What Are Cystitis And Urinary Tract Infections
Your urinary tract is made up of your kidneys, ureters, and bladder. Your body uses this system to rid itself of waste, including bacteria. Your kidneys produce urine, which travels to the bladder for storage before emptying through the urethra.
Normally, your urine does not contain bacteria. When bacteria are introduced to your body through the urethra, they can cause a urinary tract infection that is uncomfortable and potentially harmful to your body.
Cystitis and UTIs have similar causes but affect different parts of the urinary system.
Normal Protective Factors / Normal Function Of Urinary Tract System:
-
Host defense mechanisms exist to maintain sterility and prevent UTI
-
Complete bladder emptying during micturition
-
Presence of uromodulin and uroepithelium mucous secretions
-
Ureterovesical junction competence
-
Urethral sphincter competence
-
Protective uroepithelial immune response
During the normal function of the urinary tract system, the body is able to protect and rid itself from invading bacteria. The bladder and urethra maintain a sterile environment by preventing bacteria from clinging to its structures. Bacteria are expelled out of the body during urination.
The normal composition of urine provides a bactericidal effect. Urine has a low pH and high osmolarity which most organisms cannot survive in. Urine also contains uromodulin and uroepithelium mucous secretions which act against bacteria.
In women, mucous production in the urethra traps bacteria before it can enter into the bladder.
Men have a longer urethra compared to women, making it harder for bacteria to enter the bladder. Men also produce mucous secretions from the prostate to protect them against infection.
UTI occurs when there is a break or alteration in the hosts defense mechanisms and pathogens occupy host and reproduce.
Figure 4. Bladder
Figure 5. Urinary Tract Host Defenses Diagram .
What Is Acute Cystitis With Hematuria
So exactly what is acute cystitis with hematuria? The term cystitis refers to an inflammation of the bladder. Its traceable to any number of problems, the most typical one being a bacterial infection. Acute cystitis brought on by bacteria is also known as a urinary tract infection . It causes bleeding in the bladder, which then appears in your urine.
Though not uncommon among women, if a UTI is left untreated, it results in serious health consequences. The bacteria moves to your kidneys, which can lead to a major infection or renal failure. Certain drugs, radiation therapy, or even the use of spermicidal jellies, feminine douches, and hygiene sprays may trigger a bladder infection. The insertion of a catheter also increases your risk of developing acute cystitis.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Urinary Retention
Other Ways To Prevent Cystitis Coming Back
If you keep getting cystitis, there is some evidence you may find it helpful to take:
- D-mannose a sugar you can buy as a powder or tablets to take every day
- cranberry products available as juice, tablets or capsules to take every day
