What Symptoms Indicate The Need For Urine Culture
A urine culture test is generally done to determine whether or not you have urinary tract infection. However, there are certain symptoms due to which your doctor might recommend you to go for a urine culture test. The most common symptoms of a urinary tract infection include:
- A burning pain while urinating
- Increased frequency of urination
- If you face a problem in draining your bladder completely
- If you use a urinary catheter for draining urine
- If you have a weak immune system that can be due to any ongoing or previous cancer treatment, organ transplant, or autoimmune diseases.
Laboratory Diagnosis Of Urinary Tract Infections Using Diagnostics Tests In Adult Patients
Akmal Hasan SK, Naveen Kumar T, Radha Kishan N, Neetha K
Abstract
Background:The primary aim of this study was to evaluate laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infection using diagnostics tests in adult patients.
Methods:Among the diagnostic tests, urinalysis is useful mainly for excluding bacteriuria. For isolation of pathogenic bacteria semiquantitative culture techniques was used and biochemical tests were done to differentiate Gram +ve and Gram ve bacteria.
Results: The incidence of pathogenic infection caused by Escherichia coli accounts for 216 cases followed by Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella.
Physicians should distinguish urinary tract infections caused by different organisms for an effective treatment and appropriate clinical information gives clues for better diagnostic evaluation and their susceptibility to antimicrobial agents as well addressing host factors that contribute to the occurrence of infection.
Keywords
Full Text:
References
Ananthanarayan R, Jayaram Paniker CK. Urinary Tract Infections. In: Kapil A, eds. Text Book of Microbiology. 9thed. Hyderabad, India: University Press 2013: 671.
Josef Peter G, Ojan A, Michael B, Axel K. Incidence and clinical implication of nosocomial infections associated with implantable biomaterials-cathters, ventilator associated pneumonia urinart tract infections. GMS Krankenhhyg Interdiszip. 2011 6:Doc 18.
S Used To Diagnose Utis
Figure 1 shows the traditional and emerging methods used in the laboratory diagnosis of UTIs. Urine samples for analysis are most commonly obtained as clean catch mid-stream voided urine samples. The nitrite and leucocyte esterase tests are the two standard dipstick analyses used for urinalysis . The nitrite test is positive for those bacteria that can reduce nitrate to nitrite and detects bacteria at concentrations > 105 cfu/mL, and the leucocyte esterase test detects an enzyme produced by leucocytes whose level increases in the urine during infection. Positive nitrite and esterase tests can indicate UTIs, especially in the presence of diagnostic symptoms. However, it is not recommended to treat a positive nitrite or positive esterase test alone as an indication of UTI. The main drawback of these tests lies in their poor negative predictive values. They cannot be used to rule out infections because Gram-positive pathogens such as Enterococci and Staphylococcus do not produce nitrites, and leucocyte esterase levels may not be high enough to be detected early in an infection. Therefore, these dipstick tests are no longer employed at point-of-care rather, they are used in the clinical laboratory along with other tests .
You May Like: Lower Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
What Is A Urinalysis
A urinalysis is a test that examines the visual, chemical and microscopic aspects of your urine . It can include a variety of tests that detect and measure various compounds that pass through your urine using a single sample of urine.
Healthcare providers often use urinalysis to screen for or monitor certain common health conditions, such as liver disease, kidney disease and diabetes, and to diagnose urinary tract infections .
While several different aspects of your health can be tested with a urine sample, your healthcare provider will choose which tests to order under a urinalysis depending on your symptoms and situation.
