The Icd Code N390 Is Used To Code Pyuria
In medicine, pyuria /pajri/ is the condition of urine containing white blood cells or pus. Defined as the presence of 6-10 or more neutrophils per high power field of unspun, voided mid-stream urine. It can be a sign of a bacterial urinary tract infection. Pyuria may be present in the septic patient, or in an older patient with pneumonia.
What Is The Cpt Code For Urinary Tract Infection
CPT 87088, 87184, and 87186 may be used multiple times in association with or independent of 87086, as urinary tract infections may be polymicrobial. Testing for asymptomatic bacteriuria as part of a prenatal evaluation may be medically appropriate but is considered screening and, therefore, not covered by Medicare.
What Is An Acute Bladder Infection
Acute cystitis is a sudden inflammation of the urinary bladder. Most of the time, a bacterial infection causes it. This infection is commonly referred to as a urinary tract infection . Irritating hygiene products, a complication of certain diseases, or a reaction to certain drugs can also cause acute cystitis.
Read Also: Spinal Stenosis And Urinary Retention
When To Treat Uti Guidelines
This guideline is on the use of antibiotics for community-acquired UTIs affecting patients aged 18 years or older. The guideline targets asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute uncomplicated cystitis, acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis, complicated pyelonephritis related to urinary tract obstruction, and acute bacterial prostatitis.
What Does Type 1 Excludes Mean

A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means “not coded here”. A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as N39.0. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Bladder Problems In Males
Personal History Of Diseases Of Urinary System
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- History of chronic urinary tract infection
- History of febrile urinary tract infection
- History of febrile uti
- History of of recurrent uti
- History of recurrent urinary tract infection
- History of recurrent uti
- History of urinary tract infection
- History of urinary tract infection
- Z87.440 is considered exempt from POA reporting.
- 951 Other factors influencing health status
How Do You Code Recurrent Uti
- Date of Admission
- Date of indwelling urinary catheter insertion/removal if applicable
- Is patient > 65 years of age?
- Collection date and results of urine cultures including colony count
- Date and types of UTI sign/symptoms
- Collection date and results of any positive blood cultures
UTIsincluding chronic UTIscan cause the following symptoms, according to the Mayo Clinic:
- A strong, constant urge to pee
- A burning sensation when you pee
- Peeing often, in small amounts
- Pee that appears red, bright pink, or brown
- Strong-smelling pee
- Pelvic pain, especially in the center of the pelvis and around the pubic bone
Don’t Miss: Are Urinary Tract Infections Contagious
What Is The Icd 10 Code For Urinary Tract Infection
4.2/5Urinary tract infectionICD10codeICD10more on it
Codes 038.11 and 995.91 are assigned to report the systemic infection, staphylococcus aureus sepsis. Code 599.0 is reported to identify UTI as the localized infection. Code E879.
Additionally, is acute cystitis the same as UTI? Acute cystitis is a sudden inflammation of the urinary bladder. Most of the time, a bacterial infection causes it. This infection is commonly referred to as a urinary tract infection . Irritating hygiene products, a complication of certain diseases, or a reaction to certain drugs can also cause acute cystitis.
Just so, what is urinary tract?
The urinary tract is the body’s drainage system for removing urine, which is composed of wastes and extra fluid. In order for normal urination to occur, all body parts in the urinary tract need to work together in the correct order. Kidneys. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist.
What is Urosepsis?
Urosepsis is a term used to describe a type of sepsis that is caused by an infection in the urinary tract. It is a complication often caused by urinary tract infections that are not treated quickly or properly. Anyone experiencing the symptoms of urosepsis should seek emergency medical attention.
Appendix B Diagnosis And Procedure Codes Used To Identify Cutis
To identify a cUTI, patients were required to have 1 inpatient or outpatient claim with a diagnosis code in any position from Group A or 1 inpatient or outpatient claim with a diagnosis code in any position from Group B and 1 inpatient or outpatient claim with a diagnosis or procedure code in any position from Group C within 7 days of each other.
| ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code . |
|---|
Read Also: What Causes Urinary Urgency And Frequency
List Of Icd 10 Codes For Urinary Tract Infection
The ICD 10 codes for Urinary Tract Infection can be found in chapter 14 of the ICD 10 manual.
