How Is Continence Maintained
Maintaining continence is a complex process, and depends on:
- 1.
An intact bladder, sphincter, and pelvic floor function with normal innervation,
- 2.
-
An ability to communicate the need to go to the toilet if immobile,
- 3.
-
Adequate cognition to know how to find the toilet and to keep continence until on the toilet
- 4.
-
Sufficient mobility and manual dexterity to remove clothing,
- 5.
-
Ability to voluntarily initiate micturition at the appropriate time.
The frontal cortex is responsible for voluntary control of micturition
How To Deal With Elderly Incontinence
Your loved one may feel embarrassed by their accidents and avoid scheduling a doctors appointment. They may be using absorbent pads or protective underwear to help, but urinary incontinence is very treatable with medical assistance.
They may also hold off because theyre unsure what kind of doctor to see. A primary care doctor, geriatrician, nurse practitioner, or urinary specialist are viable options. If your loved one feels comfortable with their primary care doctor, its generally good to start there.
Women can also find a urogynecologist, while men can visit a urologist.
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you have any type of urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence is a common problem and you should not feel embarrassed talking to them about your symptoms.
This can also be the first step towards finding a way to effectively manage the problem.
The GP may also suggest you keep a diary in which you note how much fluid you drink and how often you have to urinate.
Find out about diagnosing urinary incontinence.
You May Like: Azo Urinary Tract Health Gummies
What Causes Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable result of aging, but it is particularly common in older people. It is often caused by specific changes in body function that may result from diseases, use of medications and/or the onset of an illness. Sometimes it is the first and only symptom of a urinary tract infection. Women are most likely to develop urinary incontinence during pregnancy and after childbirth, or after the hormonal changes of menopause.
Symptoms And Risk Factors
A comprehensive patient history includes the onset, duration and timing of urinary incontinence, and associated LUTS and voiding symptoms , recognizing that the reported symptoms often relate to the patients normal bladder function and expectations. Other risk factors or conditions that can exacerbate urinary incontinence should also be assessed and include age, obstetric history , gynaecological status , medical status and pharmacological status 57. Patients with mild cognitive impairment are 30% more likely to have urinary incontinence58. In addition, functional and lifestyle factors, such as smoking status, mobility and frequency of heavy lifting, should be considered during assessment.
You May Like: Surgical Treatment For Urinary Incontinence
Difficulty In Interpretation Of Findings
When interpreting urodynamic data in the elderly patient, it is important to realize that normal age-related physiologic changes may significantly alter the measured urodynamic parameters which may be present independently of the patients presenting symptoms. Several normal age-related changes occur in the lower urinary tract,5 including the development of uninhibited detrusor contractions in at least 10% of women and 25%35% of men an increase in nocturnal fluid excretion prostatic enlargement in men urethral shortening and sphincter weakening in women a decrease in bladder capacity in both sexes and possibly a decrease in detrusor contractility.
Physiological Changes Associated With The Ageing Lower Urinary Tract
Urinary incontinence increases with rising age. Ageing is associated with changes in the lower urinary tract which predispose an elderly to UI. As we age, bladder capacity and contractility reduce, with reduced ability to defer voiding once the urge to do so arises. The post-void residual urine volume increases with age. During the storage phase, detrusor shows increased uninhibited contractility .
Among the elderly postmenopausal women, the pelvic muscles show loss of volume and tone. The ligamentous and connective tissue support for the pelvic organs gradually fail because of ageing. The weakened pelvic floor increases the risk of pelvic organ prolapse causing cystocele, rectocele and uterine prolapse. Stage 3-4 prolapse of pelvic organs can cause UI. A weakened pelvic floor also allows a hypermobile urethra to slide downwards during sudden increase in intraabdominal pressure .
Recommended Reading: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Side Effects
Drugs Stopping Sudden Bladder Muscle Contractions
Six approved antimuscarinic drugs work because they block nerve signals regulating bladder muscle contractions the drugs help to relax the bladder muscle and to decrease urges to void. Several studies have shown that these drugs resolve urinary incontinence in one woman among every eight or nine treated . These drugs include:
However, these drugs, especially oxybutynin, may cause adverse effects which may include:
For oxybutynin, one out of every 16 women stopped using it because of intolerable side effects.
