How Long Does A Uti Last
While most UTIs last no longer than a week, there are a variety of factors that can influence when you’ll finally feel better and when your body will completely clear out the bacteria.
When thinking about how long a UTI’s going to last, the first thing to consider is whether it’s considered uncomplicated or complicated. As the American Urological Association explains, uncomplicated UTIs are far more common than complicated UTIs . They tend to be located in the lower urinary tract and don’t have other factors that could make them more difficult to treat.
How long an uncomplicated UTI lasts can vary based on what you do to treat it. Sometimes your body’s immune system can clear out the invading bacteria without any help from medications, says Courtenay Moore, MD, urologist at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center,.
“If untreated, a UTI would typically take about three to seven days to fight off on your own,” Dr. Moore tells Health.
With that said, antibiotics are considered the “gold standard” for UTI treatment and it’s always a good idea to get symptoms of a UTI checked out by a doctor.
Doctors often give people who show up with UTI symptoms a prescription for antibiotics that they think will kill the pathogen. They’ll also take a urine sample to see what’s going on. Once the lab results come back , the doctor may switch you to another antibiotic that’s better at killing the particular bacteria responsible for your infection.
How Do You Know If Pelvic Pain Is Serious
While not all pelvic pain is serious, seeking medical care when symptoms are severe is important. You should head to the nearest emergency room if:
- Pelvic pain is sharp, severe or sudden.
- Youâre unable to stand up straight.
- There is blood in your pee or poop.
- Youâre running a fever.
- Youâre pregnant or have been pregnant in the last six months.
Different Types Of Kidney Infections
You can generally classify kidney infections into 3 categories:
- Uncomplicated infections
- Chronic or recurring kidney infections.
Uncomplicated infections are simply those that start as urinary tract infections and spread, causing plenty of pain and discomfort but no long-term damage.
A complicated kidney infection is an infection accompanied by a condition that increases the potential for that infection to become severe and for treatments to become ineffective. This includes obstructions or abnormalities in the urinary system or disorders like diabetes. Complicated pyelonephritis also indicates more severe issues related to the kidneys. This includes the formation of abscesses or obstructions in the kidneys or even enlarged kidneys. Complicated kidney infections come with more severe symptoms and are often less responsive to treatments.
Chronic kidney infections are rare and often caused by birth defects, structural abnormalities, or other preexisting issues. Frequent kidney infections can cause scarring and progressive damage to the kidneys. Thankfully, most cases of chronic pyelonephritis are discovered early in childhood. Most cases of kidney infection are cured with traditional treatments and medications, with little lasting damage to the kidneys or urinary system. Most people wonât develop a kidney infection again.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Urinary Tract Food
Urinary Tract Infection Faqs
Q: What causes a urinary tract infection?A: Urinary tract infections are very common, especially in women, and are most often caused when bacteria from the bowel or genital region enter the body through the urethra. This can lead to an infection of the urethra, bladder, ureters or kidneys. Over 85 percent of UTIs are caused in this way.
UTIs can also be caused by viral, fungal or parasitic infections, but these are much less common causes.
Q: Can men develop a urinary tract infection?A: Yes, although they are rare in men under 50 years of age. Men are less likely than women to develop a UTI because the male urinary tract has more natural defences to infection, such as a longer urethra and further distance between the urethra and the anus.
For this reason, urinary tract infections in men are more likely to be due to a medical cause or an anatomical predisposition to UTIs.{^33]
Q: Can children develop a urinary tract infection?A: Yes, urinary tract infections are a common condition in babies, toddlers and children. In fact, it is the most common bacterial infection in children under two years of age. The usual cause of UTIs in children is similar to adults: bacteria from the anal region entering the urinary tract through the urethra. Some children may be at added risk of developing a UTI due to not having developed effective personal hygiene methods, such as wiping from front to back after using the toilet..
Key Points About Urinary Tract Infections
- Urinary tract infections are a common health problem that affects millions of people each year. These infections can affect any part of the urinary tract.
- Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
- The most common symptoms of UTIs include changes in urination such as frequency, pain, or burning urine looks dark, cloudy, or red and smells bad back or side pain nausea/vomiting and fever.
- Antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Other treatments may include pain relievers, and drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Other things that can be done may help reduce the likelihood of developing UTIs.
Read Also: Bard Urinary Drainage Bag Instructions
How To Feel Better
If your healthcare professional prescribes you antibiotics:
- Take antibiotics exactly as your healthcare professional tells you.
- Do not share your antibiotics with others.
- Do not save antibiotics for later. Talk to your healthcare professional about safely discarding leftover antibiotics.
Drink plenty of water or other fluids. Your healthcare professional might also recommend medicine to help lessen the pain or discomfort. Talk with your healthcare professional if you have any questions about your antibiotics.
Diagnosis Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnosis of a urinary tract infection usually begins with a consultation based on the symptoms and a physical examination. It is usual for a doctor to also ask about sexual history, medical history and any instances of previous UTIs.
A sample of urine might be requested in order to confirm a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Dipstick analysis may be done first to indicate the presence of bacteria in the urine. This quick test entails dipping a small chemical strip into a urine sample, then looking for certain color changes on the strip which may indicate abnormal levels of blood, sugar or bacteria in the urine. Looking at the urine sample under a microscope can usually confirm the diagnosis, as well as which bacteria has caused the infection.
If an upper urinary tract infection is suspected, a doctor may also recommend blood tests in order to check the infection hasnât spread to the bloodstream.
People suffering from recurring or chronic urinary tract infections may be given additional tests to determine if there are any obstructions or abnormalities causing the repeat of the condition. Such tests can include:
- An ultrasound scan of the bladder and kidneys, which uses painless soundwaves to generate an image of the urinary tract
- A CT scan or MRI scan for a more detailed analysis of the urinary tract
- A cystoscopy, in which a small camera is inserted through the urethra to see inside the urethra and bladder
Recommended Reading: Z Pack Urinary Tract Infection
What Can I Expect During A Urinalysis
