Increasing Worsening Or Changing Symptoms
If any of your symptoms increase, worsen or change from the normal UTI symptoms, it might be an STD instead. If symptoms start to include ones like discharge or smell, its far more likely to be one of the most common STDs instead.
For any repeated urinary tract infections that appear to keep coming back, see your doctor: There are many things that can cause repeated UTIs. The same is true for any symptoms that can point to more than just an STD: Again, see your doctor.
How Common Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention in men becomes more common with age.
- In men 40 to 83 years old, the overall incidence of urinary retention is 4.5 to 6.8 per 1,000 men.
- For men in their 70s, the overall incidence increases to 100 per 1,000 men.
- For men in their 80s, the incidence of acute urinary retention is 300 per 1,000 men.
Urinary retention in women is less common, though not rare. The incidence of urinary retention in women has not been well studied because researchers have primarily thought of urinary retention as a manâs problem related to the prostate.
- weakened bladder muscles
Obstruction of the Urethra
Obstruction of the urethra causes urinary retention by blocking the normal urine flow out of the body. Conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasiaâ also called BPHâurethral stricture, urinary tract stones, cystocele, rectocele, constipation, and certain tumors and cancers can cause an obstruction.
As the prostate enlarges, the gland presses against and pinches the urethra. The bladder wall becomes thicker. Eventually, the bladder may weaken and lose the ability to empty completely, leaving some urine in the bladder.
Surgery to correct pelvic organ prolapse, such as cystocele and rectocele, and urinary incontinence can also cause urethral stricture. The urethral stricture often gets better a few weeks after surgery.
Nerve Problems
Recommended Reading: Medicine To Stop Urinary Burning
Treatment Of Urinary Retention
Many treatments are available for urinary retention, including medication, devices, procedures and surgery. Treatment will depend on the cause and the disease specifics.
For acute urinary retention, medical providers will use a catheter to drain the bladder. Then the doctor will seek the cause of the urinary retention and determine a course of treatment.
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Pain Relief How To Take
What Are The Possible Complications Of Urinary Retention
The complications of urinary retention and its treatments may include:
UTIs: the normal flow of urine usually prevents germs from infecting the urine. With urinary retention, bacteria may be able to infect the urine because the urine cannot flow out of the bladder.
Bladder damage: if the bladder becomes stretched too far or for long periods, the muscles may become damaged and unable to work properly.
Chronic kidney disease: for some people, urinary retention causes urine to flow backwards into the kidneys. This backward flow is called reflux and it may damage or scar the kidneys.
Urinary incontinence: this may occur together with chronic urinary retention or after surgery .
Prostate gland surgery may cause urinary incontinence in some men. This problem is often temporary and gets better quite quickly. Most men recover their bladder control in a few weeks or months after surgery.
What Causes Chronic Urinary Retention
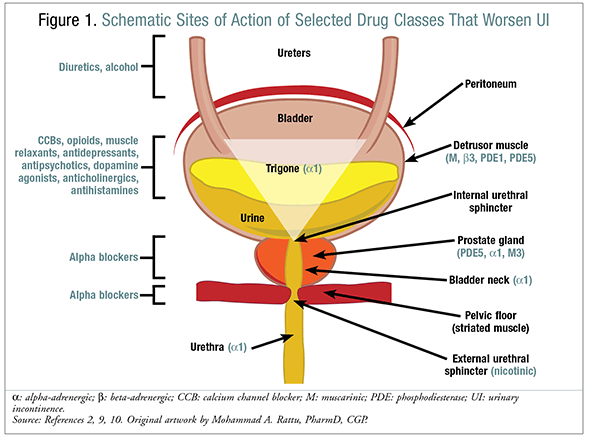
Urinary retention can happen for several different reasons. These causes can include:
- A blockage to the way urine leaves your body.
- Medications youre taking for other conditions.
- Nerve issues that interrupt the way your brain and urinary system communicate.
- Infections and swelling that prevent urine from leaving your body.
- Complications and side effects of medications given to you for a surgical procedure.
Blockage
When something blocks the free flow of urine through the bladder and urethra, you might experience urinary retention. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body. In men, a blockage can be caused when the prostate gland gets so big that it presses on the urethra. This is the most common cause of chronic urinary retention in men. One cause in women is a bladder that sags. This is called cystocele. It can also be caused when the rectum sags into the back wall of the vagina a condition called rectocele. Some causes can happen to both men and women. The urethra can get narrow due to scar tissue. This is called a stricture. Urinary stones can also block the flow of urine out of your body.