What Is Being Tested
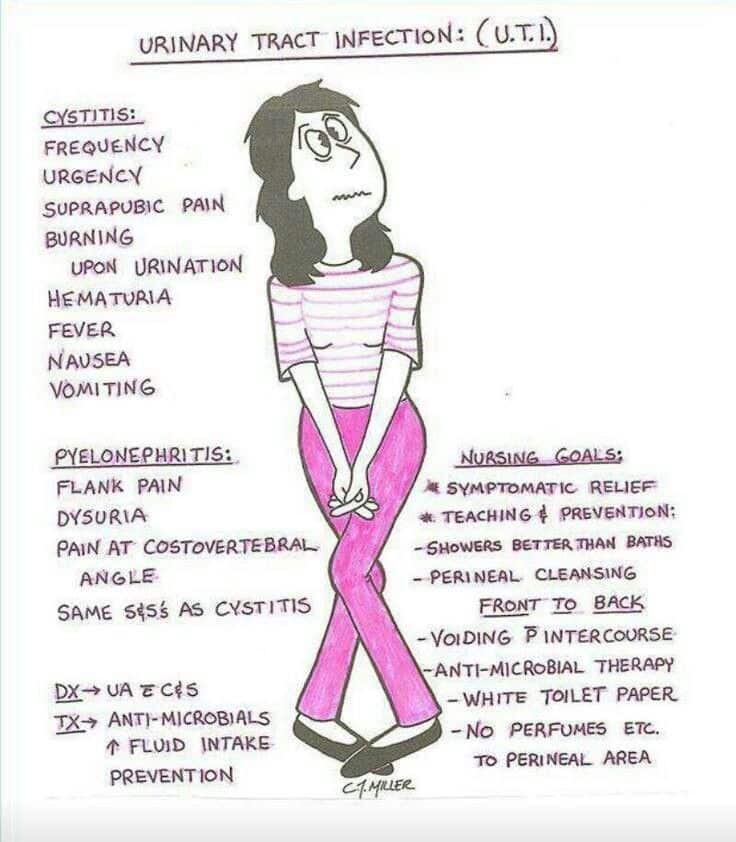
Urine is the fluid produced by the kidneys that carries water and wastes through the urinary tract and then is eliminated from the body. The urine culture is a test that detects and identifies bacteria and yeast in the urine, which may be causing a urinary tract infection .
The kidneys, a pair of bean-shaped organs located at the bottom of the ribcage in the right and left sides of the back, filter wastes out of the blood and produce urine, the yellow fluid that carries wastes out of the body. Urine travels through tubes called ureters from the kidneys to the bladder, where it is stored temporarily, and then through the urethra as it is voided. Urine contains low levels of microbes, such as bacteria or, yeast which move from the skin into the urinary tract and grow and multiply, causing a urinary tract infection.
Most UTIs are considered uncomplicated and are easily treated. However, if they are not addressed, the infection may spread from the bladder and ureters into the kidneys. A kidney infection is more dangerous and can lead to permanent kidney damage. In some cases, an untreated urinary tract infection may spread to the bloodstream and cause sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
People with kidney disease or with other conditions that affect the kidneys, such as diabetes or kidney stones, and people with weakened immune systems may be more prone to frequent, repeated and/or complicated UTIs.
How is the sample collected for testing?
Read Also: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Vs Urinary Pain Relief
Prognosis And Natural History
Placebo arms of randomized controlled trials suggest that 25 to 50% of women presenting with a combination of UTI-symptoms and bacteriuria will have recovered in one week without using antibiotics. Using data from ACUTIS, we will try to make a prognostic index. Using the prognostic index, a GP can estimate the 7-day course for women with different combinations of test results and decide which women are most likely to benefit from antibiotic treatment.
Specimen Collection Transportation And Processing
Specimen collection. Suprapubic aspiration is the best method to avoid contamination of specimens with bacteria in the distal urethra. This collection method is used infrequently because it is not indicated clinically , it is invasive and uncomfortable, and it requires too much time and too many resources to be practical. Collection of urine by use of a single catheter is the next-best technique for obtaining urine specimens with minimal contamination, but, again, it is not indicated clinically for most patients because it is too labor intensive and costly for routine use and it is invasive. It has added disadvantages, because the process of inserting a catheter through the urethra can introduce bacteria into the bladder , and rare complications have been reported.
As discussed below, correct processing and handling of urine specimens, as well as correct interpretation of test results, is dependent on the method used to collect the specimen. It is, therefore, of obvious importance for clinicians to specify the method of collection on the test requisition slip. Other information that should be included on the test requisition slip includes the date and time of specimen collection, patient demographic information, and any clinically relevant information .
Also Check: What Foods Can Cause A Urinary Tract Infection
Macroscopic And Microscopic Examination
Macroscopic examination can provide crude indicators as to the presence of some pathologies. For example, turbid urine may indicate pyuria and red coloured urine may indicate cases of haematuria. However, these examinations are highly unreliable. Microscopic examination of urine can demonstrate the presence of pus cells, red blood cells, casts and bacteria, and yeast cells. The presence of seven or more pus cells per high power field in an uncentrifuged sample is suggestive of pyuria. On the other hand, the absence of pus cells does not reliably exclude a UTI, especially in infants < 2 months of age.24,25 It is important to note that many infants with positive urine cultures but no pyuria probably have a contamination or asymptomatic bacteriuria rather than a UTI.26 It is now well understood that some paediatric patients with UTI can have normal urinalysis results at any given time.2 A Gram stain of unspun urine has a sensitivity and specificity approaching 9095% it has several advantages as it reveals the nature of the bacterium present and therefore guides the clinician to initiate antibiotic therapy. If a single bacterium is seen under one oil immersion field in a Gram stain, it is considered to be equivalent to 100,000 CFU/mL of bacteria .27
Table 1: Comparison of the diagnostic tests for UTI on uncentrifuged urine.HPF: high power field CFU: colony forming unit WBC: white blood cell.
