How Can I Prevent Utis All The Time
How to Prevent Recurrent UTIs
Alice Sparrow
How Can I Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
There are several things you can remember to do to prevent urinary tract infections :
- When you go to the bathroom, wipe from front to back after you urinate or have a bowel movement.
- Wash the area between the anus and genitals.
- Showers are better than baths. Donât use douches, or sprays and powders âdown there.â
- Go to the bathroom when you feel the need â donât hold it in. Try to urinate before and after sex.
- Donât wear tight jeans or nylon underwear .
- If you use birth control, choose a kind thatâs not a diaphragm and/or spermicidal jelly.
- Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Drink unsweetened cranberry juice or ask your doctor if cranberry supplements could help. The research on how well these work to prevent UTIs is mixed.
In rare cases doctors might prescribe antibiotics for prevention. If you get a prescription for an antibiotic, follow the instructions and take all the pills.
Show Sources
Help For All Your Menopause Symptoms
At Womens Healthcare of Princeton, we understand how hard it can be to cope with menopause-related symptoms. Thats why we offer a full range of treatment options, including complementary and alternative therapies as well as traditional medical options.
If you live in or around Princeton, New Jersey, and are tired of dealing with menopause symptoms such as chronic UTIs, call us for an appointment or book your visit online today.
You Might Also Enjoy…
- 4.87/5
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get An E Coli Urinary Tract Infection
Comparison With Existing Literature
Meta-analysis of 10 randomised trials of women aged 18 and older found long-term antibiotics reduced the risk of UTI recurrence during the prophylaxis period by almost 80% . Our analyses showed a smaller effect size and greater NNT for postmenopausal women, possibly due to more complex pathophysiology of recurrent UTI in this population. We did not identify a statistically significant increase in risk of adverse events associated with use of antibiotics. Adverse events are often poorly reported in trials, and we found heterogeneity for adverse events between trials. In addition, the studies included in this review compared long-term antibiotic therapy with various non-antibiotic treatments and not placebo, and this may have influenced effect sizes for adverse events towards the null. We found small absolute numbers of serious adverse events and cannot exclude the possibility of important effects being missed in these relatively small studies.
Only one study followed up participants after cessation of prophylaxis and found that beneficial effects had ceased after 3 months. Previous studies of younger women have reported similar findings suggesting that prophylaxis only confers protection from recurrence during the active prophylaxis phase.
Possible Preventive Strategies For Utis
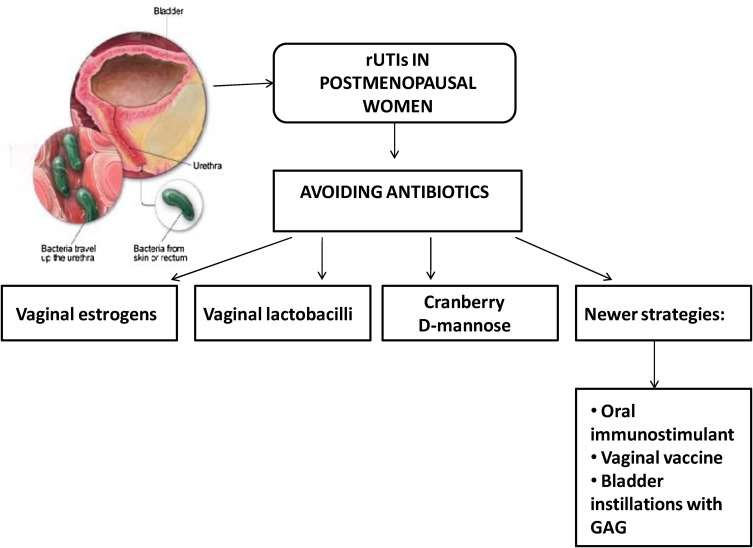
While the research is still out on the preventative strategies below, prospects are promising.
- Probiotics The probiotic strain Lactobacillus, found in fermented milk products, has been shown to prevent urinary tract infections in laboratory testing. Theres also promising research that shows the strains L. rhamnosus gr-1 and L. fermentum rc-14 could prevent UTIs as well.