In most cases, youll perform a urinalysis at your healthcare providers office or at a laboratory using the clean catch method, which is intended to help prevent contamination of your urine sample with cells from your genitals. You or your healthcare provider can also collect a urine sample using a catheter.
For the clean catch method, your provider will give you a specimen cup, sterile wipes and specific instructions for collecting your urine sample. Your provider will tell you what to do with your urine sample after youve collected it. Its important to wash your hands with soap and water before you collect the sample.
Collecting a clean catch urine sample if you have labia
If you have labia, use the following steps to get a clean catch urine sample:
- Start by sitting on the toilet with your legs spread apart.
- Using two fingers, spread your labia open. Then, use one sterile wipe to clean the inner folds of your labia, wiping from front to back.
- Use another sterile wipe to clean over your urethra, the opening where urine flows out of your body.
- Urinate a small amount into the toilet.
- Stop the flow of urine, and hold the specimen cup a few inches away from your urethra.
- Urinate into the cup, filling it about half full or however full your provider instructed you to.
- Finish urinating into the toilet.
Collecting a clean catch urine sample if you have a penis
If you have a penis, use the following steps to get a clean catch urine sample:
Lower Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
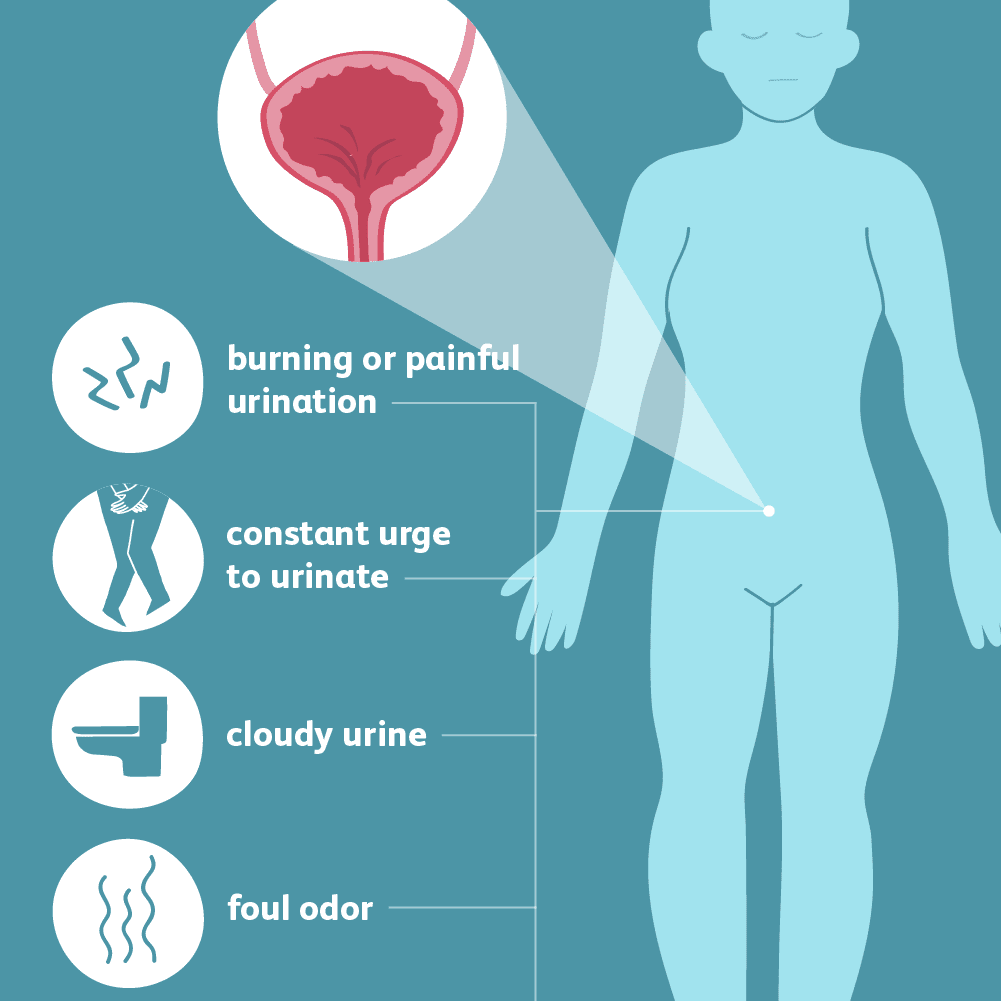
Common symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection include:
- Frequent and urgent need to urinate
- Burning or painful sensation while urinating
- Strong-smelling urine
- Urine that is bloody and/or cloudy in color
- Lower abdominal pain
Good to know: Lower urinary tract infections present similar symptoms in both men and women. However, men may also experience rectal pain, while women may experience pelvic pain.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Urinary Tract Infection Male
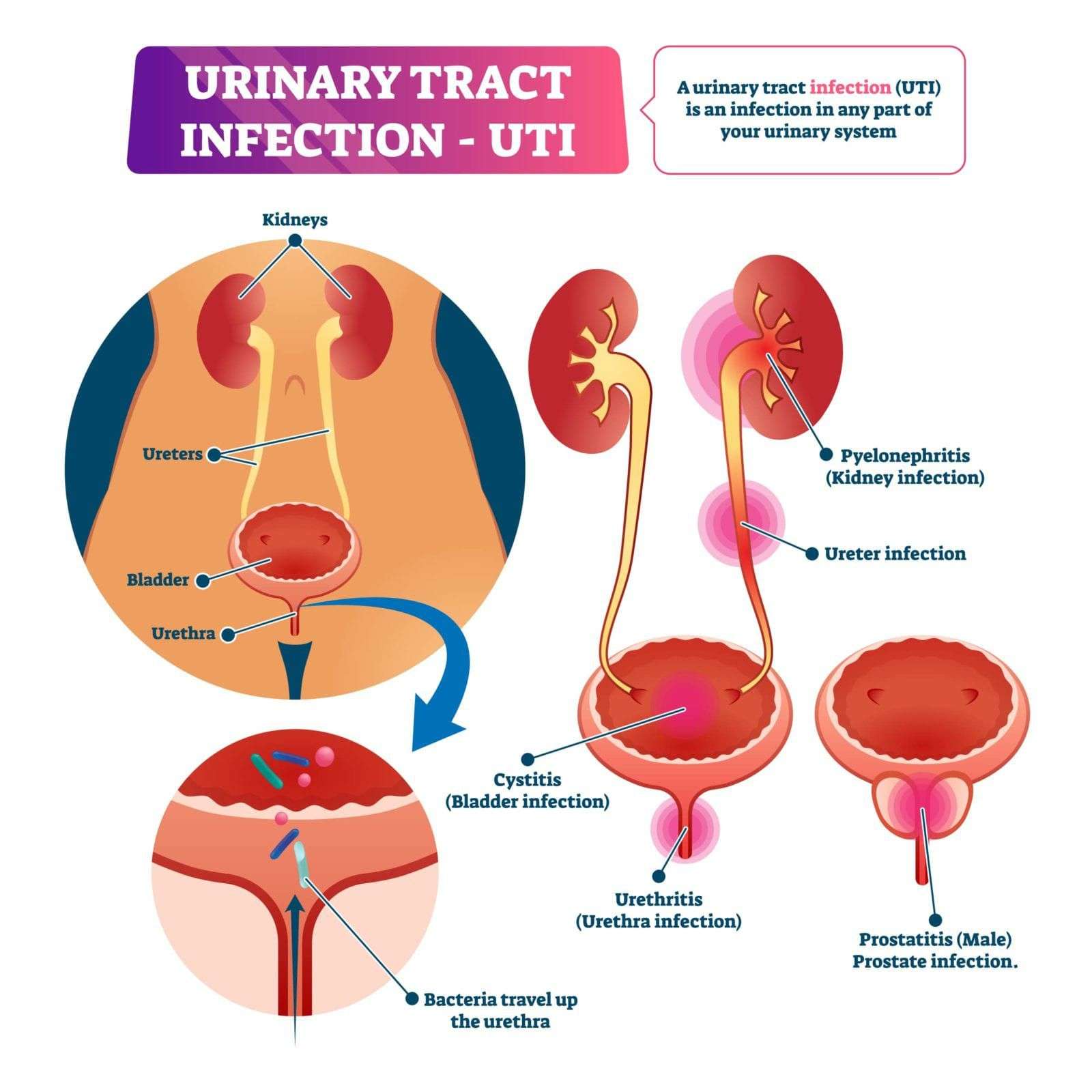
Types Of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections can occur anywhere within the urinary tract, which includes the:
- Urethra, the tube that passes urine out of the body from the bladder. Infection of the urethra is also known as urethritis
- Bladder, the organ that collects and stores urine. Infection of the bladder is also known as cystitis
