Spina Bifida And Incontinence
Originally published on: April 6th, 2017. Last modified on June 29th, 2021
Spina Bifida occurs when the spinal cord and vertebrae fail to develop properly in the womb. This fault leaves a gap or a split in the spine. Spina Bifida affects the central nervous system.
Spina Bifida can be identified by a sac or cyst located on the back covered by a fine layer of skin.
There are several types of Spina Bifida including Spina Bifida Cystica, which is split into two main conditions
- Myelomeningocele this is the most common and most serious form of spina bifida. The cyst will contain tissue, cerebro-spinal fluid, nerves and part of the spinal cord. The spinal cord is usually damaged or not fully developed. There is usually some form of paralysis or loss of sensation below the damaged area
- Meningocele the cyst will usually contain tissue and cerebro-spinal fluid only. There may be some development issues with the spine but impairment will be less than those with myelomeningocele
Spina Bifida Occulta is a very mild form of spina bifida and account from around 5 10% of those affected by the condition. Usually people with this form of spina bifida show no symptoms or have very few problems.
Encephalocele is a sac that forms when the bones of the skull fail to develop fully. The sac may contain only cerebro-spinal fluid or part of the brain which will lead to brain damage.
Perception Of Incontinence As A Problem
More than two-thirds of the patients with urinary incontinence in our study and more than three-quarters of those with faecal incontinence perceived their incontinence as a problem. Few studies have reported patients perceptions of incontinence. Krogh et al found that 66% of the patients suffering from faecal incontinence reported that faecal incontinence had some or even a major influence on their social activities or quality of life. Lie et al showed that 77% of the patients with urinary incontinence and 75% of the patients with faecal incontinence regarded this as a moderate or severe stress factor. These results are in reasonable agreement with ours.
Urological Care Of Children With Spina Bifida
The urologic care of children with spina bifida has changed in recent years. In the past, children with spina bifida often got urinary tract infections that caused serious kidney disease. Fortunately, this is no longer the case. We now try to prevent kidney disease. We also have made great progress in helping children with spina bifida become dry.
Recommended Reading: Causes Of Urinary Urgency In Males
What Is A Neurogenic Bowel And Bladder
Children with Spina Bifida higher on the spine might have paralyzed legs and use wheelchairs. The damaged nerves cause varying degrees of paralysis and decreased sensation.
The connections between the brain, spinal cord, bladder, and bowel do not correctly send messages. Therefore, sensation and voluntary emptying of bowel and bladder are not always possible. This is called a neurogenic or neuropathic bladder or bowel.
Urinary and bowel control in children and adolescents are important for short and long-term health, and also in the development of independence. Therefore, bowel and bladder continence is a central focus for children with SB.
A neurogenic bladder either does not empty completely, causing urine to back up into the kidneys or it leaks continuously .
Children with neurogenic bladder may have frequent urinary tract infections.
Refractory Cases To Medical Management

The objective of neurogenic bladder management secondary to myelomeningocele is focused on three main objectives: 1) Decrease the risk of renal damage 2) Preserve urinary continence and 3) Prevent urinary infection episodes. When these objectives are not reached with medical management, it is necessary to take more drastic decisions, otherwise, further problems regarding renal function may be encountered and quality of life may be affected. Such procedures include:
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Puppy Treatment
To Tip For Preventing Accidents During Exercise
Empty the bowels prior to the exercise, using your childs usual methods, either the night before, or the morning of, special events like school cross country or sports carnival. Then, immediately before the event, encourage the child to sit on the toilet and push, rock, cough or laugh to empty any remnants. It might still be wise to use back-up, such as a pull-up, during the event.
What Tests Will Be Done To Assess Your Child’s Urinary Tract
Ongoing assessment and monitoring of the urinary tract system will be an important part of your child’s care. This may include any of the following tests:
- Urinalysis and urine culture: To check for infection.
- Blood tests including creatinine and BUN : To check how well the kidneys are working.
- Renal/bladder ultrasound: This is a test done in the X-ray Department that checks the size and shape of the kidneys and bladder, as well as checking for other abnormalities.