When researchers compared the benefits and harms across these six different antimuscarinic drugs, they found that although these drugs demonstrate similar benefits, the potential for adverse effects was not the same . Women should discuss with their doctor what adverse effects are the most troubling for them. They can then choose the medication with the least risk for those specific side effects.
Unfortunately, none of the clinical studies evaluated the long-term safety of these antimuscarinic drugs. All drugs were tested in older women . However, we do not know long-term safety of these drugs in real-life geriatric settings. Future research should look at long-term safety in older women who are also taking several medications because of other chronic diseases.
Conditions Caused By Urinary Incontinence
UI is generally thought to be a predictor of adverse outcomes in older people. Those with UI have a greater mortality, but generally also have more significant comorbidities, which may partly explain this association. There is no universally agreed definition of frailty but it is thought of as a multi-system syndrome of impaired mobility, fatigue, muscle strength, and balance. Common conditions caused by UI are listed in Table 2.
Read Also: Difference Between Urinary Tract And Bladder Infection
Experiences Of Urinary Incontinence Management In Older Women: A Qualitative Study
- 1Student Research Committee, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran
- 2Nursing Care Research Center in Chronic Diseases, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran
- 3Community Based Psychiatric Care Research Center, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
- 4Department of Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
Introduction: Older women have various experiences regarding the management of urinary incontinence depending on the societies they live in and their cultural backgrounds. The present study aimed to determine older women’s experiences in urinary incontinence management.
Results: This study was conducted on 22 older women suffering from urinary incontinence with the mean age of 66.54 ± 5.76 years. The acquired data were put in four main categories of resilience with three subcategories, change in lifestyle with six subcategories, attempt for treatment of the condition with three subcategories, and receiving support with two subcategories.
Who Should Do Kegels
Kegel exercises are a great tool for many people, whether youre wanting to reduce symptoms of urinary incontinence or youre just looking to keep your pelvic floor healthy. Increasing the strength and tone of the pelvic floor can help relieve many symptoms, such as a bladder prolapse, bladder leakage, and urinary urgency.
Kegels are often recommended for women or men whose pelvic floor requires better support. Pelvic floor exercises, like any other strength training program, can help to tighten up the muscles and restore their natural role in pelvic organ support and pelvic stability.
However, its important to note that kegel exercises are not for everyone. In fact, some people may even do more harm than good by doing too many Kegels.
Some pelvic floor disorders are a result of the pelvic floor being too active or tense. When this happens, it makes it hard for the pelvic floor to relax and rest completely. This may lead to the pelvic floor being in a continuous overactive state.
In these cases, doing Kegels for strengthening or improving tone is NOT recommended. Its hard to know if you have a weak pelvic floor, or an overactive pelvic floor without consulting a pelvic floor therapist, which is why its always recommended to see one prior to beginning any pelvic floor exercise routine.