- Ureters, the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
- Kidneys, the organs that filter blood, eliminating waste via the urine. Infection of one or both kidneys is also known as
The majority of UTIs affect the bladder and/or the urethra. These are known as lower urinary tract infections.
However, the infection can also travel up the urinary tract to reach the kidneys. In rare cases, the ureters may also become infected. These are called upper urinary tract infections. They are less common than lower tract infections and tend to be more severe.
What Are Other Possible Causes Of Painful Urination
A painful burning feeling when you urinate is often a sign of a urinary tract infection . However, painful urination can occur even if you dont have an infection. Certain drugs, like some used in cancer chemotherapy, may inflame the bladder. Something pressing against the bladder or a kidney stone stuck near the entrance to the bladder can also cause painful urination.
Painful urination can also be caused by vaginal infection or irritation. You might be sensitive to chemicals in products such as douches, vaginal lubricants, soaps, scented toilet paper, or contraceptive foams or sponges. If it hurts to urinate after youve used these products, youre probably sensitive to them.
Read Also: Ways To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
Why Was The Uti Program Developed
- It is common to find bacteria in the urine of the elderly but it does not always mean that they have a UTI.
- Older people are often given antibiotics for what health care providers and other caregivers assume to be UTIs.
- It can be harmful to treat somebody with antibiotics when they dont need them.
- Antibiotic use can increase the risk of antibiotic resistance, which can make it more difficult to treat future infections.
For more information on the overuse of antibiotics in long term care homes, see .
Read Also: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Cause An Elevated Psa
How Does It Occur
Normally the urinary tract does not have any bacteria or other organisms in it. Bacteria that cause UTI often spread from the rectum to the urethra and then to the bladder or kidneys. Sometimes bacteria spread from another part of the body through the bloodstream to the urinary tract. Urinary tract infection is less common in men than in women because the male urethra is long, making it difficult for bacteria to spread to the bladder.