- Cranberry Juice Cranberries contain polyphenols called proanthocyanidins, which may help prevent E. coli from causing urinary tract infections in women, but data is conflicting about the effectiveness. While a meta-analysis published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine showed a decrease in UTI rates in those who consumed daily cranberry tablets, a subsequent review published in the Cochrane Database found insufficient evidence to recommend routine use of cranberry. The American Urological Association does recommend cranberry extract as a preventive measure for UTIs Ellura is a brand of cranberry extract capsules.
- Diet Adjustment Research has shown that urine with higher pH levels and higher levels of certain metabolites formed by gut microbes are better able to resist recurrent UTIs. Its thought that one can improve these levels through diet. For instance, calcium supplements raise urinary pH levels. In addition, consuming foods rich in antioxidants, like tea and colorful berries, may encourage growth of metabolites.
Recommended Reading: Best Diet For Urinary Tract Infection
What Does A Uti Feel Like
There are two main areas where you can get a UTI, the lower urinary tract and the upper urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections tend to form in the urethra and/or bladder.
Some of the most common symptoms of UTI are 1:
- Urinary urgency: Feeling a constantly strong urge to pee
- Urinary frequency: Needing to pee more often than usual
- Pain or a burning feeling when urinating
- Incontinence
- Blood in the urine / cloudy urine
- Lower stomach / lower back pain
Upper urinary tract infections can happen when an infection spreads from the urethra and/or bladder to the kidneys. .
How do you know if a UTI has spread to your kidneys? 2
- Nausea / vomiting
- Fever / chills
Infection of the kidneys can be life threatening. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms and feel that you may have a more serious infection, it is important that you seek help from a medical professional straight away.
But why are urinary tract infections so common?
Types Of Urinary Infection
Generally, urinary infections can be defined into two main types. Such as,
Recommended Reading: What Will Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
-
Recurrent urinary tract infection is one of the most common reasons for long-term antibiotic use in the frail elderly. We systematically reviewed trial evidence to address clinical uncertainties around this practice.
-
We did not identify any trials in older men nor any trials in frail care home residents.
-
We identified only three small European trials, with follow-up ranging from 6 to 15 months, in older women.
-
Only one trial measured the impact of long-term antibiotics on antibiotic resistance.
-
Trial evidence suggests long-term antibiotics reduce the risk of UTI recurrence in older women. Many clinical uncertainties remain unaddressed.
Preventing Utis With Drugs
At times, antibiotics are used as a preventative measure for those with frequent UTI recurrences. In addition, postmenopausal women can benefit from a different type of a medicinal prevention strategy.
- Antimicrobial Prophylaxis In some cases of urinary tract infection recurrences, a physician may recommend antimicrobial prophylaxis, which is the use of antibiotics to prevent another infection. This has been shown to effectively reduce ones risk of recurrent UTIs in women with two infections over the previous year.
- Postcoital Prophylaxis For those whose UTI recurrences are related to sexual intercourse, taking antibiotics after intercourse may be preferable. Depending on the frequency of intercourse, postcoital prophylaxis likely results in less antibiotic use than antimicrobial prophylaxis.
- Estrogen for Postmenopausal WomenThe use of a vaginal estrogen cream or an estradiol-releasing vaginal ring have both been shown to be an effective strategy for reducing recurrent urinary tract infections in postmenopausal women. In fact, vaginal estrogen has been shown to reduce recurrent UTIs by 36 to 75 percent.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Immediate Relief
Bladder Health For Older Adults
Everyone uses their bladder many times each day, but they may not know what to do to keep their bladder healthy.
Located in the lower abdomen, the bladder is a hollow organ, much like a balloon, that stores urine. It is part of the urinary system, which also includes the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. Urine contains wastes and extra fluid left over after the body takes what it needs from what we eat and drink.
As you get older, the bladder changes. The elastic bladder tissue may toughen and become less stretchy. A less stretchy bladder cannot hold as much urine as before and might make you go to the bathroom more often. The bladder wall and pelvic floor muscles may weaken, making it harder to empty the bladder fully and causing urine to leak.
