Signs You May Have A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection is a common condition that can cause discomfort or pain. This type of infection develops when bacteria enter any part of your urinary tract, such as your bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra.
Infections are most common in the lower tract and often result from sexual activity, poor personal hygiene, or blockages in the urinary tract.
You can have a urinary tract infection without any symptoms. As the condition worsens, you may experience noticeable side effects, including:
- Burning while urinating
Women especially may notice they have pain in the pelvic area as the infection worsens.
Because the symptoms of a urinary tract infection can be similar to other underlying health conditions, its important that you schedule a diagnostic evaluation at Primary Care & Walk-In Medical Clinic as soon as possible. They offer in-office urine testing to confirm the infection quickly.
Social And Economic Burden
Recurrent UTIs carry a substantial social and economic burden, and have a detrimental effect on patients quality of life .1517 The economic cost of UTIs to healthcare systems is considerable. In the United States, the cost of UTIs is estimated to be at least US$23 billion per annum.18 An economic study of 20 hospitals in eight European countries with a high prevalence of multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacteria estimated that the mean cost per case of complicated UTIs was 5700, ranging from 4028 to 7740 per case. Higher patient costs were associated with admission, infection source and severity, comorbidity, and the presence of multidrug resistant bacteria.19
Complicated Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infection in patients with renal calculi, those with pyelonephritis, prostatitis, orchitis, patients with long-standing indwelling catheters or those using intermittent self-catherisation are likely to be complicated. These patients are likely to have an infection that involves other parts of the renal tract apart from the urinary bladder. They often need hospitalisation and surgical intervention like nephrostomy tubes or ureteric stents.
Intravenous antibiotics are usually prescribed for this group of patients. Treatment can be modified based on known multi-drug resistant organism colonisation or previous urine culture result. Usually, patients with complicated UTI require a 10â14 day course of antibiotic treatment.
Also Check: Royal Canin Urinary Canine Treats 17.6 Oz
Don’t Miss: What Can I Take To Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
Discontinuation And Withdrawal Of Subjects
Subjects are free to discontinue their participation at any time without prejudice to further treatment. Participants developing SAEs possibly due to methenamine hippurate will discontinue study medication. Alkalising antacids can potentially reduce the effect of methenamine hippurate and should be avoided. Study participants requiring long-term use of antacids during the first 6months of study will discontinue study medication. If prophylactic urinary antibiotics are initiated after enrolment and randomisation in the study, the participants will discontinue study medication. Participants developing serious illness, making it impossible for them to continue taking the study tablets or comply with study requirements, will discontinue study medication and/or withdraw from study participation. Other reasons for discontinuing treatment or withdrawing a subject are incorrect enrolment and subjects lost to follow-up. Participants who prematurely discontinue treatment, except for patients withdrawing their consent, will be followed up in the same framework as participants receiving study medication.
