When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Nursing Care Plan For Uti 4
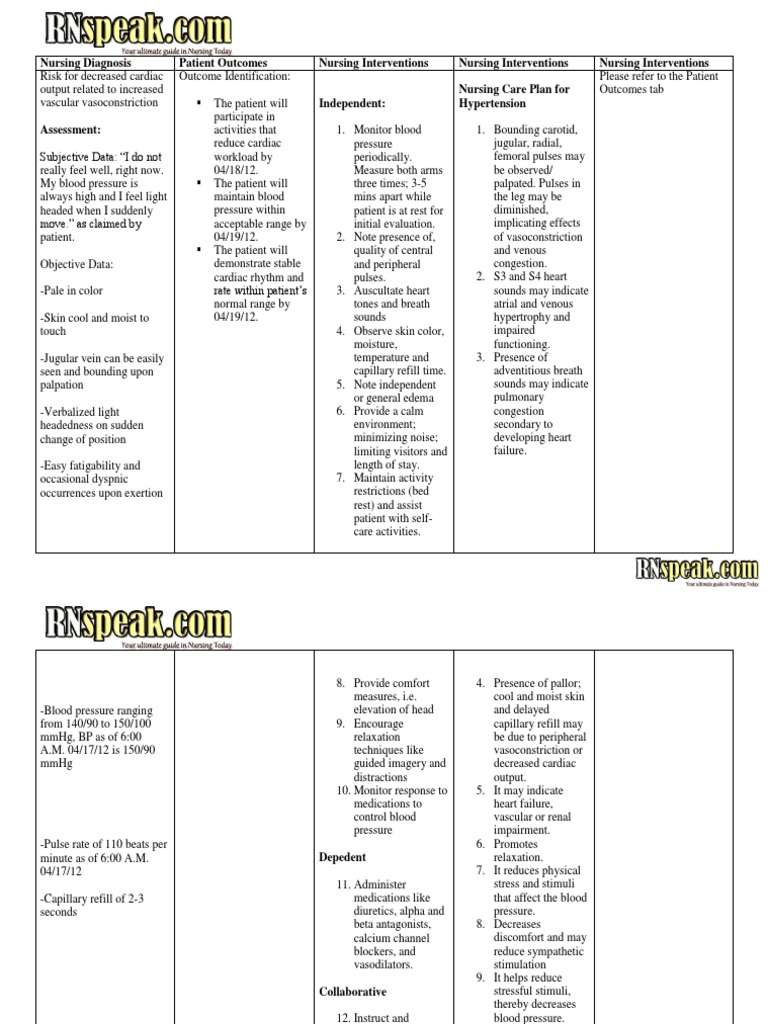
Nursing Diagnosis: Hyperthermia related to urinary tract infection as evidenced by temperature of 38.8 degrees Celsius, flushed skin, profuse sweating, and weak pulse.
Desired Outcome: Within 4 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will have a stabilized temperature within the normal range.
| Nursing Interventions for UTI | Rationales |
| Assess the patientâs vital signs at least every 4 hours. | To assist in creating an accurate diagnosis and monitor effectiveness of medical treatment, particularly the antibiotics and fever-reducing drugs administered. |
| Remove excessive clothing, blankets and linens. Adjust the room temperature. | To regulate the temperature of the environment and make it more comfortable for the patient. |
| Administer the prescribed antibiotic and anti-pyretic medications. | Use the antibiotic to treat bacterial infection, which is the underlying cause of the patientâs hyperthermia. Use the fever-reducing medication to stimulate the hypothalamus and normalize the body temperature. |
| Offer a tepid sponge bath. | To facilitate the body in cooling down and to provide comfort. |
| Encourage the patient to drink at least 2 liters of fluids per day, if not contraindicated. | To reduce the risk for dehydration related to hyperthermia episode. |
Pearls And Other Issues
Although there is no proof of prevention, women should urinate after sexual intercourse because bacteria in the bladder can increase by ten-fold after intercourse. After urination, women should wipe from front to back, not from the anal area forward, which seems to drag pathogenic organisms nearer to the urethra. Vigorous urine flow is helpful to prevention.