- VCUG : This is a test done in the X-ray department to check for reflux, which is when the urine flows backwards from bladder to the kidneys. It also shows the shape of the bladder and urethra, and how well the bladder empties.
- Urodynamic tests: This is a special study that shows how the bladder works, including:
- How much urine the bladder will hold
- At what pressures the bladder fills, stores and empties urine
- How well the bladder empties
- How well the bladder and sphincter muscle work together
- If reflux is present, information from this test helps to show which children may be at risk for developing problems. It is also helpful in keeping track of how the child’s bladder is responding to treatment.
You May Like: Cll And Urinary Tract Infections
How Does Spina Bifida Affect The Bowel
Almost all people with spina bifida have some form of bowel incontinence. However, the degree and type of incontinence varies from person to person. As with most of the conditions associated with spina bifida, bowel problems are a result of damaged nerve pathways, therefore the child may be described as having a neurogenic bowel. The nerves that control and provide sensory feedback from the bowel exit the spinal cord at the sacrum . Nerve damage generally affects:
- The speed that faecal matter moves through the bowel
- The mechanism that alerts the child that the rectum is full
- The two sphincter muscles
- The muscles that assist the bowel in expelling faeces.
Motility
Nerve damage
Nerve damage may affect the childs ability to realise when the rectum is full in two ways. The first is a limited sensation of what is happening in the bowel and the second is a decreased ability to alert the brain to empty the rectum. Therefore, when the rectum is full the child doesnt recognise the need to go, and accidents result because the child remains involved in the present activity rather than finding a toilet.
Sphincter control
Muscle control
Without implementation of a good management plan, having neurogenic bowel can lead to a series of problems such as constipation, impaction , or rectal prolapse .
Prevalence Of Incontinence And Perceiving Incontinence As A Problem
According to the definition used in the present study , 109 of the 179 patients suffered from urinary incontinence. Of these 109 incontinent patients, 76 perceived their incontinence as a problem . The prevalence of faecal incontinence was 34.1% . Of these 61 persons, 47 perceived their faecal incontinence as a problem . A total of 47 patients were both urinary and faecal incontinent, and 56 patients were not incontinent at all.
Table 1 Frequency of incontinence for urine and faeces related to the perception of incontinence as a problem by young adults with spina bifida
We also tested the predictive values of all the above-mentioned variables for the perception of urinary incontinence as a problem. The frequency of incontinence was also added in this model. Continence, hydrocephalus and level of lesion were found to be significant predictors. Patients who were incontinent for urine were 18.9 times more likely to perceive incontinence as a problem. Patients without hydrocephalus were 3.3 times more likely to perceive incontinence as a problem than those with hydrocephalus. Patients with a level of lesion of L5 and above were 3.5 times more likely to perceive their urinary incontinence as a problem than those with a level of lesion of S1 and below.
Also Check: How To Deal With Urinary Tract Infection
Will The Child Be Compliant
It is very important to ask your child if he or she wants to participate in the swimming program, and whether he or she agrees with the bowel management strategy to be used for this activity. This is particularly important for those children who may have to use temporary strategies to remain accident free in the pool.
Preparation at home simply involves the everyday routine done for an accident free day at school, such as an enema, bowel washout, or timed toileting with medications.
How Does Spina Bifida Affect The Kidneys And Bladder
Most infants with spina bifida are born with kidneys that work well, although this can change. Most children with spina bifida have what is called a neurogenic bladder. In a neurogenic bladder, the nerves going from the spinal cord to the brain do not work properly. The child may not be aware that the bladder is full and often cannot empty the bladder well. Also, the sphincter muscle may not work. It may either stay relaxed or not relax when the bladder is contracting. If the bladder doesn’t empty well, it can cause damage to the kidneys and/or lead to urinary tract infections. Only about 5 percent of children with spina bifida are able to empty their bladders without help.
Don’t Miss: Dribblestop Male Urinary Incontinence Clamp
Types Of Spina Bifida
There are four types of Spina Bifida. Each type varies in seriousness and treatment. It is important to note that you should always consult with a physician if any related symptoms are suspected.