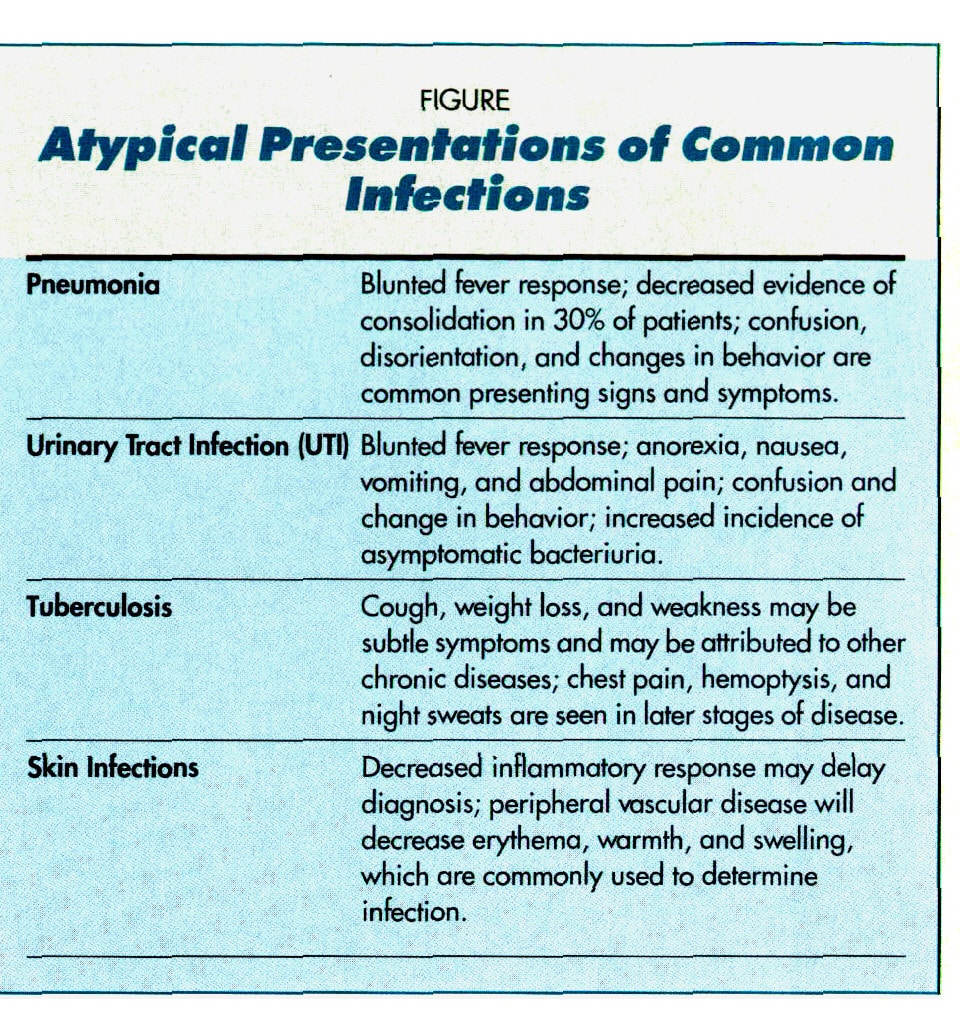
Confusion Linked To Acute Cystitis Or Pyelonephritis
Studies including hospitalised patients are likely to also include patients with pyelonephritis, a condition likely to result in confusion in a fragile elderly person. However, the typical nursing home situation usually involves the suspicion of confusion caused by a lower UTI in an afebrile patient.
The primary aim of this review was not to evaluate the association between pyelonephritis and confusion. The primary question was if lower UTI with no fever in residents without a urinary catheter, with or without localised symptoms such as acute dysuria, urgency or frequency, is associated with confusion. This review concludes that current evidence does not provide a clear answer to this question.
You May Like: Azo Urinary Tract Health Pills
Study Population Characteristics And Baseline Data
The target population for this 6-month study was mixed, males and females, aged 65years plus that were community dwelling. Recurrent UTI patients were selected specifically because of their clinical history of uncomplicated rUTIs, all attended an UTI out-patients clinic at Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, and lack of co-morbidities. The cohort included 23 females and 7 males with an average age of 74.0 and 76.7years, respectively . Patients with structural abnormalities were included if clinical records indicated no evidence of a functional defect in the urinary tract impeding bladder voidance. The study group included 11 patients with either vaginal prolapse , enlarged prostate , urethral stenosis or phimosis . Diabetic patients or females using either topical or systemic oestrogen were also not excluded .
What Is The Best Home Remedy For Cystitis
7 home remedies for cystitis
What causes a woman to have a recurrent cystitis infection?
It is usually caused by a urine infection. Some women have repeated bouts of cystitis. Doctors define a recurrent infection as either three proven separate infections in a year or as two in six months. In many cases there is no apparent reason for a woman to get frequent attacks of cystitis. There are a number of treatment options to consider.
Also Check: How To Help Urinary Incontinence
Uti In The Elderly: Signs Symptoms And Treatments
Urinary tract infections arent just a nuisance in the senior populationthey can cause serious health problems. A UTI occurs when bacteria in the urethra, bladder or kidneys multiplies in the urine. Left untreated, a UTI can lead to acute or chronic kidney infections, which could permanently damage these vital organs and even lead to kidney failure. UTIs are also a leading cause of , an extreme and potentially life-threatening response to an infection.
What Are The Dangers Of Utis In Seniors
Seniors may experience the same symptoms of UTIs as younger people, including:
- Frequent urination
- Abdominal pain and pressure
However, sometimes these classic symptoms may be absent, making the diagnosis more difficult.
