What Are Kegel Exercises
Kegel exercises, also called Kegels or pelvic floor muscle training, are exercises for your pelvic floor muscles to help prevent or reduce stress urinary incontinence. Your pelvic floor muscles support your uterus, bladder, small intestine, and rectum.
Four in 10 women improved their symptoms after trying Kegels.9 Kegels can be done daily and may be especially helpful during pregnancy. They can help prevent the weakening of pelvic floor muscles, which often happens during pregnancy and childbirth. Your pelvic floor muscles may also weaken with age and less physical activity.
Some women have urinary symptoms because the pelvic floor muscles are always tightened. In this situation, Kegel exercises will not help your urinary symptoms and may cause more problems. Talk to your doctor or nurse about your urinary symptoms before doing Kegel exercises.
Symptoms And Risk Factors
A comprehensive patient history includes the onset, duration and timing of urinary incontinence, and associated LUTS and voiding symptoms , recognizing that the reported symptoms often relate to the patients normal bladder function and expectations. Other risk factors or conditions that can exacerbate urinary incontinence should also be assessed and include age, obstetric history , gynaecological status , medical status and pharmacological status . Patients with mild cognitive impairment are 30% more likely to have urinary incontinence. In addition, functional and lifestyle factors, such as smoking status, mobility and frequency of heavy lifting, should be considered during assessment.
Risk Factors For Urinary Incontinence
The following factors may put you at higher risk for developing UI.
Being female Women experience stress incontinence twice as often as men. Men, on the other hand, are at greater risk for urge and overflow incontinence.
Advancing age As we get older, our bladder and urinary sphincter muscles often weaken, which may result in frequent and unexpected urges to urinate. Even though incontinence is more common in older people, it is not considered a normal part of aging.
Excess body fat Extra body fat increases the pressure on the bladder and can lead to urine leakage during exercise or when coughing or sneezing.
Other chronic diseases Vascular disease, kidney disease, diabetes, prostate cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and other conditions may increase the risk of urinary incontinence
Smoking A chronic smoker’s cough can trigger or aggravate stress incontinence by putting pressure on the urinary sphincter.
High-impact sports While sports don’t cause incontinence, running, jumping, and other activities that create sudden pressure on the bladder can lead to occasional episodes of incontinence during sports activities.
RELATED: Why Does Diabetes Make You Urinate So Much?
Recommended Reading: Prescription Drugs For Urinary Tract Infection
Lifestyle Changes For Mild Incontinence
Lifestyle Changes Can Help
Mild cases of incontinence may be helped with simple lifestyle changes. Drink adequate fluids to avoid dehydration about six 8-ounce glasses per day but don’t drink too much. Limit your intake of fluids after dinner in the evening to minimize nighttime accidents. Avoid caffeinated drinks like coffee, tea, and colas as caffeine is a diuretic. Avoid alcohol, smoking, and carbonated beverages which may contribute to leaks. Losing weight if you are overweight may help relieve pressure on the bladder.
The Importance of Fiber
Getting adequate fiber helps move your bowels, which in turn helps minimize the risk of incontinence. Most adults should aim to get between 25 and 30 grams of dietary fiber per day. Lentils, beans, artichokes, avocados, berries, and figs are good sources of fiber. Fiber and water work together to optimize bowel health and minimize constipation. Being constipated increases pressure in the abdomen.
Urinary Incontinence In Women: What You Need To Know
-
Urinary incontinence is the accidental loss of urine.
-
Over 25 million adult Americans experience temporary or chronic urinary incontinence.
-
This condition can occur at any age, but it is more common in women over the age of 50.
-
There are four types of urinary incontinence: urgency, stress, functional and overflow incontinence.
-
Behavioral therapies, medications, nerve stimulation and surgery are some of the treatments available for managing urinary incontinence.
Also Check: How To Keep Urinary System Clean
Urinary Incontinence: More Common Than You Think
How to Stop Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary and unintentional leaking of urine. Urinary incontinence can also be an embarrassing problem. As with many potentially embarrassing or uncomfortable symptoms, those affected may be hesitant to speak up or ask questions about their condition, even at the doctor’s office. Urinary incontinence occurs more often in women than in men, and it is a lot more common than you might expect. In fact, chances are that you know other people who have been affected by urinary incontinence.
Incontinence must not be a source of embarrassment when you speak with your physician. The fact is that this common condition is treatable by a variety of approaches, and not speaking up about the problem means that you won’t have access to effective treatments:
- dietary changes, /li>
Millions of women experience involuntary loss of urine called urinary incontinence . Some women may lose a few drops of urine while running or coughing. Others may feel a strong, sudden urge to urinate just before losing a large amount of urine. Many women experience both symptoms. UI can be slightly bothersome or totally debilitating. For some women, the risk of public embarrassment keeps them from enjoying many activities with their family and friends. Urine loss can also occur during sexual activity and cause tremendous emotional distress.
