Urinary Tract Infection Signs And Symptoms
What is a urinary tract infection?
A urinary tract infection occurs when there are bacteria in your bladder or kidneys that may disrupt your daily life.
What causes urinary tract infections?
Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria getting into your bladder and growing out of control. People who use catheters to help them urinate are at high risk for getting UTIs. The catheter provides a direct path for bacteria to enter your bladder. Often, bacteria live in your bladder without any problems this is called colonization. Sometimes, the bacteria increases and they may cause a urinary tract infection.
What are the signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection?
- Increased spasms
- Mild low back pain or other aches
- Feeling tired
- Urinary leakage or having to catheterize more often
- Nausea
- Blood or sediment in the urine
- Cloudy urine or a foul odor to the urine
- Cloudy, foul-smelling urine may be due to changes in diet and fluid intake. With no other symptoms, this is not a reason to take antibiotics for a UTI.
How do I prevent a urinary tract infection?
The best way to prevent a UTI is to drink lots of fluids. You should drink at least 64 oz of fluids a day, especially water. It is best to avoid beverages with sugar, caffeine and alcohol. These drinks may increase bladder irritation and contribute to UTIs.
I think I have a UTI, when should I call my healthcare provider?
If I have a UTI, what will my healthcare provider do?
Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but they are more common in women. This is because the urethra in females is shorter and closer to the anus, where E. coli bacteria are common. Older adults also are at higher risk for developing cystitis. This increased risk may be due to incomplete emptying of the bladder. There are several medical conditions that can be related to this, including an enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse .
If you get frequent urinary tract infections, your healthcare provider may do tests to check for other health problems such as diabetes or an abnormal urinary systemthat may be contributing to your infections. People with frequent UTIs are occasionally given low-dose antibiotics for a period of time to prevent the infection from coming back. This cautious approach to treating frequent UTIs is because your body can develop a resistance to the antibiotic and you can get other types of infections, such as C. diff colitis. This practice is used very infrequently.
Urgent Advice: Ask For An Urgent Gp Appointment Or Get Help From Nhs 111 If:
You think you, your child or someone you care for may have a urinary tract infection and:
- a very high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
- are confused, drowsy or have difficulty speaking
- have not been for a pee all day
- have pain in the lower tummy or in the back, just under the ribs
- can see blood in their pee
These symptoms could mean you have a kidney infection, which can be serious if it’s not treated as it could cause .
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
Don’t Miss: Enlarged Prostate And Urinary Incontinence
Why Do I Have So Much Cystitis In My Sixties
One of the main ones is a weakened pelvic floor preventing the bladder from emptying completely. Being less mobile is another key cause due to fewer trips to the bathroom, and diabetes which becomes more common with age is also linked to higher infection rates. The main cause is probably a weakened immune system.
Tips To Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
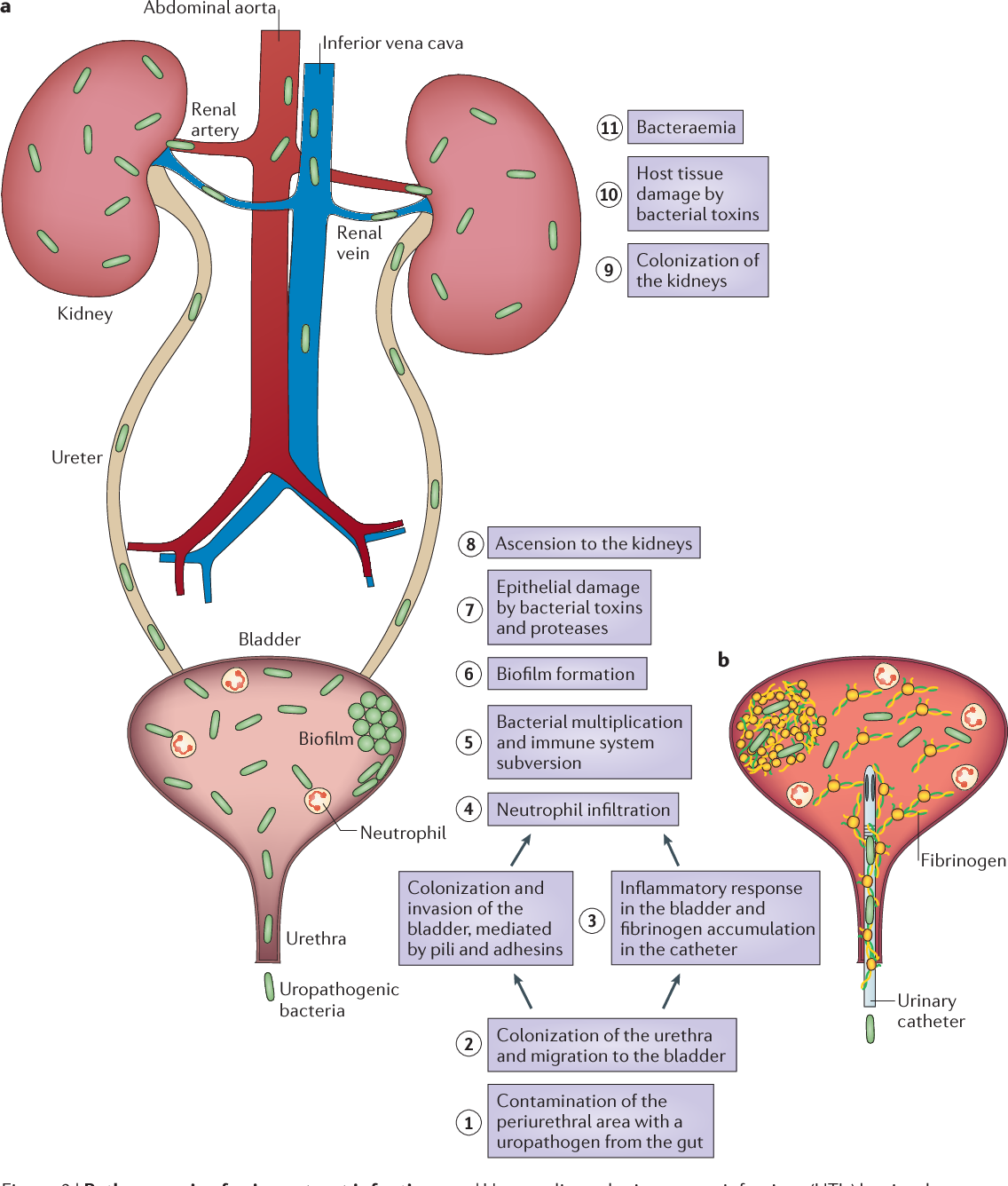
A urinary tract infection, also called a UTI, is an infection that occurs in the urinary system. This could include the urethra, bladder, ureters and kidneys. Most infections involve the bladder and urethra, known as the lower urinary tract.
The most common symptoms include painful urination, tenderness above the bladder area, urgency and frequency of urination. Cloudy and a strong odor are not signs of infection.
Women are at greater risk for a UTI because the urethra is shorter than in men, so it’s easier for bacteria to travel to the bladder. UTIs also are more common in postmenopausal women because low estrogen levels change vaginal and urethral tissue to increase the risk of infection.
It’s always better to prevent an infection rather than simply treat it. UTIs are no different.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection And Incontinence
Gender And Behavior As Factors Influencing The Pathophysiology Of Uti
Among the factors that have impact on UTI, gender and behavior are probably among the most significant. Thus, women are more exposed to UTI, sexually active, pregnant, or treated with antibiotics women in particular. Bacteria causing UTI are moving into the urinary tract from the bowel, vaginal cavity, and periurethral area . Women have a shorted distance between vaginal cavity and anal and the urethral opening. Thus, bacteria reach the bladder quicker. Cystitis is frequent among women due to the shorter urethra which increases the probability of bacterial contamination. Lower UTI affects about half of women at some time in their life .
