Acute And Chronic Prostatitis
In the 1800s, prostatitis was thought to be secondary to excessive alcohol consumption or physical or sexual activity. It was often associated with gonorrhea and could be fatal or lead to abscess formation. By the 1920s, most cases were attributed to microorganisms, and antibiotics combined with prostate massage were standard therapy after World War II. Although the role of bacteria was questioned in the 1950s, it was reemphasized in 1968 when Meares and Stamey described their “4-glass test.”
Acute prostatitis is caused by an acute infection of the entire prostate gland, resulting in fever and localized pain. Microscopically, neutrophilic infiltrates, diffuse edema, and microabscesses may be seen, which may coalesce into larger collections.
Chronic prostatitis may be caused by inflammatory or noninflammatory diseases. This condition may arise via dysfunctional voiding, intraprostatic reflux, chronic exposure to microorganisms, autoimmune mechanisms, irritative urinary metabolites, and as a variant of neuropathic pain. Chronic bacterial prostatitis often produces few or no symptoms related to the prostate, but it is probably the most common cause of relapsing UTI in men.
Chronic prostatitis has been subdivided by the National Institutes of Health into the following categories:
Ways To Prevent Acute Cystitis
Acute cystitis is usually brought on by bacteria entering the bladder through your urethra. Minimize your risk of developing a UTI and bladder infection by taking necessary precautions. Drink plenty of water, both to prevent dehydration and encourage frequent urination, which flushes bacteria out of your bladder regularly.
If youre sexually active, remember to pee as soon as possible following intercourse. Avoid using birth control that could irritate the area around your urethras opening or introduce bacteria into your bladder. Many types of spermicidal jellies, cervical sponges, and diaphragms foster increased or altered bacterial growth.
Uti Or Cystitis Whats The Difference
Is it a UTI or cystitis? Unless youre medically trained this may not be the first question you ask yourself when rushing back to the toilet for another painful experience.
A UTI is a general term used to describe an infection that can occur anywhere in the urinary tract .
When an infection has been medically diagnosed in the bladder lining, it is called cystitis and this is the most common type of UTI seen in women.
Having a better idea of what UTIs and cystitis are can help explain why you may have those painful symptoms and why different types of self-care may be useful in relieving symptoms or even preventing them reoccurring. It may also help you decide when its time to get help.
Also Check: What Causes Urinary Incontinence In Older Adults
Am I At Risk Of A Uti
While UTIs can happen to anyone, they are more common in females who are sexually active or menopausal, or have health conditions such as diabetes or urinary incontinence. Females who use spermicides or diaphragms as contraception are also at increased risk of UTIs, and may benefit from other contraceptive options if they get recurrent UTIs.