Stress Incontinence
Urge Incontinence
Overactive Bladder
- at night to urinate
Functional Incontinence
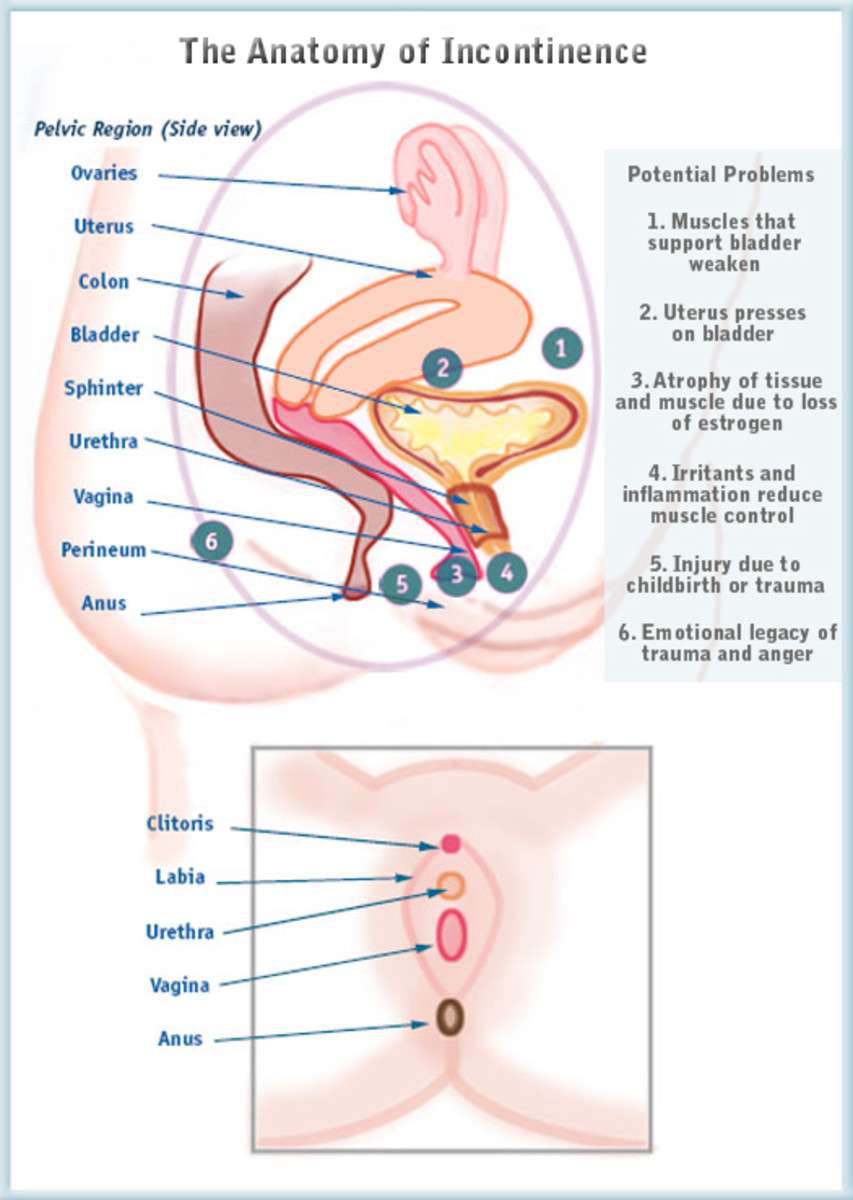
Weakening Of The Pelvic Floor Muscles And Urethral Sphincter
Weakening of the pelvic floor muscles may occur as a result of trauma of vaginal childbirth, disease process affecting the brain and spinal cord such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinsons disease, diabetes mellitus and stroke birth defects, injuries from an accident usually with fracture of the pelvic bones, or a consequence of medications or after surgery such as removal of the prostate gland.
Don’t Miss: Antibiotics For Canine Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnosis Of Urinary Incontinence
The first step in treating incontinence is to see a doctor. He or she will give you a physical exam and take your medical history. The doctor will ask about your symptoms and the medicines you use. He or she will want to know if you have been sick recently or had surgery. Your doctor also may do a number of tests. These might include:
- Urine and blood tests
- Tests that measure how well you empty your bladder
In addition, your doctor may ask you to keep a daily diary of when you urinate and when you leak urine. Your family doctor may also send you to a urologist, a doctor who specializes in urinary tract problems.
Incontinence And Alzheimers Disease
People in the later stages of Alzheimers disease often have problems with urinary incontinence. This can be a result of not realizing they need to urinate, forgetting to go to the bathroom, or not being able to find the toilet. To minimize the chance of accidents, the caregiver can:
- Avoid giving drinks like caffeinated coffee, tea, and sodas, which may increase urination. But dont limit water.
