Relationship Between Antibiotic Resistance And Virulence Or Phylogenetic Background In Upec
Previous studies show that in E. coli isolates from patients with urosepsis, resistance to antimicrobial agents such as ampicillin, sulfonamides, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and streptomycin is negatively associated with virulence and a phylogenetic group B2, but positively associated with host compromise . There is a similar negative association between FQ resistance and VFs and group B2 . This suggests that, resistance may provide a greater fitness advantage to E. coli than traditional VFs or a group B2 background, allowing them to cause infections in compromised hosts with weakened defenses who are frequently exposed to antibiotics.
Seek Medical Attention For Utis
It is important to seek medical attention if you think you may have a UTI particularly if you think you may have a bladder or kidney infection, both of which are very serious conditions. Early treatment of urinary infection can help to prevent infection spreading to the bladder or kidneys.
Your doctor will test your urine to check which micro-organism is present. Urinary tract infections usually respond quickly and well to antibiotics.
Mechanisms Of Action And Resistance To Anti
Because tetrahydrofolate is required to make both purines and pyrimidines, its synthesis is important for understanding the mechanism of cotrimoxazole, which is a combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. Trimethoprim is a structural analog of dihydrofolic acid that competitively inhibits the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid. Sulfamethoxazole, which has a sulfonyl group instead of a carbonyl group, is an analog of para-aminobenzoic acid that competitively inhibits the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid. Over two decades after its first use in 1974 , this drug has remained the first-line treatment for uncomplicated UTIs in adults . Because of the widespread resistance to the drug, cotrimoxazole has been gradually replaced by fluoroquinolones since approximately the year 2000 . The mechanism of bacterial resistance to cotrimoxazole is due to drug efflux pumps, the degradation of the antibiotics by enzymes, the alteration of antibiotic binding targets, and the loss of drug entry points, all of which can occur via chromosomal mutations or the acquisition of plasmids .
OXA family -lactamases hydrolyze oxacillin at a faster rate than that observed for benzylpenicillin. OXA-related -lactamases have recently been identified in plasmids from E. coli that exhibit low-level resistance to imipenem and resistance to ertapenem. Plasmid-mediated dissemination of OXA-48-like carbapenemases in E. coli has been observed in many European countries .
Read Also: What Is Best Treatment For Urinary Tract Infection
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
You May Like: Royal Canin Urinary Tract Food
Prevention Of Infectious Disease Is The Best Option For Antibiotic Resistance Control Especially In Recurrent Uti
Recurrent UTI is defined as recurrence of uncomplicated and/or complicated UTIs, with a frequency of at least three UTIs/year or two UTIs in the last six months. Generally, UTIs differ from other infectious diseases in which pathognomonic sources are transmitted from the outside, such as sexually transmitted infections or respiratory tract infections. The bacteria that cause UTIs have characteristics that are typically symbiotic with the human body, and when an imbalance arises for some reason, it can result in infections of the urinary tract . Even individuals who do not have a urinary system abnormality are at risk to become infected, and some individuals suffer from repeated UTIs without apparent cause. Moreover, a person with a structural or functional abnormality of the urinary tract is at a higher risk for urinary tract infections. For this reason, efforts to manage the exposure of humans to infectious agents can reduce the incidence of urinary tract infections, and these efforts may help to slow the development of antibiotic resistance .