A physical therapist will help diagnose your problem and can teach you how to properly do a Kegel, and just as important, how to relax the pelvic floor.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection In Bloodstream
Urinary Incontinence Causes And Symptoms
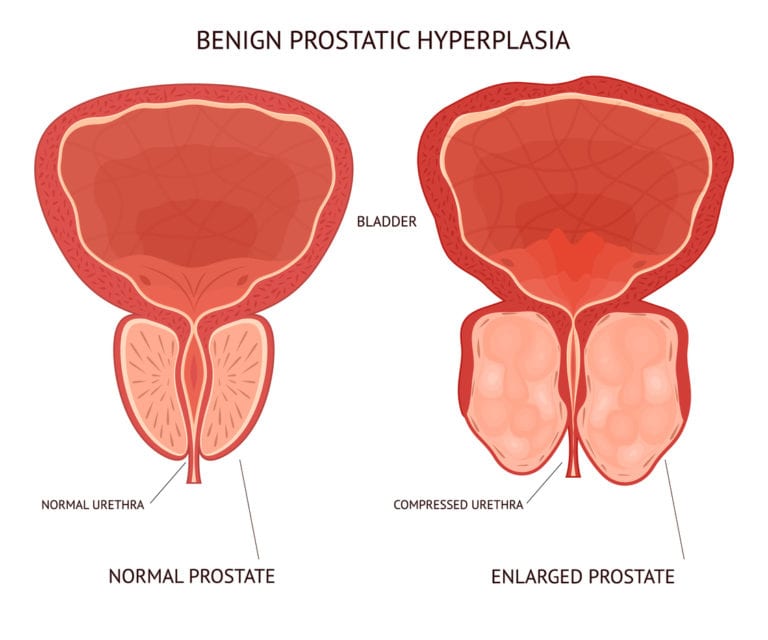
Aging itself does not cause urinary incontinence, but changes that occur with aging can increase the risk of developing urinary incontinence by interfering with a persons ability to control urination. For example, the maximum amount of urine that the bladder can hold decreases. The ability to postpone urination decreases. More urine remains in the bladder after urination , partly due to less effective squeezing of the bladder muscle. In postmenopausal women, the urinary sphincter does not hold back urine in the bladder as effectively, because the decrease in estrogen levels after menopause leads to shortening of the urethra and thinning and fragility of its lining. Also, urine flow through the urethra slows. In men, urine flow through the urethra may be impeded by an enlarged prostate gland, eventually leading to bladder enlargement.
Urinary incontinence has many possible causes. Some causes, such as a bladder infection, a broken hip, or delirium, can bring on incontinence suddenly and abruptly. Other causes, such as an enlarged prostate in men or dementia, gradually interfere with control of urination until incontinence results. Incontinence may resolve and never recur. Alternatively, it may persist, recurring sporadically or, in some cases, frequently.
Diabetes And Brain Health
If you have diabetes, your doctor may screen you for depression or cognitive impairment. Older adults with diabetes are at higher risk for these conditions, compared with others their age who do not have diabetes. Having depression or cognitive impairment can make diabetes self-care challenging.
Your diabetes management plan will cover how to:
- Track your glucose levels. Very high glucose levels or very low glucose levels can be risky to your health. Your plan will show how often you should check your glucose and how often to get the A1C test. If you are managing your diabetes without taking insulin, you may not need to check your glucose as often.
- Make healthy food choices. The food you eat affects glucose levels, so its important to learn whats best for you to eat, how much, and when. If you are overweight, work with your health care team to come up with a plan to lose weight.
- Be active. Walking and other forms of daily exercise can help improve glucose levels in older people with diabetes. Set a goal to be more active most days of the week, and create a plan for being physically active that fits into your life and that you can follow. Your health care team can help.
- Take your medicines. You should take medicine as prescribed even when you feel good. Tell your doctor if you have any side effects or cannot afford your medicines. Also, let your doctor know if you have trouble taking your medicine or keeping track of your medication schedule.
Also Check: What Is Urinary Incontinence In The Elderly
Bladder Structure And Function
The bladder, urethra and urinary sphincters work in concert to store urine at low pressure and to void voluntarily at socially convenient or appropriate times. The detrusor muscle and internal urethral sphincter are predominantly smooth muscle, whereas the external urethral sphincter and pelvic floor muscles are predominantly striated muscle. The bladder lumen is lined with epithelial cells and the basement membrane that protect the underlying detrusor muscle from toxins contained in the urine and enable communication with neural cells that coordinate storage and voiding phases .
Anatomy and histology of the female bladder
The sympathetic nervous system predominates during the storage phase and maintains continence through the paravertebral ganglia, the hypogastric nerves and hypogastric plexus. The parasympathetic system coordinates the voiding phase, through the sacral plexus and pelvic nerves 39. Afferent signals from the urothelium and bladder wall are transmitted through to the thalamus the balance between storage and voiding is maintained by the central pontine micturition centre . The neurotransmitters responsible for execution of these commands are acetylcholine and noradrenaline.
