Bladder And Bowel Dysfunctions Often Come Together
It’s only recently that health care providers have begun to notice the connection between bladder and bowel dysfunction. The impact is huge for people with neurogenic diseases. In a lot of cases, bladder and bowel symptoms coexist, side by side and interact. So it’s time for a more holistic approach for the benefit of patients.
Typical Symptoms Of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
The characteristic symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis is increased pain in the legs with walking , which can markedly diminish ones activity level. People with lumbar spinal stenosis are typically comfortable at rest but cannot walk far without developing leg pain. Pain relief is achieved within 5 to 10 minutes when they sit down or lean forward.4 Spinal nerve root involvement may cause a more sharp, shooting type of pain in the leg.
The symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis develop slowly. As the condition progresses, the symptoms may worsen and become quite debilitating. For each person, the severity and duration of lumbar stenosis symptoms are different and based on the affected neural tissue. Common symptoms may include one or more of the following:
- Radicular pain: Nerve root compression or irritation that results in leg pain, which typically travels down from the lower back into the buttock and leg on one sidecommonly called sciatica.
- Lumbar radiculopathy: Nerve root compression or irritation that results in tingling, weakness, and/or numbness that radiates from the lower back into the buttock and leg on one side.
- Neurogenic claudication: Spinal cord compression that causes a symmetrical pattern of pain affecting both legs while walking or standing for a long period of time. Neurologic deficits, such as loss of coordination, gait imbalance, numbness, and weakness affecting both legs may also occur.
Read more about Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Symptoms
Symptoms Of Spinal Stenosis
What does spinal stenosis feel like? Many people with the condition do not experience any symptoms in the beginning. Later, as the stenosis progresses and pressure on the spinal cord or nerves gets worse, there may be pain, weakness, or numbness in the legs, and/or problems with urination and bowel control.
Radiating pain
Spinal stenosis can cause pain that radiates into the limbs .
- With lumbar spinal stenosis, there is compression of a lumbar nerve root that can cause lower back pain, tingling, numbness, weakness, or loss of sensation that extends into the hips, buttocks, one or both legs, and the feet. This discomfort feels worse during walking or standing and may be eased by leaning forward, such as pushing a shopping cart or sitting.
- People with cervical spinal stenosis may have headaches or feel numbness, weakness, or reduced coordination of the arms and hands. They may have difficulty doing normally simple activities such as gripping objects, buttoning, tying, writing, and typing. In severe cases, an imbalance in your gait can occur.
Frequent Urination and Bowel Control Issues
Frequent urination or loss of bladder and bowel control is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention. It may be a marker of severe spinal stenosis due to greatly increased pressure on the nerve roots controlling the bladder or bowel . See a doctor as soon as you can for treatment.
Don’t Miss: Azo Urinary Tract Health Side Effects
What Are The Causes
A large ruptured disc can cause cauda equina syndrome. During a herniation, the gel-like center of a spinal disc can bulge or rupture through a weak area in the disc wall and compress the nerves. In the majority of cases, the disc herniation occurs at the L4-5 or L5-S1 discs in the lumbar spine. A sports injury, fall, or car accident can fracture the spine or tear a muscle and damage nerves. Other causes include a narrowing of the spinal canal , a tumor, an infection, or a hemorrhage.
Dont Miss: How To Relax The Bladder Naturally
When Should To Call My Healthcare Provider
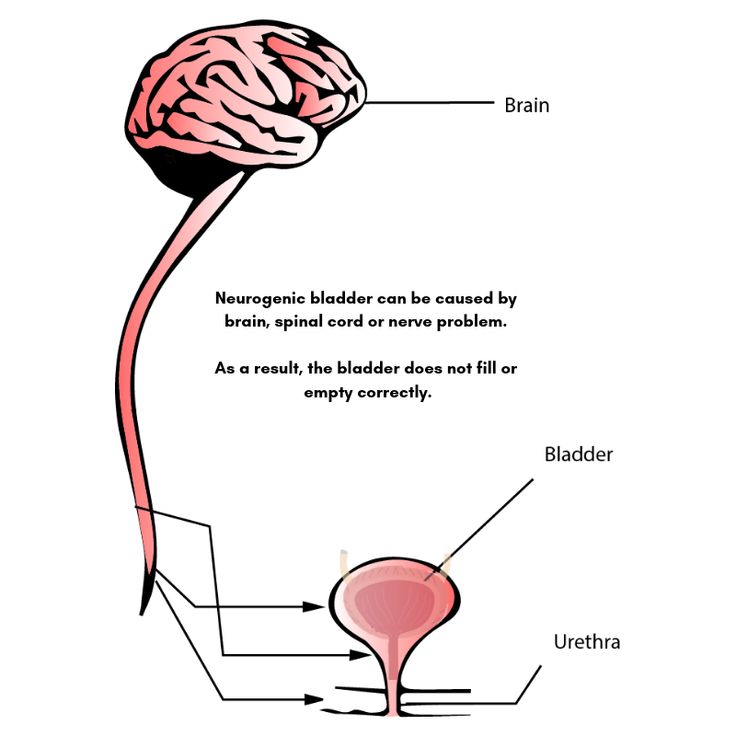
Lumbar spinal stenosis can cause cauda equine syndrome, which needs medical attention right away. Call your healthcare provider if you have:
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Severe or increasing numbness between your legs, inner thighs, or back of your legs
- Severe pain and weakness that spreads into one or both legs, making it hard to walk or get out of a chair
Read Also: What Can Treat Urinary Tract Infection
Bladder And Pelvic Floor Function In Neuromuscular Disorders
Bladder and sphincter dysfunction are seldom seen, even in advanced neuromuscular disease. The sparing of cells in the Onuf nucleus appears to limit the loss of fibers in the external urethral sphincter and the pelvic floor in general.
