Prevention Tips For Urinary Tract Infection
Adhere to these helpful tips to keep UTIs at bay.
- Do not hold urine in for long periods of time
- Drink enough water, usually 6 to 8 glasses a day
- As a woman, wipe after urination using a front-to-back motion only
- Urinate after sexual intercourse to flush out bacteria
- Empty your bladder fully when urinating and avoid rushing
- Keep genitals dry and avoid wearing nylon underwear as they trap moisture
Arming yourself with this information about UTIs helps you protect yourself from developing complicated illnesses in the long run. Knowing what to look for or being able to identify a factor that may be a potential cause for a UTI is immensely helpful, especially for the elderly or the very young. However, UTIs are quite common, especially amongst women and the best way to deal with an infection is to get medical care immediately. Here, the family primary care provider or a specialist like an OBGYN can address these symptoms with ease. Keep in mind that UTIs in men are generally regarded as complicated. So, it is best to get regular check-ups.
Children And Urinary Tract Infections
Symptoms in children are different from symptoms in adults. Urinary tract infections are quite common in children. While UTIs in very young children are often associated with an anatomic abnormality, for others the infection is related to introducing bacteria into the urinary tract. UTIs in children generally peak in infancy and then again between ages 2 and 4, coinciding with potty training.
In newborns, signs of urinary tract infection include poor feeding, lethargy, diarrhea, vomiting, mild jaundice, and fever. For babies younger than 2, foul-smelling urine may also be a sign. For older children, the more classic UTI signs, such as urgency, incontinence, and pain while urinating occur.
Can Sex Make A Uti Worse
If you already have a UTI, having sex can make the infection feel worse, exacerbating the symptoms. Using spermicides can increase discomfort because it can cause irritation. Using non-lubricated latex condoms can also increase friction leading to irritation. Using a water-based lubricant or lubricated condoms will help avoid making your UTI feel more irritated. After and before sex, be sure to urinate immediately to flush out the bacteria.
Read Also: Does Urinary Infection Go Away Its Own
How To Reduce Your Risk
As the studys researchers blame improper food handling for food-borne UTIs, you can minimize your chances of developing an E. coli infection by:
Washing your hands
Clean your hands thoroughly after using the bathroom and before food preparation.
Cooking meats thoroughly
Use a meat thermometer to ensure chicken is cooked to an internal temperature of at least 165°F .
Preventing cross contamination
Be sure to thoroughly wash your hands, counters, cutting boards, and utensils after they come in contact with raw meat.
**The epidemiological evidence gathered through our multi-year observations supports the use of herbs contained inUribiotic Formulafor urinary tract infections caused byE. coli. This evidence, however, has not been evaluated by the FDA.
Donât Miss: How Does A Person Get Urinary Tract Infection
How Is Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosed

In order to ensure a clean urine sample, a physician will likely have you clean your genital area with a special wipe beforehand, and ask that you do a midstream catch of the urine.
If a UTI is diagnosed, youll be treated with antibiotics. Its important to note that false negative results do occur and that almost all women who experience typical UTI symptoms and a negative urine culture actually do have a UTI. 30209-4/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> 11)
If youve had a prior UTI, your healthcare provider will look at prior cultures to see which bacteria were found, if any, and which antibiotics were used this often guides therapy in recurrent UTIs.
You May Like: How Long Does Urinary Incontinence Last
Complications Of Urinary Tract Infection
The most common complication of a UTI is kidney damage. Bacteria entering the urinary tract can travel to the kidneys and cause an infection. It can lead to kidney damage and even kidney failure in severe cases. Other complications of UTIs include blood poisoning, kidney stones, and an increased risk of developing a bladder or kidney infection in the future. If you think you may have a UTI, you must see a doctor and start treatment immediately.
How E Faecalis Leads To Enterococcal Infections
Enterococcus faecalis is one of the most common species of Enterococci and is the leading cause of enterococcal infections. However, researchers arenât sure what factors lead to a higher presence of this bacteria in certain people and body parts.
Additionally, the unique elements of E. faecalis make it so that many antibiotics donât work to fight against the infection. Such antibiotics include:
Recommended Reading: Will Clindamycin Treat A Urinary Tract Infection
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI.
A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service. They may be able to give antibiotics if they’re needed.
How Are Recurrent Utis Treated
Treatment for recurrent UTIs depends on whatâs causing them. Sometimes the answer is as simple as teaching a child to empty their bladder as soon as they have the urge to go.
If a condition like VUR is causing the infections, the solution is a bit more complicated. Kids with VUR must be watched closely, because it can lead to kidney infection and kidney damage. Most kids outgrow the condition. Some might need surgery to correct the reflux.