- Occult Spinal Dysraphism this variation is often detected by a dimple in the babys lower back. Other signals include red marks, hyperpigmentation on the back, tufts of hair, or small lumps.
- Spina Bifida Occulta often called hidden Spina Bifida, this variation often goes undetected with no visible signs. It usually requires an x-ray of the back to discover a case of this type of the condition. In some people, pain and neurological symptoms can occur, and further treatment would be necessary. Generally, SBO will not need to be treated.
- Meningocele a meningocele causes a portion of the spinal cord to come through the spine. In these cases, nerve fluid remains in the sac and there is hardly ever nerve damage as a result.
- Myelomeningocele, Spina Bifida Cystica this is the most serious form of the condition and usually causes nerve damage and disabilities. Portions of the spinal cord and nerves come through the open part of the spine, often resulting in pain and pressure from the lack of drainage of fluids.
Urinary Tract Infections When To Treat
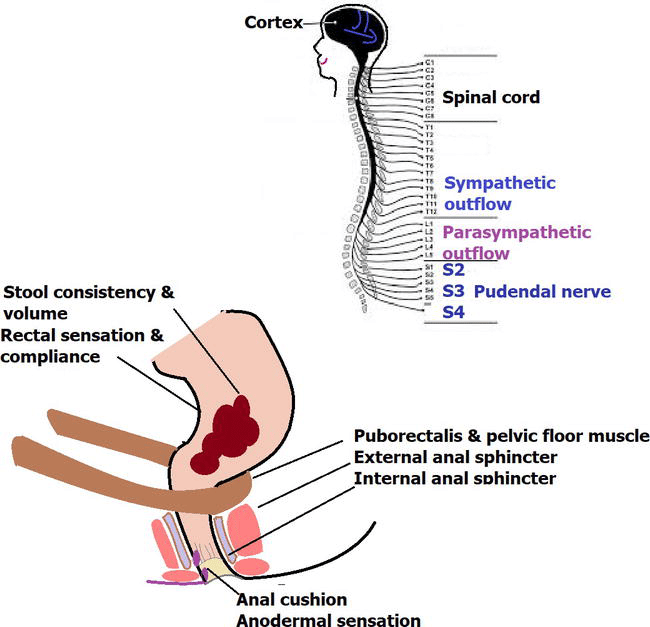
Patients with neurogenic bladder due to spinal dysraphism have several factors that potentially increase the risk of urinary tract infections, such as, vesico-ureteral reflux , hypertonic bladder and foreign bodies inside the bladder. Schlager et al. observed that 70% of patients that perform intermittent bladder catheterizations present asymptomatic bacteriuria 24 weeks after the beginning of treatment.
In patients with neurogenic bladder, including those secondary to myelomeningocele, urinary tract infections should be considered differently from those without any neurofunctional disease. The presence of bacteriuria within this group of patients is very common and unnecessary antibiotic treatment could be given if there is no acknowledgment of these facts. This could lead to future complications that develop due to antibiotic resistance and antibiotic side effects.
In patients performing intermittent bladder catheterizations, urine culture results with more than 10,000 CFU/ml are considered a clinical infection only when one or more of the following clinical features are present: foul smell, cloudy urine, fever of 38°C or more and abdominal or flank pain. Positive urine culture without other clinical features is considered as bacterial colonization and requires no antibiotic treatment.
Read Also: Urinary Infection Blood In Urine
How Does The Bowel System Work
The main parts of the bowel are:
Small intestine
A long narrow tube in which many secretions from different organs of the body, such as the liver and pancreas, are sent to break down the products moving through it. Nutrients are absorbed and the remaining undigested materials are transported to the large intestine by a series of waves of muscular contractions that squeeze the contents along, called peristalsis. Backflow of materials from the large intestine is prohibited by a muscular flap much like urine is prohibited from going back up to the kidneys from the bladder.
How Is My Childs Bowel Functioning
In order to assess bowel function, the following medical investigations are used by G.P.s, Paediatricians and Specialists:
- Physical Examination: Doctors often palpate the abdomen to feel for the presence of faecal impaction.
- Bowel Diary: You and your child may be asked to keep a record of the childs bowel movements for a week or two.