Sphincter muscle abnormalities can usually be explained by other factors. This was the case in a group of children with neuromuscular disorders studied by Dyro and Bauer: a child with myotonic dystrophy had no myotonic discharges in the sphincter. They also studied 3 boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy , 2 girls with congenital myopathy, a girl with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type II, and a boy with Kugelberg-Welander syndrome .
Motor units in the sphincter of 1 of the girls with congenital myopathy were of low amplitude another had evidence of denervation after scoliosis surgery. The boy with KWS had some increased-amplitude motor units and uninhibited detrusor contractions attributed to coexisting thoracolumbar syringomyelia. Two of the boys with DMD had detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia, but one had concomitant cerebral palsy and the other had a T10 paraplegia following scoliosis surgery.
In the anterior horn cell disordersamyotrophic lateral sclerosis, KWS, and poliolittle or no compromise of the sphincter is noted, and autopsy evidence indicates that the cells of the Onuf nucleus are spared.
Can A Bulging Disc Cause Bowel Problems
If the herniated disk presses on nerves in the nearby spinal canal, this can cause variety of nerve-related symptoms, including pain, numbness and muscle weakness. In the most severe cases, a herniated disk can compress nerves that control the bowel and bladder, causing urinary incontinence and loss of bowel control.
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes Urinary Frequency
Management Of Fecal Incontinence
Guidelines for the management of fecal incontinence in the acute and chronic phases are proposed in Tables 1, 3, along with suggestions to manage the dog’s environment and feeding.
The primary concern expressed by owners of dogs with fecal incontinence is management of the mess produced by inadvertent defecation, with secondary concerns of skin damage due to contamination with fecal material and contamination of the vulva causing urinary tract infections. Careful questioning of the owner is needed to determine when the incontinence is occurring and the nature and volume of the stool. The most practical and effective management technique is to use a low residue diet that reduces stool volume sometimes dramatically, and usually resolves loose stool or diarrhea. All dietary indiscretions should be avoided because the consequences can be challenging.
The Vagal Nerves Blood Pressure Regulation Heartbeat Regulation And Urinary Incontinence Problems Could All Trace A Common Source To The Neck
Two years later a different set of researchers from the Department of Cardiovascular Studies, at the University of Leeds in the United Kingdom published a follow-up study in the Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology. They found: that inhibition of vagus nerve activity caused by bladder distension was affected by the level of carotid sinus pressure. The filled bladder and the nerve impulses it was creating were being regulated by the carotid sinus in the neck. The vagal nerves, blood pressure regulation, heartbeat regulation, and urinary incontinence problems, could all trace a common source to the neck.
Now you would think research like this would get neurologists, urologists, and cardiologists talking. This was not the case. Lets fast forward some 25 years later to 2012.
In a published study in Polish medical journal Folia Medica Cracoviensia, doctors at the Department of Pathophysiology, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland opened their study with this sentence:
There is no evidence that vagal nerve innervates the urinary bladder. They closed their research investigation with this sentence: The modulation of vagal nerve activity affects the urinary bladder function in naive conditions, as well as in case of . These data imply the integrative action of visceral vagal nerve innervation in urinary bladder function.There is a connection.
As you can there is controversy when it comes to urinary and bladder problems and cervical neck pain.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Cranberry Juice
Incontinence And Back Problems Risk Factors
While anyone may develop a medical condition that causes back problems and incontinence simultaneously, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing both conditions. Some of the most common risk factors for developing back pain and incontinence simultaneously include:
- Age: Back problems and incontinence are age-related conditions, meaning they likely occur with age. Back pain typically occurs from spinal degeneration or injury. With age, the bladder muscles often weaken, leading to an increased risk of incontinence.
