How Are Urinary Tract Infections Treated
You will need to treat a urinary tract infection. Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria and fight an infection. Antibiotics are typically used to treat urinary tract infections. Your healthcare provider will pick a drug that best treats the particular bacteria thats causing your infection. Some commonly used antibiotics can include:
- Nitrofurantoin.
- Doxycycline.
- Quinolones .
Its very important that you follow your healthcare providers directions for taking the medicine. Dont stop taking the antibiotic because your symptoms go away and you start feeling better. If the infection is not treated completely with the full course of antibiotics, it can return.
If you have a history of frequent urinary tract infections, you may be given a prescription for antibiotics that you would take at the first onset of symptoms. Other patients may be given antibiotics to take every day, every other day, or after sexual intercourse to prevent the infection. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment option for you if you have a history of frequent UTIs.
How Is Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosed
In order to ensure a clean urine sample, a physician will likely have you clean your genital area with a special wipe beforehand, and ask that you do a midstream catch of the urine.
If a UTI is diagnosed, youll be treated with antibiotics. Its important to note that false negative results do occur and that almost all women who experience typical UTI symptoms and a negative urine culture actually do have a UTI. 30209-4/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> 11)
If youve had a prior UTI, your healthcare provider will look at prior cultures to see which bacteria were found, if any, and which antibiotics were used this often guides therapy in recurrent UTIs.
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
Read Also: How To Fight Urinary Tract Infection
Favorite Site For Urinary Health Podcasts
Podcasts arent just for politics, laughs, and murder mysteries. The American Urological Association has a fantastic one called, aptly, the Urology Care Podcast, which covers topics like sexual health myths, UTIs, prostate cancer, and more. Currently there are more than 140 episodes to listen to, ranging from about 4 minutes to 28 minutes long.
How Can I Take Care Of Myself
- Follow your healthcare provider’s treatment. Take all of the antibiotic that your healthcare provider prescribes, even when you feel better. Do not take medicine left over from previous prescriptions.
- Drink more fluids, especially water, to help flush bacteria from your system.
- If you have a fever:
- Take aspirin or acetaminophen to control the fever. Check with your healthcare provider before you give any medicine that contains aspirin or salicylates to a child or teen. This includes medicines like baby aspirin, some cold medicines, and Pepto Bismol. Children and teens who take aspirin are at risk for a serious illness called Reye’s syndrome.
- Keep a daily record of your temperature.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection After Period
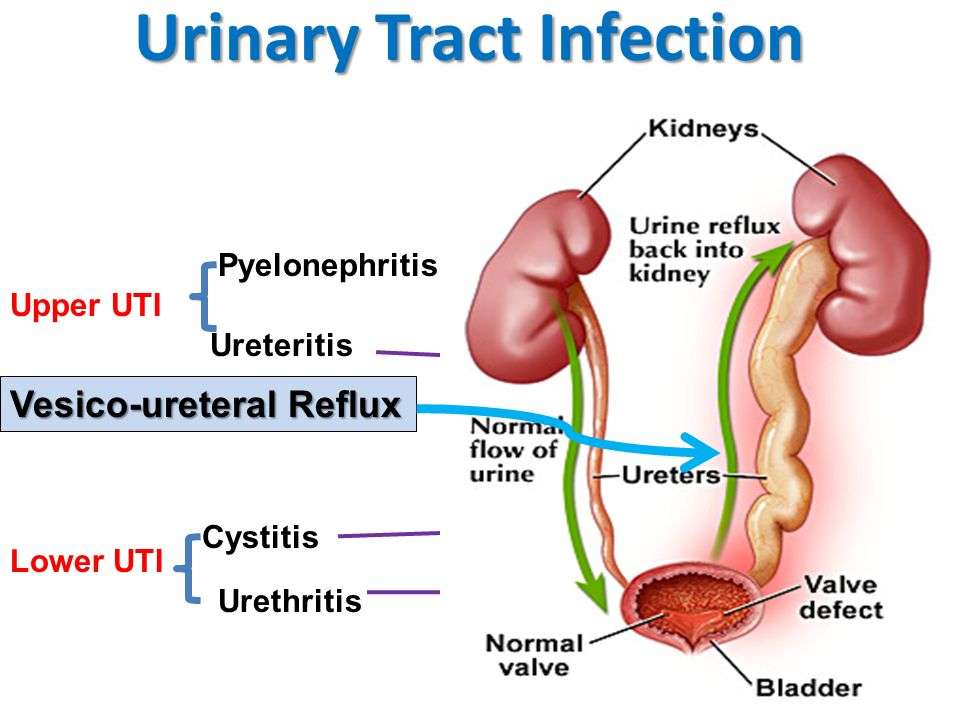
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
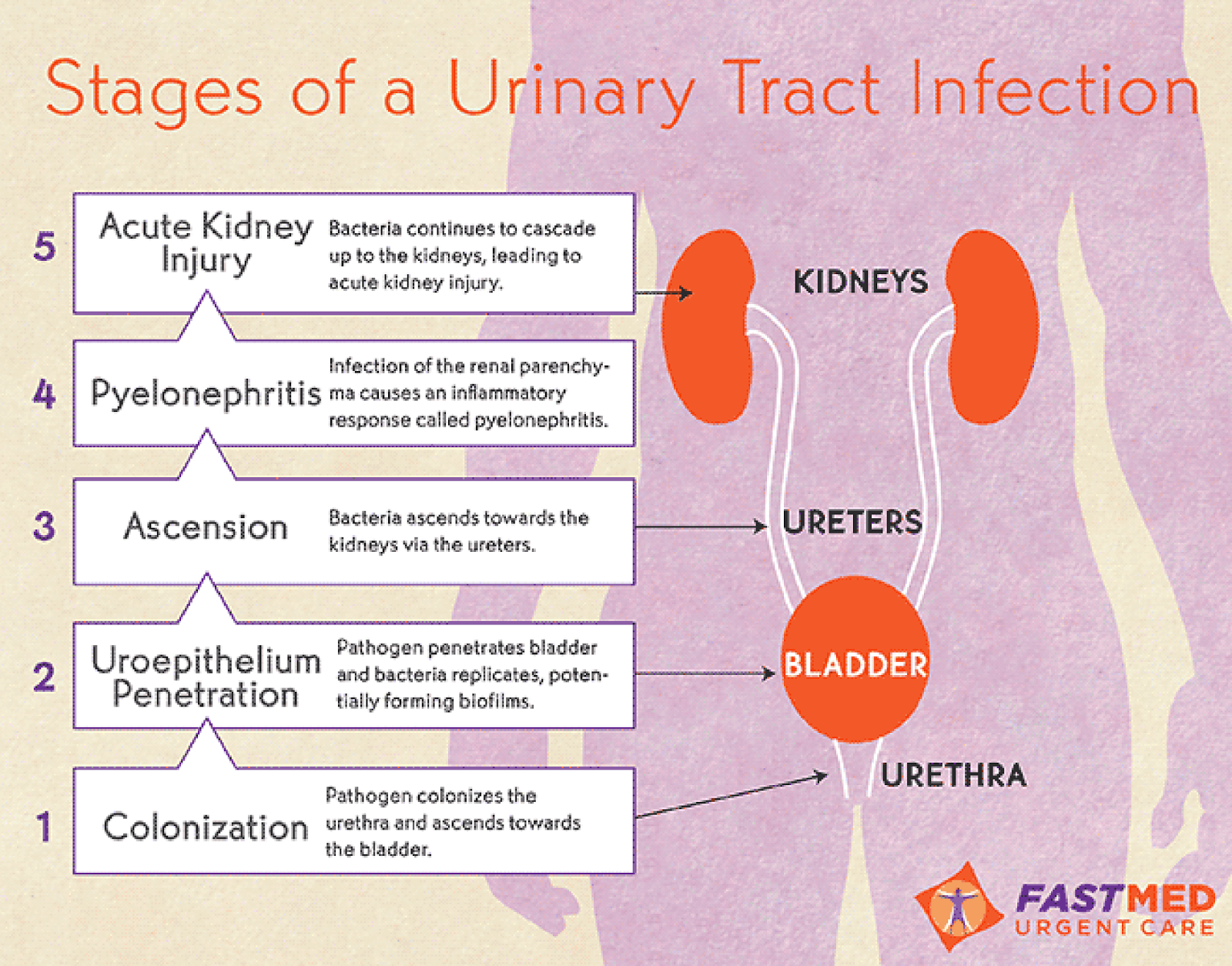
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
You Dont Pee After Sex
The threat of getting a UTI shouldnt stop you from getting it on. But that doesnt mean resigning yourself to the afterburn.
