Risk Factors You Can’t Control
White men have a greater risk for kidney stones than other groups, starting in the 40s. Women see their risk rise in the 50s. And your odds also go up if you have a family history of kidney stones. Certain medical conditions can boost the risk — high blood pressure, gout, urinary tract infections, certain kidney conditions such as polycystic kidney disease — but treating or controlling these conditions generally helps prevent stone formation.
Differentiating Kidney Stones From A Urinary Tract Infection
It can be concerning to experience pain down there. Many questions of what could be causing the pain and discomfort run circles in your mind. Your first move might be calling your primary care doctor and declaring you have a UTI. Stop right there the symptoms of UTIs and kidney stones can be similar, but treatment is very different. In this article, we will be discussing the similarities and differences between the two and when you should go see a doctor.
How Are Kidney Stones Treated
Once diagnosed, your healthcare provider will first determine if you even need treatment. Some smaller kidney stones may leave your system when you urinate. This can be very painful. If your provider decides that you do need treatment, your options include medications and surgery.
Medications. Medications may be prescribed to:
- Your healthcare provider may recommend that you take an over-the-counter medication like ibuprofen or, if youre in the emergency room, an IV narcotic.
- Manage nausea/vomiting.
- Relax your ureter so that the stones pass. Commonly prescribed medicines include tamsulosin and nifedipine .
You should ask your healthcare provider before you take ibuprofen. This drug can increase the risk of kidney failure if taken while youre having an acute attack of kidney stones especially in those who have a history of kidney disease and associated illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension and obesity.
Surgery. There are four types of surgeries used to treat kidney stones. The first three are minimally invasive, meaning that the surgeon enters your body through a natural opening , or makes a small incision.
Recommended Reading: Does Cranberry Juice Clean Urinary Tract
Whats The Outlook For Kidney Stones
The outlook for kidney stones is very positive, although there is a risk of recurrence . Many kidney stones pass on their own over time without needing treatment. Medications and surgical treatments to remove larger kidney stones are generally very successful and involve little recovery time.
Its possible to get kidney stones multiple times throughout your life. If you keep developing kidney stones, your healthcare provider may work with you to discover why the stones happen. Once the cause is found, you may be able to make dietary changes to prevent future stones.
How Are Kidney Stones Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will discuss your medical history and possibly order some tests. These tests include:
- Imaging tests: An X-ray, CT scan and ultrasound will help your healthcare provider see the size, shape, location and number of your kidney stones. These tests help your provider decide what treatment you need.
- Blood test: A blood test will reveal how well your kidneys are functioning, check for infection and look for biochemical problems that may lead to kidney stones.
- Urine test: This test also looks for signs of infection and examines the levels of the substances that form kidney stones.
Also Check: How Does Someone Get A Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are formed from substances in your urine. The substances that combine into stones normally pass through your urinary system. When they dont, its because there isnt enough urine volume, causing the substances to become highly concentrated and to crystalize. This is typically a result of not drinking enough water. The stone-forming substances are:
- Calcium.
- Cloudy, foul-smelling urine, fever, chills or weakness which might be a sign of a serious infection.
- Blood in the urine.