Some kids with VUR benefit from daily treatment with a small amount of antibiotics, which can also make surgery unnecessary. Kids with VUR should see a pediatric urologist, who can decide if antibiotic treatment is the best option.
In some cases, surgery is needed to correct VUR. The most common procedure is ureteral reimplantation, in which one or both of the ureters are repositioned to correct the backflow of urine from the bladder. This procedure requires only a small incision and, in some children, can be done using robotic-assisted laparoscopy. When surgery is necessary, the success rate is high, but not everyone is a good candidate for it.
Kids may be candidates for ureteral reimplantation if they:
- have an intolerance to antibiotics
- get recurrent infections while on antibiotic treatment
- have severe, or âhigh-grade,â reflux
- are older kids and teens with reflux
Read Also: Laser Treatment For Urinary Incontinence Reviews
How To Treat Enterococcal Infections
Infections caused by E. faecalis are challenging to get rid of because the bacteria are resistant to many antibiotics.â
One course of treatment involves combining a wall-active drug â such as penicillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin, piperacillin, or vancomycin â with whatâs called an aminoglycoside â such as gentamicin or streptomycin. However, skin infections and endocarditis often require different combinations. UTIs, on the other hand, are typically much easier to treat. Your doctor will likely only need to prescribe a single antibiotic like ampicillin.
Show Sources
âAfrican Journal of Infectious Diseases: âPrevalence of Hospital-Acquired Enterococci Infections in Two Primary-Care Hospitals in Osogbo, Southwestern Nigeria.â
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: âMultiple-Drug Resistant Enterococci: The Nature of the Problem and an Agenda for the Future.â
âFairview: âBacteremia, Suspected .â
âInfections and Immunity: âEnterococcus faecalis Tropism for the Kidneys in the Urinary Tract of C57BL/6J Mice.â
âJournal of Global Infectious Diseases: âSoft Tissue and Wound Infections Due to Enterococcus spp. Among Hospitalized Trauma Patients in a Developing Country.â
âMayo Clinic: âUrinary tract infection .â
âMedscape: âEnterococcal Infections.â
âMerck Manual: âEnterococcal Infections.â
âSeattle Childrenâs: Wound Infection.â
Treatment For More Severe Utis
Kids with a more severe infection may need treatment in a hospital so they can get antibiotics by injection or IV .
This might happen if:
- the child has high fever or looks very ill, or a kidney infection is likely
- the child is younger than 6 months old
- bacteria from the infected urinary tract may have spread to the blood
- the child is dehydrated or is vomiting and cannot take any fluids or medicine by mouth
Kids with VUR will be watched closely by the doctor. VUR might be treated with medicines or, less commonly, surgery. Most kids outgrow mild forms of VUR, but some can develop kidney damage or kidney failure later in life.
Read Also: How To Prevent Urinary Blockage In Cats
Urinary Tract Infections In Women
UTIs are common, particularly with increasing age. Women are more likely to get a UTI than men. Nearly 1 in 3 women will have a UTI needing treatment before the age of 24.
In women, the urethra is short and straight, making it easier for germs to travel into the bladder. For some women, UTIs relate to changes in their hormonal levels. Some are more likely to get an infection during certain times in their menstrual cycle, such as just before a period or during pregnancy.
In older women, the tissues of the urethra and bladder become thinner and drier with age as well as after menopause or a hysterectomy. This can be linked to increased UTIs.
During pregnancy, the drainage system from the kidney to the bladder widens so urine does not drain as quickly. This makes it easier to get a UTI. Sometimes germs can move from the bladder to the kidney causing a kidney infection. UTIs during pregnancy can result in increased blood pressure, so it is very important to have them treated as soon as possible.
Women are more at risk of repeated UTIs if they:
- use spermicide jelly or diaphragm for contraception
- have had a new sexual partner in the last year
- had their first UTI at or before 15 years of age
- have a family history of repeated UTIs, particularly their mother
- suffer from constipation
When Urinary Tract Infections Keep Coming Back
If you are prone to recurrent UTIs, you can head them off before they take hold.
Unless you’re in the fortunate minority of women who have never had a urinary tract infection , you know the symptoms well. You might feel a frequent urgency to urinate yet pass little urine when you go. Your urine might be cloudy, blood-tinged, and strong-smelling. For 25% to 30% of women who’ve had a urinary tract infection, the infection returns within six months.