Some people at greater risk of developing urinary tract infections:
- Females nearly 1 in 3 females will have a UTI that needs treatment before the age of 24.
- Males with prostate problems an enlarged prostate gland can cause the bladder to only partially empty, raising the risk of infection.
- Older people some medications and problems with incontinence mean that older people are more likely to get a UTI.
- People with urinary catheters people who are critically ill and people who cant empty their bladder are at a greater risk of infection.
- People with diabetes changes to the immune system make people with diabetes more vulnerable to infection.
- Infants babies in nappies commonly get UTIs, in particular, infants born with physical problems of the urinary system are at greater risk.
Table 1 Symptoms/signs Of Uti Used For Classification
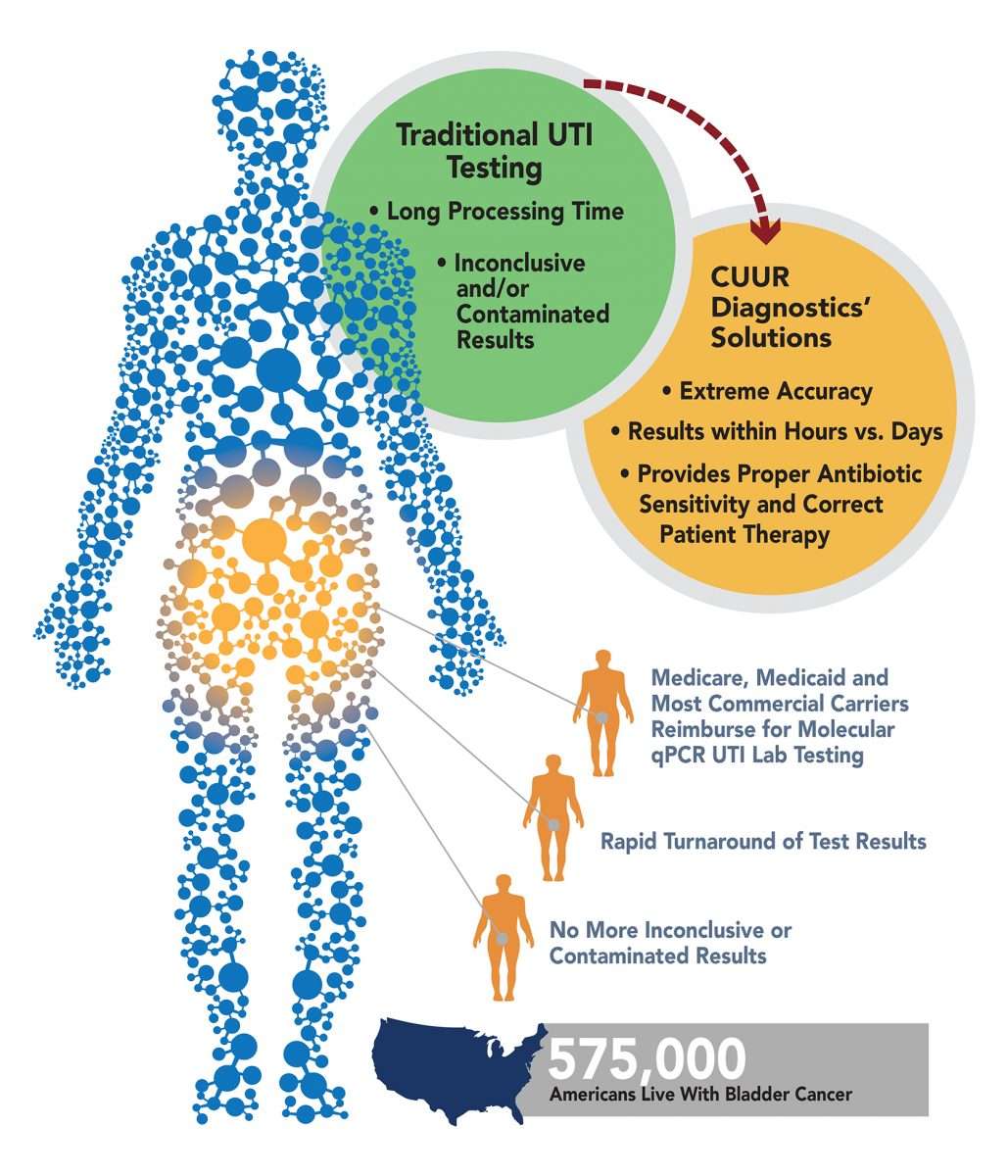
|
Cystitis18,21,22 |
|
No testing required if symptoms of UTI or systemic infection are absent6,16 If patient is symptomatic, collect urine for culture after removal of old catheter or from a newly inserted catheter.16 |
Catheters can be colonized with bacteria after 24 hours of insertion, and 100% are colonized within 1 month.5,16 |
Read Also: Natural Remedies For Male Urinary Tract Infection
Which Individuals Are At Greater Risk Of Developing Pyelonephritis/complicated Urinary Tract Infection
-
Complicated UTI risk is greatest in patients with abnormal voiding and may be suggested by a history of urinary retention, recurrent UTI, or urinary procedures, including stent or catheter placement. Any condition or foreign body resulting in obstruction of normal urinary flow predisposes to complicated UTI. Diabetes increases the risk of perirenal abscess and emphysematous pyelonephritis.
-
Specific factors include:
Beware: there are other diseases that can mimic pyelonephritis/complicated urinary tract infection:
-
Urethritis due to sexually transmitted pathogens can mimic cystitis.
-
Nephrolithiasis mimics pyelonephritis.
-
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome in males mimics prostatitis.
-
Systemic conditions and non-GU infections can result in fever, tachycardia, mental status change, and/or hypotension and may be misdiagnosed as UTI because of the presence of pyuria or asymptomatic bacteriuria. When making a diagnosis of complicated UTI on the basis of systemic symptoms alone, other diagnoses need to be excluded.
What Other Clinical Manifestations May Help Me To Diagnose And Manage Pyelonephritis/complicated Urinary Tract Infection
Additional diagnostics depend on the specific patient risk factors and may require urologic consultation for cystoscopy and voiding studies for assessment for anatomical or functional abnormalities.
UTI has an acute onset .
Men with recurrent UTI should be evaluated for prostatitis.
Women with recurrent UTI may not have any complicating factors, because recurrence is part of the natural history of acute cystitis in women.
The physical exam may be normal in patients with complicated UTI.
In patients with primarily systemic findings or infection without focal GU symptoms, the exam should include evaluation for other infections.
