How Are Utis Diagnosed
Only a health care provider can treat urinary tract infections. The first thing a doctor will do is confirm that a person has a UTI by taking a clean-catch urine specimen. At the doctor’s office, you’ll be asked to clean your genital area with disposable wipes and then pee into a sterile cup.
The sample may be used for a urinalysis or a urine culture . Knowing what bacteria are causing the infection can help your doctor choose the best treatment.
Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but they are more common in women. This is because the urethra in females is shorter and closer to the anus, where E. coli bacteria are common. Older adults also are at higher risk for developing cystitis. This increased risk may be due to incomplete emptying of the bladder. There are several medical conditions that can be related to this, including an enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse .
If you get frequent urinary tract infections, your healthcare provider may do tests to check for other health problems such as diabetes or an abnormal urinary systemthat may be contributing to your infections. People with frequent UTIs are occasionally given low-dose antibiotics for a period of time to prevent the infection from coming back. This cautious approach to treating frequent UTIs is because your body can develop a resistance to the antibiotic and you can get other types of infections, such as C. diff colitis. This practice is used very infrequently.
Eating Diet & Nutrition
Experts dont think eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in preventing or treating bladder infections. If you have any type of UTI, talk with a health care professional about how much to drink each day to help prevent or relieve your infection.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and other components of the National Institutes of Health conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
Also Check: How To Use Tea Tree Oil For Urinary Tract Infection
How Can This Be Treated
Antibiotics are used to treat urinary tract infections. The sort of antibiotic to use and how long it should be used depends on the bacteria that caused the infection as well as the severity of the infection.
Because an untreated UTI might resurface or spread, it’s critical to ensure that the drugs given have completely cured the infection. So, after a few days of medication, your doctor may ask you to repeat the urine tests to be sure the infection has gone away.