- X-ray of the abdomen: The X-ray picture can show the faeces in the bowel. If a buildup of faeces is detected the doctor or nurse will make a plan to clear the blockage. If the build-up is allowed to continue, a megacolon may develop, which involves the bowel becoming over-stretched and the bowel walls thinning.
Also Check: How To Flush Urinary Tract
If Reconstructive Continent Bladder Surgery Was Undertaken Would You Do It Again
Guidelines
Bladder And Bowel Retraining
Bladder management programs are recommended for people with Spina Bifida. This can help bladder control become better overtime. Bowel retraining and bladder retraining means establishing your bladder or bowel into a regular routine, retraining your brain to hold on rather than going whenever you feel urge to go. Retraining is a gradual process, which involves increasing the length of time until the you feel more confident with your control. Bladder and bowel retraining also involves regulating the times that you visit the toilet, until progression is made.
Don’t Miss: What Is Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
Focus On Your Diet And Lifestyle
It is important to eat a healthy, balanced diet with plenty of fibre and consume enough fluid to regulate the bowel. You should also ensure you keep stools at the right consistency to avoid constipation. Keeping a healthy diet includes reducing the consumption of caffeine and fizzy drinks as these are common bladder irritants. Many people often like to keep a bladder/bowel diary to test which foods or drinks affect function.
What Is The Urinary Tract System
The urinary tract system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder, the sphincter muscle, which controls the flow of urine and the urethra, which brings the urine from the bladder to the outside world.
The kidneys filter the blood and make urine. Urine goes from the kidneys to the bladder through tubes called the ureters. Where the ureters and the bladder join, there are one-way valves that stop the urine from going backwards into the kidneys. The bladder holds the urine, and then releases it through the urethra every few hours. Normally, as urine fills the bladder, it stretches to hold more and more urine at a low bladder pressure. When the bladder becomes full, a message is sent to the brain. Signals from the brain then tell the sphincter muscle to relax, and the bladder muscle to contract at the same time, so the bladder can empty. Normally, a person can wait until it is the right time to empty the bladder.
Don’t Miss: What To Do When Urinary Tract Infection
Other Aspects Of Bladder And Bowel Management
Use of napkins
Two-thirds of our population used napkins, which is in agreement with the findings of other studies., , , No relationship was found between the use of napkins and the perception of incontinence as a problem. Apparently, the possible social embarrassment of having accidents of urine or faecal soiling does not outweigh the discomfort of wearing a napkin.
Assistance with daily toileting
Several studies have reported that independence is an important aspect of personal care., , A minority of our study population needed assistance with daily toileting. Other studies reported much higher figures for the need of assistance, which seems to depend on methods of bladder and bowel management., , , The highest percentages have been reported for bowel management, especially manual evacuation and retrograde colonic washout., Krogh et al found that 59% needed help with defecation. In our study, patients who needed assistance were not more likely to perceive incontinence as a problem.
Time needed for defecation
Bladders That Do Not Empty Completely

A bladder will not empty if the muscle that controls the opening stays closed all the time. If it stays closed, the urine cant pass through. If too much urine builds up in the bladder, it will cause a rise in pressure. This will then force the urine back via the ureters into the kidneys. Over time, this will cause pressure on the kidneys and, if it is not treated will damage the kidneys. Urinary tract infections can also be a problem if the bladder is not emptied of urine. If your child has a UTI, their urine may look cloudy, discoloured, may have a strong fishy smell and can be painful when passing it. Repeated UTIs can lead to kidney infections and kidney damage.
The usual way to manage this type of bladder is with clean intermittent catheterisation . CIC is when a disposable catheter is inserted into the bladder via the urethra to empty it. It is not a sterile procedure but cleanliness is important. Once the catheter has drained as much urine from the bladder as possible, it is slowly removed. This is done during the day but not usually at night while your child is asleep. How many times it is done can vary, but it is usually repeated up to 6 times a day at regular times, and usually not at night while asleep.
CIC is used to improve urinary control for people with abnormal bladder function. It helps prevent urinary infection, and helps to relieve pressure on the kidneys.
You May Like: Best Otc For Urinary Tract Infection