Don’t Miss: Nasal Spray For Urinary Incontinence
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A UTI is caused by bacteria that get inside your urinary tract. Your urinary tract includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urine is made in your kidneys, and it flows from the ureters to the bladder. Urine leaves the bladder through the urethra. A UTI is more common in your lower urinary tract, which includes your bladder and urethra.
Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Incontinence 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Urinary Incontinence related to loss of bladder control secondary to Parkinsonsâ disease as evidenced by leakage of urine, sudden urges to urinate, and increase in urine frequency
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to cope with urinary incontinence while preventing any complications such as poor hygiene, skin breakdown, or feelings of shame and embarrassment.
You May Like: How Do Urinary Tract Infections Happen
Which Priority Is Nursing Diagnosis Applicable For A Patient With Indwelling Urinary Catheter
The patient may feel pain and discomfort, which is related to the procedure of inserting a urinary catheter inside the body. Therefore, the patient may have an altered sense of wellbeing due to fear, anxiety, and emotional shock from being subjected to perform such a procedure. Other than this factor, the patients can also experience adverse effects from being given certain medications for pain as well as side effects from antibiotics which was used to treat the underlying urinary tract infection.
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
You May Like: Pain In Urinary Tract Male
Assessment And Diagnostic Findings
Results of various tests help confirm the diagnosis of UTI.
- Urine cultures. Urine cultures are useful in identifying the organism present and are the definitive diagnostic test for UTI.
- STD tests. Tests for STDs may be performed because there are UTIs transmitted sexually.
- CT scan. A CT scan may detect pyelonephritis or abscesses.
- Ultrasonography. Ultrasound is extremely sensitive for detecting obstruction, abscesses, tumors, and cysts.
Management Of Symptomatic Uti
The choice of antibiotic to treat UTI in LTC facilities should be individualized on the basis of the patients allergy history and renal clearance, local practice patterns, prevalence of resistance at the patients LTC facility, availability and cost of the antibiotic, and the threshold for noncompliance. In addition, treatment requires microbiological confirmation and should be tailored toward bacterial susceptibility empiric treatment can be based on prior urine cultures, if available. The duration of treatment of UTI in noncatheterized LTC residents has not been studied, but SHEA recommends that women with lower UTI be treated for 7 days and that women with pyelonephritis and men with any UTI be treated for 10 to 14 days. Ruling out coexistent prostatitis in older men is important because this condition requires 6 to 12 weeks of treatment. In catheter-associated UTI, the IDSA recommends urine culture and catheter removal or replacement before initiating antibiotics. The early removal of the IUC shortens the duration of febrile episodes and decreases the risk of relapse. The duration of treatment is 10 to 14 days.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection What Causes It
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract is made up of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The renal system filters waste from the bloodstream and remove it in a fluid known as urine. Immediately after leaving the kidney, this urine travels through the ureter to reach the bladder. Urine will remain in the bladder until urination occurs.
Can I Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
You can usually prevent a urinary tract infection with lifestyle changes. These tips can include:
In some post-menopausal women, a healthcare provider may suggest an estrogen-containing vaginal cream. This may reduce the risk of developing a UTI by changing the pH of the vagina. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have recurrent UTIs and have already gone through menopause.
Over-the-counter supplements are also available for UTIs. These are sometimes recommended for people who have frequent UTIs as another way to prevent them. Talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplements and ask if these could be a good choice for you.
Read Also: How Does Sickle Cell Affect The Urinary System
Pyelonephritis Nursing Care Plan 4
Deficient Knowledge
Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge related to unknown background, nature, and treatment of urinary tract infection secondary to pyelonephritis, as evidenced by multiple questions about the disease, recurrent urinary tract infection, and giving inaccurate information about the disease.
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to verbalize knowledge of pyelonephritis causes and treatments, manage the risk factors, and complete the medical treatment.
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Home Test Walgreens
Urinary Incontinence Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Urinary Incontinence NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Urinary incontinence is a common condition that involves the loss of bladder control. This leads to leaking of urine which can be frequent or occasional.
This leakage can be triggered by movement, or even when the person coughs or sneezes. More often than not, people with urinary incontinence would not have ample time to get to the toilet.