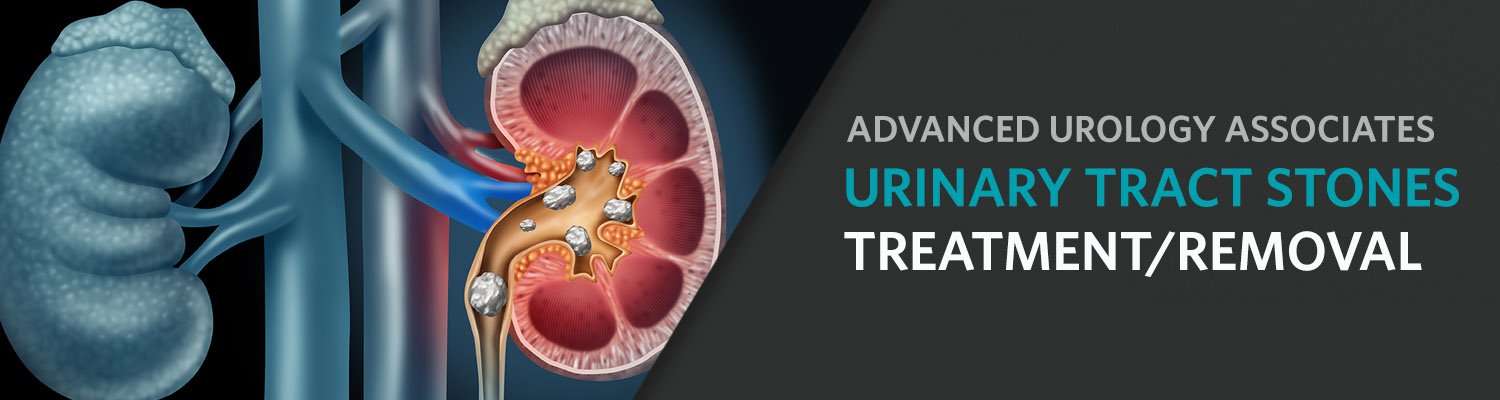
Most pediatric kidney stones remain in the kidney, but up to a third may migrate from the kidney and get stuck in a ureter. Stones that remain in the kidney, although often painless, can be the source of recurrent urinary tract infections. Those that lodge in the ureter can create severe colicky pain.
Overview Of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are mainly lodged in the kidney . Mankind has been afflicted by urinary stones since centuries dating back to 4000 B.C. , and it is the most common disease of the urinary tract. The prevention of renal stone recurrence remains to be a serious problem in human health . The prevention of stone recurrence requires better understanding of the mechanisms involved in stone formation . Kidney stones have been associated with an increased risk of chronic kidney diseases , end-stage renal failure , cardiovascular diseases , diabetes, and hypertension . It has been suggested that kidney stone may be a systemic disorder linked to the metabolic syndrome. Nephrolithiasis is responsible for 2 to 3% of end-stage renal cases if it is associated with nephrocalcinosis .
The symptoms of kidney stone are related to their location whether it is in the kidney, ureter, or urinary bladder . Initially, stone formation does not cause any symptom. Later, signs and symptoms of the stone disease consist of renal colic , flank pain , hematuria , obstructive uropathy , urinary tract infections, blockage of urine flow, and hydronephrosis . These conditions may result in nausea and vomiting with associated suffering from the stone event . Thus, the treatment and time lost from work involves substantial cost imposing an impact on the quality of life and nation’s economy.
Recommended Reading: Can Smoking Weed Cause Urinary Problems
How To Prevent Kidney Stones
There are various kidney stone treatment options available, but about half of people who have a kidney stone develop another one at a later time in their lives. Drinking plenty of water each day may help in preventing kidney stones in future.
For the few people who have a high level of certain chemicals in the body, further advice and treatment to reduce the amount of these chemicals may be needed.
How Small Is Small Enough
The smaller the kidney stone, the more likely it will pass on its own. If it is smaller than 5 mm , there is a 90% chance it will pass without further intervention. If the stone is between 5 mm and 10 mm, the odds are 50%. If a stone is too large to pass on its own, several treatment options are available.
Don’t Miss: Severe Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms In Elderly
The Urinary System And Stones
The urinary filtrate is formed in the glomerulus and passes into the tubules where the volume and content are altered by reabsorption or secretions. Most solute reabsorption occurs in the proximal tubules, whereas fine adjustments to urine composition take place in the distal tubule and collecting ducts. The loop of Henle serves to concentrate urine composed of 95% water, 2.5% urea, 2.5% mixture of minerals, salts, hormones, and enzymes. In the proximal tubules, glucose, sodium, chloride, and water are reabsorbed and returned to the blood stream along with essential nutrients such as amino acids, proteins, bicarbonate, calcium, phosphate, and potassium. In the distal tubule, the salt and acid-base balance of blood is regulated . The location of stones may vary as indicated in .
Kidney stone locations in the urinary system. Adopted from . Adopted from .