You should encourage your child to drink plenty of water in addition to the antibiotics given by the doctor. Pain might also be relieved with a warm pack or medication.
Why Do Women Get Urinary Tract Infections More Often Than Men
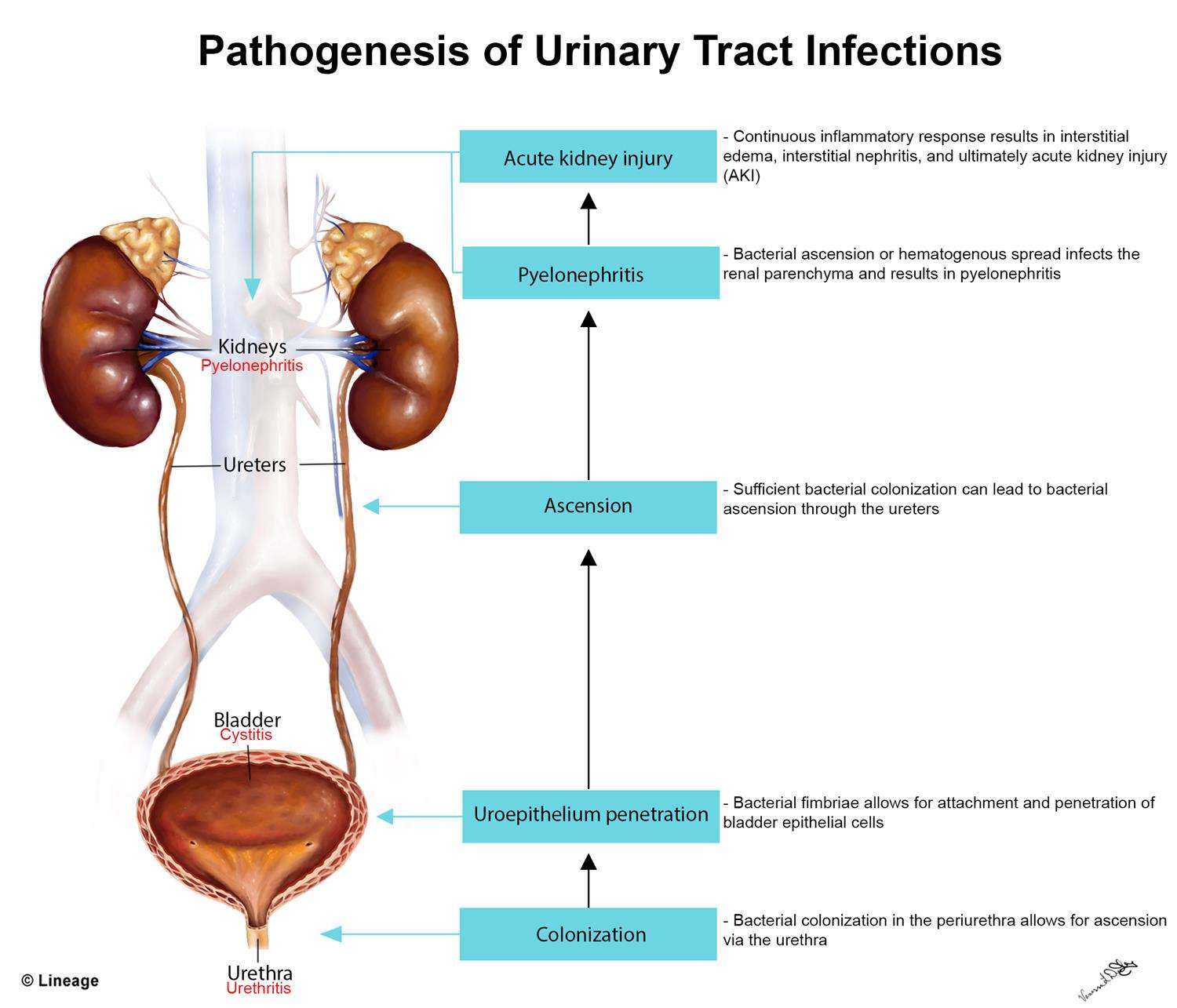
Women tend to get urinary tract infections more often than men because bacteria can reach the bladder more easily in women. The urethra is shorter in women than in men, so bacteria have a shorter distance to travel.
The urethra is located near the rectum in women. Bacteria from the rectum can easily travel up the urethra and cause infections. Bacteria from the rectum is more likely to get into the urethra if you wipe from back to front after a bowel movement. Be sure to teach children how to wipe correctly.
Having sex may also cause urinary tract infections in women because bacteria can be pushed into the urethra. Using a diaphragm can lead to infections because diaphragms push against the urethra and make it harder to completely empty your bladder. The urine that stays in the bladder is more likely to grow bacteria and cause infections.
Frequent urinary tract infections may be caused by changes in the bacteria in the vagina. Antibacterial vaginal douches, spermicides, and certain oral antibiotics may cause changes in vaginal bacteria. Avoid using these items, if possible. Menopause can also cause changes in vaginal bacteria that increase your risk for urinary tract infection. Taking estrogen usually corrects this problem but may not be for everyone.
Also Check: Antibiotics For Urinary Tract Infection Men
Pregnancy And Urinary Tract Infections
Pregnant women with a UTI that develops into a kidney infection are at higher risk of developing additional complications, which may affect both them and the fetus. Such complications include anemia, premature labor, low birth weight and, in very rare cases, stillbirth.
Fortunately, early medical intervention means that urinary tract infections in pregnant women can usually be treated successfully. If the affected person has a lower urinary tract infection, a course of oral antibiotics is the most common treatment method. If an upper urinary tract infection is suspected, the doctor may recommend administering antibiotics intravenously in hospital instead.
Once the infection has cleared, a doctor may choose to prescribe low-level, prophylactic antibiotics for the remainder of the pregnancy to reduce the risk of a UTI returning.
Pregnancy can increase the likelihood of developing a UTI. This is due to numerous factors, including hormonal changes and the increased weight of the uterus putting pressure on the bladder.