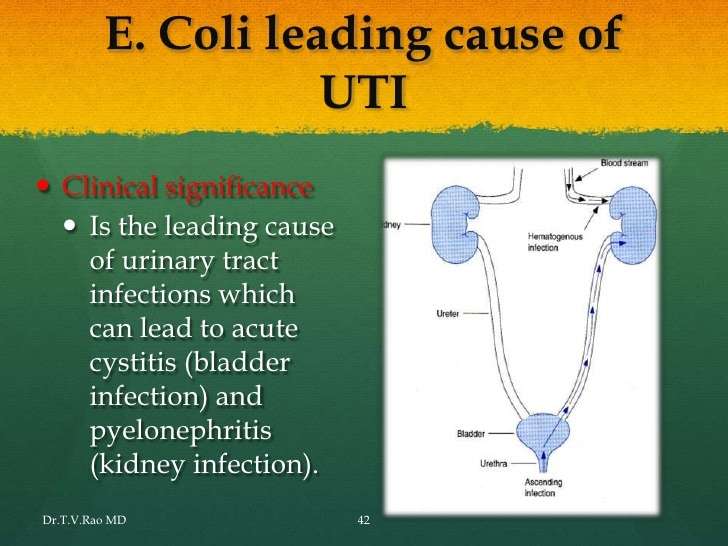
When E Coli Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, is the cause of approximately 85% of urinary tract infections . E. coli can develop in raw produce, unpasteurized fruit juice, raw and undercooked beef, and contaminated water. In most cases, individuals with healthy immune systems do not experience negative symptoms when exposed to E. coli. If an individual has a weakened immune system, he or she can become ill from E. coli exposure. One of the ways a victim can suffer from this type of food poisoning is a UTI.
UTI Symptoms
- Blood in the urine, which can cause it to appear red or brown
- An unusually foul smell to the urine
- Back pain
- An overwhelming, persistent urge to urinate
- Painful urination and
- Discharge from the urethra.
It can be easy to mistake UTI symptoms for symptoms of other conditions. This is especially common with older UTI patients and women who might mistake UTI symptoms for PMS and menstruation.
How E.Coli can Cause a UTI
Treating a UTI
UTIs must be treated with antibiotics. It is a common belief that cranberry juice and other products can treat UTIs, but the truth is that these products can only lessen an individual’s risk of developing one, and even then, data is mixed. They cannot treat an existing infection.
Work with an Experienced Libertyville Food Poisoning Attorney
Recommended Reading: What’s The Signs Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Other Than Diarrhea Are There Serious Illnesses Caused By Stec Strains Of E Coli
Most cases of E. coli infections are mild and do not cause a serious health risk. Cases resolve on their own with rest and drinking plenty of fluids. However, some strains can cause severe symptoms and even life-threatening complications, such as hemolytic uremic syndrome, which can lead to kidney failure and death.
Who Is Prone To Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections may affect anybody, although they are more frequent in women. UTIs are the most common bacterial infection encountered in the outpatient setting: by the age of 24, one in every three women will have a UTI that requires antibiotic therapy, and half of all women will have at least one UTI in their lifetime.
Recommended Reading: What Is Urinary Tract Health
What Happens There Is Resistance To Antibiotics
As time goes by, more and more E. coli bacteria become resistant to antibiotics.
In fact, between 2000 and 2010, scientists discovered that the amount of E. coli resistance to common antibiotics increased substantially.
This is a real problem. If antibiotics do not work, we may have a real problem when an infection becomes severe.
Why is it happening?
First, antibiotics are being widely prescribed. About 80% of people who come to the doctor with sinus problems will receive a round of antibiotics, although it is entirely possible that it is a virus and not a bacterial infection.
We are also increasing our exposure to the foods we eat. Antibiotics are also prescribed strongly to animals . Then we eat those animals.
One study showed that the prevalence of E. coli resistant to antibiotics in broilers is quite high.
So what else can we do with E. coli bacteria and urinary tract infections?
Is there any hope for treating urinary tract infections when antibiotics are less and less effective?
Absolutely! Here are some natural health boosters that have been scientifically proven to help urinary tract infections:
Take a D-mannose supplement: this natural sugar was observed in a study of more than 300 women. Some received D-mannose, other antibiotics and others no treatment.
In six months, the D-mannose group only had a recurrent urinary infection rate of 14.6% the group of antibiotics had 20.4%. In addition, the D-mannose group showed fewer side effects.
About The Author
Causes Of E Coli Infection In Cats
While all E. coli infections are caused by an overgrowth of pathogenic strains of the bacteria, each manifestation of the disease has its own method of transmission.
With UTIs, introduction of bacteria from the anus to the urinary tract is often thought to be caused by the routine act of a cat performing normal grooming, such as licking one spot and then the next. While this does not generally cause a problem, the bacteria may grow beyond normal proportions in older cats with weaker immunity, or those with underlying diseases.