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar. If you’re taking warfarin, you should avoid cranberry products.
Page last reviewed: 11 February 2022 Next review due: 11 February 2025
How Are Utis Diagnosed
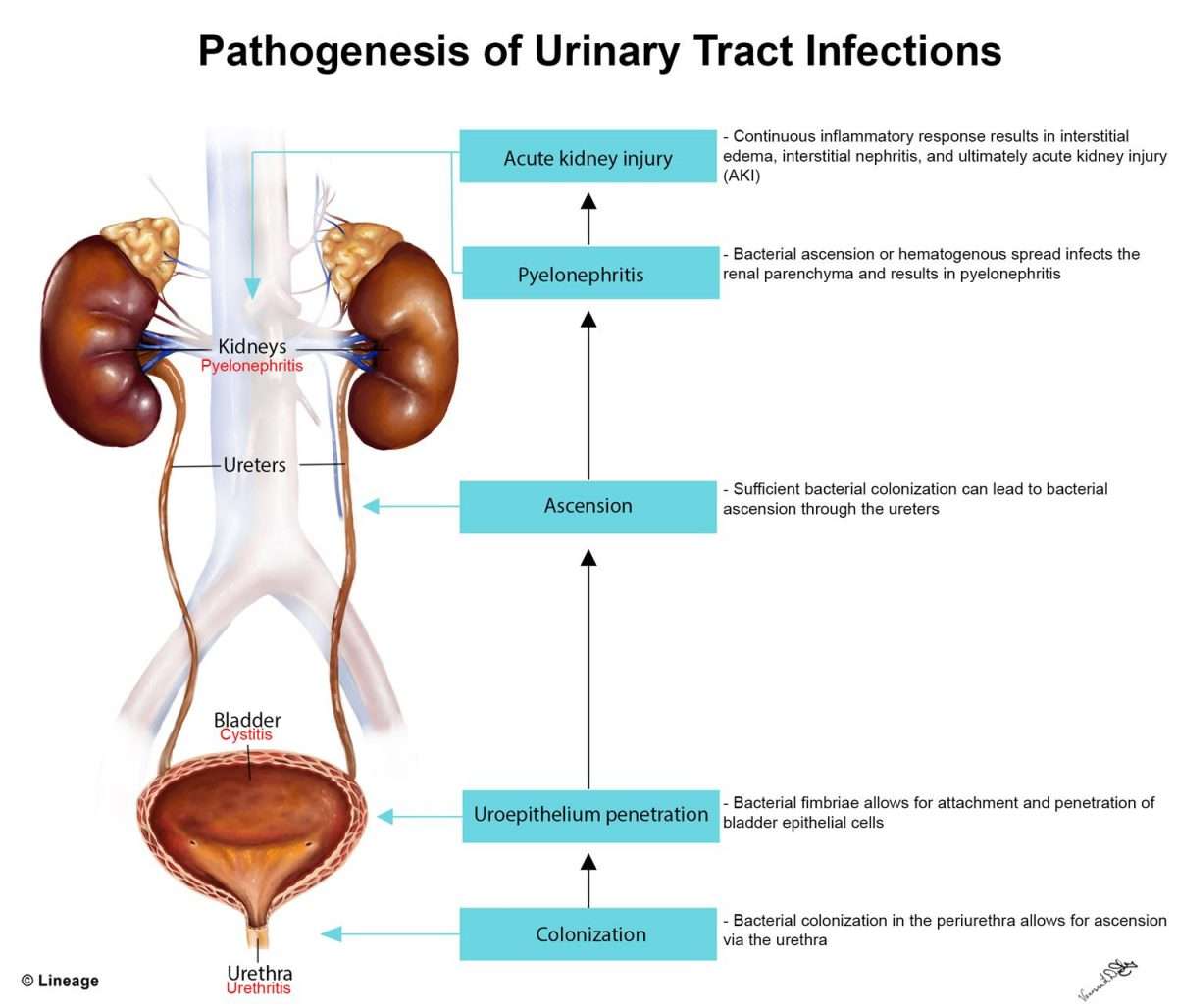
Only a health care provider can treat urinary tract infections. The first thing a doctor will do is confirm that a person has a UTI by taking a clean-catch urine specimen. At the doctor’s office, you’ll be asked to clean your genital area with disposable wipes and then pee into a sterile cup.
The sample may be used for a urinalysis or a urine culture . Knowing what bacteria are causing the infection can help your doctor choose the best treatment.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Azo Cranberry
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections
Normal urine is sterile and contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It does not contain bacteria, viruses, or fungi. A UTI occurs when germs, most often bacteria from the digestive tract, get into the opening of the urethra and start to multiply.
Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
Read Also: Meds For Urinary Tract Infection Over The Counter
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
UTIs can cause such signs as:
- pain, burning, or a stinging sensation when peeing
- an increased urge or more frequent need to pee
- waking up at night a lot to go to the bathroom
- belly pain in the area of the bladder
- foul-smelling pee that may look cloudy or contain blood
If you have any symptoms of a UTI, you’ll need to go to a doctor right away. The sooner you begin treatment, the less uncomfortable you’ll be. Call your doctor’s office or clinic. If you can’t reach your doctor, you can visit an urgent care center or hospital emergency room. The most important thing is to take action as soon as possible.
Diagnosis And Differential Diagnosis
A. Establishing the diagnosis
If acute cystitis is suspected, the clinician should obtain a urine specimen for analysis and culture. Ideally, the specimen should be obtained by sterile urethral catheterization. If catheterization cannot be performed for some reason or the patient declines the procedure, a midstream sample should be obtained for culture. Surprisingly, the midstream specimen seems to be comparable to a first morning void or a more elaborate midstream clean catch void in preventing contamination from vaginal organisms. One portion of the specimen should be used for point-of-care analysis by dipstick. The key dipstick findings suggestive of bacterial infection are positive tests for nitrites and leukocyte esterase. Clinicians should remember that the nitrite test may be falsely negative if the patient is infected by gram-positive organisms or if the urine has only incubated in the bladder for a very short period of time. In addition, the dipstick methodology is primarily applicable to symptomatic patients. It is not sufficiently sensitive to be used in lieu of culture for detecting bacteriuria in asymptomatic pregnant women.