You May Like: How Does A Urinary Tract Infection Feel
Senior Toileting Tips For Preventing Uti
A senior could be having problems emptying their bladder. If possible, when they urinate in the toilet, count to thirty once they have finished and then encourage him to give it another push. In potty-training my disabled son, an autism specialist told me that after the initial urge is gone, the brain can stop/reduce the message that they still needed to go. I know Ive tried it myself and I am always amazed at how much Ill go again after the count. Sorry if thats TMI! Lastly, if they are wearing adult diapers, you may need to be changing them more frequently since they are bacteria sponges. Rainmom
Encourage/help older folks get to the toilet at least every 2 hours. Sometimes, older folks dont feel thirsty, sometimes they forget to drink, but sometimes, they are afraid of urinary accidents and avoid drinking enough fluids. Its very important to keep going to the bathroom to empty that bladder. MomDaughterRN
You May Like: How To Cure Urinary Retention
Recommended Reading: What Level Of Spinal Cord Injury Causes Urinary Incontinence
Risk Factor Of Treating Utis Without Antibiotics
Some research has found that about 25 to 40 percent of uncomplicated UTIs may wither away on their own. In other words, the bacteria from E.coli may flush out from the urinary tract without any medications. However, this usually happens in women with no other health issues, which can complicate things.
But, one may have some serious risks due to leaving a UTI untreated. The person can have pyelonephritis and sepsis, which is why it becomes very important for the patient to consult with the doctor and seek treatment for betterment if any suspicious symptoms arrive.
However, there is some risk factor that can make the infection more complicated
-
bacteria species are already resistant
-
to conditions that affect the immune system and can have HIV, cardiac disease, or, at worst, cause lupus
-
changes in the urinary tract or organs can help in swollen prostate or reduce the urine flow.
What Is Lactobacillus

Also, as well as anatomical changes, lower oestrogen levels have an important effect on the bacteria living in the urinary tract. Oestrogen helps with the production of glycogen. This is very important because glycogen is food for Lactobacillus . Therefore, less oestrogen means less glycogen, which means less food for good bacteria to grow and thrive. And that good bacteria is needed to create a protective environment.7
Without as much Lactobacillus, harmful bacteria are more likely to invade the urinary tract and cause an infection.
To put this in perspective, one study found that when looking at urine samples from premenopausal women, Lactobacillus accounted for 78% of bacteria in the sample, whereas for post-menopausal women it was found that Lactobacillus accounted for only 42% of the bacteria in the urine sample.8
This is why having lower oestrogen levels is one of the most significant risk factors for cystitis in post-menopausal women.
You May Like: Bard Urinary Drainage Bag Instructions
How To Treat Utis
Its important to recognize the earliest signs of a UTI for rapid diagnosis and treatment, particularly for frail elderly people who may show fewer symptoms and suffer more severely. So, keep a look out and communicate about changes with your loved one in your day-to-day routines.A full diagnosis will be made by a physician. They will base this on urine test results and on symptoms of the infection. If an Upper or Lower UTI has been diagnosed and treatment is needed, the doctor will decide on which antibiotic to prescribe and at what dosage.
What Are The Signs Of Uti During/after Menopause
Getting a UTI can be a pain for women of any age, but women Peri-Menopause post-menopause are especially at risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
The prevalence of lower UTI in women increases with age, and up to 15% of women over the age of 60 will develop recurring UTIs. 33
Many older women believe that urinary symptoms such as needing to go to the toilet a lot, or continence issues, are just a normal sign of aging. 33 Also, scientific research into womens health issues is lacking, and there is still a lot we dont know about the causes and mechanisms of certain illnesses. Healthcare providers often dont have answers when it comes to chronic conditions, leave their female patients in the dark, and show a lack of empathy and understanding. For these reasons, it is understandable why you might put off a visit to the doctor about urinary symptoms. 34
But these symptoms could be a sign of UTI, and UTI shouldnt be ignored, so it is important that you get appropriate care and the treatment that you need.
