What Medications Can I Use For Overactive Bladder
Your doctor may suggest trying behavioral techniques before having you use a medication to treat overactive bladder. However, medications can work very well to return normal function to the bladder. Ask your doctor about the risks and benefits of using the following commonly prescribed medications:
Anticholinergic medications
These medications control muscle spasms in the bladder:
- Oxybutynin , oxybutynin XL , oxybutynin TDDS .
- Tolterodine .
- Mirabegron .
What Behavioral Changes Can I Make To Help With Overactive Bladder
There are many techniques and changes to your typical behavior that you can try to help with an overactive bladder. These can include:
Keeping a log: During a typical day, write down your fluid intake, the number of times you urinate, the number of accidents and when they occur. Make a note about what happened when the accident happened, like when you:
- Cough.
- Laugh.
- Were unable to reach the bathroom in time.
Monitoring your diet: Eliminate or decrease foods or beverages that may worsen your bladder symptoms. These could include:
- Tea.
- Spicy and acidic foods and drinks.
- Foods and drinks that contain artificial sweeteners.
Maintaining bowel regularity: Constipation can place added pressure on the bladder and have a negative effect on your bladder function. By keeping healthy bowel habits, you may be able to avoid constipation and help to lessen bladder symptoms. The following are some suggestions for maintaining bowel regularity:
- Increase your fiber intake by eating foods like beans, pasta, oatmeal, bran cereal, whole wheat bread, and fresh fruit and vegetables.
- Every morning, take 2 tablespoons of this mixture: 1 cup apple sauce, 1 cup unprocessed wheat bran, and ¾ cup prune juice.
- Exercise regularly to maintain regular bowel movements.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight can add pressure on your bladder, which may contribute to bladder control problems. If you are overweight, weight loss can reduce the pressure on your bladder.
What Tests Will I Need
Your GP will take a history which will include:
- Your urinary symptoms.
- Any past history of any medical problems.
- A review of the medicines that you are taking .
Your GP will also perform an examination of your tummy to feel for any increase in size of the bladder and any abnormality of your kidneys. An examination of the prostate gland is important for men. A vaginal examination is important for women in order to help find the cause of the urinary retention.
Your GP may be able to diagnose and treat the cause of your problems passing urine on the basis of the history and examination. Blood tests may be arranged, including a test of how well your kidneys are working.
If you have sudden urinary retention and cannot pass any urine then you will need to be seen straightaway in hospital. If you have persistent urinary retention your GP will often refer you to see a urology specialist for tests. These are undertaken to find out the cause of your urinary retention and the best ways to treat the problem.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection In Babies
How Can Nerve Stimulation Help Overactive Bladder
There are several treatments that involve stimulating your nerves to help improve overactive bladder. Your nerves help communicate the message that your bladder needs to be emptied to your brain. By treating the nerves, your healthcare provider can improve your bladder control. Nerve stimulation is a reversible treatment that is considered when conservative treatments have not worked or have not been tolerated. Conservative treatments include behavioral therapies and medications.
There are several types of nerve stimulation treatments. These can include:
Managing Bladder And Bowel Incontinence
Some common treatments are:
-
Changes in food or drink. Increasing your fiber intake can help manage diarrhea and constipation. Drinking plenty of fluids can also ease constipation. Not drinking fluids at certain times can help manage overactive bladder and urinary incontinence.
-
Exercises. Kegel exercises can strengthen the sphincter muscles and pelvic floor. This can help you have better control.
-
Medicines. Some medicines can help control bowel incontinence. Antidiarrheal medicines can help manage diarrhea. And medicine can help bladder muscles relax to give you better control.
-
Keeping a bathroom schedule. Setting a regular schedule for using the toilet can give you better control. This includes attempting to urinate or move your bowels at the same time each day.
-
Electrical stimulation. This therapy can stimulate damaged nerves. This may give you better muscle control in your bladder or bowel.
-
Surgery. In rare cases, you may need surgery to repair damage to muscles or nerves.
Your healthcare provider will work with you to create a treatment plan.