Peoples behavior or lifestyles also have a significant influence on the development of UTI. Thus, poor hygiene stimulates pathological processes and increases the risk of bacterial contamination. Active sexual life is also a factor that increases the probability of developing a UTI because it assists the movement of bacteria into the urethra thus causing infection.
Youve Got A Cold The Flu Or Allergies
You may be tempted to curse your seasonal sneezes, a cold, or the dreaded flu for making your life even more miserable with a UTI, but these ailments arent the cause. The meds you take to manage symptoms could be.
Though theyre the bomb at keeping your runny or stuffy nose in check, antihistamines and decongestants might make you go less by causing urinary retention. And see No. 6 that may lead to a UTI.
Also Check: Does Dehydration Cause Urinary Tract Infections
What Is The Best Home Remedy For Cystitis
7 home remedies for cystitis
What causes a woman to have recurrent cystitis?
It is usually caused by a urinary tract infection. Some women have repeated episodes of cystitis. Doctors define a recurrent infection as three separate proven infections in one year or two in six months. In many cases, there is no apparent reason for a woman to have frequent attacks of cystitis. There are a number of treatment options to consider.
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections In Older Women
The main cause of UTIs, at any age, is usually bacterial. Escherichia coli is the main cause, but other organisms can also cause a UTI. In older people who use catheters or live in a nursing home or other full-time care facility, bacteria such as enterococci and staphylococci are more common causes.
You May Like: Best Yogurt For Urinary Tract Infection
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection is an infection of the urinary system. This type of infection can involve your urethra , kidneys or bladder, .
Your urine typically doesnt contain bacteria . Urine is a byproduct of our filtration systemthe kidneys. When waste products and excess water is removed from your blood by the kidneys, urine is created. Normally, urine moves through your urinary system without any contamination. However, bacteria can get into the urinary system from outside of the body, causing problems like infection and inflammation. This is a urinary tract infection .
Also Check: Can High Blood Pressure Cause Urinary Problems