This happens because control over the urinary sphincter has either weakened or is completely lost.
Assess For Presence Of Complicating Factors
Once it has been determined that the patient has symptoms consistent with UTI, evaluation for complicating factors is essential. UTIs are considered complicated when they are associated with structural, functional or metabolic conditions that promote UTI. These patients have an increased likelihood of resistant pathogens and may be more likely to experience treatment failure.2,11 Examples of complicating factors include UTIs in males, chronic obstruction, nephrolithiasis, poorly controlled diabetes, indwelling urinary catheter, chronic renal insufficiency, pregnancy and immunosuppression .
Recommended Reading: Ams 800 Urinary Control System
Pyelonephritis Nursing Care Plan 5
Activity Intolerance
Nursing Diagnosis: Activity Intolerance related to acute lower back pain and difficulty in urination secondary to pyelonephritis, as evidenced by facial grimace, guarding behavior, limited movements, and inability to perform activities of daily living.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to perform activities of daily living.
- The patient will verbalize relief from pain or total absence of pain.
Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Incontinence 5
Recurrent cystitis
Nursing Diagnosis: Urinary Incontinence related to loss of bladder control secondary to recurrent cystitis as evidenced by leakage of urine and increase in urine frequency
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to cope with urinary incontinence while preventing any complications such as poor hygiene, skin breakdown, or feelings of shame and embarrassment.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Without Doctor
Nursing Care Plan For Uti 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Disturbed Sleep Pattern related to nocturia and acute pain due to UTI as evidenced by verbalization of inability to sleep, delayed sleep onset, bladder pain or discomfort, frequent urination, restlessness, and irritability
Desired Outcome: The patient will report an improved rest/sleep pattern and verbalize feeling well-rested.
| Nursing Interventions for UTI | Rationales |
| Assess the patientâs current pattern of sleep and rest and compare with his/her normal pattern . | To establish baseline data on rest/sleep pattern. |