In addition, older adults may also develop confusion while suffering from an infection. UTI-related confusion may mimic the signs of dementia, such as:
- Withdrawal from people and activities
UTI-related confusion may make it difficult for an older adult to complete their daily living tasks and increase their risk of falls, which could cause serious injury.
In addition, untreated urinary tract infections can develop into serious kidney infections, putting seniors at risk of organ damage and potentially fatal systemic infections like sepsis. Signs of kidney infection include:
- Pain in the back and side
Seniors are vulnerable to urinary tract infections for many reasons, including:
You May Like: Can You Have A Urinary Tract Infection Without Symptoms
Primary And Secondary Statistical Analyses And Management Of Missing Data
The primary statistical analysis is intention to treat. Patients who have completed only a part of the first 6months will contribute data up until they leave the study. Their data will be recalculated as if they had participated in all 6months. Patients leaving during the second 6-month period will also contribute with data as above. Patients leaving the study before the second 6-month period commences will have their value for this period set to be the median value for both groups. A complete case analysis and a per-protocol analysis will also be made as secondary analysis and reported.
When To See A Doctor
If you suspect you or a loved one has a UTI, its best to see a healthcare provider. Symptoms like painful, urgent or frequent urination shouldnt be ignored, Dr. Slopnick stresses.
Your doctor will ask about symptoms and perform a urine culture and possibly other tests to confirm if a UTI is to blame. If youre experiencing multiple UTIs a year, your doctor may also order other tests to better understand if a prolapsed bladder, enlarged prostate or other condition is causing frequent infection.
You May Like: Can Stomach Ulcers Cause Urinary Problems
Does Drinking Water Help Cystitis
Drinking the recommended daily amount of fluid will help prevent bladder irritation and ease the symptoms of cystitis or bladder infections.
Does cranberry juice get rid of cystitis?
Cranberry juice DOESNT treat cystitis, say experts Instead, NICE recommends treating a UTI at home by taking painkillers and drinking plenty of water, as the body can often clear a mild infection by itself.
Tips For Preventing Utis In The Elderly
The following lifestyle and personal hygiene changes can significantly reduce a seniors risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Drink cranberry juice or use cranberry tablets, but NOT if the elder has a personal or family history of kidney stones.
- Avoid or limit caffeine and alcohol, which irritate the bladder.
- After toileting, always wipe from front to back .
- If incontinence is not an issue, wear breathable cotton underwear and change them at least once a day.
- Change soiled incontinence briefs promptly and frequently.
- Keep the genital area clean and dry.
- Set reminders/timers for seniors who are memory impaired to try to use the bathroom instead of an adult brief.
Recommended Reading: What Antibiotics Are Given For Urinary Tract Infections
Can Utis Be Prevented
These tips can help prevent UTIs:
- School-age girls should avoid bubble baths and strong soaps that might cause irritation. They also should wear cotton underwear instead of nylon because it’s less likely to encourage bacterial growth.
- All kids should be taught not to “hold it” when they have to go. Pee that stays in the bladder gives bacteria a good place to grow.
- Kids should drink plenty of fluids but avoid those with caffeine.
How To Help Your Loved One Avoid Utis
Do you give the older adult in your life cranberry juice or probiotics to prevent a UTI? These products wont hurt them, but whether theyll help is unclear.
We dont have enough research to support their effectiveness in UTI prevention, although their medical benefits cant be ruled out completely, says Dr. Goldman.
Instead, he recommends these tried-and-true prevention strategies:
- Encourage sufficient fluid intake
- Promote genital and urinary hygiene
- Ask the doctor about low-dose vaginal cream for postmenopausal women
Dr. Goldman says researchers are also studying D-Mannose for UTI prevention. The supplement, which has few side effects, sticks to bladder receptors that normally attract the E. coli bacteria usually responsible for UTIs.
Researchers also believe D-Mannose may keep bad bacteria from colonizing the digestive tract, which can harbor the bacteria responsible for UTIs in women.
Following these tips should help your aging relative stay healthy, productive and out of the hospital.
You May Like: Botox Injections For Urinary Incontinence
Let Our Care Assessment Guide You
Our free tool provides options, advice, and next steps based on your unique situation.
That stress can result in confusion and abrupt changes in behavior in older adults with a UTI. And for seniors with Alzheimers disease or other types of dementia, any kind of stress, physical or emotional, will often make dementia temporarily worse, Forciea says.