Medications
Nerve issues
- Trauma to the spine or pelvis.
- Pressure on the spinal cord from tumors and a herniated disk.
- Vaginal childbirth.
Urinary retention from nerve disease occurs at the same rate in men and women.
Infections and swelling
Surgery
Also Check: Urinary Pain Relief Dollar General
Inflammation Of The Prostate Gland
Bacteria sometimes cause prostatitis . More commonly, the underlying cause is uncertain. Consult your doctor promptly if you experience:
- fever
- pain in the groin
- urgent and frequent urination.
Treatment with antibiotics is essential for acute bacterial prostatitis. Admission to hospital is often necessary and, as with chronic bacterial prostatitis, specific antibacterial drugs are required for a long time.
Initial Management Of Urinary Retention
Acute urinary retention should be managed by immediate and complete decompression of the bladder through catheterization. Standard transurethral catheters are readily available and can usually be easily inserted. If urethral catheterization is unsuccessful or contraindicated, the patient should be referred immediately to a physician trained in advanced catheterization techniques, such as placement of a firm, angulated Coude catheter or a suprapubic catheter.5 Hematuria, hypotension, and postobstructive diuresis are potential complications of rapid decompression however, there is no evidence that gradual bladder decompression will decrease these complications. Rapid and complete emptying of the bladder is therefore recommended.34
For hospitalized patients requiring catheterization for 14 days or less, a Cochrane review found that silver alloy-impregnated urethral catheters have been associated with decreased rates of UTI versus standard catheters.41 Another Cochrane review concluded that patients requiring catheterization for up to 14 days had less discomfort, bacteriuria, and need for recatheterization when suprapubic catheters were used compared with urethral catheters.42 In a recent meta-analysis of abdominal surgery patients, suprapubic catheters were found to decrease bacteriuria and discomfort and were preferred by patients.43 Although evidence suggests short-term benefit from silver alloy-impregnated and suprapubic catheters, their use remains somewhat controversial.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Causing Hallucinations
When To See A Doctor
Anyone experiencing symptoms of acute urinary retention should go to the emergency room.Chronic urinary retention is not a medical emergency, but it does usually indicate a potentially serious underlying problem.
A person should schedule an appointment with a doctor for urinary retention that lasts longer than a few days or that goes away and then returns.
People who experience temporary urinary retention due to medication or anesthesia may not need medical treatment if the symptoms disappear and do not return.
Although anyone can develop urinary retention, it is more common as a person ages. Males are also more likely than females to have urinary retention due to prostate issues and partial blockages of the urethra.
Some other risk factors include:
4 sourcescollapsed
- Carnevale, F. C., et al. . Quality of life and clinical symptom improvement support prostatic artery embolization for patients with acute urinary retention caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia.
How Is Chronic Urinary Retention Diagnosed
History and physical exam: During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and how long you have had them. He or she will also ask about your medical history and your drug use. A physical exam of the lower abdomen may show the cause or give your provider additional clues. After this, certain tests may be needed. Men may have a rectal exam to check the size of their prostate.
Your urine may be saved and checked to look for infection.
Ultrasound of the bladder: The amount of urine that stays in your bladder after urinating may be measured by doing an ultrasound test of the bladder. This test is called a postvoid residual or bladder scan.
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a test in which a thin tube with a tiny camera on one end is put into your urethra. This lets the doctor look at pictures of the lining of your urethra and bladder. This test may show a stricture of the urethra, blockage caused by a stone, an enlarged prostate or a tumor. It can also be used to remove stones, if found. A computed tomography scan may also help find stones or anything else blocking the flow of urine.
Urodynamic testing: Tests that use a catheter to record pressure within the bladder may be done to tell how well the bladder empties. The rate at which urine flows can also be measured by such tests. This is called urodynamic testing.
Read Also: Z Pack Urinary Tract Infection
Complications Of Urinary Retention
Frequent urinary tract infections resulting from bacteria if the urine stays in the bladder.
Long term obstruction of the urinary tract may lead to painful bladder stones.
Serious bladder damage, such as losing the ability to contract if it becomes stretched for a lengthy period of time.
If urine backs up into the kidneys, it can lead to congestion, reducing kidney function. It can also leave you with a high risk of falling prey to chronic kidney disease.