Urinary tract infection may be caused by a sexually transmitted disease. Sometimes a stone in the urinary tract blocks the flow of urine and causes an infection. In older men, an enlarged prostate can cause a urinary tract infection by keeping urine from draining out of the bladder completely. Infection might also be caused by the use of a catheter used to drain the bladder or by urethral stricture, which is a narrowing of the urethra by scar tissue from previous infections or surgical procedures.
You may be more likely to have a UTI if you have diabetes or another medical problem that affects the immune system.
Recommended Reading: Sphincter Surgery For Urinary Incontinence
What Are The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
These are the most common symptoms of a UTI:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Fever
- Urine looks dark, cloudy, or reddish in color
- Urine smells bad
- Feeling pain even when not urinating
- Tiredness
- Pain in the back or side, below the ribs
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Despite an strong urge to urinate, only a small amount of urine is passed
- Women may feel an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone
The symptoms of UTI may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always see a health care provider for a diagnosis.
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease symptoms of a urinary tract infection :
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day
- avoid having sex
Some people take cystitis sachets or cranberry drinks and products every day to prevent UTIs from happening, which may help. However, there’s no evidence they help ease symptoms or treat a UTI if the infection has already started.
You May Like: Urinary Incontinence In Women Treatment
How K Health Can Help
Did you know you can get affordable UTI treatment with the K Health app? Download K to check your symptoms using our AI-driven symptom checker and, if needed, text with a doctor in minutes. K Healths board-certified, U.S.-based doctors can provide a treatment plan and prescription to resolve your symptoms as soon as possible.
How Does Urination Occur
To urinate, your brain signals the sphincters to relax. Then it signals the muscular bladder wall to tighten, squeezing urine through the urethra and out of your bladder.
How often you need to urinate depends on how quickly your kidneys produce the urine that fills the bladder and how much urine your bladder can comfortably hold. The muscles of your bladder wall remain relaxed while the bladder fills with urine, and the sphincter muscles remain contracted to keep urine in the bladder. As your bladder fills up, signals sent to your brain tell you to find a toilet soon.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Prescription Online
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
Preventing Future Urinary Tract Infections
BATHING AND HYGIENE
To prevent future urinary tract infections, you should:
- Choose sanitary pads instead of tampons, which some doctors believe make infections more likely. Change your pad each time you use the bathroom.
- Do not douche or use feminine hygiene sprays or powders. As a general rule, do not use any product containing perfumes in the genital area.
- Take showers instead of baths. Avoid bath oils.
- Keep your genital area clean. Clean your genital and anal areas before and after sexual activity.
- Urinate before and after sexual activity. Drinking 2 glasses of water after sexual activity may help promote urination.
- Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom.
- Avoid tight-fitting pants. Wear cotton-cloth underwear and pantyhose, and change both at least once a day.
DIET
The following improvements to your diet may prevent future urinary tract infections:
- Drink plenty of fluids, 2 to 4 quarts each day.
- Do not drink fluids that irritate the bladder, such as alcohol and caffeine.
RECURRING INFECTIONS
Some women have repeated bladder infections. Your provider may suggest that you:
- Use vaginal estrogen cream if you have dryness caused by menopause.
- Take a single dose of an antibiotic after sexual contact.
- Take a cranberry supplement pill after sexual contact.
- Have a 3-day course of antibiotics at home to use if you develop an infection.
- Take a single, daily dose of an antibiotic to prevent infections.
Also Check: Can Azo Urinary Tract Defense Get Rid Of Uti
Preventing Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are most often caused by bacteria spreading from the anal or genital region and entering the urinary tract. Because of this, there are a number of preventative methods that can minimize the risk of experiencing a UTI:
- Regular urination
- Emptying the bladder after sexual intercourse
- Drinking lots of water, ideally at least 1.5 liters a day. Avoid alcohol and caffeine, which can irritate the bladder
- Wiping from front to back after using the toilet to avoid spreading bacteria from the anal region
- Maintaining good personal hygiene and keeping the genital area clean and dry
- Taking showers instead of baths