Risk Factors You Can Control
Drinking too little water is the most common cause of kidney stones. Diet also plays an important role. Eating a lot of animal protein, sodium, and high-oxalate foods, such as chocolate or dark green vegetables, can boost the risk for kidney stones in some people. Other risk factors include drinking sweetened beverages, putting on weight, and taking certain medications.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Health Cranberry Pills
Prevention Of Future Stones
Once your health care provider finds out why you are forming stones, he or she will give you tips on how to prevent them. This may include changing your diet and taking certain medications. There is no “one-size-fits-all” diet for preventing kidney stones. Everyone is different. Your diet may not be causing your stones to form. But there are dietary changes that you can make to stop stones from continuing to form.
Diet Changes
Drink enough fluids each day.
If you are not producing enough urine, your health care provider will recommend you drink at least 3 liters of liquid each day. This equals about 3 quarts . This is a great way to lower your risk of forming new stones. Remember to drink more to replace fluids lost when you sweat from exercise or in hot weather. All fluids count toward your fluid intake. But it’s best to drink mostly no-calorie or low-calorie drinks. This may mean limiting sugar-sweetened or alcoholic drinks.
Knowing how much you drink during the day can help you understand how much you need to drink to produce 2.5 liters of urine. Use a household measuring cup to measure how much liquid you drink for a day or two. Drink from bottles or cans with the fluid ounces listed on the label. Keep a log, and add up the ounces at the end of the day or 24-hour period. Use this total to be sure you are reaching your daily target urine amount of at least 85 ounces of urine daily.
Reduce the amount of salt in your diet.
Eat the recommended amount of calcium.
Are Home Remedies Effective For Kidney Stones
For some people who have had many kidney stones, home care may be appropriate. When passing a kidney stone, drinking lots of fluid is important. In fact, this is the most important home care measure. Medications may help control the pain . However, if it is the first time one has had symptoms suggestive of a kidney stone, it is important to see a doctor right away.
You May Like: Azithromycin For Urinary Tract Infection
Whos Most Likely To Get Kidney Stones What Are The Risk Factors
White men in their 30s and 40s are most likely to get kidney stones. However, anyone can develop kidney stones.
There are several risk factors for developing kidney stones. These include:
- Not drinking enough liquids.
- Having a diet that includes the substances that form the stones .
- Having a family history of kidney stones.
- Having a blockage in your urinary tract.
Certain medical conditions can also increase your risk of developing stones. This is because they may increase or decrease levels of the substances that make up a kidney stone. These conditions can include:
- Hypercalciuria .
Certain foods can also place you at risk of a kidney stone. These foods include:
- Meats and poultry .
- Sodium .
- Sugars .
Causes Of Urinary Tract Stones
Stones may form because the urine becomes too saturated with salts that can form stones or because the urine lacks the normal inhibitors of stone formation. Citrate is such an inhibitor because it normally binds with calcium that is often involved in forming stones.
, dehydration Dehydration Dehydration is a deficiency of water in the body. Vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, burns, kidney failure, and use of diuretics may cause dehydration. People feel thirsty, and as dehydration… read more , and renal tubular acidosis Renal Tubular Acidosis In renal tubular acidosis, the kidney tubules malfunction, resulting in excess levels of acid in the blood. The tubules of the kidneys that remove acid from the blood are damaged when a person… read more ) and among people whose diet is very high in animal-source protein or vitamin C or who do not consume enough water or calcium. People who have a family history of stone formation are more likely to have calcium stones and to have them more often. People who have undergone surgery for weight loss may also be at increased risk of stone formation.
Rarely, drugs and substances in the diet cause stones.
You May Like: Amoxicillin For Urinary Tract Infection
Treatment: Shock Wave Therapy
The most common medical procedure for treating kidney stones is known as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy . This therapy uses high-energy shock waves to break a kidney stone into little pieces. The small pieces can then move through the urinary tract more easily. Side effects can include bleeding, bruising, or pain after the procedure.
Treatment For Kidney Stones
Most kidney stones can be treated without surgery. Ninety per cent of stones pass by themselves within three to six weeks. In this situation, the only treatment required is pain relief. However, pain can be so severe that hospital admission and very strong pain-relieving medication may be needed. Always seek immediate medical attention if you are suffering strong pain.
Small stones in the kidney do not usually cause problems, so there is often no need to remove them. A doctor specialising in the treatment of kidney stones is the best person to advise you on treatment.