Urinary retention may also promote the formation of small pouches in the bladder wall, similar to those in the bowel which can trap bladder stones, causing pain and discomfort. Bacteria present in the pouches can multiply and are liable to cause infections.
Urinary Retention In Men: Symptoms Causes And Treatments
Discussing bladder control problems, even with the doctor, can cause discomfort, and embarrassment.
Bladder control, however, is an issue that affects far more people than perceived. So bear in mind, if you are unable to empty your bladder properly, you are definitely not alone.
Urinary retention is defined as having great difficulty in completely, or even partially, emptying the bladder.
Many people have problems starting urination, as well as keeping the urine volume going, which results in the bladder not being fully drained.
The bladder is a very integral part of the body, and when it is not functioning as it should, it is very distressing, and at times, even painful.
Fortunately, there are several treatments available, most of which have a good record of success.
You May Like: Signs Of A Urinary Tract Infection In A Man
When To Seek Urgent Medical Care
On its own, a weak urine stream may not be cause for concern, but if its accompanied by other symptoms, it could be an indication of a more serious medical issue. Urinary hesitancy could be an issue if you also experience:
- Chills and/or fever
- Shakes
- Lower back pain
If your urine stream stops entirely, a condition called urinary retention, youll need emergency medical attention, since this can become a serious problem without immediate treatment.
Cause Of Urinary Problems As Men Age
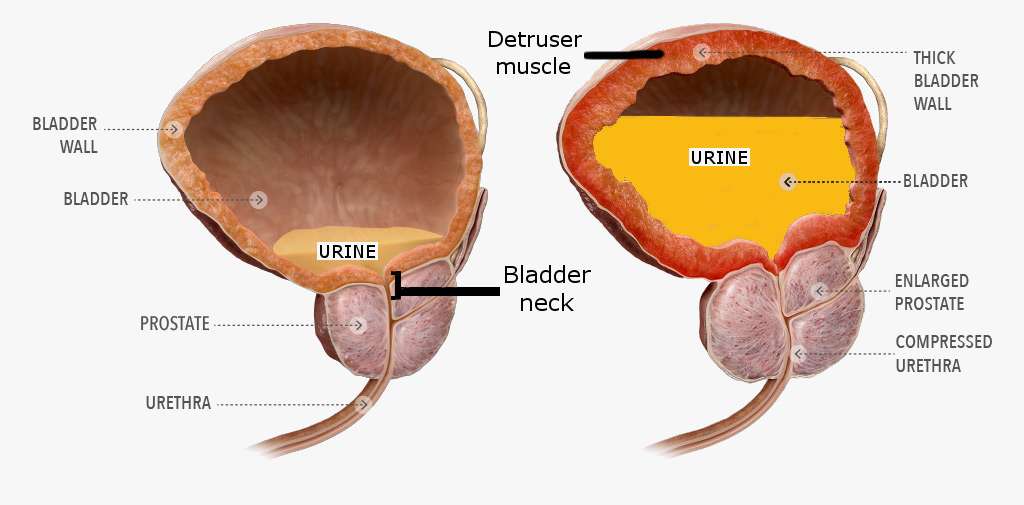
Many men experience urinary symptoms as they age, which may be caused by inflammation of the prostate gland . In older men, symptoms may be due to a blockage in the tubes due to a benign enlargement of the prostate gland . The most common symptom is difficulty emptying your bladder. Urinary symptoms may become bothersome enough that they require treatment. Not all urinary symptoms are due to changes to the prostate. Also, some men have enlarged prostates and yet experience few, if any, symptoms.
Read Also: Sacral Nerve Stimulation For Urinary Incontinence
The Main Causes Of Urinary Retention In Women And How To Deal With It
While anyone can experience urinary retention, it is most common in men who are in their fifties or sixties. This means that much of the information available is specific to older men even though it is possible for women to develop the same condition.
Urinary retention in women is relatively rare, with an estimated 3 cases per 100,000 women every year. By contrast, roughly one out of every three men over the age of 80 will experience this condition.
Are you wondering what you should know about urinary retention and its causes?
Lets take a look at what you need to know.
Helpful Tips For Managing Urinary Retention And Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is a prevalent issue, with anywhere from 25-50 percent of women reporting an episode in the past year.
Managing urinary conditions can be frustrating and time consuming, but there are helpful tips and lifestyle changes that can reduce the burden this condition causes.
Topics in this Post
Urine retention can be uncomfortable and symptoms might include:
- Pain and bloating in the lower abdominal area.