- Keep pathways clear and the bathroom clutter-free, with a light on at all times.
- Make sure you provide regular bathroom breaks.
- Supply underwear that is easy to get on and off.
- Use absorbent underclothes for trips away from home.
For more ways to deal with incontinence and other common medical problems in someone with Alzheimers, visit Alzheimers Disease: Common Medical Problems.
You May Like: Do Guys Get Urinary Tract Infections
Specialized Tests To Diagnose Incontinence
Urology Specialists
Sometimes routine testing does not reveal the underlying cause, and further evaluation is required. You may be referred to a urologist or a urogynecologist for more specialized testing if your health concern is accompanied by pain, recurrent UTIs, blood or protein in the urine, neurological symptoms or muscle weakness, or pelvic organ prolapse. Women with this issue who have a history of radiation or surgery to the pelvic region may also be referred to a urologist.
Urodynamic Testing
Specialized testing can assess how well the bladder, urethra, and sphincters store and dispose of urine. There are many different types of instruments that can be used for urodynamic testing. Cystometry is a test that is used to help diagnose urge incontinence. It measures bladder pressure. The structures in the pelvis can be visualized with ultrasound. Uroflowometry can measure the volume of urine and flow rate. This test is used to determine the strength of related muscles and helps assess whether urine flow is blocked. There are other tests a urologist may perform depending on your symptoms.
Management Of Stress Incontinence
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and learning how to contract them correctly is an important step in managing SUI. About one in two women are unable to contract their pelvic floor correctly. Nurse Continence Advisors or physiotherapists specialised in pelvic floor management can assist you with a personalised training program of pelvic floor muscle contractions. They will also teach you “the knack. The knack is contracting your pelvic floor before coughing, sneezing, or doing anything that raises the pressure in your abdomen. The training can also help you learn how to isolate the muscles of your pelvic floor around the anal area, to help control any anal incontinence and the passage of wind.
Recommended Reading: Hills Urinary Care C D
Am I At A Higher Risk Of Incontinence At An Older Age
Your body constantly changes throughout your life. As you age, the muscles that support your pelvic organs can weaken. This means that your bladder and urethra have less support often leading to urine leakage. Your risk for developing incontinence as you age might be higher if you have a chronic health condition, have given birth to children, went through menopause, have an enlarged prostate or have had prostate cancer surgery. Its important to talk to your healthcare provider over time about the risks of incontinence and ways you can manage it without interference to your daily life.
When To Seek Medical Advice

See a GP if you have any type of urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence is a common problem and you should not feel embarrassed talking to them about your symptoms.
This can also be the first step towards finding a way to effectively manage the problem.
Urinary incontinence can usually be diagnosed after a consultation with a GP, who will ask about your symptoms and may do a pelvic or rectal examination, depending on whether you have a vagina or a penis.
The GP may also suggest you keep a diary in which you note how much fluid you drink and how often you have to urinate.
Find out about diagnosing urinary incontinence.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection While Pregnant
History And Physical Examination
A preliminary diagnosis of urinary incontinence can be made on the basis of a history, physical examination and a few simple office and laboratory tests. Initial therapy may be based on these findings. If complex conditions are present or if initial treatments are unsuccessful, definitive specialized studies are required. Because urinary incontinence is a common condition, patients being examined for another problem may mention episodes of urinary incontinence. For instance, patients presenting with cold symptoms may remark that every time they cough, they leak urine. Rather than attempt a complete evaluation for urinary incontinence during that visit, the physician can ask a few simple screening questions.
Table 1 lists a few key questions that can provide information on the severity of urinary incontinence and help distinguish the major subtypes. If the patient answers affirmatively to these screening questions, a 24-hour bladder diary can be given to the patient to complete . The diary entries can then be reviewed at a subsequent office visit. An algorithm for the evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence is provided in Figure 2.
Initial Evaluation and Work-up for Urinary Incontinence
FIGURE 2.
Algorithm for the evaluation urinary incontinence.
Initial Evaluation and Work-up for Urinary Incontinence
FIGURE 2.
Algorithm for the evaluation urinary incontinence.
Treatment Of Urinary Incontinence
Now that you know about some of the common causes of urinary incontinence in women, taking the next step towards diagnosis and treatment should be done as early as possible.
At All About Women, our patients in Lake City, Gainesville and all across the northern region of Florida come to us for our compassionate OB/GYN specialists who have considerable experience treating urinary incontinence in women.
Remember that losing control of your bladder is often a symptom of other underlying diseases or conditions, so it is important to seek care and treatment right away.
