Pain Relief Vs Antibiotics
New Zealand guidelines do not currently support the use of NSAIDs in favour of antibiotics. The results of two recent large randomised trials found that antibiotics reduce symptom duration on average by around 2 days, and reduce the risk of pyelonephritis. On the beneficial side, around half to two thirds of women who use NSAIDs do not end up needing antibiotics. Shared decision making should used in conjunction with your patient. Kronenberg A, Bütikofer L, Odutayo A, et al. Symptomatic treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in the ambulatory setting: randomised, double blind trial. BMJ 2017 359:j4784.
Who Else Has A Higher Risk Of A Uti
There are a handful of other factors that can boost your odds of developing a UTI. They include:
- Age
- Uncontrolled or inadequately controlled diabetes
- Certain forms of birth control, such as diaphragms that put pressure on the urethra
- Being sexually active, particularly with a new partner
- Anatomical abnormalities or blockages along the urinary tract, such as kidney stones
- Enlarged prostate
Because UTIs are so common, theyre also subject to a greater spread of misinformation than other conditions. Contrary to myth, you cannot get a UTI from using tampons or sanitary napkins, wearing tight clothing, riding a bike, or failing to urinate after intercourse.
What Is The Best Treatment For Urinary Tract Infection Utis
In most cases, the best treatment for a urinary tract infection is a course of antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescription medications that kill bacteria that cause the infection.
Which antibiotics are prescribed depend on the type of bacteria responsible for the UTI, which can be detected via a urine culture and sensitivity test.
Also Check: Stages Of Urinary Tract Infection
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
Ask The Doctor: Do I Need To Take Antibiotics For A Urinary Tract Infection
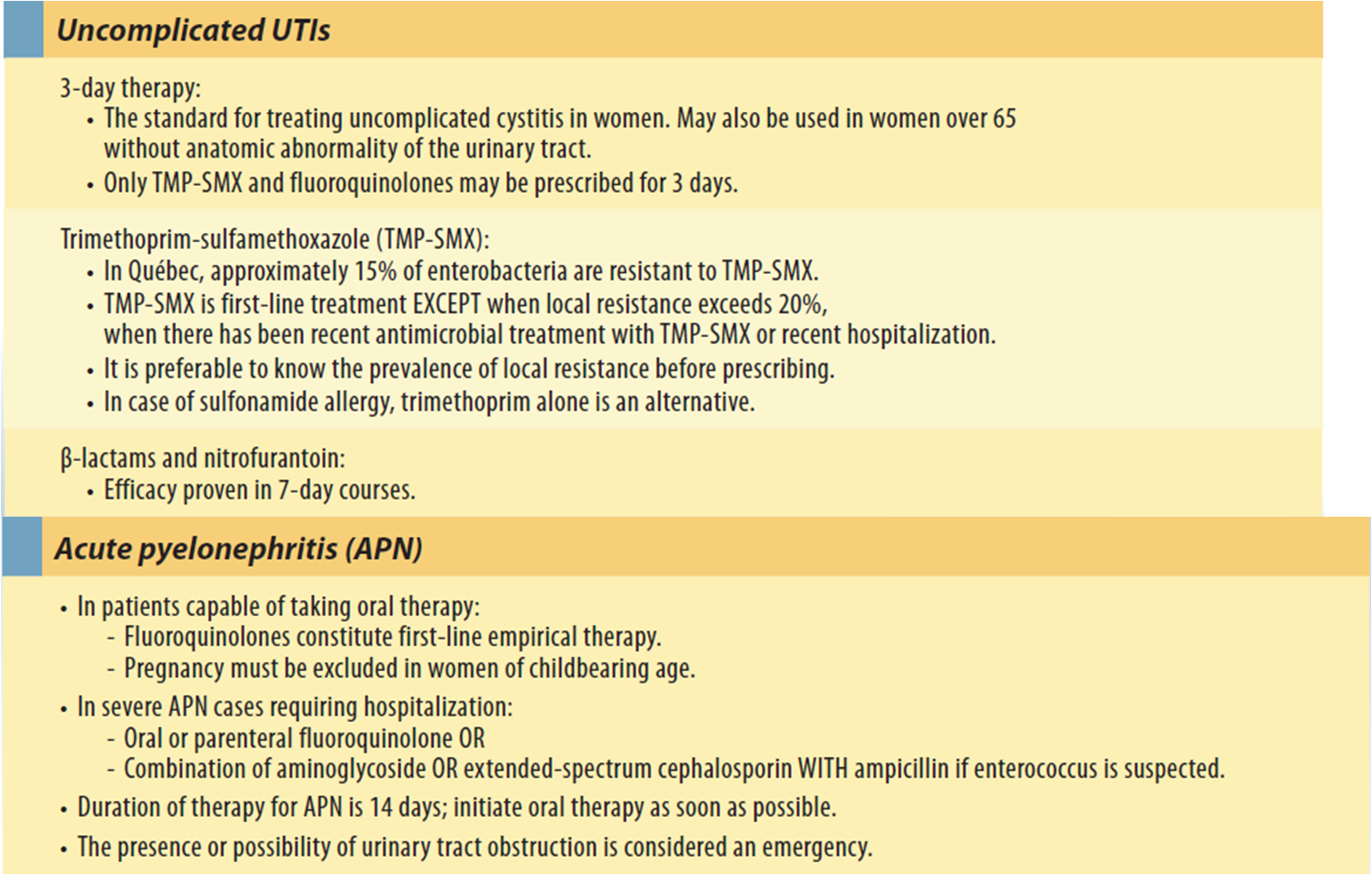
Q.Every time I get a urinary tract infection, my doctor prescribes antibiotics. Is there any other way to treat my infections?
A. Urinary tract infections are a common affliction in women, especially as we get older. Antibioticsusually a three-day courseare the standard treatment for women younger than 65. Once you are older than 65, your doctor will likely treat you for seven to 10 days. Although there have been studies in which women’s UTIs went away on their own without treatment, taking antibiotics prevents the infection from spreading to your kidneys, which can lead to complications such as permanent kidney damage.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctor’s visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
You May Like: Best Probiotic For Urinary Tract Infection
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Can A Urinary Tract Infection Be Prevented
Many methods have been suggested to reduce or prevent UTIs. The single most important prevention measure is increased fluid intake. Many people develop UTIs simply because they do not drink enough fluids. Some of these are considered home remedies and have been discussed . There are other suggestions that may help prevent UTIs. Good hygiene for males and females is useful. For females, wiping from front to back helps keep pathogens that may reside or pass through the anal opening away from the urethra. For males, retracting the foreskin before urinating reduces the chance of urine lingering at the urethral opening and acting as a culture media for pathogens. Incomplete bladder emptying and resisting the normal urge to urinate can allow pathogens to survive and replicate easier in a non-flowing system. Some clinicians recommend washing before and urinating soon after sex to reduce the chance of urethritis and cystitis. Many clinicians suggest that anything that causes a person irritation in the genital area may encourage UTI development. Wearing underwear that is somewhat adsorptive may help wick away urine drops that otherwise may be areas for pathogen growth.
Recommended Reading: Hills Urinary Care C D
How To Cope With Side Effects
What to do about:
- feeling sick take nitrofurantoin with or after a meal or snack. It may also help if you avoid rich or spicy food.
- being sick and diarrhoea drink lots of fluids, such as water or squash to avoid dehydration. Take small, frequent sips if you feel sick. Signs of dehydration include peeing less than usual or having strong-smelling pee. Do not take any other medicines to treat diarrhoea or vomiting without speaking to a pharmacist or doctor.
- loss of appetite eat when you would usually expect to be hungry. If it helps, eat smaller meals more often than usual. Snack when youre hungry. Have nutritious snacks that are high in calories and protein, such as dried fruit and nuts.
- headaches make sure you rest and drink plenty of fluids. Do not drink too much alcohol. Painkillers you can buy without a prescription, such as paracetamol and ibuprofen, are safe to take with nitrofurantoin. Speak to your doctor if these do not help with the headaches or the headaches are severe.
- dizziness or feeling sleepy if nitrofurantoin makes you feel dizzy, stop what youre doing and sit or lie down until you feel better.
Is It Possible To Prevent Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections With A Vaccine
Currently, there are no commercially available vaccines for UTIs, either recurrent or first-time infections. One of the problems in developing a vaccine is that so many different organisms can cause infection a single vaccine would be difficult to synthesize to cover them all. Even with E. coli causing about most infections, the subtle changes in antigenic structures that vary from strain to strain further complicates vaccine development even for E. coli. Researchers are still investigating ways to overcome the problems in UTI vaccine development.
Recommended Reading: Men’s Urinary Tract Problems
Can I Treat A Uti Without Antibiotics
UTI treatment without antibiotics is NOT usually recommended. An early UTI, such as a bladder infection , can worsen over time, leading to a more severe kidney infection . However, a small study has suggested early, mild UTIs might clear up on their own. It’s always best to check with your doctor if you are having UTI symptoms.
Pregnant women should always see a doctor as soon as possible if they suspect they might have a UTI, as this can lead to a greater risk of delivering a low birth weight or premature infant.
What Are Some Common Side Effects Of Uti Medicine
As with any medication, there are always potential side effects. Common side effects associated with UTI medications include sensitivity of the skin to sunlight, changes in urination, seizures, confusion, uneven heartbeat, and diarrhea or stomach problems. Contact your doctor or pharmacist if your side effects persist or worsen.
UTI medications may also cause allergic reactions that result in hives or difficulty breathing. Allergic reactions can be life-threatening. You should seek immediate medical care if you believe you are experiencing an allergic reaction.
This list of side effects is not comprehensive. Ask a healthcare professional for more details regarding the possible side effects of a particular medication.
Recommended Reading: What Clears Up A Urinary Tract Infection
Who Can And Cannot Take Nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin can be taken by adults including pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Nitrofurantoin is not suitable for everyone. To make sure its safe for you, tell your doctor if you have:
- ever had an allergic reaction to nitrofurantoin or any other medicines in the past
- either of the rare inherited conditions: porphyria or glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
- severe kidney disease
- any illness causing severe weakness
- anaemia or vitamin B deficiency
Related Resources For Utis

* Prescription savings vary by prescription and by pharmacy, and may reach up to 80% off cash price.
Pharmacy names, logos, brands, and other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This article is not medical advice. It is intended for general informational purposes and is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. If you think you may have a medical emergency, immediately call your physician or dial 911.
Also Check: How Does Myasthenia Gravis Affect The Urinary System
Benefits Of Antibiotics For Utis
Antibiotics are the standard treatment for UTIs because they kill the bacteria responsible for the infections. Most UTIs develop when bacteria enter the urinary tract from outside the body. The species most likely to cause UTIs include:
- E. coli, which cause of up to
- abnormal liver function, as indicated with testing
More severe risks of using antibiotics include:
How Is A Uti Diagnosed
To diagnose a UTI, your GP will examine you and ask you questions about your general health. Sometimes that might be enough to diagnose a UTI. Your doctor may want you to provide a urine sample to identify what bacteria is causing the infection. Your doctor may also do a blood test and check your temperature and heart rate.
Read Also: Home Remedy For Urinary Tract Infection In Goats
Antibiotics Used To Fight Kidney Infection
Many individuals need to know what prescription antibiotics are used for kidney infection? There are many kinds of over-the-counter medicine for kidney infection that treat the illness in various methods depending on the severity of the case, the bacteria involved, and the patients history, consisting of medication allergies. Dont rely on natural home remedy alone to look after kidney infections as bacteria growth can result in even worse conditions. More information on the main kinds of antibiotics administered are noted below.
Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin group of drugs and is a widely utilized antibiotic to deal with infections triggered by bacteria. Using amoxicillin for kidney infection will avoid bacteria from growing in addition to kills them off. It is typically taken two times a day. Amoxicillin is also a typical drug used to deal with bronchitis, pneumonia, and to avoid chlamydia throughout pregnancy. It is safe for pregnant women and can avoid bacterial infection in babies. It can be taken orally, as a dry tablet, chewable tablet, capsule, or liquid preparation.
How Do I Know If My Particular Strain Of Uti Is Resistant To A Particular Drug
The only way is to get a urine culture. The lab results will identify the germ and what would be effective in treating the infection. But it can take several days to get the results.
Most patients want an immediate prescription so doctors usually make a best-guess determination of what drug will work given a patients symptoms and history.
The importance of history cannot be overstated if you have had a previous U.T.I., a previous resistant U.T.I., or have traveled outside the country, your history can help a doctor decide which drug to use.
Increasingly, experts tell us that you should ask for a culture when you go in for a U.T.I. treatment, even if you get an immediate prescription. The culture will allow a doctor to change the drug if the first one does not work.
That said, there is an important catch about when to do a urine culture. Often, it will show bacteria in the bladder even when an infection is not present. Some amount of bacteria is normal. The Infection Disease Society of America cautions doctors against doing cultures when symptoms of a U.T.I. are not present. The culture likely presence of bacteria can then lead to prescription of unnecessary antibiotics, contributing to the rise of resistance through overuse of the drugs.
Finally, some U.T.I.s, even when there are symptoms, can clear up on their own. This is one of many reasons to seek the care of an informed professional.
Read Also: What Treatment Options Are Available For Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Tract Infections And Antibiotic
The standard treatment for most urinary tract infections is antibiotics. However, some E. coli strains are resistant to most antibiotic drugs. These strains are called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase -producing E. coli. Researchers found that UTIs caused by E. coli, which are resistant to ciprofloxacin, increased from 3-17 percent in 2000 up to 2010. Moreover, E. coli strains that are resistant to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole also increased from 18-24 percent.
What Is The Prognosis For A Urinary Tract Infection
A good prognosis is usual for spontaneously resolved and quickly treated UTIs. Even patients that have rapidly developing symptoms and early pyelonephritis can have a good prognosis if quickly and adequately treated. The prognosis begins to decline if the UTI is not quickly recognized or treated. Elderly and immunosuppressed patients may not have the UTI recognized early their prognosis may range from fair to poor, depending on how much damage is done to the urinary tract or if complications like sepsis occur. Like adults, most adequately treated children will have a good prognosis. Children and adults with recurrent UTIs may develop complications and a worse prognosis recurrent UTIs may be a symptom of an underlying problem with the urinary tract structure. These patients should be referred to a specialist for further evaluation.
Read Also: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Antibacterial Protection
Determinants Of Antibiotic Prescribing
Results of uni- and multivariable analyses for guideline recommended treatments of uUTI are reported in Table . In multivariable analysis, only increasing age of the GP was significantly associated with reduced odds of prescribing any guideline recommended antibiotic treatment or a guideline adherent treatment .
Table 4 Logistic regression analysis for guideline recommended and guideline adherent antibiotic prescriptions in uUTI
Including all UTI patients, the diagnosis of a cUTI and the sex of the patient were additionally identified as significant determinants associated with reduced odds of prescribing fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin or TMP/SMX. In addition, the age of the GP and the diagnosis of a cUTI were significant associated with increased odds of prescribing any FC antibiotic in multivariable analysis. Particular noteworthy are the relative high intra-cluster correlation coefficient in multivariable analysis . Differentiating antibiotic prescribing patterns between patients with a uUTI and cUTI, a female gender of the GP in cUTI and increasing age of the GP in uUTI were associated with higher odds of prescribing a FC in multivariable analysis . Analysing determinants for each prescribed antibiotic separately showed results that are more heterogeneous and were provided in Supplemental Table c.
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection

A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
Don’t Miss: How To Clean My Urinary Tract
Antibiotics Or Nsaids For Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection
Pain relief and a delayed antibiotic prescription is a pragmatic and balanced approach
Urinary tract infection is second only to respiratory tract infection in the use of antibiotics. It is an international priority to rationalise antibiotic use in primary care given the dangers of antibiotic resistance and the evidence that prescribing in primary care is likely to be a key driver of antibiotic resistance.1 The trial by Kronenberg and colleagues 2 provides a welcome addition to the literature, providing a head-to-head comparison of an antibiotic compared with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and extending the findings of a previous German trial of antibiotics compared with the NSAID ibuprofen.3
The results show that an initial prescription for antibiotics is superior to NSAIDs for symptomatic management and inferior in terms of net antibiotic usage. However, the difference in symptom control may not be as stark as the 27% absolute difference in symptom resolution by day 3 would suggest, since the reduction in symptom score
Antibiotics For Bladder Infection
This article gives you a list of the various antibiotics used to treat bladder infections. The same also outlines a few tips on how to prevent this infection.
This article gives you a list of the various antibiotics used to treat bladder infections. The same also outlines a few tips on how to prevent this infection.
Bladder infections can be painful and annoying. Their main symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating, frequent urges to urinate, abdominal cramps, and cloudy and strong-smelling urine. Women are more affected by these infections than men. As annoying as bladder infections may be, they can be easily cleared up if treated early. People who keep getting these infections may be at risk of kidney infection. Such cases, however, are rare. Depending on how severe a bladder infection is, its causal pathogen, and the health of the affected person, antibiotics are recommended for the treatment.
*This information should NOT, in any way, substitute or be used in place of, the advice of a qualified medical practitioner. The same is intended only for educational purposes.
Antibiotics Prescribed for Bladder InfectionsThe following gives you the generic names of antibiotics commonly prescribed for the treatment of bladder infections. These drugs are available only with a doctors prescription. Some of the side effects caused by these drugs have also been mentioned below.
#1. Ciprofloxacin
How Can You Prevent Bladder Infections
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Or Bladder Infection