Diagnostic Hallmarks Of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infection is among the leading causes for treatment in adult primary care medicine and represents a significant proportion of antibiotic prescriptions. A UTI can involve any part of the urinary system, including the lower urinary tract urethra and bladder and the upper urinary tract ureters and kidneys . UTI impacts both genders, however, women are much more vulnerable due to their anatomy and reproductive physiology. Escherichia coli accounts for about 80-85 percent of all UTIs, followed by Staphylococcus species, accounting for 10-15 percent. Other bacterial pathogens including Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Proteus, and Enterococcus species are also infrequently implicated. More rarely, infections may be from fungal or viral pathogens that would require alternative treatment strategies.1
Further sub-classifications of UTIs are based on location of the infection, presence or absence of symptoms, and the presence of relevant complicating factors that dramatically increase the patient risk profile. Complications can include all UTIs in children, men and pregnant women, renal insufficiency or transplant, diabetes mellitus, physical obstruction, immune compromised patients, etc.2
You May Like: Is There A Home Remedy For Urinary Tract Infection
The Role Of Uti Testing
UTI testing may be performed if a doctor suspects a UTI based on a patients symptoms and a physical examination. Laboratory tests can diagnose or rule out UTIs. UTI testing can also identify the bacteria or other microbes that are causing the infection, which helps doctors decide how to best treat the infection.
Nonculture Methods For The Laboratory Diagnosis Of Uti
Detection of bacteriuria by urine microscopy. Bacteriuria can be detected microscopically using Gram staining of uncentrifuged urine specimens, Gram staining of centrifuged specimens, or direct observation of bacteria in urine specimens. Gram stain of uncentrifuged urine specimens is a simple method. A volume of urine is applied to a glass microscope slide, allowed to air dry, stained with Gram stain, and examined microscopically. The performance characteristics of the test are not well-defined, because different criteria have been used to define a positive test result. In one study, the test was found to be sensitive for the detection of 105 cfu/mL but insensitive for the detection of lower numbers of bacteria . Other investigators have found the test to be of low sensitivity for the detection of UTI .
Performance characteristics of Gram staining for detection of bacteriuria.
Performance characteristics of leukocyte esterase and nitrite tests, alone or in combination, for detection of bacteriuria and/or pyuria.
A number of drugs can change the color of urine abnormal urine color may affect urine tests that are based on the interpretation of color changes. In some cases, this can mask color changes, and in others, it may result in false-positive interpretations .
Read Also: Alka Seltzer Urinary Tract Infection
Study Protocol And Samples
This was a cross-sectional study, conducted at the Clinical Pathology Laboratory, Dr. Soetomo Hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia. It examined the urinalysis, urine sediment, and urine culture from March 2020 to September 2020. A total of 13,822 urine samples were received during this period at Dr. Soetomo Hospital Clinical Pathology Laboratory. The study aimed to target UTI patients of the outpatient clinic, representing community-acquired UTIs. This group of patients required rapid laboratory results to enable appropriate treatment. For statistical analysis, groups of patients with and without UTIs were established .
Flow chart of urine specimen analysis.
All urine samples were processed for 15 different parameters of urine chemistry using a UC-3500 analyzer . Only two parameters were used for inclusion criteria: leukocyte esterase and nitrite. The inclusion criteria for urine samples were first-void midstream urine and being processed within 2 hours after specimen collection thus, urine specimens processed over 2 hours after the sample collection were excluded. Patients with indwelling catheters were also excluded. Applying these inclusion criteria, a total of 100 urine samples were included for analysis.