- Weight: Being overweight places additional strain on the spine, causing or aggravating painful spinal conditions like pinched nerves or herniated discs. Excess weight also increases pressure on the bowels, bladder and surrounding muscles. Excess weight can increase the risk of stress incontinence, which can further weaken muscles and lead to worsening incontinence.
- Pre-existing medical conditions: Certain pre-existing medical conditions may increase the risk of back pain and incontinence. For example, diabetes and arthritis are two conditions that can cause incontinence and back pain.
What Are The Symptoms Of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Early lumbar spinal stenosis may have no symptoms. In most people, symptoms develop gradually over time. Symptoms may include:
- Pain in the back
- Burning pain going into the buttocks and down into the legs
- Numbness, tingling, cramping, or weakness in the legs
- Loss of sensation in the feet
- A weakness in a foot that causes the foot to slap down when walking
- Loss of sexual ability
Pressure on nerves in the lumbar region can also cause more serious symptoms known as cauda equine syndrome. If you have any of these symptoms, you need to get medical attention right away:
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Severe or increasing numbness between your legs, inner thighs, and back of the legs
- Severe pain and weakness that spreads into one or both legs. This makes it hard to walk or get out of a chair
Recommended Reading: What Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics
Types Of Incontinence Related To Back Pain
Urinary Incontinence: This can occur when someone no longer has bladder control and has unintentional losses of urine.
Overactive Bladder : This type of incontinence occurs when you have a sudden urge to urinate that may lead to frequent bathroom trips or accidental leakage. If you have OAB and lower back pain together, its possible that you may be overweight, have prostate or kidney issues, or have cancer. Other symptoms you may experience with OAB and lower back pain include:
- Bloody or cloudy urine.
- Inability to void urine or void completely.
Fecal Incontinence: Bowel incontinence is when you lose control of your bowels and fecal matter. This can occur alongside lower back pain if your
Overflow Incontinence: Overflow incontinence occurs when youre unable to pass urine completely, otherwise known as urinary retention, and your urine overflows out of your urethra.
Stress Incontinence: Stress incontinence happens when urine leaks when you sneeze, cough, laugh, lift heavy objects, or exercise. This is due to stress being put on your bladder muscles. After giving birth, stress incontinence and lower back pain are both common in women.
Can Spinal Stenosis Cause Bladder Problems
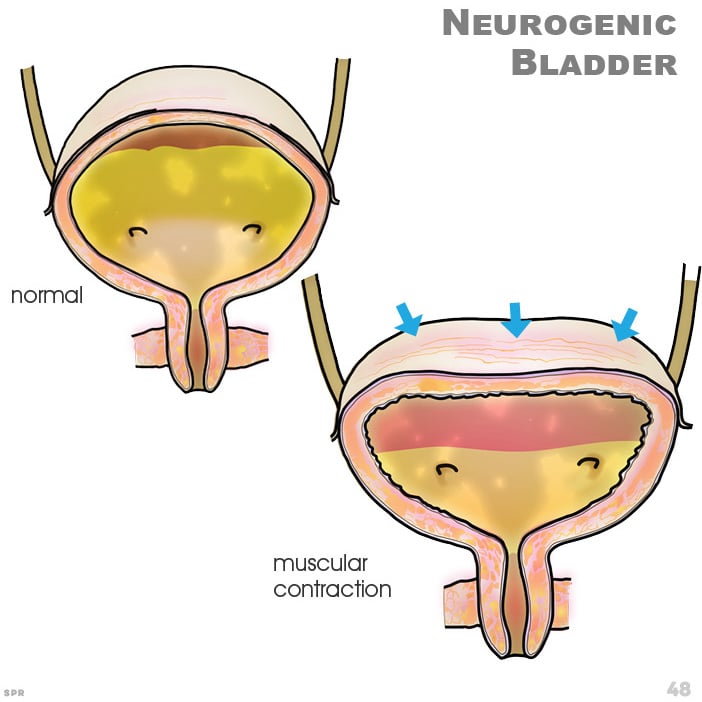
Can spinal stenosis cause bladder problems
Can Spinal Stenosis Cause Bladder Problems. Spinal stenosis spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. You loose all bladder control and it is a very serious matter.that is when you call your surgeon and get you butt into surgery asap. If left untreated, this syndrome can cause permanent nerve damage. The higher up in the spinal cord an injury occurs, the more muscles are affected.
What are the dangers of a stenosis in the neck? Quora From quora.com
If you are unable to void urine you should immediately go to the emergency room for treatment. You may also have pain or numbness in your legs. Lumbar spinal stenosis can cause cauda equine syndrome, which needs medical attention right away. Disturbance or loss of bladder or bowel function. Pain is often most noticeable in the arm for cervical spinal stenosis and progresses, developing more severe symptoms if not adequately treated , such as a loss of sensation and function in all limbs . The higher up in the spinal cord an injury occurs, the more muscles are affected.