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically respond very well to treatment. A UTI can be uncomfortable before you start treatment, but once your healthcare provider identifies the type of bacteria and prescribes the right antibiotic medication, your symptoms should improve quickly. Its important to keep taking your medication for the entire amount of time your healthcare provider prescribed. If you have frequent UTIs or if your symptoms arent improving, your provider may test to see if its an antibiotic-resistant infection. These are more complicated infections to treat and may require intravenous antibiotics or alternative treatments.
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
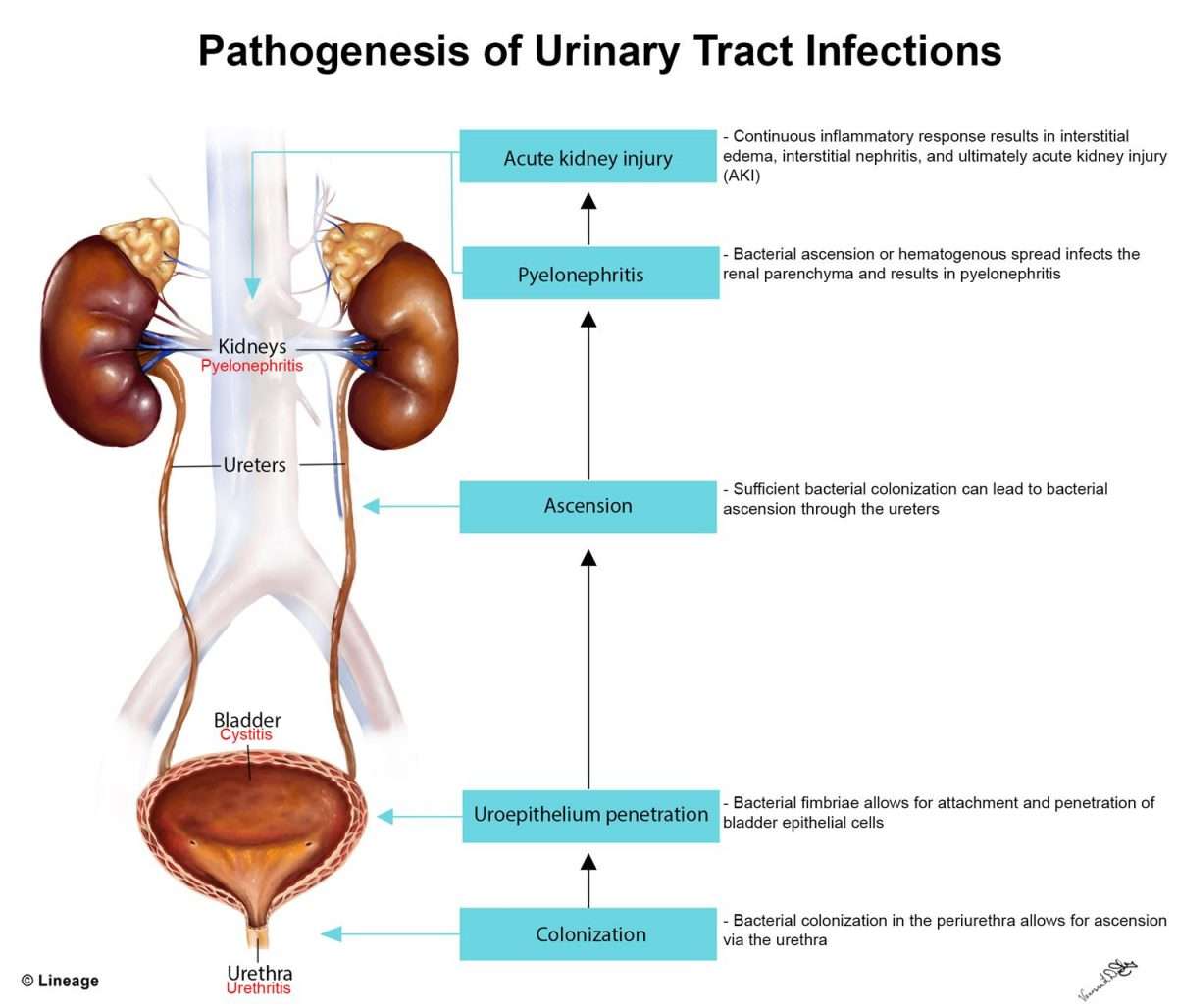
Symptoms of a urinary tract infection may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy, dark or has a strong smell
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
You May Like: Can Stress Cause Urinary Tract Infection
How Is Cystitis Treated In The Elderly
Nitrofurantoin should only be considered for the treatment of cystitis in the elderly. Nitrofurantoin may have pulmonary toxicity. Patients receiving this drug with new pulmonary symptoms should be promptly evaluated. For more resistant bacterial isolates, fosfomycin may be effective for the elderly.
Why do I suddenly have cystitis?
Acute cystitis is a sudden inflammation of the bladder. Most of the time, a bacterial infection is the cause. This infection is commonly called a urinary tract infection . Irritating hygiene products, a complication of certain illnesses, or a reaction to certain medications can also cause acute cystitis.
Please enable JavaScript
Complicated Cystitis: Antibiotic Selection And Duration
Prescribe longer courses of antibiotics for male patients with cystitis and for patients who have complicating factors, including: uncontrolled diabetes, pregnancy, nephrolithiasis, catheter use, anatomic or functional abnormalities, or immunosuppression. As a general rule, 7 days of oral antibiotics are recommended for complicated cystitis.
Follow-up. Follow up urinalysis and urine cultures are not indicated for patients with uncomplicated cystitis. Approximately 5-10% of women treated for uncomplicated cystitis will have persistent bacteriuria after therapy completion. The vast majority of these women will be symptomatic and return for medical attention. Those who are asymptomatic require no treatment except in pregnant patients, or patients undergoing urologic procedures.