ICD 10 Code N30.00: Acute cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.01: Acute cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.10: Interstitial cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.11: Interstitial cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.20: Other chronic cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.21: Other chronic cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.30: Trigonitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.31: Trigonitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.40: Irradiation cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.41: Irradiation cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.80: Other cystitis without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.81: Other cystitis with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.90: Cystitis, unspecified without hematuria.ICD 10 Code N30.91: Cystitis, unspecified with hematuria.ICD 10 Code N34.0: Urethral abscess.ICD 10 Code N34.1: Nonspecific urethritis.ICD 10 Code N34.2: Other urethritis.ICD 10 Code N34.3: Urethral syndrome, unspecified.ICD 10 Code N39.0: Urinary tract infection, site not specified.ICD 10 Code N39.9: Disorder of urinary system, unspecific.
How To Stop A Chronic Recurring Urinary Tract Infection
They can be prevented by:
- Staying hydrated aka drinking plenty of water, ideally a gallon per day, to flush out bacteria.
- Being cautious when using a diaphragm during sex. Diaphragms can push up against the urethra, which makes it harder to fully empty the bladder during urination. …
- Avoiding spermicides, vaginal douches, and certain oral antibiotics. …
Read Also: Is Coconut Water Good For Urinary Tract Infection
How Is Uti Icd 10 Diagnosed
There are two types of UCTs that lead to UTIs urine infections and urethritis . Urinary tract infections happen when the bacteria in the urinary tract get into the urine or small amounts of urine.
If a doctor suspects that the UTI is caused by bacteria, they may use a simple urine test to diagnose the infection. A negative result is sufficient to diagnose a UTI, which is quite easy to diagnose.
If a person has a culture test, the lab technicians will take the urine and culture it to see if there are bacteria in the urine. If the test is positive, it means that the bacteria got into the urine. The test takes at least 2 days, but usually takes 8 days to be fully positive.
What Is The Most Common Bacterial Infection In Women

Urinary tract infections are one of the most common, recurrent bacterial infections in individuals, mostly women. Bacteria, such as Escherichia coli , enters the urethra and infects one or several parts of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, or kidneys. UTIs can be mild to serious and even result in death.
Also Check: How Do You Treat A Urinary Tract Infection At Home
Study Design And Population
A retrospective observational cohort study of adult patients with cUTIs in IBM MarketScan Databases between July 1, 2016, and June 30, 2020, was performed . Two IBM MarketScan Research Databases were used in the study: the MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database and the MarketScan Medicare Supplemental Database . Patients were included if they had 1 IP or OP nondiagnostic claim meeting the diagnosis for a cUTI between January 1, 2017, and June 30, 2019 , were 18 years old as of index date, had 6 months of continuous enrollment with medical and pharmacy benefits before the index date, had 12 months of CE following the index date or evidence of IP death, and had no evidence of a prior cUTI during the 6-month baseline period.
What Is Uti In Women
Urinary Tract infection is a very common infectious disease occurs commonly in aged women. As age goes up there will be structural changes happening in kidney. Muscles in the bladder, urethra and ureter become weaken. Urinary retention gets increased in the bladder and this creates an environment for bacterial growth.
You May Like: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Go Away Without Antibiotics
Personal History Of Other Infectious And Parasitic Diseases
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
Z87.440 Personal history of urinary infections
Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Diagnosis Coding For Utis
Coding for urinary tract infections in ICD-10 requires a knowledge of theICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting and the chapter-specific guidelines in Chapter 14, Diseases of the Genitourinary System .
The codes for UTIs are located in different blocks within Chapter 14 based on anatomical site.
Codes for pyelonephritis are found in block N10-N16, Renal tubulointerstitial diseases, under categories N10-N12:
- N10 Acute pyelonephritis
- N11 Chronic tubulo-interstitial nephritis
- N12 Tubulo-interstitial nephritis, not specified as acute or chronic
N10 and N12 are billable codes however, N11 requires requires a 4th digit to describe the condition in more detail, such as:
- N11.0, Nonobstructive reflux-associated chronic pyelonephritis
- N11.1, Chronic obstructive pyelonephritis
- N11.8, Other chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis
- N11.9, Chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis, unspecified
Codes for cystitis are found in block N30-N39, Other Diseases of the Urinary System, under category N30, Cystitis. N30 is further classified into these subcategories:
- N30.1, Interstitial cystitis
If the documentation does not state the site of the infection for the UTI, assign:
N39.0, Urinary tract infection, site not specified
N39.0 is listed under category N39, Other disorders of urinary system.