Examination of the urethral meatus in men with cystitis symptoms should be performed to detect a discharge that would indicate urethritis. Likewise, in women with cystitis symptoms, a pelvic exam can be useful for ruling out vaginitis or cervicitis.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Otc Antibiotics
How To Treat Blood In Urine Without Infection
Blood in urine or Hematuria is not something which should be neglected. However, in order to treat the same, the exact cause of such blood in urine should be known to the medical practitioner. Thus, an appointment with the doctor at the earliest is the most important step that one should undertake in case he/she finds blood in urine.
The doctor would advise a thorough urine test in order to find out what can cause blood in urine without infection and then start the appropriate treatment schedule. For example, in case of bleeding due to strenuous exercises, the doctor might need to advise limiting the exercises or not practising heavy exercises till the time the injury heals.
Medically Reviewed By
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or a diaphragm or cap with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Read Also: Natural Remedies For Urinary Frequency
What Could Be Mistaken For A Uti
There are several conditions whose symptoms mimic UTIs. Sexually transmitted infections cause symptoms also common in UTIs, such as painful urination and discharge.
Vaginitis, caused by bacteria or yeast, can result in a burning sensation when urinating and similar discomfort that may mimic a UTI.
Often mistaken for a UTI, interstitial cystitis , or painful bladder condition, is a chronic condition affecting the bladder that does not improve with antibiotic treatment. Symptoms of IC include increased urgency and more frequent urination as well as pain in the pelvic area.
Other conditions to rule out are overactive bladder, pregnancy, prostatitis, diabetes, cancer, and kidney stones.
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
The systematic search, the conservative inclusion criteria, the inclusion of additional data from authors, and the quality assessment of the included studies can be seen as strengths of this study. In addition, given the lack of consensus regarding reference standard thresholds for UTI, the current study is the first study to determine the diagnostic accuracy of symptoms and signs across the three thresholds 102 CFU/ml, 103 CFU/ml and 105 CFU/ml. Lastly, this study highlights the additional importance of using dipstick test, particularly tests for nitrites, as an additional diagnostic tool when ruling in a UTI diagnosis based on particular symptomatology.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Multifunction Urinary And Hydrolyzed Protein Canine
Other Disorders Of Urinary System
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- Acute lower urinary tract infection
- Acute upper urinary tract infection
- Acute urinary tract infection
- Chronic lower urinary tract infection
- Chronic urinary tract infection
- Escherichia coli urinary tract infection
- Infection, urinary tract , upper
- Klebsiella urinary tract infection
- Lower urinary tract infection, acute
- Lower urinary tract infection, chronic
- Lower urinary tract infectious disease
- Persistent urinary tract infection
- Recurrent urinary tract infection
- Upper urinary tract infection
- Upper urinary tract infection, acute
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary tract infection with fever
- Urinary tract infection due to enterococcus
- Urinary tract infection due to klebsiella
- Urinary tract infection due to pseudomonas
- Urinary tract infection due to urinary catheter
- Urinary tract infection, acute
- Uti after procedure
- 689 Kidney and urinary tract infections with mcc
- 690 Kidney and urinary tract infections without mcc
- 791 Prematurity with major problems
- 793 Full term neonate with major problems
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
UTIs are best managed in an interprofessional fashion, and besides physicians, most nurses will encounter a patient with a UTI. The key to preventing recurrences is patient education. Once a UTI has been diagnosed, the patient should be encouraged to drink more fluids. Sexually active women should try to void right after sexual intercourse as this can help flush the bacteria out of the bladder. Some women with recurrent UTIs may benefit from the prophylactic use of antibiotics. Several other non-medical remedies may help some women with UTIs. Anecdotal reports indicate that using cranberry juice and probiotics may help reduce the severity and frequency of UTIs in some women. Primary clinicians should refer patients with recurrent UTIs to the urologist to rule out reflux and anatomical defects.
Outcomes
The majority of women with a UTI have an excellent outcome. Following treatment with an antibiotic, the duration of symptoms is 2 to 4 days. Unfortunately, nearly 30% of women will have a recurrence of the infection. Morbidity is usually seen in older debilitated patients or those with renal calculi. Other factors linked to recurrence include the presence of diabetes, underlying malignancy, chemotherapy, and chronic catheterization of the bladder. The mortality after a UTI is close to zero.
Don’t Miss: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Cause An Elevated Psa
What Can Cause Blood In Urine Without Infection
Our body is a unique yet complex mechanism complete in itself. While it knows how to process the required and essential nutrients out of the food and beverages we consume, our body also completes the operations by systematically and regularly excreting out the waste products in the form of stool and urine . These by-products of metabolism thus hold the key indicators of any issue or problem that the body might face.
Urine mostly is an aqueous solution excreted from the body which is composed of mainly water . Some other constituents of urine include urea, chloride, sodium, potassium, creatinine and other dissolved ions, and inorganic and organic compounds. At times, urine also contains some amount of blood which might indicate some problem. Let us understand what can cause blood in urine without infection?