Telephone triage-nurse managed evaluation. Most UTIs in women are uncomplicated and resolve readily with a short course of antibiotics. Therefore, many women can be assessed and safely managed without an office visit or laboratory evaluation. Studies have found that use of a telephone triage guideline decreased cost and increased appropriate antibiotic use with no increase in adverse outcomes.,
Don’t Miss: Over The Counter Urinary Tract Infection Remedy
Risk Factors For Urinary Tract Infections
And now a brief note about reproductive parts: Although people with penises do get UTIs, people with vaginas are more at risk. It all boils down to the anatomy, Minkin says.
Bacteria that cause UTIs often make their way from the back door to the front and then up the urethra to wreak havoc on the urinary system.
Because the male reproductive system has a longer urethra than the female reproductive system, the bacteria have farther to travel, which makes it more difficult for a UTI to develop.
But regardless of anatomy, once youve had one UTI, youre more likely to get another, especially if you have a vagina. Hickling DR, et al. . Management of recurrent urinary tract infections in healthy adult women.
You Wipe From Back To Front
Wiping from back to front can transport E. coli, the bacteria thats behind most UTIs, from the rectal region to the urethra. Moral of the story: Always wipe from front to back. Al-Badr A, et al. . Recurrent urinary tract infections management in women: A review.
Read Also: How To Read Walgreens Urinary Tract Infection Test Strips
Complicating Factors And Medical Conditions
The most severe complication of UTI is urosepsis, with a mortality rate of 20-40%. The underlying infection usually is a complicated UTI involving a urogenital organ, typically prostate or kidney. Obstructive pyelonephritis due to urolithiasis is the most common cause of urosepsis, but about 17% of cases are associated with urological procedures. The elderly, diabetics, and immunosuppressed are at highest risk. Management of urosepsis is beyond the scope of this guideline, but rapid diagnosis and prompt intensive care are essential.
Patients with complicating factors and medical conditions are at increased risk of developing pyelonephritis or infection with resistant organisms. Complicating factors are listed in . It is necessary to differentiate these patients from those with uncomplicated UTI in terms both of evaluation and treatment. Unlike patients with uncomplicated UTI, care for those with complicating factors may include:
- Culture. Obtain pretreatment urine culture and sensitivity.
- Treatment. Initiate longer antibiotic treatment course.
- Possible structural evaluation. If there is concern for concurrent urolithiasis or urinary tract structural or functional abnormality, consider CT with and without IV contrast and urology consultation for cystoscopy.
You Dont Pee After Sex
The threat of getting a UTI shouldnt stop you from getting it on. But that doesnt mean resigning yourself to the afterburn.
One simple way to cut your risk: Head to the potty after youve finished your romp. Youll possibly flush out the bacteria that may have made their way into your urinary tract. Urinary Tract Infection. .
You May Like: Do Urinary Tract Infection Go Away On Their Own
Other Ways To Prevent Some Utis Coming Back
If you keep getting a bladder infection , there is some evidence it may be helpful to take:
- D-mannose a sugar you can buy as a powder or tablets to take every day
- cranberry products available as juice, tablets or capsules to take every day
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
If you’re taking warfarin, you should avoid cranberry products.