What Are The Symptoms Of Utis In The Elderly
Like anyone with a UTI, older adults may experience typical physical symptoms. Yet they may not notice a mild infection right away. This is because chronic urinary problems common in seniors, such as urinary incontinence or frequency, may have similar symptoms to a UTI, masking an infection.
Common symptoms of a UTI include:
- Burning, painful sensation with urination
- Frequent, intense urge to urinate even when theres little urine to pass
- A feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied
- Blood in the urine
- Inability to perform common daily tasks, such as getting dressed or feeding themselves
You May Like: Side Effects Of Azo Urinary Tract Defense
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
The study protocol was approved in March 2014 by the Newcastle Research Ethics Committee and sample collections took place between April 2014 and November 2015. Patients were recruited with written informed consent through UTI clinics led by the Urology Department at Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK.
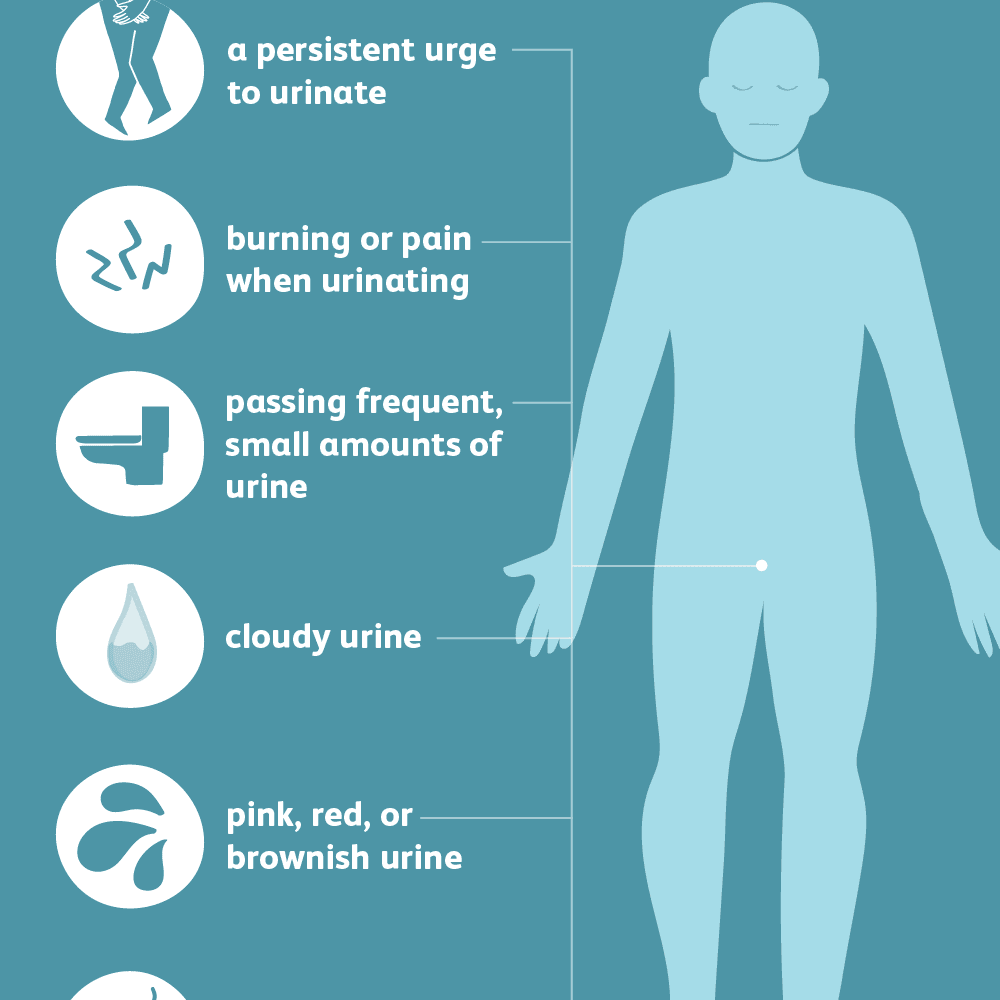
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a urinary tract infection may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy, dark or has a strong smell
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Also Check: Can Sex Cause Urinary Tract Infection
What About Confusion And Disorientation
While confusion or disorientation are sometimes associated with UTIs in older adults, particularly those ages 70 or older, Dr. Slopnick says its important to understand that a UTI doesnt necessarily come with any signs of confusion. And signs of confusion dont necessarily point to a UTI.