I Might Have A Uti What Should I Do Now
If you are experiencing the symptoms of a urinary tract infection, it is important to receive prompt medical care, said Dr. Shalev. These infections do not go away on their own, and homeopathic remedies rarely are enough. You will need proper medical treatment to ensure the infection doesnt travel up the system to reach the kidneys and become a full-blown kidney infection. Go to your nearest ER or come to Advance ER for fast, top quality care.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection In Men
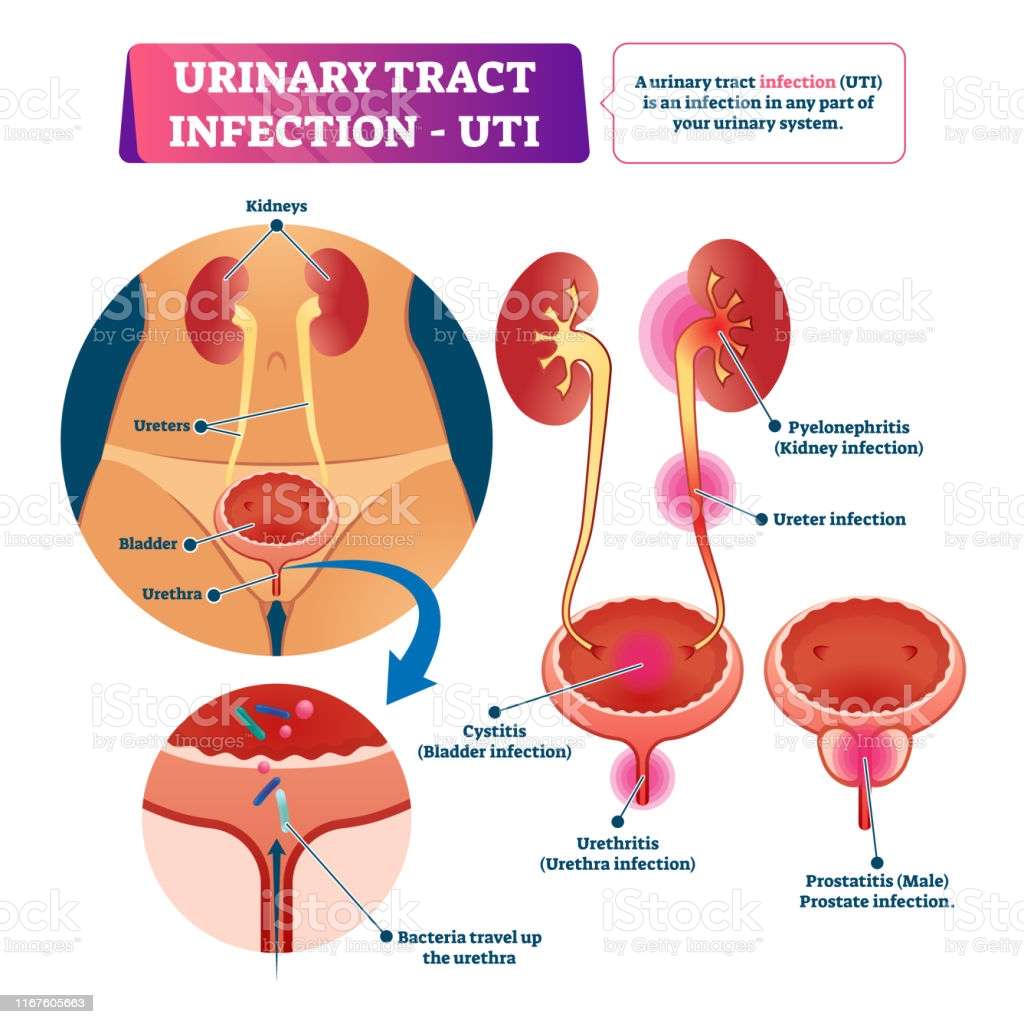
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection in any part of your urinary system, which includes your kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra.
If you’re a woman, your chance of getting a urinary tract infection is high. Some experts rank your lifetime risk of getting one as high as 1 in 2, with many women having repeat infections, sometimes for years. About 1 in 10 men will get a UTI in their lifetime.
Here’s how to handle UTIs and how to make it less likely you’ll get one in the first place.
About Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are common infections that can affect the bladder, the kidneys and the tubes connected to them.
Anyone can get them, but they’re particularly common in women. Some women experience them regularly .
UTIs can be painful and uncomfortable, but usually pass within a few days and can be easily treated with antibiotics.
This page is about UTIs in adults. There is a separate article about UTIs in children.