Attention also should be paid to the urine pH, which normally is in the 5-6 range. An elevation of the pH to 8 is highly suggestive of an infection caused by Proteus species. Identification of this particular organism is of great importance when deciding upon empiric antibiotic therapy, as noted below.
B. Differential diagnosis
Also Check: Can Hep C Cause Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Best Antibiotic For Uti In Elderly
Today, amoxicillin is commonly prescribed as first-line treatment for UTIs in older adults. Other common narrow-spectrum must be used with caution when patients have chronic kidney disease or take blood pressure medication, as many older adults do or because their side effects can be serious in older adults.
Causes Of Hematuria In Acute Cystitis
The amount of blood in your urine depends on how severe your bladder damage is. There could be just enough hematuria to tinge your urine pink. Or there might be enough to produce bright, red blood, not to mention spotting on your underwear.
Severe instances of hematuria in acute cystitis are known as hemorrhagic cystitis. It typically occurs in cancer patients undergoing radiation and some types of chemotherapy. It presents suddenly, with pain and pressure in and around your bladder. Hemorrhagic cystitis is serious when accompanied by significant bleeding. But with proper medical attention, it can be treated successfully.
While bladder and kidney infections are the likeliest reason behind hematuria, vigorous exercise, kidney injury, and kidney stones offer other possible explanations. Symptoms of kidney stones include pain on one side of your lower back that makes it difficult to stand up straight.
Other urinary tract diseases, such as kidney and bladder cancer, produce blood in your urine as well. However, this rarely occurs and must be diagnosed by a doctor.
Also Check: Will A Urinary Tract Infection Go Away Without Antibiotics
Is Treatment For Cystitis Different From A Uti
Sometimes. The most common cause of cystitis is an infection, so in those cases the treatment is the same as with any UTI. Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics. If the cystitis is not caused by an infection, your healthcare provider may recommend medications to help reduce the symptoms, like pain relievers, as well as lifestyle changes. Mild cases of cystitis may heal on their own.
Urgent Advice: Ask For An Urgent Gp Appointment Or Get Help From Nhs 111 If:
You think you or someone else has cystitis and:
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a low temperature, or shaking and shivering
- pain in the lower tummy or in the back, just under the ribs
- are confused, drowsy or have difficulty speaking
- are feeling or being sick
- have not had a pee all day
- blood in your pee
These symptoms could mean you have a kidney infection, which can be serious if its not treated as it could cause .
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
Recommended Reading: Purina One Urinary Tract Reviews
Pediatric Diagnosis And Management
Urinary tract infection â occurs frequently in the pediatric population,1-3 affecting an estimated 6.5% of girls and 3.3% of boys in their first year of life.3 Approximately 3% to 5% of all girls and 1.0% of all boys have at least one UTI between infancy and late teenage years.4 There is a striking female preponderance after 1 to 2 years of age, with a 10:1 female-to-male ratio.2,4 UTI in children is often underdiagnosed. Both diagnosis and treatment, especially in infants and young children, are challenging to the general pediatrician.
In 1999, the Urinary Tract Subcommittee of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Quality Improvement developed an evidence-based practice parameter on the diagnosis, treatment, and evaluation of an initial UTI in febrile infants and young children between the ages of 2 months and 2 years. The recommendations included emphasis of the need for culturing appropriately collected specimens: transurethral catheterization or suprapubic bladder tap are needed to obtain an uncontaminated urine specimen in this age group.3,11
The classic signs and symptoms of urinary cystitis in older children include dysuria , increased frequency, nocturnal enuresis, abdominal and suprapubic pain, urgency, and cloudy or bloody urine .12
Things You Can Try Yourself
If you have mild symptoms of cystitis, it can help to:
- take paracetamol up to 4 times a day to reduce pain
- give children liquid paracetamol follow the instructions on the bottle
- drink plenty of water
- avoid drinks that may irritate your bladder, like fruit juices, coffee and alcohol
Some people take cystitis sachets or cranberry drinks and products every day to prevent cystitis from happening, which might help. However, theres no evidence they help ease symptoms or treat cystitis if the infection has already started.