Aging naturally increases the incidence of confusion and delirium, especially among those who are cognitively impaired, depressed, malnourished or completely dependent.
If someone is suddenly showing signs of confusion, your doctor may check for a UTI. But confusion alone isnt a telltale sign of a UTI, Dr. Slopnick says. Other causes should be investigated as well, especially if the person isnt showing other classic UTI symptoms.
Why More Women Get Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are most common in women because of the natural design of their urinary tract. Females have shorter urethra and bacteria need to travel much less of a distance to reach the urinary tract.
Women are also more likely to develop urinary tract infections if they use diaphragms and spermicides for birth control. As women head toward the transition to menopause, underlying hormone changes can lead to changes in the urinary tract making them more susceptible to infections in their urinary tract.
You May Like: Corn Silk For Urinary Incontinence
Treatment From A Gp For Utis That Keep Coming Back
If your UTI comes back after treatment, or you have 2 UTIs in 6 months, a GP may:
- prescribe a different antibiotic or prescribe a low-dose antibiotic to take for up to 6 months
- prescribe a vaginal cream containing oestrogen, if you have gone through the menopause
- refer you to a specialist for further tests and treatments
In some people, antibiotics do not work or urine tests do not pick up an infection, even though you have UTI symptoms.
This may mean you have a long-term UTI that is not picked up by current urine tests. Ask the GP for a referral to a specialist for further tests and treatments.
Long-term UTIs are linked to an increased risk of bladder cancer in people aged 60 and over.
Why Are Seniors At Risk For Utis
Men and women older than 65 are at greater risk for UTIs. This is because both men and women tend to have more problems emptying their bladder completely as they age, causing bacteria to develop in the urinary system.
In older men, this often happens because of a common condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia , or an enlarged prostate gland. The enlarged prostate blocks the flow of urine and prevents the bladder from fully emptying.
Other risk factors for UTIs in older adults include:
- Using a catheter to empty the bladder
- Having kidney stones, which can block the flow of urine
- Having a suppressed immune system, which lowers the bodys defense against infection
You May Like: Does Melatonin Cause Urinary Retention
Handling Storage And Destruction Of Biological Samples
At inclusion, a urine specimen will be collected for culture and dipstick urinalysis. After analysis, the urine specimen will be destroyed. However, we will freeze isolates of E. coli from the inclusion urine culture. Bacteria are not regarded human material and do not need biobank registration. The study team will order copies of medical records from acute UTI episodes including laboratory urinalysis results.
Implications For Research And Practice
Based on the data we analysed, a pragmatic approach is required when considering prescribing long-term antibiotics in older patients with recurrent UTI. Although long-term antibiotics may reduce the risk of UTI recurrence in women, this benefit diminishes on cessation of treatment. Little is known about optimal prophylaxis period, long-term effects on health, risk of antibiotic resistant infections, effect in older men, effect in frail care home residents or impact on important patient-centred outcomes. These unknowns must be balanced against benefits and patient preferences.
Future research efforts on recurrent UTI should focus on improving the design and reporting of trials and developing a core set of outcomes to allow better synthesis of trial data. Antibiotic prophylaxis should be compared with non-antibiotic prophylaxis with some evidence of efficacy rather than those with little or poor evidence of efficacy. Researchers should address unanswered questions regarding long-term effects, duration of use, adverse effects and antibiotic resistance.
Recommended Reading: Discomfort In Urinary Tract Male
Study Design And Procedures
This study is a triple-blind, randomised, controlled phase IV trial in women 70 years with recurrent UTIs. Recurrent UTIs are defined as 3 episodes of antibiotic-treated UTIs during the last 12 months or 2 episodes during the last 6months. Antibiotic treatment is defined as receiving any course of urinary antibiotics for a suspected UTI regardless of dose regimen. The participants will be recruited from general practice, and the included patients will be randomised to active intervention or control for 6months. To evaluate if there is a prolonged effect of treatment, another 6 months of follow-up will be performed. A total of 400 patients will be randomised, approximately 100 patients in each participating country. Study visits and procedures are listed in .
-
*An antibiotic stewardship intervention to improve antibiotic prescribing for UTIs in frail older adults.