This page covers:
Recommended Reading: Can Peyronies Cause Urinary Problems
How Do Utis Affect Pregnancy
Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy raise your risk for UTIs. UTIs during pregnancy are more likely to spread to the kidneys.
If you’re pregnant and have symptoms of a UTI, see your doctor or nurse right away. Your doctor will give you an antibiotic that is safe to take during pregnancy.
If left untreated, UTIs could lead to kidney infections and problems during pregnancy, including:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
Heres Whats Up With Utis
The foreboding term UTI is often used to talk about bladder infections, but its actually an umbrella term for an infection that can occur in any part of the urinary tract, which includes your kidneys, ureters , urethra, and bladder.
Clearing waste via your pee is a primary function of the urinary tract. This would ideally also flush out any lurking pathogens and help keep infections at bay. But sometimes potentially harmful bacteria are still able to reproduce in the urinary tract and cause infections. This often happens when the messiness of sex transports gastrointestinal bacteria like E. coli from the anus and its surrounding skin to your urethra, hence the well-worn advice to pee after sex. STIs like herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma can also infect and irritate the urethra, the Mayo Clinic explains .
All of this might make it sound like UTIs should be classified as sexually transmitted infections, but theyre not. You dont need to be sexually active to get a UTI, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention explains. Other risk factors include previous UTIs, hormone changes from pregnancy, and changes to your vaginal microbiome from menopause. You can also raise your risk of getting a UTI by not wiping front to back, since wiping back to front can give G.I. bacteria a free ride to your urethra.
Those are the tell-tale signs of a UTI, Dr. Dweck says. The tell-tale signs of a yeast infection are very different.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection And Bv
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Treated
You will need to treat a urinary tract infection. Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria and fight an infection. Antibiotics are typically used to treat urinary tract infections. Your healthcare provider will pick a drug that best treats the particular bacteria thats causing your infection. Some commonly used antibiotics can include:
- Nitrofurantoin.
- Doxycycline.
- Quinolones .
Its very important that you follow your healthcare providers directions for taking the medicine. Dont stop taking the antibiotic because your symptoms go away and you start feeling better. If the infection is not treated completely with the full course of antibiotics, it can return.
If you have a history of frequent urinary tract infections, you may be given a prescription for antibiotics that you would take at the first onset of symptoms. Other patients may be given antibiotics to take every day, every other day, or after sexual intercourse to prevent the infection. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment option for you if you have a history of frequent UTIs.