Why Is Urine Culture Done

Urine culture is generally done for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections . The urinary tract infection occurs due to the presence of bacteria in the urethra. The urinary tract infection starts from your urinary bladder and can reach your kidneys and prostate gland as well. The urine culture test identifies the type of bacteria or yeast causing the infection so that the most effective treatment plan can be decided for you. It also determines whether the bacterial infection is resistant to certain drugs or not.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Strip Test
Antibiotic Resistance Among Uropathogens
The overuse of antibiotics, particularly the large-scale use of antibiotics in the poultry and cattle industry, is the primary reason for the increase in multi-drug resistance . Inappropriate prescriptions contribute to the spread of resistance genes in the microbial community. A large study performed in the US showed that 3050% of antibiotic prescriptions for outpatient visits in 20102011 were incorrect for either the indication, the dosage, or the duration . Another study with data from more than 300 hospitals showed that antibiotic use among hospitalized patients could have been decreased by 40% . Previous antibiotic therapy or prophylactic treatments or hospitalizations increase the risk of multi-drug resistant infections. Multi-drug resistance is higher among hospital-acquired UTIs than community-acquired UTIs and higher among elderly patients in nursing care homes and other institutes than those who are not . Previous unnecessary treatments of asymptomatic bacteriuria, particularly during long-term catheterization, can result in later resistant infections.
Getting Tested For A Uti
Testing for a UTI usually takes place in a doctors office, laboratory, or hospital. Most tests for UTIs involve a urine sample obtained by clean-catch or catheterization. Your doctor can help determine which method is appropriate for you.
- Clean catch urine samples are collected by patients with special precautions to prevent outside germs from getting into the urine sample. Patients are given instructions on obtaining a clean catch sample and avoiding contamination.
- Catheterization involves inserting a thin rubber tube through the urethra into the bladder. When performing this procedure, the urine is collected in a sterile container for testing before removing the catheter.
Read Also: How To Heal Urinary Tract Infection Without Antibiotics
How Do I Prepare For A Urinalysis
Before your urinalysis test, youll need to make sure youve drunk enough liquids, such as water, to be able to go to the bathroom and produce a urine sample.
Depending on the reason for the urinalysis, your healthcare provider may want the urine sample to be the first time you pee in the morning . Your provider will let you know if this is the case.
Certain medications can change the color of your urine. Your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking certain medications that can affect urinalysis test results. Only stop taking medications if your provider tells you to do so.
If youre menstruating , its important to let your provider know before collecting your urine sample. Menstrual blood, as well as vaginal discharge, can interfere with certain urinalysis test results.
What Is Urine Culture
Urine or your bodys liquid waste can contain various infection-causing microorganisms. Urine culture is a laboratory test done to check whether or not there are germs present in your urine sample. A growth-promoting substance is added to your urine sample in the laboratory. Thus, if bacteria or yeast is present in your urine, it will start multiplying. The growth of microbes indicates presence of urinary system infection.
Also Check: Does Tummy Tuck Help With Urinary Incontinence
Laboratory Diagnosis Of Urinary Tract Infections
Laboratory Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections Dr S. Hekmat MD.CAP Reference Laboratories of Iran Microbiology Department UTI
Introduction The aim of microbiology laboratory in the management of urinary tract infection is to reduce morbidity and mortality through accurate and timely diagnosis with appropriate antimicrobial sensitivity testing. UTI
Infections of Urinary Tract Epidemiology: UTIs are among the most common bacterial infections that lead patients to seek medical care. Approximately 10% of humans will have a UTI at some time during their lives. UTI
Urine sample make up a large proportion of samples submitted to the routine diagnostic laboratory. A large laboratory may examine 200-300 urine sample each day .This heavy workload reflects the frequency of UTI both in general practice and hospital settings. UTI
Although optimal specimen collection ,processing ,and interpretation should provide the clinician with a precise answer ,no single evaluation method is fool proof and applicable to all patients group. UTI
predisposing factor for UTI Age , sex Pregnancy Diabetes Renal disease Kidney stones Renal transplantation urinary catheters Immune defficency Structural and neurological abnormalities UTI
Clinical presentation of UTI The clinical presentation of UTIs may vary ranging from asymptomatic infection to pyelonephritis. Urethritis Cystitis Acute uretheritis syndrome Prostatis Pyelonephritis UTI
Microfluidics Platforms For Ast
Miniaturized microfluidic devices are very attractive options for emerging diagnostic tools for antibiotic susceptibility testing. Microfluidic platforms are cost-effective and amenable to automation, multiplexing, high-throughput processing, and single-cell analysis. Their portability confers great potential as point-of-care devices . Their small size enables them to use minimal volumes of samples and reagents. Small confined spaces within the microfluidic device allow the detection of bacterial cell division and growth in far less time than conventional phenotypic AST assays. Various groups have developed microfluidic platforms capable of direct testing on urine samples. Some platforms offer both pathogen identification and AST , , , , while some only deliver AST . It can be argued that AST information is more relevant than pathogen identification for prescribing treatment.
Also Check: Causes Of Urinary Incontinence In Females