Read Also: Can Males Have Urinary Tract Infections
What Is The Evidence For Specific Management And Treatment Recommendations
Stamm, WE, Counts, GW, Running, KR. Diagnosis of coliform infection in acutely dysuric women. N Engl J Med. vol. 307. 1982. pp. 463-8. was not appropriate for acutely symptomatic patients. The authors demonstrated that this criterion identified only 51% of women whose bladders contained uropathogens. They also confirmed that in symptomatic patients, especially when the urine is obtained by catheterization, a colony count of greater than or equal to 100 colonies/ml was a much more sensitive predictor of bladder infection.)
Dunlow, S, Duff, P. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant uropathogens in obstetric patients with acute pyelonephritis. Obstet Gynecol. vol. 76. 1990. pp. 241-4.
Stamm, WE, Hooton, TM. Management of urinary tract infections in adults. N Engl J Med. vol. 329. 1993. pp. 1328-34.
Gupta, K, Scholes, D, Stamm, WE. Increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among uropathogens causing acute uncomplicated cystitis in women. JAMA. vol. 281. 1999. pp. 736-8.
Fihn, SD. Acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. N Engl J Med. vol. 349. 2003. pp. 259-66.
Hooton, TM, Scholes, D, Gupta, K. Amoxicillin-clavulanate vs ciprofloxacin for the treatment of uncomplicated cystitis in women. A randomized trial. JAMA. vol. 293. 2005. pp. 949-55.
Duff, P, Creasy, R, Resnik, R, Iams, J, Lockwood, C, Moore, T. Maternal and fetal infections. 2012.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2015. MMWR. vol. 64. 2015. pp. 1-137.
What Should I Do If I Think I Have An Infection
See your doctor as soon as possible. You will need to give a urine sample. Most doctors will be able to tell you right away if you have an infection. Sometimes a urine culture is needed, which means your urine sample will be sent to a laboratory. It takes about three to five days to get the results.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Pills Cvs
A Pharmacist Can Help With Cystitis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for cystitis. A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a cystitis management service. They may be able to give antibiotics if they’re needed.
Cystitis In Men And Older People
Men tend to get cystitis later in life. Where trouble with urine flow is a symptom, this may indicate that the underlying cause is a problem with their prostate gland.
Cystitis is common in older people, particularly if they are unwell. Bladder catheters and some urinary-tract operations may also increase the risk of cystitis.
Don’t Miss: Medline Urinary Drainage Bag 2000ml
What Causes The Infection
Bladder infection usually happens in healthy women of reproductive age. It is normal to have bacteria that live around your urethra , which is where urine comes out. These bacteria usually are not harmful. However, sometimes they can get into your bladder. You may be more likely to get a bladder infection if you hold your urine for a long time, if you have sex often, or if you are pregnant.
When To See Your Gp
You should see your GP if you or your child have symptoms of cystitis for the first time.
Cystitis isn’t usually a cause for serious concern, but the symptoms can be similar to several other conditions, so it’s important to get a proper diagnosis.
If you’re a woman who has had cystitis before, you don’t necessarily need to see your GP again. Cystitis is very common in women and mild cases often get better on their own. Speak to a pharmacist if you need any advice about treating cystitis.
However, you should see your GP if your symptoms are severe or don’t start to get better in a few days, you get cystitis frequently, or you’re pregnant.
Children and men should always be seen by a GP if they have symptoms of cystitis, as the condition is less common and could be more serious in these groups.
Don’t Miss: Does Apple Cider Vinegar Help Urinary Tract Infections
Key Points About Urinary Tract Infections
- Urinary tract infections are a common health problem that affects millions of people each year. These infections can affect any part of the urinary tract.
- Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
- The most common symptoms of UTIs include changes in urination such as frequency, pain, or burning urine looks dark, cloudy, or red and smells bad back or side pain nausea/vomiting and fever.
- Antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Other treatments may include pain relievers, and drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Other things that can be done may help reduce the likelihood of developing UTIs.
Can A Uti Cause Cystitis
While not all urinary tract infections lead to cystitis, it is possible for untreated UTIs to spread to the bladder. A bladder infection causing cystitis is a specific type of urinary tract infection that often occurs when bacteria from another part of the urinary tract enter the bladder. To prevent this from occurring, see your healthcare provider to obtain treatment for a UTI promptly.
Recommended Reading: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Urinary Problems
Antibiotic Treatment Of Complicated Lower Utis
- Antibiotic therapy must be adapted to culture results and is commonly given for 7â14 days.
- Options for the initial empiric treatment of complicated lower UTIs include:
Treatment regimens for UTI in men should include antibiotics that are able to penetrate prostate tissue . Fosfomycin or nitrofurantoin are generally not adequate.