One simple way to cut your risk: Head to the potty after youve finished your romp. Youll possibly flush out the bacteria that may have made their way into your urinary tract. Urinary Tract Infection. .
Read Also: Labs For Urinary Tract Infection
You May Like: How To Treat Urinary Tract Infection In Elderly
Home Health Caregivers Recognize The Connection Between Dementia And Urinary Tract Infections
The term dementia refers to several medical conditions that reduce an individuals ability to function. Pegasus professionals are trained to meet the special needs of dementia patients. As expert caregivers, they are aware of the connection between dementia and urinary tract infections .
Dementia results from damage to the cells and nerves in the brain. Damaged cells lose the ability to communicate with other cells. The lack of nerve and cellular communication leads to memory loss and a decline in cognitive function.
Dementia patients experience impaired ability to:
- Remember new information
- Speak or interact effectively with others
- Focus or understand activity around them
- Use reason or make good judgments
- Accurately perceive what is seen
Family members will also notice behavioral changes in the dementia patient.
Dementia doesnt occur overnight in most instances. Damage occurs over time. Because its gradual, symptoms often arent noticed until the disease is in advanced stages.
Caring for a dementia patient can be exceptionally difficult for family members. The level of care needed can become exhausting.
Often, a dementia patient does better at home than in a facility. Pegasus home health care makes staying at home possible, as well as relieving the stress family caregivers feel. Home health caregivers provide a much-needed break for families.
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Toxins And Proteases
The UPEC pore-forming toxin HlyA has also received attention as a potential vaccine target and was evaluated in a mouse model of pyelonephritis to assess protection against renal damage,. Vaccination with HlyA reduced the incidence of renal scaring compared with controls however, it did not protect against UPEC colonization of the kidneys. In addition, in a mouse model of UTI, vaccination with the P. mirabilis haemolysin, HpmA, did not provide protection against bacterial colonization. However, vaccination with Pta, an alkaline protease with toxic effects towards epithelial cells, displayed promising results in a mouse model of UTI, protecting against upper UTI, although bacterial burdens in the bladder remained unaffected. Thus, although haemolysins and proteases might provide effective vaccine targets for preventing upper UTIs, additional studies are needed to determine the effectiveness of these enzymes as targets for vaccines.
Don’t Miss: Can Urinary Tract Infection Cause Urine Leakage
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Watch a video of NIDDK Director Dr. Griffin P. Rodgers explaining the importance of participating in clinical trials.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
The NIDDK would like to thank:Ariana L. Smith, M.D., FPMRS,University of Pennsylvania Health System
Common Questions & Answers
UTI symptoms can be uncomfortable or painful. They include the following:
- A strong urge to urinate
- Pain or burning during urination
- Passing small amounts of urine
- Cloudy, strong-smelling, red or pink urine
- Mucus or discharge
- Incontinence
- Fever, shaking, chills, or pain in the upper back, side, or groin
E. coli
Don’t Miss: Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And A Bladder Infection
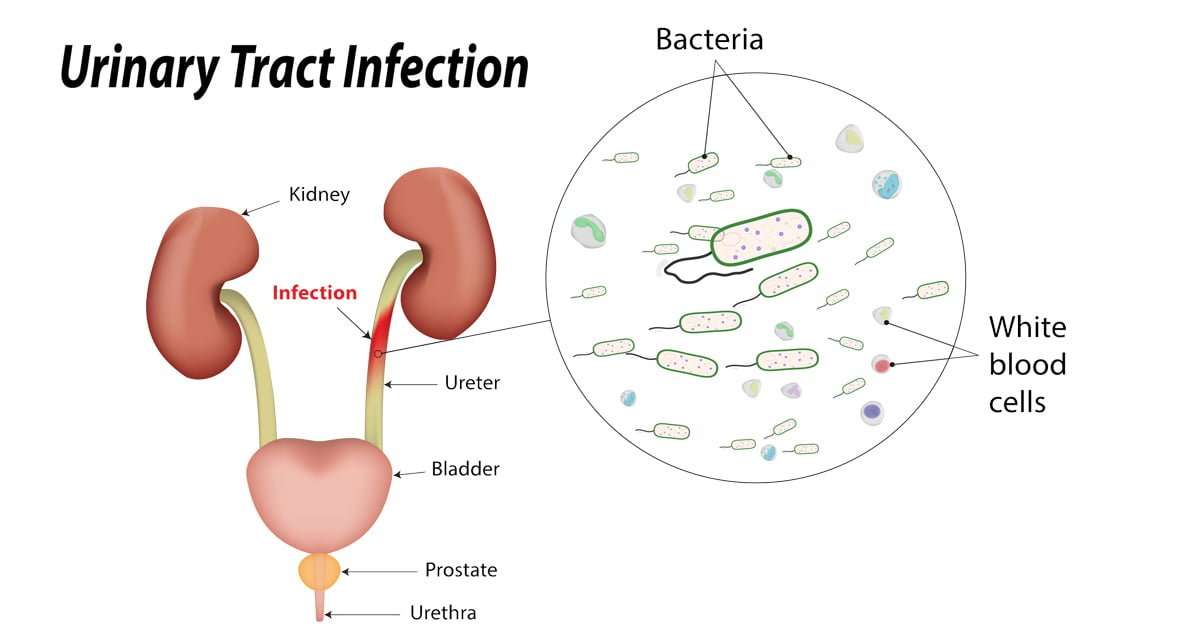
About The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract is where our bodies make and get rid of urine. It’s made up of:
- the kidneys two bean-shaped organs, about the size of your fists, that make urine out of waste materials from the blood
- the ureters tubes that run from the kidney to the bladder
- the bladder where urine is stored until we go to the toilet
- the urethra the tube from the bladder through which urine leaves the body
Elimination Of Urinary Tract Infections
Once you have a urinary tract infection, immediate relief is first and foremost on the mind of the sufferer. Too often, antibiotics are the first choice, but this is NOT a good first choice, for the following reasons:
-
Antibiotics have terrible side effects and can cause allergic reactions.
-
Antibiotics kill the good bacteria, as well as the bad, which can set you up for other infections in the future.
-
Antibiotic treatment does not successfully kill ALL the bacteria bringing on the infection, and can encourage many of them to persist.
Instead, your first choice should be a remedy you can immediately access within your home, or through a quick trip to the health food store. Two proven remedies include:
Antibiotic tonic An extremely potent antibacterial formula that can be whipped up by using a good quality juicer or blender. Simply make 2 ounces ahead of time and store in a cool, dark cupboard . Alternatively, you can make it fresh on the spot for even more power. For the recipe and directions, go here.
In addition to this, consume plenty of probiotic and antioxidant rich foods, drink plenty of purified water, and eliminate any carbohydrates , alcohol, and caffeinated beverages.
Typically, with either of these 2 methods you could feel relief in as little as 4 hours.
Read Also: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Make You Tired
Bladder Infections In Women
40 percent of women in the United States develop a urinary tract infection at some point in their life.
This is because women have shorter urethras, making the path to the bladder easier for bacteria to reach. Womens urethras are also located closer to the rectum than mens urethras. This means there is a shorter distance for bacteria to travel.
During pregnancy, changes in the urinary tract increase the risk of an infection. Changes in the immune system also increase risk during pregnancy.
Some forms of birth control, like diaphragms and spermicides, may increase your risk of urinary tract infections.
Women are also more prone to recurring infections. About of women will experience a second infection within 6 months of their first infection.
How Are Utis Treated And Prevented
A UTI is often a once-off illness that resolves quickly and responds to treatment with antibiotics if needed. However, for some people, UTIs are a recurring problem.