- A frequent, urgent need to urinate but then having trouble doing it.
You May Like: How Can I Get Urinary Tract Infection
Read Also: Male Urinary Tract Infection Over The Counter Treatment
What Are The Types Of Urinary Retention
Urinary retention can be classified as:
Acute urinary retention, which is an emergency situation where the patient presents with a sudden inability to pass urine and pain. Conditions that can trigger acute urinary retention include surgery, a urinary tract infection, excessive fluid intake or the use of certain medications. It is more common in men and often due to untreated enlargement of the prostate.
Chronic urinary retention, which is a painless condition present over a longer duration. The patient may experience dribbling of the urine once the bladder is full. Sometimes, the patient may not notice the chronic retention, and therefore, it is necessary for the doctor to suspect the condition before it can cause complications including kidney failure.
Sometimes, the patient may pass urine partially and some urine may remain in the bladder this remaining urine in the bladder due to incomplete evacuation is called post-void residual urine.
Urinary retention may also be classified as:
- Complete or partial, depending on the degree of retention
- Obstructive or non-obstructive, depending on whether an anatomical obstruction exists that stops the passage of urine
- High or low pressure, depending on the pressure generated in the bladder
Urinary retention may occur due to the following:
The causes of urinary retention include the following:
- Obstruction: The obstruction to the urinary flow may be present within the urinary tract or outside the urinary tract
Extrinsic causes include:
Other Causes Of Urinary Hesitancy
Both women and men are susceptible to urinary hesitancy resulting from:
- Dysfunction of bladder muscles
- Surgery and surgical anesthetics
- Psychological influences, including shy bladder syndrome
Women can also suffer nerve damage resulting from pregnancy that causes urinary problems, including a weak urine stream.
Read Also: Medicine For Urinary Tract Infection Male
What Are The Risks Of Urinary Retention
Urinary retention exposes men to a number of risks and requires prompt evaluation.
Is very important to find out the cause of urine retention. Prostate enlargement can be caused by prostate swelling from infection, enlargement of the prostate that slowly grows beginning at around age 40. Urinary obstruction and urine retention can also be caused by prostate cancer and other serious problems, including bladder cancer and urinary stricture.
Urinary retention man can lead to damage to the kidneys and occasionally leads to a need for dialysis and kidney transplantation if not addressed promptly.
Urinary retention can also cause UTIs, urinary incontinence, and if not treated promptly, can over time cause damage to the bladder to the point that it will not work.
Did you know?Dr. Shteynshlyuger has performed over 1,000 surgeries and procedures for enlarged prostate, including Rezum, Urolift, prostate enucleation, laser ablation of the prostate, and TURP. He performs over 100 prostate procedures a year.
Medication For Urinary Problems
Your doctor may suggest various medications to help ease your urinary problems, including:
- medications to reduce the tone of the muscles of the urethra and prostate to minimise any constriction to urine flow caused when these muscles contract
- medication to reduce the size of the prostate gland. These medications work by blocking the action of male hormones produced by the prostate gland
- medications to relax the bladder, making unwanted contractions less likely and reducing the symptoms of urgency and frequency of urination
- the over-the-counter preparation ‘saw palmetto’ is sometimes used. This may help some men, especially if frequent urination at night is a problem.
However, recent reviews of the evidence for using saw palmetto as a treatment for mild or moderate urinary symptoms did not show any improvement, compared to no treatment, in men with BPH.
You May Like: Azo Cranberry Urinary Tract Health
Obstruction In People With A Penis
Possible causes of obstruction in people with a penis
- Cystocele. Cystocele occurs when the bladder lowers and pushes against your vagina.
- Rectocele. This is when the rectum expands and pushes against your vagina.
- Uterineprolapse. Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus lowers and pushes against the bladder.
What The Patient Can Do
Here are some things that may help make urine retention less of a problem:
- Empty your bladder at least every 4 hours, even if you don’t feel the urge to do so.
- Empty your bowels regularly.
- If tolerated, drink 6 to 8 glasses of fluid daily, preferably water.
- Talk to your doctor about all medicines, vitamins, herbs, and supplements youre taking.
- Avoid drinks with caffeine or alcohol and citrus juices, which can irritate the bladder.
- Avoid hygiene products and chlorinated pools and hot tubs that may irritate the bladder
- Avoid smoking.
Read Also: Herbal Remedy For Urinary Tract Infection