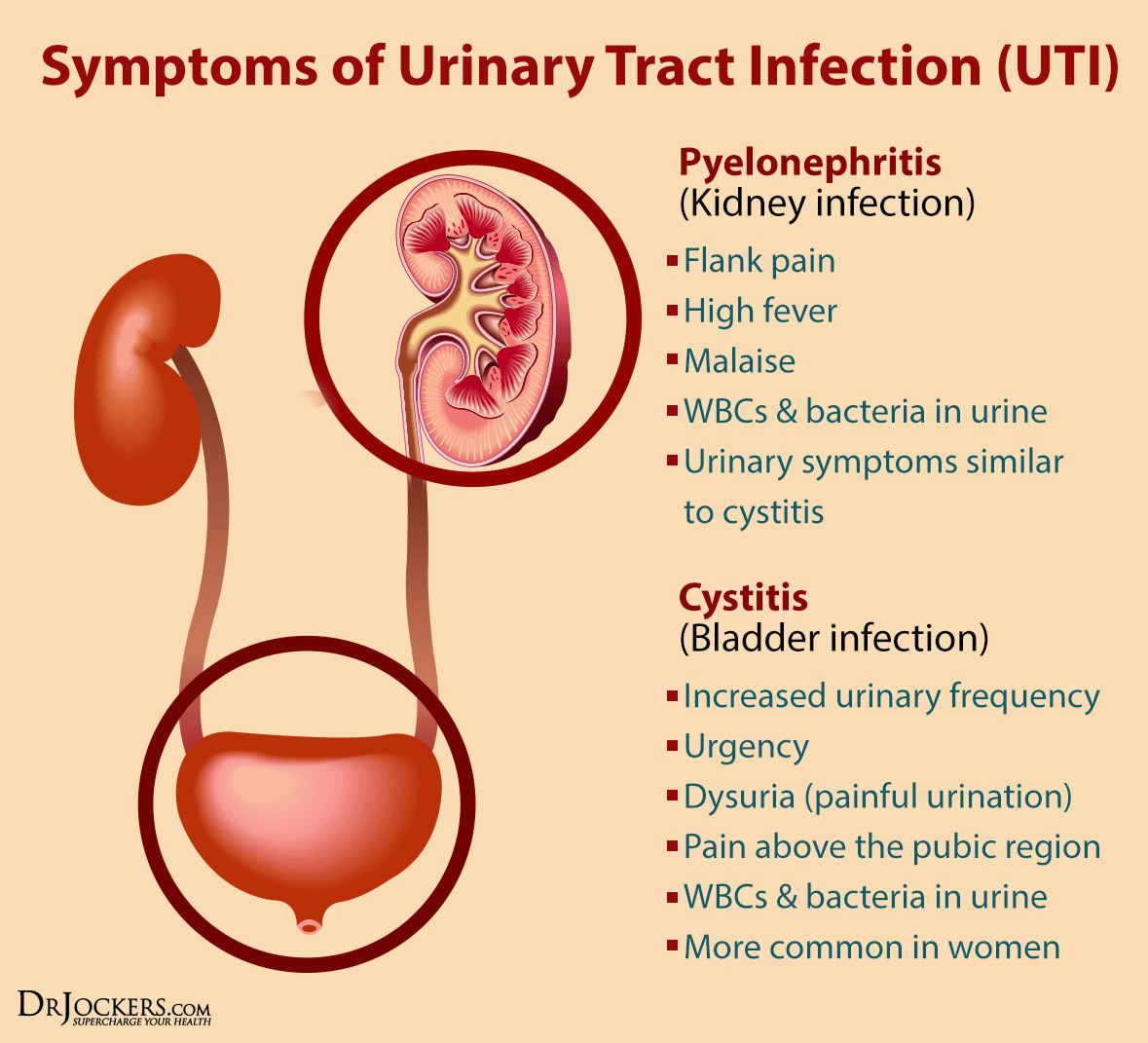
Signs And Symptoms Of Cystitis
The main symptoms of cystitis include:
- pain, burning or stinging when you pee
- needing to pee more often and urgently than normal
- urine that’s dark, cloudy or strong smelling
- pain low down in your tummy
- feeling generally unwell, achy, sick and tired
Possible symptoms in young children include a high temperature of 38C or above, weakness, irritability, reduced appetite and vomiting.
Read more about treating cystitis
Also Check: How Much Cranberry Juice For Urinary Tract Infection