How To Help Your Loved One Avoid Utis
Do you give the older adult in your life cranberry juice or probiotics to prevent a UTI? These products wont hurt them, but whether theyll help is unclear.
We dont have enough research to support their effectiveness in UTI prevention, although their medical benefits cant be ruled out completely, says Dr. Goldman.
Instead, he recommends these tried-and-true prevention strategies:
- Encourage sufficient fluid intake
- Promote genital and urinary hygiene
- Ask the doctor about low-dose vaginal cream for postmenopausal women
Dr. Goldman says researchers are also studying D-Mannose for UTI prevention. The supplement, which has few side effects, sticks to bladder receptors that normally attract the E. coli bacteria usually responsible for UTIs.
Researchers also believe D-Mannose may keep bad bacteria from colonizing the digestive tract, which can harbor the bacteria responsible for UTIs in women.
Following these tips should help your aging relative stay healthy, productive and out of the hospital.
Role Of Urinary Testing In Diagnosing Symptomatic Utis In Older Adults
The utility of urinary dipstick testing, urinalysis, and urine culture is challenging in the older adult because of the high prevalence of bacteriuria and pyuria that may not be clinically important. As in the case of Mrs M, all urinary studies to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, pyuria, and bacteriuria over a 2-year period were positive.
The urinary dipstick, although easy and convenient, has variable test characteristics. Sensitivity and specificity for urinary dipstick testing to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or both vary in older adults by the age of study participants, clinical suspicion of UTI, and laboratory definition for UTI used . The sensitivity and specificity for a positive dipstick test in older patients with was 82% and 71% , respectively. Other studies of elderly patients showed the negative predictive value for dipstick testing ranges from 92% to 100%., Urinary dipstick analysis should be performed in the out-patient setting primarily to rule out and not to establish a diagnosis of UTI. In a patient with a low pretest probability of UTI, if the dipstick is negative for leukocyte esterase and nitrites, it excludes the presence of infection and mitigates the need to obtain urinalysis and urine culture . High false-positive rates limit dipstick testing effectiveness. Further urinary studies are warranted for patients with a high pretest probability of UTI.
When Should People Seek Medical Care For A Uti
Any adult or child who develops any of the symptoms of a urinary tract infection needs to be evaluated by a medical professional, preferably within 24 hours. Most medical offices can test urine for infection by using a quick urine “dipstick” test.
- Someone who has symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection should call a health care professional for an appointment, preferably on the same day that symptoms are recognized.
- Someone who has symptoms of an upper urinary tract infection involving the kidneys should call a health care professional immediately. Depending on the situation, he or she will recommend either a visit to the office or a hospital emergency department.
If someone has symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection and any of the following applies, he or she may be at risk for complications of the urinary tract infection.
- Vomiting and inability to keep down clear fluids or medication
- Not better after taking antibiotics for two days
- Pregnant
- Having diabetes or another disease that affects the immune system
- Taking medication that suppresses the immune system such as cancer chemotherapy
Infants, children, and elderly people with any of the signs and symptoms of UTI should see their health care professional as soon as possible or go to an emergency department for evaluation.
- People who have blood in the urine
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Male Urinary Tract Infection
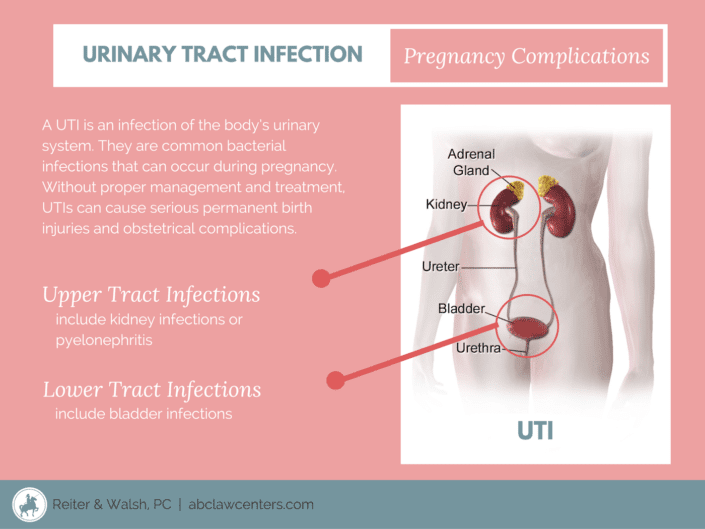
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the body’s liquid waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body removing waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
Join Our Community Sign Up To Our Newsletter

Restorative Medicine
Restorative medicine is an evidence based, scientifically sound medical sub-speciality. Its goal is to extend lifespan, prolong youthspan, and healthspan, through early detection, prevention, treatment, and reversal of all age-related dysfunctions, disorders, and disease, in both men and women alike. Restorative medicine has been embraced by thousands of physicians. Menopause Woman does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. See more information.
You May Like: Z Pack Urinary Tract Infection
Who To See For Urinary Tract Infection
Your primary care providerusually a family doctor, nurse practitioner, or internal medicine physiciancan diagnose and treat urinary tract infections. However, if you have frequent UTIs, your healthcare provider may refer you to a urologist, a physician who specializes in the urinary system, or a urogynecologist, a physician who specializes in treating women urinary and reproductive systems. If your UTIs commonly turn into kidney infections, you may also see a nephrologist, or kidney doctor.
The sooner you notice the symptoms of a urinary tract infection and begin treatment, the sooner youll feel better. When in doubt, consult your healthcare provider.
Are Some Women More At Risk For Utis
Yes. You may be at greater risk for a UTI if you:1,5
- Are sexually active. Sexual activity can move germs that cause UTIs from other areas, such as the vagina, to the urethra.
- Use a diaphragm for birth control or use spermicides with a diaphragm or with condoms. Spermicides can kill good bacteria that protect you from UTIs.
- Are pregnant. Pregnancy hormones can change the bacteria in the urinary tract, making UTIs more likely. Also, many pregnant women have trouble completely emptying the bladder, because the uterus with the developing baby sits on top of the bladder during pregnancy. Leftover urine with bacteria in it can cause a UTI.
- Have gone through menopause. After menopause, loss of the hormone estrogen causes vaginal tissue to become thin and dry. This can make it easier for harmful bacteria to grow and cause a UTI.
- Have diabetes, which can lower your immune system and cause nerve damage that makes it hard to completely empty your bladder
- Have any condition, like a kidney stone, that may block the flow of urine between your kidneys and bladder
- Have or recently had a catheter in place. A catheter is a thin tube put through the urethra into the bladder. Catheters drain urine when you cannot pass urine on your own, such as during surgery.
Read Also: How Can You Get A Urinary Tract Infection
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Uti Tests And Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a urinary tract infection, go to the doctor. You’ll give a urine sample to test for UTI-causing bacteria.
If you get frequent UTIs and your doctor suspects a problem in your urinary tract, they might take a closer look with an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan. They might also use a long, flexible tube called a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Immediate Relief
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will use the following tests to diagnose a urinary tract infection:
- Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is used to determine the type of bacteria in your urine. This is an important test because it helps determine the appropriate treatment.
If your infection does not respond to treatment or if you keep getting infections over and over again, your doctor may use the following tests to examine your urinary tract for disease or injury:
- Ultrasound: In this test, sound waves create an image of the internal organs. This test is done on top of your skin, is painless and doesnt typically need any preparation.
- Cystoscopy: This test uses a special instrument fitted with a lens and a light source to see inside the bladder from the urethra.
- CT scan: Another imaging test, a CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes cross sections of the body . This test is much more precise than typical X-rays.
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of A Severe Urinary Tract Infection
Common Causes Of Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection or bladder infection occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system. Bacteria typically enter via the urethra and multiply in the bladder.
Factors that contribute to the development of UTI include:
-
Sex: Womens urethras are shorter than mens, so its easier for bacteria to migrate up to the bladder.
-
Age: Post-menopausal women face an additional risk of UTIs because decreased estrogen levels cause changes in the urinary track that increase susceptibility to infection.
-
Urinary tract abnormalities: Some people are born with unusually shaped urinary tracts that cause urine retention and increased the risk of infection.
-
Blockages:Kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can make it difficult to fully empty the bladder, which may enable bacteria to multiply.
-
Suppressed immune system:Cancer treatments that decrease the immune response can increase the risk of UTI. Diabetes also suppresses the immune system and is associated with increased risk of UTI.
-
Catheter use: Some people who are hospitalized, paralyzed or have certain neurological diseases use a flexible tube to empty the bladder. However, contaminating microorganisms can also enter the bladder via the tube and cause a UTI.
What Are Causes And Risk Factors For A Urinary Tract Infection

The urine is normally sterile. An infection occurs when bacteria get into the urine and begin to grow. The bacterial infection usually starts at the opening of the urethra where the urine leaves the body and moves upward into the urinary tract.
- The culprit in at least 90% of uncomplicated infections is a type of bacteria called Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli. These bacteria normally live in the bowel and around the anus.
- These bacteria can move from the area around the anus to the opening of the urethra. The two most common causes of this are improper wiping and sexual intercourse.
- Usually, the act of emptying the bladder flushes the bacteria out of the urethra. If there are too many bacteria, urinating may not stop their spread.
- The bacteria can travel up the urethra to the bladder, where they can grow and cause an infection.
- The infection can spread further as the bacteria move up from the bladder via the ureters.
- If they reach the kidney, they can cause a kidney infection , which can become a very serious condition if not treated promptly.
The following people are at increased risk of urinary tract infection:
The following special groups may be at increased risk of urinary tract infection:
You May Like: Thin Pads For Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
How Do Utis Affect Pregnancy
Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy raise your risk for UTIs. UTIs during pregnancy are more likely to spread to the kidneys.
If you’re pregnant and have symptoms of a UTI, see your doctor or nurse right away. Your doctor will give you an antibiotic that is safe to take during pregnancy.
If left untreated, UTIs could lead to kidney infections and problems during pregnancy, including:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
Also Check: Royal Canin Vet Diet Urinary S O
Is That Burning Sensation A Urinary Tract Infection
Reviewed By:
Melindia Mann, M.S.N, C.N.M., W.H.N.P.-B.C.
Chances are, it has happened to you: You go to the bathroom and feel a burning sensation when you urinate. That feeling is a telltale symptom of a urinary tract infection , and its one that most women are familiar with. UTIs are incredibly common. In fact, the risk of a woman contracting one in her lifetime ranges from 40% to more than 50%.
UTIs are inconvenient and can make a woman feel miserable from the pelvic pain, frequent urination and that burning feeling. Prompt treatment is key to relieving these symptoms and preventing possible complications, such as kidney infection.
Melindia Mann, a womens health nurse practitioner who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of UTIs at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, talks about the common causes of urinary tract infections, how to prevent them and when to see a doctor or practitioner.
Who Is At Risk
Women at greater risk of contracting a UTI:
- are sexually active
- have diabetes
- have urinary incontinence.
Frequent UTIs in women need further assessment. High fever and pain in the back can indicate a kidney infection and this needs urgent medical treatment.
A partner is not at risk of catching a UTI if you have sex. However, the symptoms may be uncomfortable and you may not feel like having sex.
Recommended Reading: How Does Kidney Failure Affect The Urinary System
How Long Does A Uti Last After Treatment With Antibiotics
- Symptoms of lower urinary tract infections usually resolve within 24 hours of starting the medication. The full amount of prescribed antibiotics should be taken even if the symptoms are fully gone.
- Upper urinary tract symptoms will usually take longer to respond to treatment. The patient will usually improve within 24 hours, but it will often take long until all symptoms resolve.
How Do I Know If Its A Urinary Tract Infection
Common symptoms of uncomplicated UTI in women include the following:
- Strong urge to urinate, often resulting in only a small amount of urine
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Pain in the lower abdomen
In addition to these symptoms, urine may appear cloudy, have a strong smell, or contain traces of blood.
If the symptoms below are also present, it is likely a more serious kidney infection, in which case it is important to see a doctor immediately:
- Fever higher than 38.5°C
- Back or side pain
You May Like: What Is The Best Urinary Tract Infection Medicine
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
A Pharmacist Can Help With Utis
You can ask a pharmacist about treatments for a UTI. A pharmacist can:
- offer advice on things that can help you get better
- suggest the best painkiller to take
- tell you if you need to see a GP about your symptoms
Some pharmacies offer a UTI management service and can prescribe antibiotics if they’re needed.
Also Check: Hills Urinary Care C D Multicare
What Are Urinary Tract Infection Risk Factors
There are many risk factors for UTIs. In general, any interruption or impedance of the usual flow of urine is a risk factor for a UTI. For example, kidney stones, urethral strictures, an enlarged prostate, or any anatomical abnormalities in the urinary tract increases infection risk. This is due in part to the flushing or washout effect of flowing urine in effect, the pathogens have to “go against flow” because the majority of pathogens enter through the urethra and have to go retrograde to reach the bladder, ureters, and eventually the kidneys. Many investigators suggest that women are far more susceptible than men to UTIs because their urethra is short and its exit is close to the anus and vagina, which can be sources of pathogens.
People who require catheters have an increased risk as the catheter has none of the protective immune systems to eliminate bacteria and offers a direct connection to the bladder. Catheters that are designed to reduce the incidence of catheter-related infections are available , but are not used by many clinicians because of short-termed effectiveness, cost, and concern about antibiotic resistancedevelopment in bacteria.