You May Like: How To Treat Male Urinary Incontinence
When To See A Doctor
In many cases, a herniated disk can be a progressive condition. A person might experience back pain for some time. If the disk begins to slip out of place significantly, incontinence can occur.
As a result, the sudden onset of unexplained urinary incontinence can indicate that a person may need to seek immediate medical attention.
The following signs may also indicate that back pain and incontinence together could be a medical emergency:
- a fever higher than 103°F
- loss of ability to move the legs or sense the lower body
- tingling or numbness down both legs
In most instances, incontinence and back pain are a medical emergency when they suddenly occur together.
If a person experiences either symptom separately, they should talk to their doctor. Many treatment options are available for both incontinence and back pain.
The Link Between Spinal Stenosis And Walking Concerns
Your lumbar region is where your spinal cord ends in a collection of nerves that look like a horses tail, called the cauda equina. These nerves send and receive messages to and from your pelvic area and legs.
Stenosis of your spinal canal interrupts these messages. As a result, lumbar spinal stenosis can cause walking problems.
Contact your doctor right away if you have severe pain and difficulty standing up. You may have developed cauda equina syndrome, which puts stronger pressure on the nerves at the bottom of your spinal cord. If left untreated, this syndrome can cause permanent nerve damage.
Symptoms of cauda equina syndrome include:
- disturbance or loss of bladder or bowel function
- severe pain or weakness in your legs that makes it difficult to stand up
If you have lumbar spinal stenosis, you may notice symptoms while walking or standing. These can include:
- lower back pressure when upright
- pain in your back, buttocks, or legs
- leg numbness, cramping, or tingling
- muscle weakness
- a weak foot that drops when you walk
You may feel relief from these symptoms when you lean forward, sit, or crouch, or while riding a bike or pushing a shopping cart. This is because a forward-leaning position reduces pressure on your nerves.
Recommended Reading: Purina One Urinary Tract Health
What Is Incontinence From Spinal Stenosis
Incontinence describes a condition in which the patient can not hold off the need to release their bladder or void their bowels. The patient will urinate and/or defecate without intent and will obviously be in a very bad situation.
The majority of cases of incontinence related to a spinal stenosis issue come on acutely, due to a known trauma, such as a car crash, serious fall or sporting injury. However, a slower onset and progressive variety of incontinence may start gradually with a bit of leaking or an occasional accident. These symptoms may also be the result of traumatic injury, but are more commonly related to known stenosis which continues to worsen in the cervical or lumbar spinal areas.
Incontinence is perhaps one of the most disruptive of all spinal symptoms and is unfortunately commonly associated with significant central stenosis cases.
What Are Some Types Of Bladder Management
There are many types bladder management following SCI, each with various advantages and disadvantages. Several of the more common types of bladder management are listed below. It is important to speak with your health care provider to determine which option is best for you.
If you continue to have significant problems affecting your kidneys or bladder or your lifestyle despite non-surgical bladder management options, your doctor might in rare cases suggest a surgical option such as a urinary diversion. For more information on surgical management, see MSKTC factsheet entitled Surgical Alternatives for Bladder Management Following SCI. This factsheet will focus on some of the more common non-surgical options of bladder management.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Can Cause A Urinary Tract Infection
What Is Bladder Management
Bladder management is an ongoing set of treatments and practices that help keep your bladder and kidneys healthy and free from infection and other problems.
- Bladder management cannot fix or solve the problems caused by your SCI, but it can help you manage them to improve your health and quality of life. With appropriate management you can prevent incontinence and damage to the kidneys.
- You can work with your doctor to choose which bladder management option fits into your lifestyle and maintains bladder and kidney health.
What Are The Types Of Cauda Equina Syndrome
There are two types and two classifications of cauda equina syndrome. The syndrome is acute or chronic, and its either complete or incomplete.
Types of cauda equina syndrome
Acute cauda equina syndrome
Severe symptoms start suddenly. Youll likely need surgery within 24 to 48 hours.
Chronic cauda equina syndrome
This name means long-lasting cauda equina syndrome. It describes two scenarios:
Emergency surgery might stop permanent damage. See your healthcare provider if you have symptoms.
Classifications of cauda equina syndrome
Complete cauda equina syndrome
Complete cauda equina syndrome causes urinary and/or bowel retention or incontinence. Retention means that youre unable to pee or poop, and incontinence means that you cant stop yourself from peeing or pooping. It affects about 60% of people with cauda equina syndrome.
Incomplete cauda equina syndrome
This affects the other 40% of people with cauda equina syndrome. Typical symptoms include loss of urgency or increased urgency sensation in the bladder and bowels without retention or incontinence. This means you cant feel that you have to poop or pee, or you feel the sensation stronger than before.
Also Check: Natural Herbs For Urinary Tract Infection