What to look out for
Common signs of a UTI include cloudy urine, a burning or stinging feeling when you pee, abdominal pain, and needing to go to the toilet more urgently and more often than usual. 35
Incontinence can also be a sign of cystitis, although it is also a very common issue in women, becoming more prevalent with age, and is not necessarily indicative of an infection.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Urinary Incontinence
Data Synthesis And Analysis
Outcomes measured in only one trial were reported narratively. Outcomes measured in more than one trial were synthesised quantitatively. We estimated between trial heterogeneity using the I2 statistic and used random effects meta-analyses to estimate pooled risk ratios and 95% CIs. We undertook sensitivity analyses to examine treatment effects according to study quality and assessed the impact of including data from a potentially eligible trial where the study author did not reply to our request for data on older participants.
How Do Utis Affect Pregnancy
Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy raise your risk for UTIs. UTIs during pregnancy are more likely to spread to the kidneys.
If you’re pregnant and have symptoms of a UTI, see your doctor or nurse right away. Your doctor will give you an antibiotic that is safe to take during pregnancy.
If left untreated, UTIs could lead to kidney infections and problems during pregnancy, including:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
You May Like: Purina One For Urinary Tract Health
Urine Infection: Definition Types Symptoms And Treatment
Exams Prep Master| Updated On -Jul 15, 2022
Urinary Infection is mainly concerned with the existence of harmful microorganisms in any of the bodily organs related to urinary function such as kidneys, bladder, ureters, or urethra. Urinary Infection and its symptoms are moderately visible and involve multiple easy to complex treatment procedures. There are two types of urine infection, the upper urinary tract infection, and the lower urinary tract infection. These infections are generally caused by the growth of harmful microorganisms or pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and are quite common in both genders and among all ages. Here, we will learn more about urinary infection, its symptoms and the types of treatments, and discuss some important questions.
Key Takeaways: Urine, odour, urinary infection, e coli, bacteria, males, females, lower urinary tract infection, upper urinary tract infection.
|
Table of Content |
Read More: Population Interaction
How To Manage Recurrent Utis In Postmenopausal Women
Although there is no clear-cut solution to the problem of recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women, “various strategies can be employed that have found success,” write Wade Bushman, MD, PhD, and Brian V. Le, MD, MA.
Recurrent urinary tract infections in postmenopausal women can be a particularly challenging problem. We acknowledge there is no clear-cut solution to this vexing problem, but various strategies can be employed that have found success.
Read – New Products: Nasal spray launched to treat nocturia due to nocturnal polyuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is common in postmenopausal women, and the incidence increases with age, diabetes, and sexual activity. There is a correlation of bacteriuria with risk for symptomatic UTI however, it is not recommended to treat asymptomatic bacteriuria, as it may paradoxically increase the risk of symptomatic UTI. The goal, then, is to treat as necessary but to avoid overtreatment.
Also see – How do you manage noncompliant OAB patients?
Next: Detailed history
Have you read: Is there a silver lining to value-based pay initiatives?
First, a detailed history must be taken to elicit symptoms, severity , frequency , microbiology , comorbidities, prior evaluations, treatments, and responses to date. Contributing conditions may be identified on physical examination, bimanual and vaginal exam, and post-void residual measurement.
Also see: Is autonomy dead for the practicing urologist?
Next: Treatment of contributing factors
Also Check: What Type Of Antibiotics Are Used For Urinary Tract Infections
Utis And The Female Anatomy
Infection-causing bacteria typically gain entrance to your urinary tract through the urethra, that tiny tube-like structure that carries urine away from your bladder and out of the body. Once they gain a foothold in the urethra, bacteria can quickly multiply and spread upward into the bladder and other structures in your urinary system.
The male urethra exits the body at the tip of the penis and takes a relatively long and winding path from the bladder, making it somewhat difficult for bacteria to settle in and multiply. The female urethra, however, is short and straight, leads directly to your bladder, and exits just behind the clitoris, very near the vaginal and rectal openings where bacteria naturally thrive.
These structural differences help explain why women are much more likely to develop UTIs than men. Female anatomy and hormonal changes also play significant roles in recurrent postmenopausal UTIs.