder cancer come back?
- How do you treat recurrent bladder cancer?
- Are there any cutting-edge clinical trials available?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have bladder cancer, it may help to know about half of all people with the condition receive treatment when their tumors are limited to the inner layer of their bladder wall. For them, surgery to remove tumors means theyre cancer-free. But bladder cancer often comes back . If youre worried about recurring cancer, talk to your healthcare provider. Theyre your best resource for information on risk factors that increase the chance youll have another bout of bladder cancer. Theyll help you stay vigilant about symptoms that may be signs of recurring bladder cancer and be there for you if you need more bladder cancer treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/26/2022.
References
Also Check: How Do You Get Urinary Tract Infection Male
Bladder Cancer In Men Vs Women
Bladder cancer is 3 to 4 times more common in people assigned male at birth than in people assigned female at birth.
Researchers believe the increased prevalence of bladder cancer in those assigned male at birth may be due to differences in how carcinogens are metabolized before they pass through the bladder . Or it may be that male sex hormones promote tumor formation in the bladder, whereas female sex hormones inhibit this progression.
In contrast, people assigned female at birth tend to be diagnosed at later stages of the disease, do not respond as well to treatment, and have a higher cancer-specific mortality rate, so its especially important for those assigned female at birth to be aware of early symptoms and seek prompt evaluation.
One study looked at the prevalence of the early cancer symptoms in both sexes, concluding that:
- Visible hematuria was present in 65% of men and 68% of women.
- Dysuria was present in 32% of men and 44% of women.
- Urgency was present in 61% of men and 47% of women.
- Nocturia was present in 57% of men and 66% of women.
Painful urination is often dismissed as due to a bladder infection or friction and may be less likely to be investigated, particularly in women. One study found that 47% of female bladder cancer patients were treated for symptoms up to a year before a diagnosis was made, without receiving any further evaluation. A lower percentage of females than males saw a urologist as well.
What Is Bladder Cancer
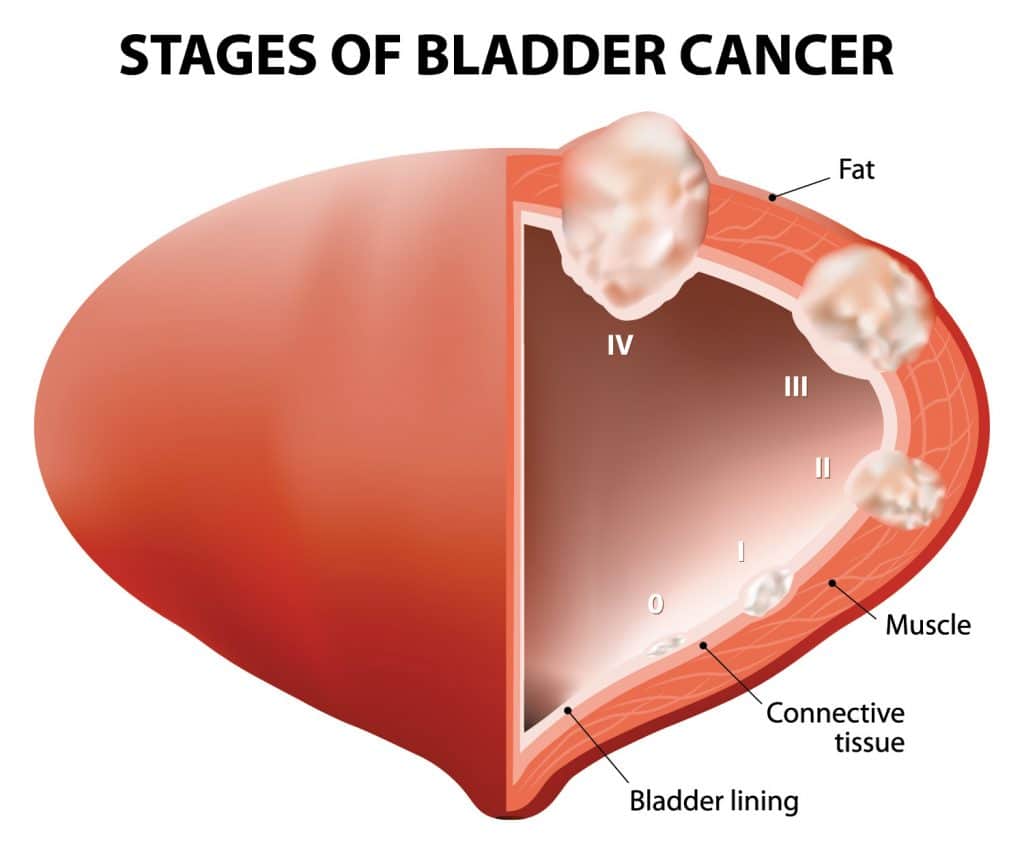
Bladder cancer is a relatively rare form of cancer that starts in the lining of your bladder. Your bladder is a small hollow organ that holds your pee . Healthcare providers have many ways to treat bladder cancer, including surgery to remove bladder cancer. Bladder cancer may come back after treatment, so people with bladder cancer should be vigilant about following up with their healthcare providers.
Healthcare providers can treat early-stage bladder cancer cancer thats found and treated before it can spread but about 75% of early-stage bladder cancers come back.
How does this condition affect my body?
Your bladder is a triangle-shaped organ thats centered between your hip bones, above your urethra and below your kidneys. Pee from your kidneys drains into your bladder, which is lined with tissue called urothelium. Urothelium is made of cells that stretch when your bladder fills with pee and collapses when its empty.
Bladder cancer happens when certain cells in the tissue lining your bladder mutate or change, becoming abnormal cells that multiply and cause tumors in your bladder. Left untreated, bladder cancer may grow through your bladder walls to nearby lymph nodes and then other areas of your body, including your bones, lungs or liver.
What are bladder cancer types?
There are three types of bladder cancer. Each type is named for the cells that line the wall of your bladder where the cancer started. Bladder cancer types include:
How common is bladder cancer?
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of A Urinary Tract Infection Fast
What Is Upper Urinary Tract Cancer
Cancer is when cells in the body grow out of control, often forming a mass or tumor. In upper urinary tract cancer, abnormal cells are found in the:
Cancers of the upper urinary tract are relatively rare. The most common of all upper urinary tract cancers are those found in the renal pelvis and renal calyces. Cancer in the ureters makes up about a quarter of all upper urinary tract cancers.
Tumors of the renal calyces, renal pelvis and ureters start in the layer of tissue that lines the bladder and the upper urinary tract, called the urothelium. Cancer that starts in the urothelium is called urothelial cancer. This is the most common type of cancer found in the bladder, as well. Because many of the organs in the urinary system share common cells, cancers found in these organs often look and act alike.
The urothelium is special in the way that it swells and shrinks to push urine through the urinary tract. Because it is in direct contact with the urine, this lining is exposed to chemicals filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. These chemicals can cause cells to change and grow out of control as cancer.
Because the bladder stores urine, it may be at greater risk for cancer than other parts of the upper tract. Its cells are exposed to harmful substances for a longer time. When urine has a high percent of harmful chemicals, cancer may also grow in the kidney or ureters.