Gastrointestinal E. coli can usually be traced to the ingestion of undercooked or raw foods. Outdoor cats who hunt and eat prey are particularly prone, but commercial pet foods are sometimes to blame. Raw meat diets can also be problematic, and many veterinarians warn against feeding raw meat.
Pyometra occurs when there is a bacterial overgrowth in the uterus triggered by hormonal changes. Pyometra has been known to arise even when no external source of exposure can be identified.
Newborn kittens sometimes develop colibacillosis after E. coli exposure, which can occur in a number of ways:
- In utero via bacteria in the mother’s system
- During birth from bacteria in the birth canal
- While nursing from infected mammary glands
- When housed in unsanitary conditions
You May Like: Does Cvs Minute Clinic Do Urinary Tract Infections
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
How Many Strains Of E Coli Cause Diarrhea
Six different strains of E. coli are known to cause diarrhea. These strains are:
- Shiga toxin-producing E. coli : This is the bacteria most commonly known for E. coli food contamination. This strain is also called enterohemorrhagic E. coli and verocytotoxin-producing E. coli .
- Enterotoxigenic E. coli : This strain is commonly known as a cause of travelers diarrhea.
- Enteroaggregative E. coli .
- Diffusely adherent E. coli .
Read Also: Medicine To Take For Urinary Tract Infection
Do I Have A Urinary Tract Infection Or Something Else
If you have pain or discomfort when you urinate, its possible that you have a urinary tract infection. But what you may not realize is that other conditions can cause similar symptoms. And since these conditions have different treatments, its important to know what the actual underlying problem is.
Here we discuss what a urinary tract infection is, how its treated, and other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
What is a urinary tract infection?
A urinary tract infection often called a UTI is an infection of any part of your urinary system. This includes your:
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Bladder
- Urethra
UTIs can be classified as involving the upper tract or the lower tract . Since infections usually come into the urethra from the outside, most infections involve the lower tract. UTIs can affect people of all ages, and they tend to be more common in women. In fact, some studies have shown that women are eight times more likely than men to develop a UTI.
The most common cause of a UTI is a bacteria called Escherichia coli , which causes more than 80% of infections outside of the hospital. Other types of bacteria and certain types of fungi and viruses can also cause UTIs.
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms usually bacteria that enter the urethra and bladder, causing inflammation and infection. Though a UTI most commonly happens in the urethra and bladder, bacteria can also travel up the ureters and infect your kidneys.
More than 90% of bladder infection cases are caused by E. coli, a bacterium normally found in the intestines.
Don’t Miss: Artificial Urinary Sphincter Surgery Recovery
Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs result in considerable economic and public health burdens and substantially affect the life quality of afflicted individuals. Currently, antibiotics such as trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin are the most commonly recommended therapeutics for UTIs. However, increasing rates of antibiotic resistance and high recurrence rates threaten to greatly enhance the burden that these common infections place on society. Ideally, alternative therapies will be established that will be recalcitrant to the development of resistance. Many promising approaches are being developed, from leveraging what we have learned about the basic biology of UTI pathogenesis to specifically target virulence pathways. These antivirulence therapeutics should theoretically allow us to effectively neutralize, or disarm, the capacity of UTI pathogens to cause disease, without altering the gut commensal microbiota, because antivirulence therapeutics target processes that are critical for UTI pathogenesis but that are not required for the essential processes of growth and cell division .
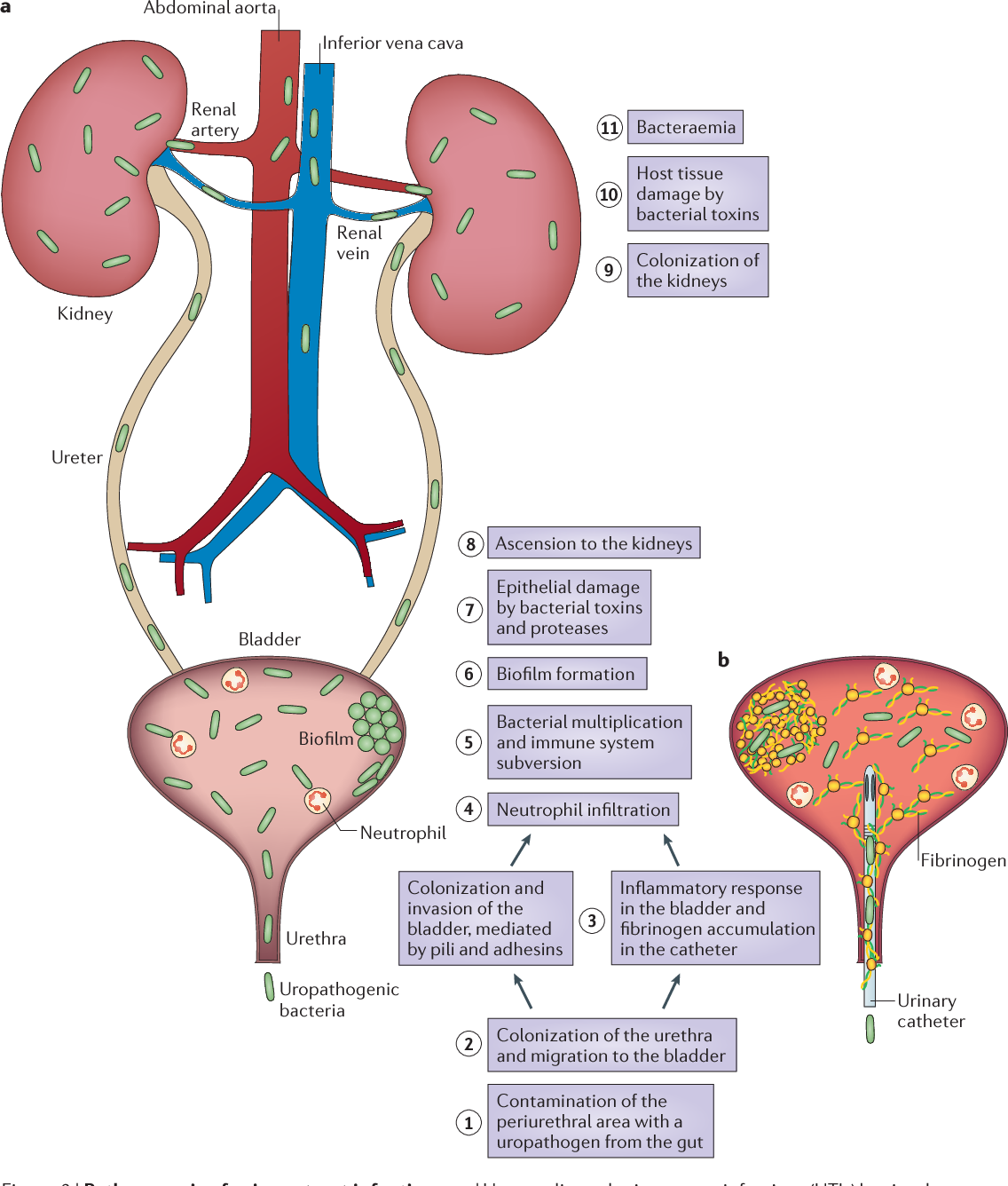
Risk Factors For Acquisition Of Antimicrobial Resistance In E Coli
Colonization has also been suggested to be risk factor for the selection of antimicrobial resistance. Most clinical factors associated with colonization and infection by ESBL-producing organisms involve healthcare exposure, such as hospitalization, residence in a long-term care facility, hemodialysis use, and the presence of an intravascular catheter . In a study of Dutch individuals who had no ESBL colonization prior to international travel, 34 percent overall and 75 percent of individuals who travelled to southern Asia became colonized by ESBL-producing strains following their travels . Another report showed an ESBL prevalence of 49.0-64.0% for residents and 5.2-14.5% for staff . Thus, travelers to endemic areas, hospitalized patients, care-givers in health care unit, guardians of in-patients, and hospital workers, including residents, are at an increased risk of colonization by antimicrobial resistant bacteria, showing the importance of environmental hygiene and taking precautions against contact with MDR bacteria. Once a cluster of resistant bacteria colonizes any part of the human body, it is possible that the bacteria will grow and horizontally transfer plasmid-encoded resistance genes to other susceptible bacteria or to different species .