Neurological control of the urinary bladder
Caring For Someone With Incontinence
So far, weve covered managing your own incontinence, but what if youre caring for an older adult? Incontinence is a common issue faced by dementia caregivers, and can be one of the most challenging parts of providing care. Research shows that:
- Those with dementia have a 2-3-fold increased chance of urinary incontinence
- The more severe the dementia, the more likely that there will be incontinence
- Urinary incontinence contributes to caregiver burden and increases the risk that someone will be admitted to a nursing home.
Steps to take
Dementia may not be the only cause of incontinence, so the first step is to look for other causes, like those reversible ones mentioned earlier .
If there doesnt seem to be any of those issues going on, then managed continence is the approach that is most likely to help. Rather than using the bladder medications, which can worsen confusion and dampen alertness, managed continence includes the use of continence products and a schedule of timed toileting .
In some cases, environmental adjustments and equipment, like bedside commodes, catheters, and urinals, can make frequent toileting easier and less disruptive, especially overnight.
You May Like: Urinary Incontinence Is Caused By
Medical Devices: Treatment For Urinary Incontinence In Elderly Females
In addition to medicinal treatments, these medical devices may be prescribed for women:
Urethra insert
This is a tampon-like insert that a woman places in her urethra, usually during activities related to her incontinence episodes, such as exercising. While wearing the insert, youll be able to urinate and have bowel movements. Its a good option for senior women who want to remain active. It can be worn safely for up to eight hours, but just like a tampon, it will need to be changed as directed to avoid health and hygiene issues.
Pessary
This is an intravaginal device, similar to a diaphragm, that supports the bladder. It comes in different sizes. After its placed, it will need to be taken out, inspected, and cleaned by a health care provider every three months. You can purchase a single-use disposable pessary over the counter, but its best to check with your doctor or nurse practitioner to determine which option is best for you.
Types And Causes Of Incontinence In Aging Adults
Simply put, the bladder does two things: it stores urine and empties of urine.
When storage goes wrong, this can result in symptoms of urgency, frequency, and stress incontinence. When these symptoms are severe, like having to void more than 13 times a day, or more than twice at night, quality of life can be significantly impaired.
There can also be problems with getting the bladder to empty at the right time and place. Two types of issues that often come up for older adults are:
Heres a chart reviewing the different types of incontinence:
| Symptom |
| A mixture of the above symptoms |
So far, Ive talked mostly about chronic incontinence, but there can be a few reasons why an older person would suddenly start losing bladder control. As a geriatrician, I always want to rule out these potentially treatable issues before embarking on a long-term continence management plan.
Read Also: Severe Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
Sign Up For The Nafc Newsletter And Receive A Free Book
The NAFC newsletter, On The Go, provides the latest news in incontinence, expert opinions, and patient stories to offer you more ways to manage your condition and stay up to date with the most recent treatment and management options. It also includes information about research opportunities, special offers, and information about whats new at NAFC.
And, when you sign up for our newsletter, youll receive our FREE eBook: 21 Ways To Manage Bladder Leaks, after you confirm your subscription.
Learn how to take charge of your bladder health with these tips, resources, and helpful tools, all gathered into one concise place!
Not sure what your symptoms are? Try keeping a bladder diary. It can help you learn more about when and why you experience incontinence and may help provide you with a good tool to use when talking about your condition with your doctor.
Will I Have Incontinence For My Entire Life
Sometimes incontinence is a short-term issue that will go away once the cause ends. This is often the case when you have a condition like a urinary tract infection . Once treated, frequent urination and leakage problems caused by a UTI typically end. This is also true for some women who experience bladder control issues during pregnancy. For many, the issues end in the weeks after delivery. However, other causes of incontinence are long-term and related to conditions that are managed throughout your life. If you have a chronic condition like diabetes or multiple sclerosis, you may have incontinence for a long period of time. In those cases, its important to talk to your provider about the best ways to manage your incontinence so that it doesnt interfere with your life.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
It can be embarrassing to talk about bathroom habits with your healthcare provider. This embarrassment shouldnt stop you from treating incontinence, though. Often, your healthcare provider can help figure out the cause of your bladder control issue and help make it better. You dont need to deal with it alone. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best ways to treat incontinence so that you can lead a full and active life without worrying about leakage.
Read Also: Medicine Used For Urinary Tract Infection