| Administer the prescribed antibiotic for UTI. The antibiotic choice is based on the result of the urine culture and sensitivity test. The usual course of antibiotics for UTI runs for 7 to 10 days. Administer pain relief medication. | To treat the underlying infection. Trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and augmentin are the most commonly used antibiotics for UTI. To help alleviate bladder pain. |
| Encourage the patient to limit oral hydration during night time. Advise the patient to avoid caffeine-containing drinks in the evening. | To reduce urinary frequency during bed time. Caffeine blocks sleep-inducing chemicals produced in the brain, thereby increasing level of alertness. |
| Reduce sleep disturbance in the environment such as room temperature, noise and light. Provide comfort measures such as back rub, warm bath, and relaxation techniques. | To provide a sleep-conducive environment. |
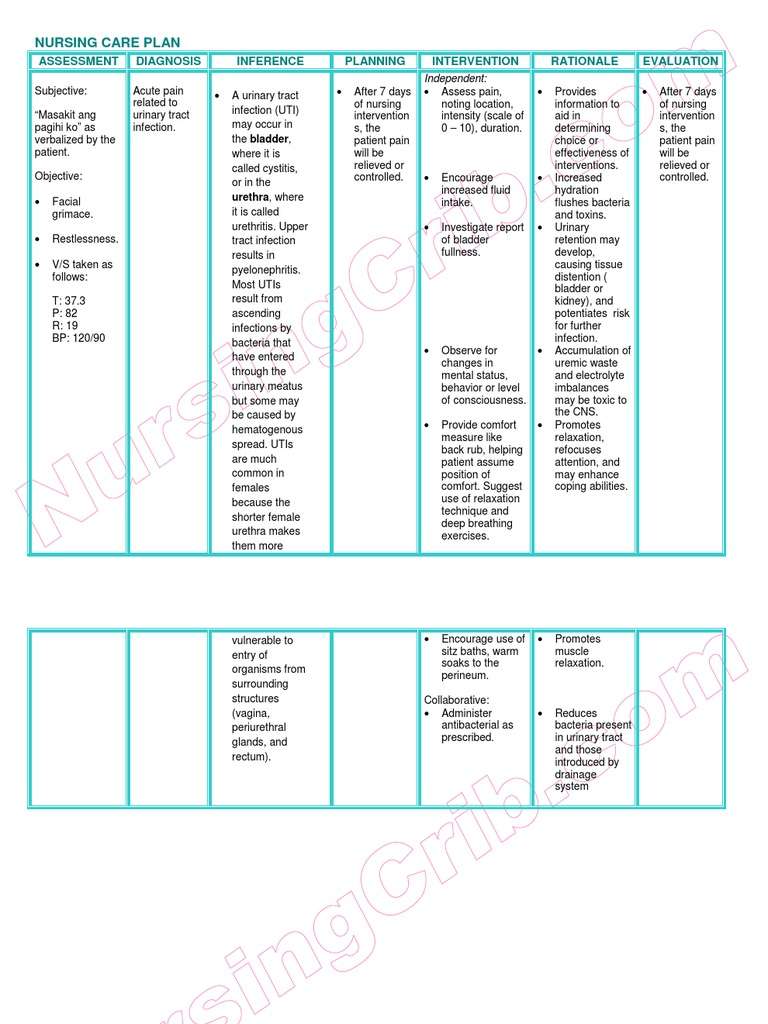
Nursing Care Plan For Uti 1
Nursing Diagnosis: Infection related to urinary retention as evidenced by presence of leukocytes and nitrates in the urine upon urinalysis, positive bacteria urine culture result, foul-smelling urine, burning sensation when passing urine, temperature of 38.9 degrees Celsius, and increased white blood cell count
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to avoid the development of an infection.
Don’t Miss: Petsmart Purina One Urinary Tract
Signs And Symptoms Of Urinary Incontinence
The symptoms of urinary incontinence may vary on a case-by-case basis. The main symptom, however, is the unintentional leakage of urine.
The general symptom of Urinary Incontinence include:
- Urine will suddenly leak while one is either coughing, laughing, sneezing, or exercising
- Sudden and uncontrollable urges to urinate
- Sleep disturbance with the urge to urinate
- High frequency in urination
- Urinating while asleep
Pyelonephritis Nursing Care Plan 1
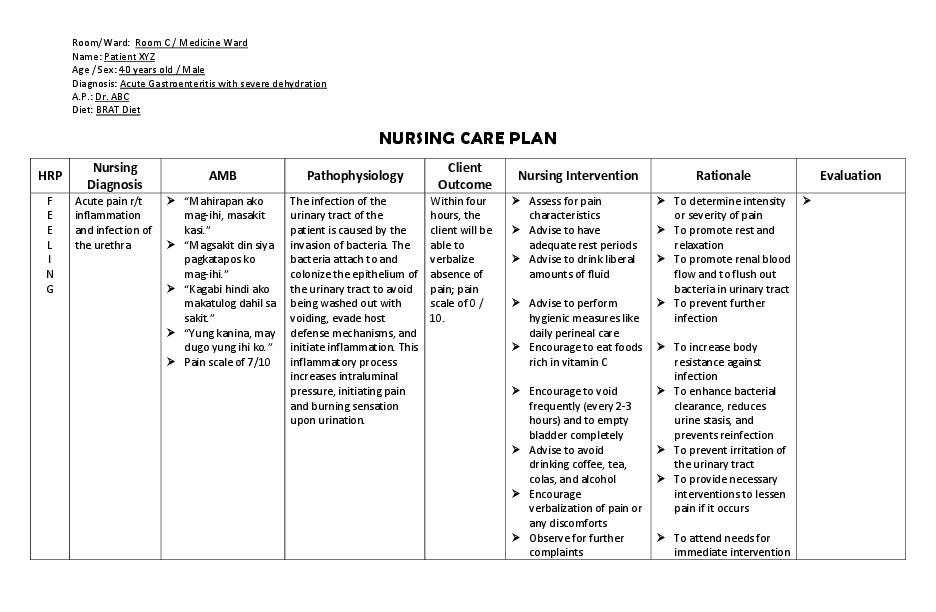
Acute Pain
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain related to the infection or inflammation of the urinary tract including the urethra, bladder, and other urinary tract structures secondary to Pyelonephritis, as evidenced by burning urination, decreased physical activity, guarding behavior, lower back and bladder area spasm.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to use pharmacological and nonpharmacological strategies to relieve pain.