If you have repeated UTIs there are some self-help measures that may help prevent further infections:
- drink more fluids to help flush out bacteria
- urinate immediately after intercourse
- gently wipe from front to back after urinating
- wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting pants
- eat natural yoghurt to restore normal vaginal environment
- find an alternative method of birth control if you use spermicides
There is conflicting evidence for drinking cranberry juice to prevent UTIs. If you want to try cranberry products, ask your doctor for advice.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop A Urinary Tract Infection Without Antibiotics
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or a diaphragm or cap with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need any tests, such as urinalysis?
- What is the likely cause of my urinary tract infection ?
- Do I need medicine? How should I take it?
- What are the possible side effects of the medicine?
- When should I expect relief from my symptoms?
- What symptoms would indicate that my infection is getting worse? What should I do if I experience these symptoms?
- I get UTIs a lot. What can I do to prevent them?
- Do I need preventive antibiotics? If so, should I be concerned about antibiotic resistance?
- My child gets UTIs a lot. Could an anatomical problem be causing his or her UTIs?
Recommended Reading: Constipation And Urinary Tract Infection
About Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are common infections that can affect the bladder, the kidneys and the tubes connected to them.
Anyone can get them, but they’re particularly common in women. Some women experience them regularly .
UTIs can be painful and uncomfortable, but usually pass within a few days and can be easily treated with antibiotics.
This page is about UTIs in adults. There is a separate article about UTIs in children.
This page covers:
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
Read Also: Royal Canin Urinary Treats Feline 7.7 Oz
Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infection
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of getting a UTI:
- Drink plenty of water and other liquids to help flush out bacteria.
- Urinate frequently, or about every two to three hours.
- For women: Wipe from front to back after urinating or having a bowel movement.
- Urinate before and soon after having sexual intercourse.
- Avoid synthetic underwear, tight pants, and lingering in wet gym clothes or a bathing suit. Though none of this can cause a UTI, these habits can increase the spread of bacteria.
- Avoid vaginal deodorants, douches, powders, and other potentially irritating feminine products.
- Use a method of birth control other than a diaphragm, spermicide, or unlubricated condoms.
Living With Urinary Tract Infections
If you have 3 or more urinary tract infections each year, your doctor may want you to begin a preventive antibiotic program. A small dose of an antibiotic taken every day helps to reduce the number of infections. If sexual intercourse seems to cause infections for you, your doctor many suggest taking the antibiotic after intercourse.
Also Check: Chronic Urinary Tract Infection Causes
How Does It Occur
Normally the urinary tract does not have any bacteria or other organisms in it. Bacteria that cause UTI often spread from the rectum to the urethra and then to the bladder or kidneys. Sometimes bacteria spread from another part of the body through the bloodstream to the urinary tract. Urinary tract infection is less common in men than in women because the male urethra is long, making it difficult for bacteria to spread to the bladder.
Urinary tract infection may be caused by a sexually transmitted disease. Sometimes a stone in the urinary tract blocks the flow of urine and causes an infection. In older men, an enlarged prostate can cause a urinary tract infection by keeping urine from draining out of the bladder completely. Infection might also be caused by the use of a catheter used to drain the bladder or by urethral stricture, which is a narrowing of the urethra by scar tissue from previous infections or surgical procedures.
You may be more likely to have a UTI if you have diabetes or another medical problem that affects the immune system.
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will use the following tests to diagnose a urinary tract infection:
- Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is used to determine the type of bacteria in your urine. This is an important test because it helps determine the appropriate treatment.
If your infection does not respond to treatment or if you keep getting infections over and over again, your doctor may use the following tests to examine your urinary tract for disease or injury:
- Ultrasound: In this test, sound waves create an image of the internal organs. This test is done on top of your skin, is painless and doesnt typically need any preparation.
- Cystoscopy: This test uses a special instrument fitted with a lens and a light source to see inside the bladder from the urethra.
- CT scan: Another imaging test, a CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes cross sections of the body . This test is much more precise than typical X-rays.
Also Check: Reasons For Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections