Similar Articles In Pubmed
- Review The role of combination medical therapy in benign prostatic hyperplasia.Greco KA, McVary KT. Int J Impot Res. 2008 Dec 20 Suppl 3:S33-43.
- Review EAU guidelines on the treatment and follow-up of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction.Oelke M, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A, Emberton M, Gravas S, Michel MC, N’dow J, Nordling J, de la Rosette JJ, European Association of Urology.. Eur Urol. 2013 Jul 64:118-40. Epub 2013 Mar 13.
- Review Tadalafil – a therapeutic option in the management of BPH-LUTS.Carson CC, Rosenberg M, Kissel J, Wong DG. Int J Clin Pract. 2014 Jan 68:94-103.
- Twelve-week, prospective, open-label, randomized trial on the effects of an anticholinergic agent or antidiuretic agent as add-on therapy to an alpha-blocker for lower urinary tract symptoms.Shin YS, Zhang LT, Zhao C, Kim YG, Park JK. Clin Interv Aging. 2014 9:1021-30. Epub 2014 Jul 10.
- Extended-release tolterodine with or without tamsulosin in men with lower urinary tract symptoms and overactive bladder: effects on urinary symptoms assessed by the International Prostate Symptom Score.Kaplan SA, Roehrborn CG, Chancellor M, Carlsson M, Bavendam T, Guan Z. BJU Int. 2008 Nov 102:1133-9. Epub 2008 May 26.
Diagnosis And Differential Diagnosis
BPH is diagnosed in cases of nonpainful symmetrical swelling of the prostate gland in intact male dogs, with normal hematologic profiles and urinalysis characterized by hemorrhage, at most. Differential diagnoses include squamous metaplasia of the prostate, paraprostatic cysts, bacterial prostatitis, prostatic abscessation, and prostatic neoplasia . These differential diagnoses also increase in frequency with age and, except for squamous metaplasia, can also occur in castrated dogs. As such, these conditions do not necessarily abate or resolve when castration is used for treatment of prostatic enlargement.
What Is The Difference Between Prostate Cancer And Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Prostate cancer is a common type of cancer that develops in your prostate gland. Early-stage prostate cancer rarely causes symptoms. However, as it progresses, it shares many of the same symptoms as BPH. These symptoms include a weak urine flow, pain when ejaculating or peeing and frequent urges to pee. Prostate cancer may spread to your bones, lymph nodes or other parts of your body. Treatment options include radiation therapy and surgery.
BPH symptoms are similar to prostate cancer symptoms. However, BPH isnt cancer, and it doesnt increase your risk of developing cancer. It wont spread to other parts of your body. Treatment options include medicines, surgery and minimally invasive procedures.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection In A Male
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia include a constellation of symptoms that are often progressive, known collectively as lower urinary tract symptoms :
-
Urinary frequency
Pain and dysuria are usually not present. Sensations of incomplete emptying, terminal dribbling, overflow incontinence Types Urinary incontinence is involuntary loss of urine some experts consider it present only when a patient thinks it is a problem. The disorder is greatly underrecognized and underreported. Many… read more , or complete urinary retention Urinary Retention Urinary retention is incomplete emptying of the bladder or cessation of urination. Urinary retention may be Acute Chronic Causes include impaired bladder contractility, bladder outlet obstruction… read more may ensue. Straining to void can cause congestion of superficial veins of the prostatic urethra and trigone, which may rupture and cause hematuria. Straining also may acutely cause vasovagal syncope and, over the long term, may cause dilation of hemorrhoidal veins or inguinal hernias.
B Searching For The Evidence: Literature Search Strategies For Identification Of Relevant Studies To Answer The Key Questions

We will search Ovid Medline, Ovid PsycInfo, Ovid Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials to identify randomized controlled trials for primary health outcomes published and indexed in bibliographic databases. We will attempt to assess long-term or rare harms with nonrandomized controlled trials and large controlled observational studies if RCTs are not available. Our search strategy includes relevant medical subject headings and natural language terms for LUTS/BPH . These concepts were combined with filters to select trials. We will supplement the bibliographic database search with forward and backward citation searching of relevant systematic reviews and other key references. We will update searches while the draft report is under public/peer review.
We will search for grey literature in ClinicalTrials.gov and to identify completed and ongoing studies. We will search for conference abstracts from the past three years to identify ongoing studies. Grey literature search results will be used to identify studies, outcomes, and analyses not reported in the published literature. Information from grey literature will also be used to assess publication and reporting bias and inform future research needs. Additional grey literature will be solicited through a notice posted in the Federal Register and Scientific Information Packets and other information solicited through the AHRQ Effective Health Care Web site.
Recommended Reading: Medicine To Treat Urinary Tract Infection
How Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, ask you questions and perform a physical examination. Part of the physical exam involves a digital rectal exam.
During a digital rectal exam, your healthcare provider will carefully insert their gloved digit into your rectum. Theyll feel the edges and surface of your prostate, estimate the size of your prostate and detect any hard areas that could be cancer.
Your healthcare provider may also order:
- A survey to evaluate the severity of your symptoms.
- A urine flow test to measure the speed of your pee stream.
- A study to detect how much pee remains in your bladder after youve finished peeing.
- A cystoscopy to look into your bladder.
History And Physical Examination
In men with bothersome lower urinary tract symptoms, a history should be performed to establish the severity of symptoms, evaluate for causes other than BPH , and identify contraindications to potential therapies. The American Urological Association Symptom Index is a validated seven-question instrument that can be used to objectively assess the severity of BPH.6
| Clinical finding |
|---|
| Prostate cancer | Mechanical obstruction |
Symptomatic men should have a digital rectal examination to assess the size and contour of the prostate.6 Prostate volume predicts the response to finasteride therapy. Finasteride is more effective if the prostate volume is greater than 40 mL8 . A palpable nodule suggests prostate cancer and requires biopsy. Abnormal sphincter tone suggests a neurologic abnormality, which may contribute to urinary symptoms.6 Cognitive or ambulatory impairment may exacerbate incontinence problems.
Read Also: Cvs Urinary And Prostate Plus
Appendix A: Search Strategy
Surgery Surgery Is Used To Treat Bph When Drug Therapy Stops Workingor To Treat Those Who Can’t Urinate At All It Can Also Be Used To Relievesevere Symptoms
Transurethral resection of the prostate
Transurethral resection of the prostate removesprostate tissue through the urethra. It is the surgery most commonly used totreat BPH. While TURP relieves urinary symptoms in most men, urinary problemscan come back over time if the prostate starts to grow again. This is why youngermen may need to have this surgery more than once.
This surgery is done in an operating room. The doctor passes a resectoscope through the urethra to reach the prostate. A resectoscope is a type of endoscope . It has a thin wire that carries an electric current. The doctor uses the electric current to cut away prostate tissue around the urethra. The doctor then removes this tissue through the resectoscope.
The most common side effects of TURP include:
In rare cases, you may develop erectile dysfunction orincontinence after TURP. But this surgery has a lower risk of these sideeffects than surgery to remove the prostate .
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Blood Clots
Guidelines For The Treatment Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Yunuo Wu, PharmDCreighton University School of Pharmacy and Health Professions
Michael H. Davidian, MD, MSAssociate Professor of MedicineCreighton University School of Medicine
Edward M. DeSimone II, RPh, PhD, FAPhAProfessor of Pharmacy SciencesCreighton University School of Pharmacy and Health ProfessionsOmaha, Nebraska
US Pharm. 2016 41:36-40.
ABSTRACT:Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common disorder in men with an incidence that increases with age. BPH often requires therapy when patients begin to experience lower urinary tract symptoms that affect quality of life. Current management strategies involve lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy, phytotherapy, and surgical interventions as indicated. Pharmacists are in the unique position of being accessible sources of healthcare information for the BPH patient population. Understanding the symptoms of this disorder and therapy options will be beneficial for pharmacists who have increased chances to answer BPH-related questions from their patients.
What Is Overactive Bladder
According to the Urology Care Foundation, around 33 million Americans have OAB. They say estimate that 30 percent of men and 40 percent of women in the United States experience symptoms.
OAB is believed to occur due to malfunctioning nerves that trigger uncontrolled bladder muscle contractions that happen while the bladder is filling. The main symptom of OAB is a sudden urge to urinate thats hard to control. It can be stressful, and it can get in the way of your day-to-day life. It normally responds well to medical therapy.
Read Also: Can Kidney Stones Cause Urinary Incontinence
When Is Bph Treatment Necessary
The course of BPH in any individual is not predictable. Symptoms, as well as objective measurements of urethral obstruction, can remain stable for many years and may even improve over time for as many as one-third of men, according to some studies. In a study from the Mayo Clinic, urinary symptoms did not worsen over a 3.5-year period in 73% of men with mild BPH. A progressive decrease in the size and force of the urinary stream and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying are the symptoms most correlated with the eventual need for treatment. Although nocturia is one of the most annoying BPH symptoms, it does not predict the need for future intervention.
If worsening urethral obstruction is left untreated, possible complications are a thickened, irritable bladder with reduced capacity for urine infected residual urine or bladder stones and a backup of pressure that damages the kidneys.
- Inadequate bladder emptying resulting in damage to the kidneys
- Complete inability to urinate after acute urinary retention
- Incontinence due to overfilling or increased sensitivity of the bladder
- Recurrent severe hematuria
- Symptoms that trouble the patient enough to diminish his quality of life
Does Having Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Increase The Risk Of Prostate Cancer
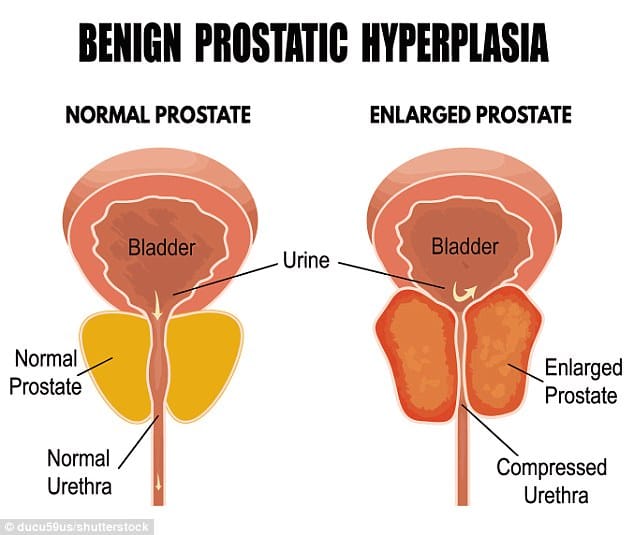
Research shows that having BPH doesnt increase your risk of developing prostate cancer. However, BPH and prostate cancer have similar symptoms. If you have BPH, you may have undetected prostate cancer at the same time.
To help detect prostate cancer in its early stages, every person with a prostate should get a prostate screening every year between the ages of 55 and 69. You have an increased risk of getting prostate cancer if youre Black or have a family history of prostate cancer. If you have an increased risk of prostate cancer, you should start getting prostate screenings at age 40.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection In Males
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Healthcare outcomes can be optimized through the use of IPSS or AUA scoring systems. These can help stratify patients according to disease severity and guide physician decision making. Adherence to lifestyle factors affecting BPH may also be addressed through diet advice, weight loss, and glycaemic control. The role of primary care/endocrine/diabetic nurse specialists can help address these areas, and early referral to these areas can help ensure medical conditions are optimized. Optimizing these factors prior to surgery can also be beneficial in reducing the risk of co-morbidity and the risk of post-operative complications.
Catheter-care is an important process for those performing intermittent self-catheterization due to symptoms or with long-term catheters. This can be addressed by specialist nurses who can help educate the patient in order to ensure adequate training, support, and follow-up in the community. In the UK, the department of health advocates accesses to integrated continence services for those with long-term bladder problems. Those who are involved in catheter care and management in the community should be aware of the indications for catheterization, and when to refer to the hospital for intervention, implementation of a catheter passport can help assist this.
Bph Tends To Progress
Understanding the natural history of BPH is imperative to appropriately counsel patients on management options, which include watchful waiting, behavioral modification, pharmacologic therapy, and surgery.
In a randomized trial, men with moderately symptomatic BPH underwent either surgery or, in the control group, watchful waiting. At 5 years, the failure rate was 21% with watchful waiting vs 10% with surgery . In the watchful-waiting group, 36% of the men crossed over to surgery. Men with more bothersome symptoms at enrollment were at higher risk of progressing to surgery.
In a longitudinal study of men with BPH and mild symptoms , the risk of progression to moderate or severe symptoms was 31% at 4 years.
The Olmsted County Study of Urinary Symptoms and Health Status Among Men found that the peak urinary flow rate decreased by a mean of 2.1% per year, declining faster in older men who had a lower peak flow at baseline. In this cohort, the IPSS increased by a mean of 0.18 points per year, with a greater increase in older men.
Though men managed with watchful waiting are at no higher risk of death or renal failure than men managed surgically, population-based studies have demonstrated an overall risk of acute urinary retention of 6.8/1,000 person-years with watchful waiting. Older men with a larger prostate, higher symptom score, and lower peak urinary flow rate are at higher risk of acute urinary retention and progression to needing BPH treatment.,
Also Check: What Do You Do For A Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Difference Between Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia And Benign Prostatic Enlargement
BPH is the name of a condition that causes your prostate to increase in size.
Benign prostatic enlargement is a term that healthcare providers use to describe the increased size of your prostate gland due to BPH.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a very common condition that affects men and people assigned male at birth. BPH usually develops around the age of 55. If you have mild BPH, you and your healthcare provider may choose to monitor your symptoms through regular appointments. If BPH affects your quality of life, treatments can help shrink your prostate.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of BPH. Together, you can discuss the best course of action.
A Criteria For Inclusion/exclusion Of Studies In The Review
Studies will be included in the review based on the PICOTS framework outlined above and the study-specific inclusion criteria described in Table 3.
|
|
| Publication type | |
|---|---|
| Language of Publication | English |
Recommended Reading: Urinary Incontinence Treatment Home Remedies
D Assessment Of Methodological Risk Of Bias Of Individual Studies
Risk of bias of eligible studies will be assessed using instruments specific to RCTs. We will develop an instrument based upon AHRQ guidance.20 Relevant items will include participant selection, method of randomization, attrition, blinding, allocation concealment, and appropriateness of analytic methods.
One investigator will independently assess risk of bias for eligible studies a second investigator will review the risk of bias assessment. Investigators will consult to reconcile any discrepancies in overall risk of bias assessments. Overall summary risk of bias assessments for each study will be classified as low, moderate, or high based upon the collective risk of bias inherent in each domain and confidence that the study results are believable given the study’s limitations.
What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth.
Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone , a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Recommended Reading: Can High Blood Pressure Cause Urinary Problems
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Developing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The best ways to reduce your risk of developing BPH are to make lifestyle changes that improve your prostate and heart health and take supplements.
Exercising at least 30 minutes each day may help prevent BPH or slow prostate growth. Maintaining normal cholesterol, blood pressure and blood sugar levels is also important.
The following herbal supplements may also help reduce your risk of developing BPH:
- Beta-sitosterol. Beta-sitosterol is a micronutrient in plants that may help keep your heart healthy.
- Pygeum africanum. Pygeum africanum is an herbal extract from African cherry tree bark that may help shrink your prostate.
- Flaxseed. Flax is a good source of dietary fiber and omega-3 fatty acids that may help lower your cholesterol.
- Pumpkin seed oil. Pumpkin seed oil comes from pumpkin seeds. It may help shrink your prostate.
Talk to your healthcare provider before taking any new supplements. They may adversely react to other supplements or medications youre currently taking.