You May Like: Instant Relief For Urinary Tract Infection
Can Incontinence Be Prevented
Different events throughout your life can lead to many of the things that cause incontinence. The muscles that support your pelvic organs can weaken over time. For women, these muscles can also be weakened by big life events like pregnancy and childbirth. However, in the same way you work out to build strength in your legs or arms, you can do exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. Doing exercises to strengthen your pelvic muscles may not prevent you from having any issues with incontinence, but it can help you regain control of your bladder. Maintaining a healthy body weight can also help with bladder control. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best ways to maintain strong pelvic floor muscles throughout your life.
Where To Seek Further Help/ Information:
Your GP can start management, and if necessary, refer you onto a Gynaecology or Urogynaecology clinic.
Helpful online resources include:
- Australian Physiotherapy Association website: then click Find a Physio and choose a Women’s Health & Continence physio in your area
- www.UGSA.com.au then click Patient Information
- www.yourpelvicfloor.org
If you have any concerns or questions about options to manage your menopausal symptoms, visit your doctor or go to the Find an AMS Doctor service on the AMS website.
NOTE: Medical and scientific information provided and endorsed by the Australasian Menopause Society might not be relevant to an individuals personal circumstances and should always be discussed with their own healthcare provider. This Information Sheet may contain copyright or otherwise protected material. Reproduction of this Information Sheet by Australasian Menopause Society Members, other health professionals and their patients for clinical practice is permissible. Any other use of this information must be agreed to and approved by the Australasian Menopause Society.
Content updated May 2020
Recommended Reading: How To Cure A Urinary Tract Infection In A Woman
Additional Treatments For Urinary Incontinence
Nerve Stimulation
If behavioral and lifestyle interventions do not bring relief of urinary incontinence, electrical nerve stimulation may be an option to consider. Small devices implanted near the tibial nerve in the ankle or the sacral nerve in the lower back deliver impulses that help relieve urinary incontinence symptoms. Stimulation of the tibial nerve interrupts the impulses from the bladder that go to the brain. Stimulation of the sacral nerve may improve blood flow to the bladder and make pelvic muscles that control the bladder stronger. Nerve stimulation may also trigger the relief of chemicals that block pain.
Other Procedures
In some cases of urinary incontinence unresponsive to other treatments, a physician may inject bulking agents near the urinary sphincter to help close the bladder opening. A mixture of collagen and carbon beads are injected under local anesthesia. About 40% of those who undergo the procedure have a successful outcome. If a neurological condition is contributing to the issue, Botox injections to the bladder may provide relief by decreasing bladder contractions. In cases where weak or prolapsed pelvic organs play a role, surgery may be required.
Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Incontinence can happen for many reasons. For example, urinary tract infections, vaginal infection or irritation, constipation. Some medicines can cause bladder control problems that last a short time. When incontinence lasts longer, it may be due to:
- Weak bladder muscles
- Overactive bladder muscles
- Weak pelvic floor muscles
- Damage to nerves that control the bladder from diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, or Parkinsons disease
- Blockage from an enlarged prostate in men
- Diseases such as arthritis that may make it difficult to get to the bathroom in time
- Pelvic organ prolapse, which is when pelvic organs shift out of their normal place into the vagina. When pelvic organs are out of place, the bladder and urethra are not able to work normally, which may cause urine to leak.
Most incontinence in men is related to the prostate gland. Male incontinence may be caused by:
- Prostatitisa painful inflammation of the prostate gland
- Injury, or damage to nerves or muscles from surgery
- An enlarged prostate gland, which can lead to Benign Prostate Hyperplasia , a condition where the prostate grows as men age.
Also Check: Are Grapes Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Incontinence In Women
Expert reviewer, Emma Mitchell, Physiotherapist at Bupa UK and Dr Elizabeth Rogers, Associate Clinical Director, Bupa Health Clinics Next review due October 2024
Urinary incontinence is when you pass urine without meaning to. Its common in women, particularly as you get older. If you have urinary incontinence, it can be embarrassing and may affect every area of your life. If you find yourself just putting up with it, youre not alone. But theres actually a lot of help available and incontinence can often be treated.
What To Expect At Your Healthcare Providers Appointment
During your appointment, your healthcare provider will likely ask questions about your symptoms. Theyll probably want to know how long youve been incontinent, which types of incontinence youve experienced, and other details.
They may also ask about your daily habits, including your typical diet and any medications or supplements that you take.
Depending on your symptoms and medical history, your healthcare provider may order additional tests, including:
- Collecting a sample of urine for analysis. Laboratory staff can check the urine sample for signs of infection or other problems.
- Measuring the amount of urine that you release when urinating, the amount left over in your bladder, and the pressure in your bladder. This information is gathered by inserting a catheter, or a small tube, into your urethra and your bladder.
- Conducting a cystoscopy. During this test, theyll insert a small camera into your bladder to examine it up close.
Also Check: Pomegranate Juice For Urinary Tract Infection