- The patient will be able to report a remarkable pain control at less than 3 to 4 on a scale of 0-10 level.
- The patient will be able to report relief or total absence of pain.
Read Also: What Vitamins Are Good For Urinary Tract Infections
Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections
The treatment of urinary tract infection is dependent on the severity of the symptoms and what type of UTI has been contracted.
They are either treated with an antibiotic, or a catheter is passed to drain the infected urine from the bladder. A CT scan may also be required to diagnose the patients condition more accurately or for post-surgery purposes.
The important thing to do when treating a UTI is to make the patient relaxed. Also, the patient needs to follow instructions given by a doctor and take all the medications as prescribed.
The patient should take enough fluids to help flush out the infection and to keep hydrated. To ensure the patient does not get dehydration, the medical practitioner should assess the frequency of fluids intake and the urine output frequency .
Nursing Interventions For Risk For Infection
These nursing interventions help reduce the risk for infection, including implementing strategies to prevent infection. If the infection cannot be prevented, the goal is to prevent the spread of infection between individuals and treat the underlying infection. Use the nursing interventions below to help you create your nursing care plan for risk for infection:
1. Maintain strict asepsis for dressing changes, wound care, intravenous therapy, and catheter handling.Aseptic technique decreases the chances of transmitting or spreading pathogens to or between patients. Interrupting the chain of infection is an effective way to prevent the spread of infection.
2. Ensure that any articles used are properly disinfected or sterilized before use.This reduces or eliminates germs.
3. Wash hands or perform hand hygiene before having contact with the patient. Also, impart these duties to the patient and their significant others and know the instances when to perform hand hygiene or 5 moments for hand hygiene:1. Before touching a patient.2. Before clean or aseptic procedure .3. After body fluid exposure risk4. After touching a patient5. After touching the patients surroundings.
4. Educate clients and SO about appropriate cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing items.Knowledge of ways to reduce or eliminate germs reduces the likelihood of transmission.
SEE ALSO: Infection Control in Nursing »
Also Check: Herbal Remedy For Urinary Tract Infection
Uti Tests And Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a urinary tract infection, go to the doctor. You’ll give a urine sample to test for UTI-causing bacteria.
If you get frequent UTIs and your doctor suspects a problem in your urinary tract, they might take a closer look with an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan. They might also use a long, flexible tube called a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
Also Check: How To Improve Urinary Health
Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but they are more common in women. This is because the urethra in females is shorter and closer to the anus, where E. coli bacteria are common. Older adults also are at higher risk for developing cystitis. This increased risk may be due to incomplete emptying of the bladder. There are several medical conditions that can be related to this, including an enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse .
If you get frequent urinary tract infections, your healthcare provider may do tests to check for other health problems such as diabetes or an abnormal urinary systemthat may be contributing to your infections. People with frequent UTIs are occasionally given low-dose antibiotics for a period of time to prevent the infection from coming back. This cautious approach to treating frequent UTIs is because your body can develop a resistance to the antibiotic and you can get other types of infections, such as C. diff colitis. This practice is used very infrequently.
How To Prevent Uti Re
Following some tips can help you avoid getting another UTI:
- Empty your bladder often as soon as you feel the need to pee don’t rush, and be sure you’ve emptied your bladder completely.
- Wipe from front to back after you use the toilet.
- Drink lots of water.
- Choose showers over baths.
- Stay away from feminine hygiene sprays, scented douches, and scented bath products they’ll only increase irritation.
- Cleanse your genital area before sex.
- Pee after sex to flush out any bacteria that may have entered your urethra.
- If you use a diaphragm, unlubricated condoms, or spermicidal jelly for birth control, you may want to switch to another method. Diaphragms can increase bacteria growth, while unlubricated condoms and spermicides can irritate your urinary tract. All can make UTI symptoms more likely.
- Keep your genital area dry by wearing cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothes. Donââ¬â¢t wear tight jeans and nylon underwear they can trap moisture, creating the perfect environment for bacteria growth.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: Male Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Over The Counter