If a stone doesnt pass and blocks urine flow or causes bleeding or an infection, then it may need to be removed. New surgical techniques have reduced hospital stay time to as little as 48 hours. Treatments include:
Recommended Reading: Is Urinary Incontinence A Normal Part Of Aging
Kidney Stone Or Something Else
If you have sudden, severe pain in the back or belly, it’s best to seek medical care right away. Abdominal pain is associated with many other conditions, including emergencies like appendicitis and ectopic pregnancy. Painful urination is also a common symptom of a urinary tract infection or an STD.
Kidney Stone Causes Symptoms Treatments & Prevention
Your kidneys remove waste and fluid from your blood to make urine . Sometimes, when you have too much waste and not enough fluid in your blood, these wastes can build up and stick together in your kidneys. These clumps of waste are called kidney stones.
You May Like: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Urinary Tract Infections
Can Children Get Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are found in children as young as 5 years. In fact, this problem is so common in children that some hospitals conduct ‘stone’ clinics for pediatric patients. The increase in the United States has been attributed to several factors, mostly related to food choices. The two most important reasons are not drinking enough fluids and eating foods that are high in salt. Kids should eat less salty potato chips and French fries. There are other salty foods: sandwich meats, canned soups, packaged meals, and even some sports drinks. Sodas and other sweetened beverages can also increase the risk of stones if they contain high fructose corn syrup.
If you would like more information, please contact us.
Save this content:
Differentiating Kidney Stones And Urinary Tract Infections
| Kidney stones | ||
| Complications | Recurring kidney stones | Recurrent infections, permanent kidney damage due to an untreated UTI, delivering premature infant risk in pregnant women, urethral narrowing in men, sepsis. |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, urine testing, imaging tests, and analysis of any stones that have passed. | Analyzing urine samples, growing urinary tract bacteria in a lab, creating images of the urinary tract, and using a scope to see inside of the bladder. |
| Treatment | Increasing your intake of fluids, medications, lithotripsy, tunnel surgery, ureteroscopy, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy , and percutaneous nephrolithotomy . | Drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding drinks that irritate the bladder, using a heating pad to relieve any pain, prescription antibiotics such as Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, Fosfomycin, Nitrofurantoin, etc. |
Recommended Reading: What Is Best Treatment For Urinary Tract Infection
Epidemiology Of Kidney Stones
Globally, kidney stone disease prevalence and recurrence rates are increasing , with limited options of effective drugs. Urolithiasis affects about 12% of the world population at some stage in their lifetime . It affects all ages, sexes, and races but occurs more frequently in men than in women within the age of 2049 years . If patients do not apply metaphylaxis, the relapsing rate of secondary stone formations is estimated to be 1023% per year, 50% in 510 years, and 75% in 20 years of the patient . However, lifetime recurrence rate is higher in males, although the incidence of nephrolithiasis is growing among females . Therefore, prophylactic management is of great importance to manage urolithiasis.
Recent studies have reported that the prevalence of urolithiasis has been increasing in the past decades in both developed and developing countries. This growing trend is believed to be associated with changes in lifestyle modifications such as lack of physical activity and dietary habits and global warming . In the United States, kidney stone affects 1 in 11 people , and it is estimated that 600,000 Americans suffer from urinary stones every year. In Indian population, about 12% of them are expected to have urinary stones and out of which 50% may end up with loss of kidney functions .
Mechanisms Of Renal Stone Formation
The pathogenesis of kidney stone or biomineralization is a complex biochemical process which remains incompletely understood . Renal stone formation is a biological process that involves physicochemical changes and supersaturation of urine. Supersaturated solution refers to a solution that contains more of dissolved material than could be dissolved by the solvent under normal circumstances . As a result of supersaturation, solutes precipitate in urine leads to nucleation and then crystal concretions are formed. That is, crystallization occurs when the concentration of two ions exceeds their saturation point in the solution . The transformation of a liquid to a solid phase is influenced by pH and specific concentrations of excess substances. The level of urinary saturation with respect to the stone-forming constituents like calcium, phosphorus, uric acid, oxalate, cystine, and low urine volume are risk factors for crystallization . Thus, crystallization process depends on the thermodynamics and kinetics of a supersaturated solution . Therefore, lithiasis can be prevented by avoiding supersaturation.
Read Also: Tea For Urinary Tract Health