Notice that there is a Use additional code listed for all of the codes listed in the above categories:
Use additional code to identify infectious agent
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Have Urinary Incontinence
Candidiasis Of Other Urogenital Sites
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- 2020 – New Code20212022Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- Applicable To annotations, or
What Are The Symptoms Of An Uti
People are also reading
- Omaha company’s workers removed from plane after unruly behavior
- Lincoln Northwest will not have a senior class when it opens due to lower-than-expected enrollment
- Omaha company fires employee for behavior on plane
- Recruiting, love for Betts and ‘stand-up comedy’: Inside Scott Frost’s Omaha coaching clinic show of force
Don’t Miss: Can Smoking Weed Cause Urinary Problems
Symptoms Signs And Abnormal Clinical And Laboratory Findings Not Elsewhere Classifiednote
Diagnosis Coding For Urinary Tract Infections In Icd
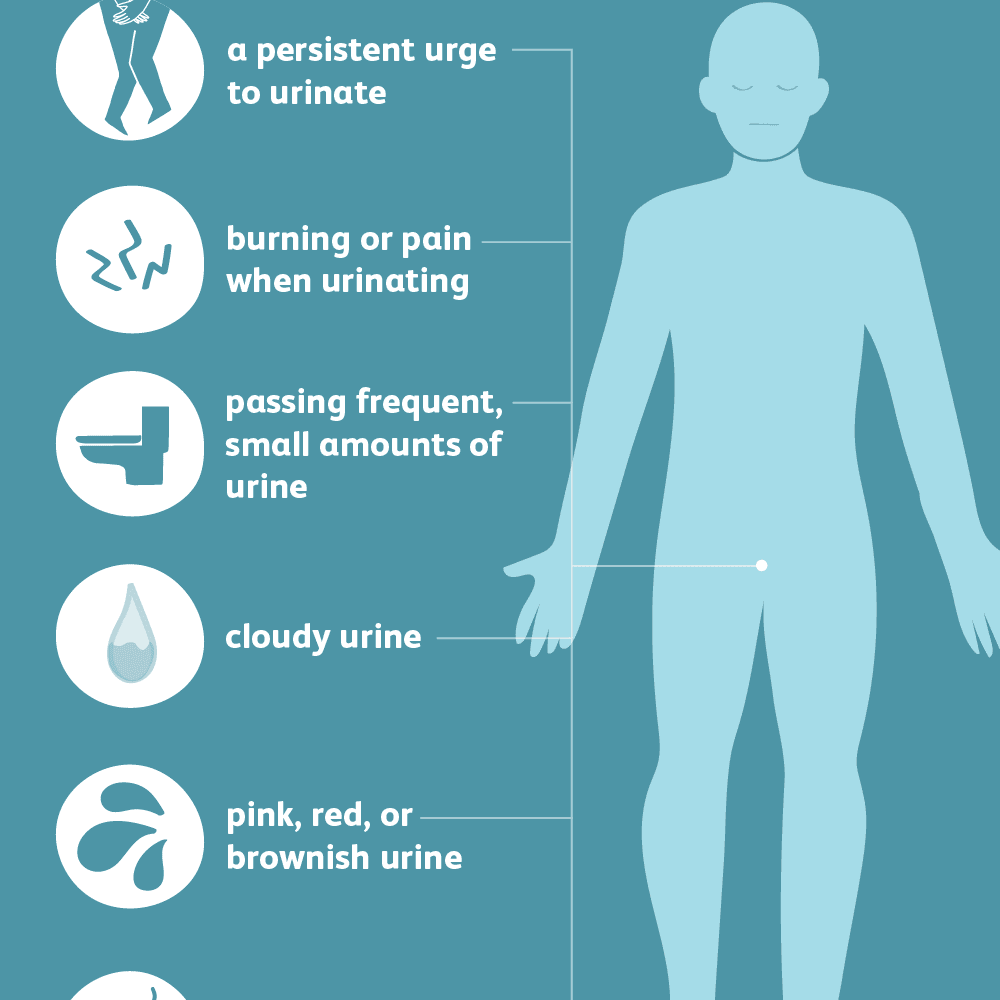
A patient sees her physician due to a burning feeling when she urinates and an increased urge to urinate. Could she have a urinary tract infection? Possibly, in which case, there are certain guidelines that a medical coder must adhere to when coding for urinary tract infections in ICD-10. You have come to the right place to find out what they are.