If you have repeated UTIs, you’ve experienced the toll they take on your life. However, you may take some comfort in knowing that they aren’t likely to be the result of anything you’ve done. “Recurrent UTIs aren’t due to poor hygiene or something else that women have brought on themselves. Some women are just prone to UTIs,” says infectious diseases specialist Dr. Kalpana Gupta, a lecturer in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Don’t Miss: How To Ease Urinary Pain
Home Remedies For Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
In addition to antibiotics, many people seek natural, at-home remedies to help UTIs. A heating pad can relieve pressure and pain, and wearing loose cotton clothing is recommended. For those with recurrent UTIs, modifying certain habits may help: Choose fragrance-free personal care products to reduce the risk of irritation, and cut back on foods that can irritate the bladder caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, raw onions, citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and artificial sweeteners.
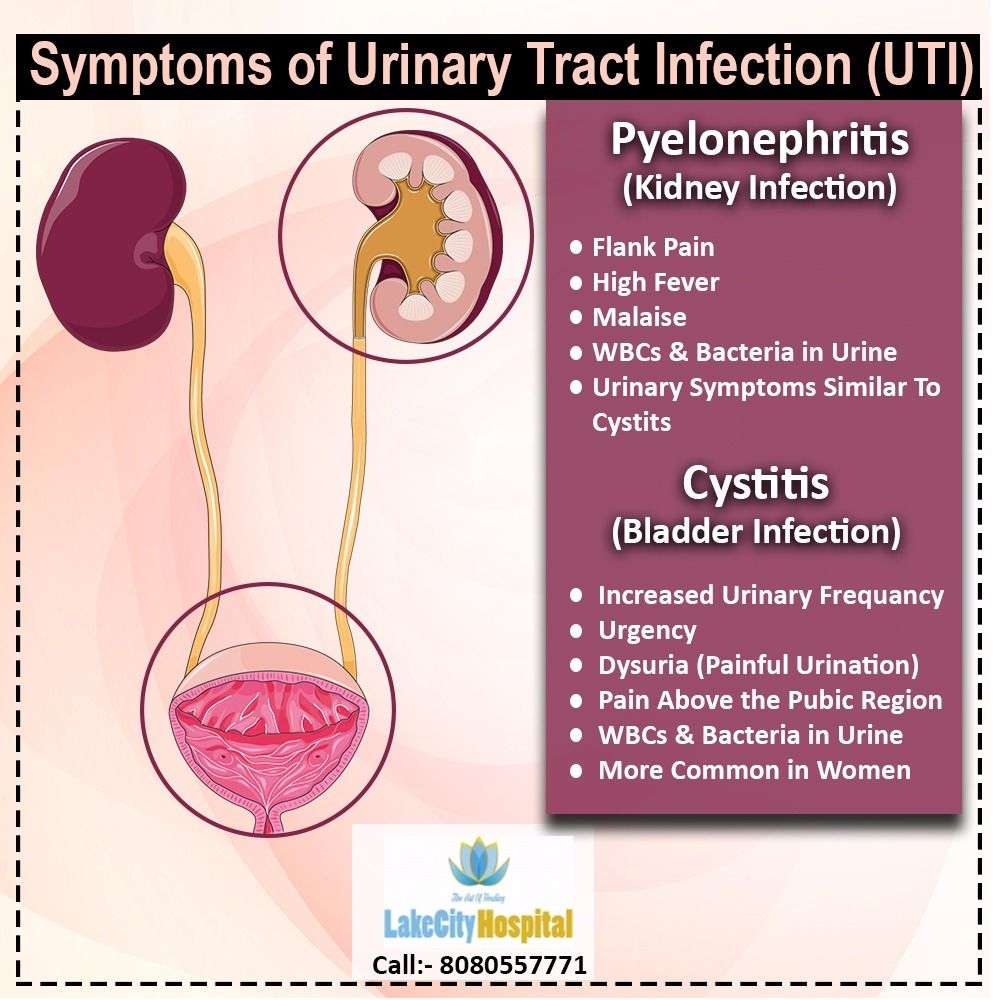
What Are The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
These are the most common symptoms of a UTI:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Urine looks dark, cloudy, or reddish in color
- Urine smells bad
- Feeling pain even when not urinating
- Pain in the back or side, below the ribs
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Despite an strong urge to urinate, only a small amount of urine is passed
- Women may feel an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone
The symptoms of UTI may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always see a health care provider for a diagnosis.
Read Also: Btl Emsella For Urinary Incontinence
Favorite Site For Urinary Health Podcasts
Podcasts arent just for politics, laughs, and murder mysteries. The American Urological Association has a fantastic one called, aptly, the Urology Care Podcast, which covers topics like sexual health myths, UTIs, prostate cancer, and more. Currently there are more than 140 episodes to listen to, ranging from about 4 minutes to 28 minutes long.