Is It Possible To Have A Uti Without Any Symptoms
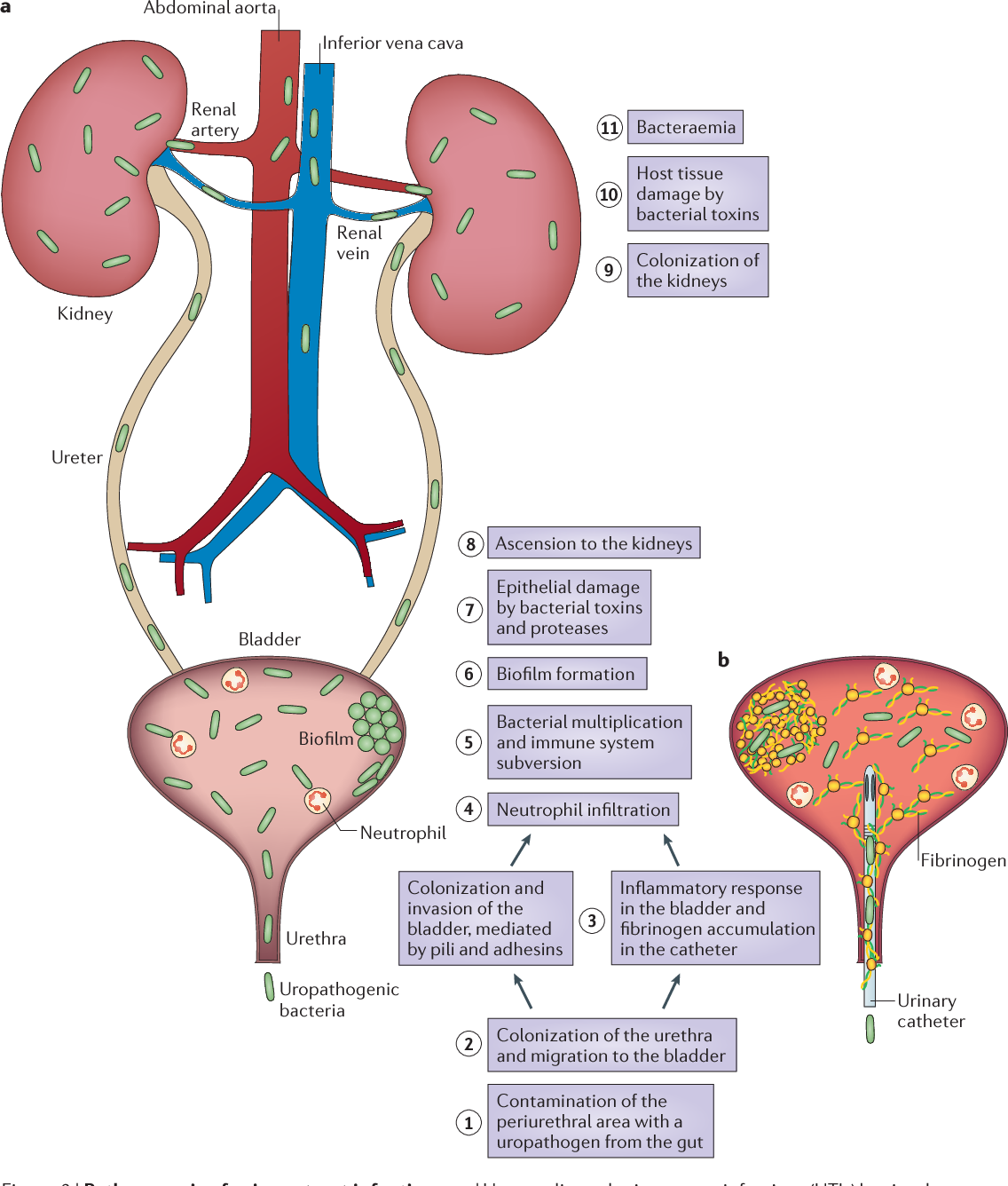
Yes. Symptoms of a UTI can vary, and it’s not entirely uncommon for someone to experience no symptoms of a urinary tract infection. Its estimated that 1 to 5 percent of younger women experience asymptomatic bacteriuria , which is a UTI without the classic symptoms. While its unclear why the bacteria involved with urinary tract infections sometimes don’t cause symptoms for these people, we do know that instances of symptom-free UTIs increase with age. Up to 16 percent of women older than 65 have been found to have ASB, and that number grows to almost 20 percent for women over 80. Other factors that increase your chances of an asymptomatic UTI are:
- Urinary catheter use
Read Also: Men’s Urinary Health Supplements
Did You Know That Kids Can Also Develop Urinary Tract Infections If Your Child Is Suffering From The Infection Here’s What You Need To Know
Written by Editorial Team | Updated : February 4, 2022 11:18 AM IST
When germs enter the urine and travel up to the bladder, this is known as a urinary tract infection or UTI. It’s an infection that can damage the bladder, kidneys, and urethra, among other parts of the urinary tract. Kidney injury is more common in young children than in older children or adults as a result of UTI. In the first few years of life, UTIs afflict up to 8 out of every 100 girls and 2 out of every 100 boys. UTI causes kidney injury more frequently in young children than in older children or adults.
Urinary tract infections are among the irritating disorders that can bring your child pain and suffering. They are quite frequent in youngsters, particularly girls, but the symptoms of this infection might be difficult to detect at times. It’s critical to have your child treated since a urinary tract infection might progress to a more serious kidney infection. Cystitis is an infection of the lower urinary tract , which is more prevalent.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti
One of the most common symptoms of a UTI is a frequent and urgent need to pee. You might feel like you need to pee all the time, even if you just went. Other UTI symptoms include:
-
pain or burning when you pee
-
bad-smelling or cloudy urine
-
blood or pus in your urine
-
soreness, pressure, or cramps in your lower belly, back, or sides
If the infection goes to your kidneys, your UTI symptoms may also include:
-
pain in your mid-back
-
fever
Read Also: Symptoms Of Pinworms In Urinary Tract
When Should I Worry
An unchecked UTI can turn into a very serious kidney infection. In can also become a blood infection if you do not treat it right away, or turn into a life-threatening problem. A UTI may happen anywhere along the urinary tract, though some parts are more problematic than others. For example, the urethra is easier to deal with than the opposite end your kidneys.