Quick Links to Information in this Post
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Urinary And Hydrolyzed Protein
What Is The Diagnosis Code For Uti
Diagnosis Coding for UTIs Coding for urinary tract infections in ICD-10 requires a knowledge of the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting and the chapter-specific guidelines in Chapter 14, Diseases of the Genitourinary System . The codes for UTIs are located in different blocks within Chapter 14 based on anatomical site.
Baseline Characteristics In The 6
Demographics collected during the 6-month pre-index cUTI period included age, sex, US Census Bureau geographic region, place of residence , and payer type . Baseline clinical characteristics measured during the 6-month pre-index cUTI period included the Deyo-Charlson Comorbidity Index and the following clinical conditions: bacteremia, cancer, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, infective endocarditis, pregnancy, renal failure, sepsis, systemic inflammatory response syndrome , urinary stones, and uncomplicated UTI . Collected urinary tract procedures and surgeries included cystoscopy, cystectomy, cystolithalopaxy, cystourethrogram, lithotripsy, nephrolithotomy, prostate biopsy, retrograde pyelogram, transurethral resection of the prostate, transurethral resection of the bladder, ureteroscopy, urethroplasty, and urodynamics.
Also Check: Best Pads For Male Urinary Incontinence
Cms Poa Indicator Options And Definitions
| POA Indicator Code | CMS will pay the CC/MCC DRG? | |
|---|---|---|
| Y | Diagnosis was present at time of inpatient admission. | YES |
| Diagnosis was not present at time of inpatient admission. | NO | |
| Documentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. | NO | |
| W | Clinically undetermined – unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. | YES |
| Unreported/Not used – Exempt from POA reporting. | NO |
What Is Urinary Tract Infection Icd 10
The urinary tract is the small tubes that carry urine out of the kidneys to the bladder and out of the body. The urethra is the narrow passage through which urine passes and normally they are relatively free from germs.
When an infection develops, an infection in the urinary tract, there is a slight chance of it passing into the ureters or the kidneys. This is what we call bladder infection, kidney infection or both.
The main sources of urethral infection are bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites. There are also some other infections in the urinary tract, which are asymptomatic.
Also Check: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Cause Urinary Tract Infections
Factors Influencing Health Status And Contact With Health Servicesnote
Urinary Tract Infection Site Not Specified
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- N39.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N39.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N39.0 – other international versions of ICD-10 N39.0 may differ.
“use additional code”
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Severe Urinary Tract Infection
Is Andrea A Diabetic
Andrea is a 50-year-old woman coming to emergency room for pain when urinating and burning sensation. She does feel lower back pain from 3 weeks. She never had any urinary problems earlier. She is a diabetic patient and takes insulin daily. Physical examination shows abdominal tenderness. Pelvic examination is normal. No signs of vaginitis or cervicitis found. Urinalysis is done based on the examination. After reviewing the results the case was diagnosed as UTI.
Helpful Snippets From A Coding Director
Cathie Wilde, RHIA, CCS – Director, Coding Services May 24, 2021 IR/Catheters
As coders, we often encounter common coding scenarios that seem straightforward, but we may need to be reminded of applicable guidelines and coding advice. Sometimes this requires us to seek further clarification if the documentation is not clear. With awareness of the documented circumstances and pertinent guidance, the potential implications for inaccurate coding can be avoided. Read more for an overview of various coding scenarios for which you might be looking for some extra tips.
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections
According to the National Healthcare Safety Network , urinary tract infections are the most common type of healthcare-associated infections . UTIs are not only caused by various bacterial, viral and candidal infectious agents but catheter use may also play a role as an etiologic source for the infection. The infectious organism is introduced into the urinary tract via the urinary catheterization. NHSN reports that of the UTIs acquired during hospitalization, 75% are associated with a urinary catheter.
When coding UTIs, be aware of the presence of a urinary catheter and seek physician clarification regarding its association to the patients infection. This is particularly true in conditions where urinary catheters are common such as in spinal cord injuries, spina bifida and multiple sclerosis.
Fracture Injuries Resulting from Trauma vs. Pathological
Also Check: What Are The Different Types Of Urinary Incontinence