How Can Pyelonephritis/complicated Uti Be Prevented
Single dose antimicrobial prophylaxis is recommended for prevention of urosepsis in patients undergoing invasive GU procedures, such as transrectal prostate biopsy and bladder biopsy. The regimen of choice has been ciprofloxacin however, increased resistance to ciprofloxacin has led to breakthrough episodes of sepsis and bacteremia. Optimal prophylaxis regimens other than the fluoroquinolones are currently being evaluated but can be guided by local resistance data or by rectal cultures.
Antimicrobial prophylaxis with TMP-SMX is used in patients undergoing renal transplantation.
Patients with recurrent episodes of complicated UTI due to a nidus of infection, such as stone, stent, or other foreign body, may be managed with antimicrobial prophylaxis while definitive management of the underlying disease process is planned. This strategy is not effective long-term because of issues of antibiotic resistance and adverse effects.
Reducing the use of urinary catheters is the primary method for preventing catheter-associated UTI.
You May Like: Mesh Surgery For Urinary Incontinence
Urgent Advice: Ask For An Urgent Gp Appointment Or Get Help From Nhs 111 If:
You think you, your child or someone you care for may have a urinary tract infection and:
- a very high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
- are confused, drowsy or have difficulty speaking
- have not been for a pee all day
- have pain in the lower tummy or in the back, just under the ribs
- can see blood in their pee
These symptoms could mean you have a kidney infection, which can be serious if it’s not treated as it could cause .
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
How Did The Patient Develop Pyelonephritis/complicated Urinary Tract Infection What Was The Primary Source From Which The Infection Spread
-
Pyelonephritis and complicated UTI most commonly occur by migration of enteric bacteria from the intestinal tract into the urethra and ascension into the urinary system.
Basic epidemiology
-
The term complicated, as opposed to uncomplicated, suggests there is a predisposing reason for the infection, including the presence of abnormal voiding or a foreign body . Known or suspected multi-drug resistance is also a complicating factor.
-
Complicated UTI can occur in any gender and at any age but is most common in men after the fifth decade when benign prostatic hypertrophy is present and in both men and women who have voiding abnormalities related to other conditions.
-
Most UTIs in young premenopausal nonpregnant women and in young adult men are not complicated.
-
UTIs in patients with diabetes or in postmenopausal women should be considered complicated if there is abnormal voiding associated with those conditions.
-
Additional factors that suggest complicated UTI include conditions that make treatment more difficult, such as pregnancy, multidrug resistance, and immunosuppression.
Don’t Miss: Discomfort In Urinary Tract Male
Context Of Previous Studies
The findings of this systematic review are consistent with a previous systematic review which concluded that no sign or symptom on its own is powerful enough to ‘rule in’ or ‘rule out’ the diagnosis of UTI . However, the relative diagnostic importance of individual symptoms and signs varies between this review and the previous systematic review . The previous systematic review found that presence of dysuria, frequency, hematuria, back pain and costovertebral angle tenderness increase the probability of UTI using a diagnostic threshold ranging from between 102 CFU/ml and 105 CFU/ml, also history of vaginal discharge, history of vaginal irritation and vaginal discharge on examination decrease the probability of a UTI. In this systematic review we found that dysuria and frequency increase the probability of UTI across different reference standard thresholds 102 CFU/ml, 103 CFU/ml and 105 CFU/ml. Hematuria is also significant in the present study using a diagnostic threshold of 102 CFU/ml and 103 CFU/ml. However, in contrast to the previous systematic review back pain is not significantly associated with UTI across the different reference standard thresholds. Vaginal discharge is identified as an important symptom for decreasing the probability of UTI in the present study.
Candidiasis Of Other Urogenital Sites
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- 2020 – New Code20212022Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- Applicable To annotations, or
Also Check: Over The Counter Medicine For Urinary Urgency
Common Uti Symptoms And Signs
The urine of most healthy, properly hydrated people appears light yellow or clear and is nearly free of odor. It also causes zero pain or discomfort to pass.
But for the majority of people who experience a urinary tract infection, thats not the case. Instead, they will likely encounter at least one of the following indicators:
When the kidneys are infected, other noticeable symptoms may include:
- Fever, shaking, and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Upper back, side, or groin pain
While its been long noted that confusion in the elderly is a sign of UTI, a 2019 report in BMC Geriatrics concludes that theres insufficient evidence connecting the symptom to that diagnosis.
RELATED: Causes and Risk Factors of Urinary Tract Infections
Diseases Of The Genitourinary Systemtype 2 Excludes

Read Also: Over The Counter Urinary Incontinence