The best time to worry and do something about it? The second you realize you have a UTI. If treated properly and early on, a UTI is barely a problem and is more of an annoyance, as it may itch or burn. Unchecked, however, it can lead to serious consequences.
Preventing Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are most often caused by bacteria spreading from the anal or genital region and entering the urinary tract. Because of this, there are a number of preventative methods that can minimize the risk of experiencing a UTI:
- Regular urination
- Emptying the bladder after sexual intercourse
- Drinking lots of water, ideally at least 1.5 liters a day. Avoid alcohol and caffeine, which can irritate the bladder
- Wiping from front to back after using the toilet to avoid spreading bacteria from the anal region
- Maintaining good personal hygiene and keeping the genital area clean and dry
- Taking showers instead of baths
Also Check: How To Control Urinary Incontinence
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or diaphragms with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Increased Frequency Of Urination
Urinary tract infection is one of the most common causes of frequent urination.
Frequent urination is defined as the need to urinate more than usual. This symptom is often confused with urinary urgency. It is an inconvenient symptom that can greatly disrupt daily life for a person with UTI.
The byproducts of the infection will create inflammation and irritation in the linings of the urethra and bladder. As a result, the irritation of the bladder wall creates the urge to empty the bladder frequently.
Furthermore, the bladder also often feels full. During each trip to the bathroom, the amount of urine is often less than the usual amount.
The bladder also sends confusing signals to the brain. The body would feel the need to pee even when the bladder might not be full.
Typically, the bladder can often hold as much as 600 ml of urine . The urge to urinate is usually felt when the bladder contains about 150 ml of urine .
Most people urinate between 4 to 8 times, depending on fluid intake, over a 24-hour period.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Otc Antibiotics
Can I Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
You can usually prevent a urinary tract infection with lifestyle changes. These tips can include:
In some post-menopausal women, a healthcare provider may suggest an estrogen-containing vaginal cream. This may reduce the risk of developing a UTI by changing the pH of the vagina. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have recurrent UTIs and have already gone through menopause.
Over-the-counter supplements are also available for UTIs. These are sometimes recommended for people who have frequent UTIs as another way to prevent them. Talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplements and ask if these could be a good choice for you.
How To Prevent Uti Re
Following some tips can help you avoid getting another UTI:
- Empty your bladder often as soon as you feel the need to pee don’t rush, and be sure you’ve emptied your bladder completely.
- Wipe from front to back after you use the toilet.
- Drink lots of water.
- Choose showers over baths.
- Stay away from feminine hygiene sprays, scented douches, and scented bath products they’ll only increase irritation.
- Cleanse your genital area before sex.
- Pee after sex to flush out any bacteria that may have entered your urethra.
- If you use a diaphragm, unlubricated condoms, or spermicidal jelly for birth control, you may want to switch to another method. Diaphragms can increase bacteria growth, while unlubricated condoms and spermicides can irritate your urinary tract. All can make UTI symptoms more likely.
- Keep your genital area dry by wearing cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothes. Donââ¬â¢t wear tight jeans and nylon underwear they can trap moisture, creating the perfect environment for bacteria growth.
Show Sources
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection In Babies
How Are Utis Treated And Prevented
A UTI is often a once-off illness that resolves quickly and responds to treatment with antibiotics if needed. However, for some people, UTIs are a recurring problem.
If you have repeated UTIs there are some self-help measures that may help prevent further infections:
- drink more fluids to help flush out bacteria
- urinate immediately after intercourse
- gently wipe from front to back after urinating
- wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting pants
- eat natural yoghurt to restore normal vaginal environment
- find an alternative method of birth control if you use spermicides
There is conflicting evidence for drinking cranberry juice to prevent UTIs. If you want to try cranberry products, ask your doctor for advice.