Page last reviewed: 22 March 2022 Next review due: 22 March 2025
Host Response To Pathogenic Adherence
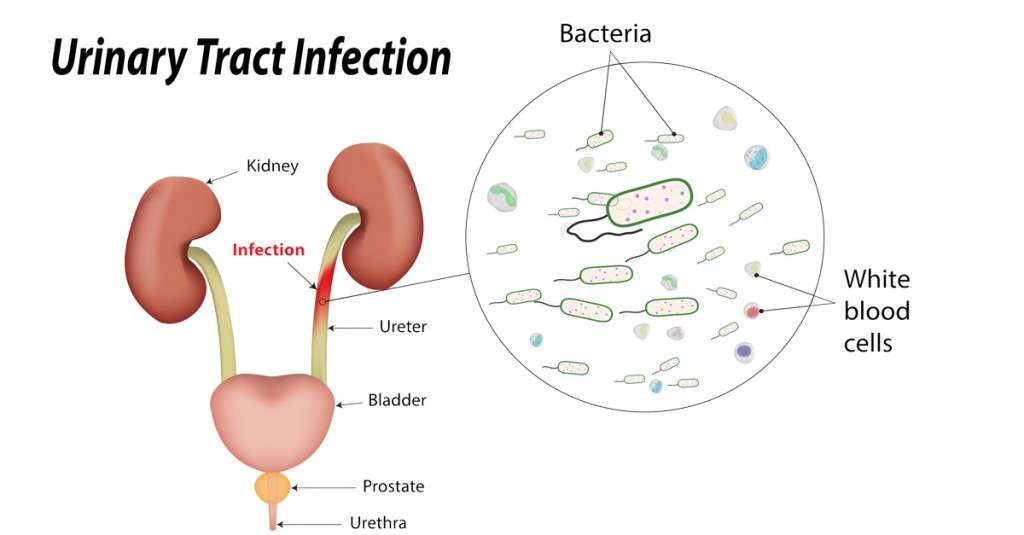
A series of defence pathways are activated by the host after the uropathogen adheres to the mucosal surface. Epithelial cells exfoliate within hours of the initial infection and infected urothelial cells are shed during this process . Secretion and excretion of the infected urothelial cells is mediated by type 1 piliated bacteriae that induce cell apoptosis . In healthy patients the epithelium lining the surface of the bladder is quiescent as the umbrella cell layer is renewed every few months. However these normally repressed proliferation and differentiation cascades are rapidly activated after the infective process in the murine cystitis model. These proliferation cascades have the potential to induce effective regeneration of an umbrella cell layer within 24 hours of the exfoliation process Another study in mice has demonstrated that exfoliation of urothelial cells prevents uropathogenic E. coli from forming clusters . Notably, mice that elicited a mild exfoliation process in response to the uropathogen were more likely to form biofilms that migrated into deeper layers.
Figure 8.
Don’t Miss: Purina One Urinary Tract Reviews
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
UTIs are best managed in an interprofessional fashion, and besides physicians, most nurses will encounter a patient with a UTI. The key to preventing recurrences is patient education. Once a UTI has been diagnosed, the patient should be encouraged to drink more fluids. Sexually active women should try to void right after sexual intercourse as this can help flush the bacteria out of the bladder. Some women with recurrent UTIs may benefit from the prophylactic use of antibiotics. Several other non-medical remedies may help some women with UTIs. Anecdotal reports indicate that using cranberry juice and probiotics may help reduce the severity and frequency of UTIs in some women. Primary clinicians should refer patients with recurrent UTIs to the urologist to rule out reflux and anatomical defects.
Outcomes
The majority of women with a UTI have an excellent outcome. Following treatment with an antibiotic, the duration of symptoms is 2 to 4 days. Unfortunately, nearly 30% of women will have a recurrence of the infection. Morbidity is usually seen in older debilitated patients or those with renal calculi. Other factors linked to recurrence include the presence of diabetes, underlying malignancy, chemotherapy, and chronic catheterization of the bladder. The mortality after a UTI is close to zero.
Risk Factors For Recurrent Utis Include:
- Frequent sexual intercourse, which increases the likelihood of bacteria entering the urethra and bladder.
- Using spermicide with or without a diaphragm, as this can harm protective bacteria in the urinary tract that defend against infection.
- Urinary retention or incomplete bladder emptying caused by medications narrowing of the urethra prolapse of the bladder, uterus or vagina neurological conditions or sometimes unknown reasons.
- Vaginal atrophy, which is a postmenopausal condition caused by decreased estrogen levels.
- Genetics, especially the inherited genes that regulate the body’s immune response to infections.
It’s common for some people to have bacteria in their urine but not experience any symptoms. In these cases, no treatment is necessary.
Talk with your health care team if you think you have a UTI. You may need an appointment to discuss your symptoms and collect a urine sample.
You should seek medical attention if you develop a fever, chills, disorientation, or back or side pain. These could be signs of a kidney infection, which requires treatment, or a systemic infection of the bloodstream that requires hospitalization.
Read Also: Complete Natural Products Urinary Tract Complete