Finally, indwelling catheters, which lead to complicated UTIs, are a known a risk factor for the acquisition of MDR bacteria .
Don’t Miss: Baking Soda For Urinary Tract Infection
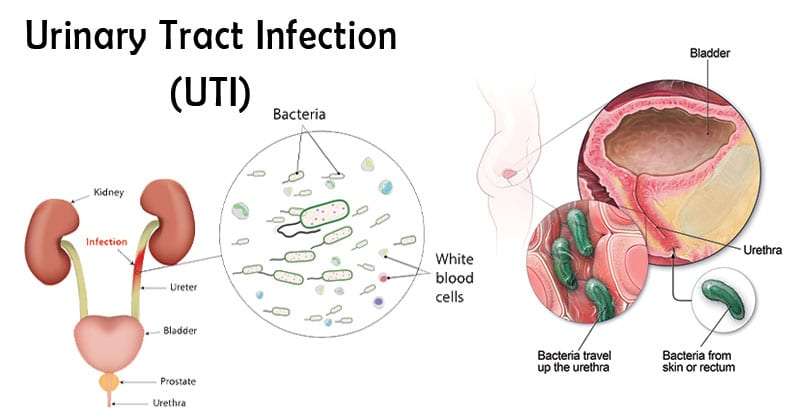
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection is an infection of the urinary system. This type of infection can involve your urethra , kidneys or bladder, .
Your urine typically doesnt contain bacteria . Urine is a byproduct of our filtration systemthe kidneys. When waste products and excess water is removed from your blood by the kidneys, urine is created. Normally, urine moves through your urinary system without any contamination. However, bacteria can get into the urinary system from outside of the body, causing problems like infection and inflammation. This is a urinary tract infection .
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Toxins And Proteases
The UPEC pore-forming toxin HlyA has also received attention as a potential vaccine target and was evaluated in a mouse model of pyelonephritis to assess protection against renal damage,. Vaccination with HlyA reduced the incidence of renal scaring compared with controls however, it did not protect against UPEC colonization of the kidneys. In addition, in a mouse model of UTI, vaccination with the P. mirabilis haemolysin, HpmA, did not provide protection against bacterial colonization. However, vaccination with Pta, an alkaline protease with toxic effects towards epithelial cells, displayed promising results in a mouse model of UTI, protecting against upper UTI, although bacterial burdens in the bladder remained unaffected. Thus, although haemolysins and proteases might provide effective vaccine targets for preventing upper UTIs, additional studies are needed to determine the effectiveness of these enzymes as targets for vaccines.
Also Check: What Do You Do For A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infections
A UTI can cause the following symptoms:
How Do You Get Infected
You can become infected when you swallow even a small amount of E. coli bacteria. Among the ways this can happen:
- Ground meat: You eat ground meat that carries E. coli, and the meat wasnât cooked enough to kill the bacteria. When meat is processed, sometimes bacteria from the animalsâ intestines make their way into the meat. This happens more with ground meat because it comes from more than one animal.
- Untreated milk: You drink unpasteurized milk, which hasnât been heated to kill bacteria. E. coli can get into the milk from the cowâs udder or from milking equipment.
- Vegetables and fruit: You might eat fresh vegetables or fruit thatâs been tainted by water that has the bacteria. This happens most often when manure from nearby animals mixes with the water supply.
- Other foods and beverages: You might also get E. coli from unpasteurized fruit juices and yogurt and cheese made from raw milk.
- Water: You swallow water that contains E. coli, perhaps while swimming in a pool, lake, or pond.
- Other people: You might get E. coli from another person who has it, such as a child. The bacteria can be passed to you if you clean up after an infected person and then donât wash your hands really well before you touch your mouth.
- Animals: It can be found at petting zoos or animal exhibits at fairs.
You can also contaminate food in your own kitchen if you allow a knife or cutting board that has touched uncooked meat to come into contact with food that will be eaten raw .
Recommended Reading: Foods For Healthy Urinary Tract