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection
Microorganisms typically bacteria that enter the urethra and bladder, producing Inflammation and infection, are responsible for urinary tract infections.
Some common causes of a UTI include:
- A new sexual partner or multiple sex partners
- Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle
- Wiping from back to front after a bowel movement rather than front to back
- Using an intrauterine device for birth control
- Not enough intake of fluids and dehydrated state
- Kidney stones that block the flow of urine or keep the bladder from emptying
- A weakened immune system due to certain disorders, such as diabetes or cancer
- Menopause, which can cause changes in the urinary tract
- Pregnancy, which can cause hormonal changes that promote infection
- Narrowing of the urethra in males due to prostate enlargement, which blocks the flow of urine
You May Like: How To Help A Urinary Tract Infection At Home
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically respond very well to treatment. A UTI can be uncomfortable before you start treatment, but once your healthcare provider identifies the type of bacteria and prescribes the right antibiotic medication, your symptoms should improve quickly. Its important to keep taking your medication for the entire amount of time your healthcare provider prescribed. If you have frequent UTIs or if your symptoms arent improving, your provider may test to see if its an antibiotic-resistant infection. These are more complicated infections to treat and may require intravenous antibiotics or alternative treatments.
Prostatitis Epididymitis Urethritis And Orchitis
In contrast to UTI, prostatitis affects men of all ages and, from 1990-1994, accounted for almost 2 million office visits per year in the United States. Prostatitis syndromes account for 25% of male office visits for genitourinary complaints, 8% of visits to urologists, and 1% of visits to primary care physicians. Of these men, 5% have bacterial prostatitis, 64% have nonbacterial prostatitis, and 31% have prostatodynia. Digital examination of the prostate in the setting of probable or possible UTI should be avoided to prevent the risk of inciting bacteremia.
Epididymitis has a bimodal distribution, corresponding to different age groups and pathogens. Most cases in men younger than 35 years are due to sexually transmitted pathogens. Older patients are more likely to have obstructive prostatism or a history of instrumentation or catheterization.
Gonococcal urethritis is more common in ethnic minorities, lower socioeconomic groups, and persons living in urban centers. The risk to a male having intercourse with an infected female is 17%. Some of these associations may be limited by confounding. The peak age for urethritis is 20-24 years.
Mumps orchitis occurs in 18% of postpubertal boys infected with the mumps virus.
John L Brusch, MD, FACP Corresponding Faculty Member, Harvard Medical SchoolJohn L Brusch, MD, FACP is a member of the following medical societies: American College of Physicians, Infectious Diseases Society of AmericaDisclosure: Nothing to disclose.
Recommended Reading: Food And Drink For Urinary Tract Infection
How Long Will The Effects Last
For most UTIs, the symptoms go away within 24 hours after you begin treatment. Take all of the medicine your healthcare provider prescribes, even after the symptoms go away. If you stop taking your medicine before the scheduled end of treatment, the infection may come back.
Without treatment, the infection can last a long time. If it is not treated, the infection can permanently damage the bladder and kidneys, or it may spread to the blood. If the infection spreads to the blood, it can be fatal.
When To See A Doctor

It is always recommended to see a doctor as soon as you experience symptoms of a UTI because leaving a UTI untreated increases the risk of kidney infection or more severe complications.
Additionally, if you exhibit signs of a kidney infection, it is recommended to seek urgent care services.
While there is OTC medication aimed toward UTIs, the only way to get an oral antibiotic is with a prescription.
Also Check: Urinary Catheterization Procedure In Female
Key Points About Urinary Tract Infections
- Urinary tract infections are a common health problem that affects millions of people each year. These infections can affect any part of the urinary tract.
- Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
- The most common symptoms of UTIs include changes in urination such as frequency, pain, or burning urine looks dark, cloudy, or red and smells bad back or side pain nausea/vomiting and fever.
- Antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Other treatments may include pain relievers, and drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Other things that can be done may help reduce the likelihood of developing UTIs.
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will use the following tests to diagnose a urinary tract infection:
- Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is used to determine the type of bacteria in your urine. This is an important test because it helps determine the appropriate treatment.
If your infection does not respond to treatment or if you keep getting infections over and over again, your doctor may use the following tests to examine your urinary tract for disease or injury:
- Ultrasound: In this test, sound waves create an image of the internal organs. This test is done on top of your skin, is painless and doesnt typically need any preparation.
- Cystoscopy: This test uses a special instrument fitted with a lens and a light source to see inside the bladder from the urethra.
- CT scan: Another imaging test, a CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes cross sections of the body . This test is much more precise than typical X-rays.
Recommended Reading: Is Urinary Incontinence A Normal Part Of Aging