You May Like: Candida Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
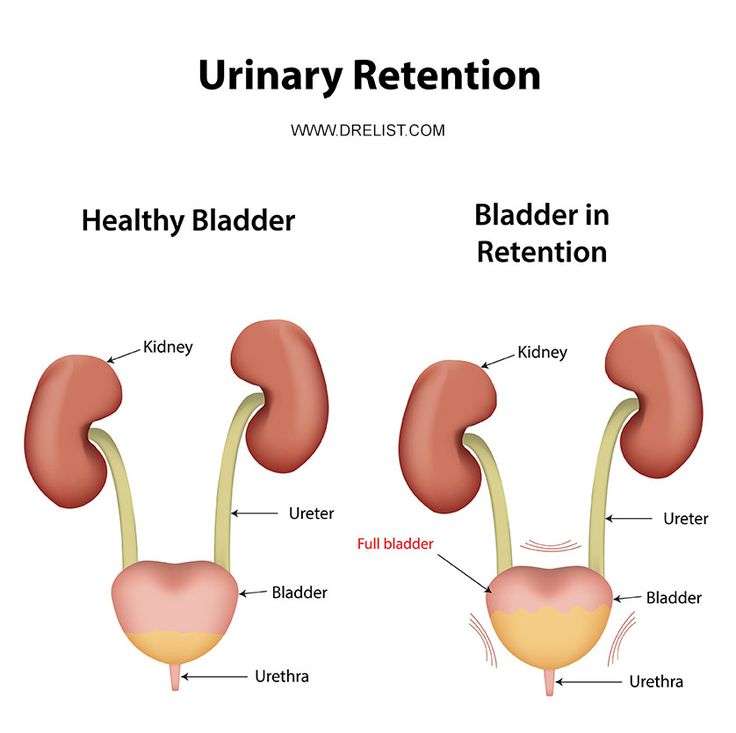
Causes Of Urinary Retention
There are many different causes.
Blockage In men, the urethra may be constricted by an enlarged prostate a common condition for men over 50. In women, blockage can be caused by certain types of pelvic prolapse, including Cystocele and Rectocele .
Other blockage reasons for both men and women include urethral stricture and urinary stones.
Infection / Swelling In men, prostatitis , can cause swelling that blocks the free flow of urine. Urinary Tract Infections and Sexually Transmitted Diseases can also cause swelling that leads to urinary retention.
Nerve Problems Urinary retention could be caused by a problem with the nerves that control the bladder. If the nerves are damaged, it can cause a breakdown in the signals between the brain and bladder. Some causes of nerve damage include:
- Stroke
Terminology Prevalence Epidemiology And Economic Impact
The International Continence Society is the governing body that has historically taken the lead in the standardization of terminology. The terminology used to describe OAB and associated symptoms has changed numerous times. The ICS recommends the use of symptoms, signs, and validated investigations to form workable diagnoses. In 2020, the ICS used the following terms:
It is important to note that, although the current definition of OAB is based on symptoms, DO is a urodynamic observation. By definition, to diagnose a patient with DO, one must observe involuntary detrusor contractions during the filling phase of CMG during urodynamics testing. OAB and DO are thus not interchangeable terms, and it is important that the clinician use each term correctly.
The number of individuals affected by OAB is difficult to establish. The populations studied vary substantially from one publication to another, and the symptoms or signs used to define OAB may also vary between publications. Overall, however, the incidence of OAB is high, ranging between 7% and 27% in males and between 9% to 43% in females .
Men were shown to have a higher prevalence of OAB dry, or OAB without UUI , and women had a higher prevalence of OAB wet, or OAB with UUI . In women, the presence of OAB wet rose from 2% in the youngest group to 19.1% in those 65 to 74 years of age .
You May Like: Bard Urinary Drainage Bag With Anti Reflux Dome
Natural Remedies For An Overactive Bladder
1. Kegel Exercises
If a weak pelvic floor is at the root of your OAB then kegel exercises can help a lot. These pelvic floor exercises can be done anywhere at anytime and they benefit both men and women. When done regularly, they can really help an overactive bladder.
Melody Denson, MD, a board-certified urologist with the Urology Team in Austin, TX, recommends these exercises for OAB. She says, They will trigger a reflex mechanism to relax the bladder. If you feel a tremendous urge to urinate, doing a kegel before you run to the bathroom will help settle down the bladder spasm and help you hold it until you get there.
2. Avoid Dietary Triggers
Significantly reduce the following foods and drinks that are known to contribute to overactive bladder:
- Alcohol
- Soda and other carbonated beverages
- Spicy foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- Milk and milk products
- Sugar and high sugar foods
Caffeine, alcohol and certain medications like diuretics are known to be major causes of acute incontinence, especially in the elderly population. Cranberry juice is surprisingly another thing to avoid if you have OAB. Although cranberry juice is often recommend for bladder health, it actually acts as an irritant if you have OAB.
3. Watch Fluid Intake
4. Double-Void
5. Schedule bathroom trips
6. Delay Urination
7. Try Acupuncture
8. Stop Smoking
Depression Anxiety Attention Deficit Disorder And Oab
It is probably too simplistic to view OAB with urge UI as just a myogenic or afferent disorder. Certain individuals seem predisposed to OAB. Circumstantial evidence suggests individuals with depression, anxiety, and attention deficit disorder may experience symptoms of OAB more often than the general population. Wolfe and colleagues59 suggested that depression, anxiety, feeding disturbances, pain, irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and changes in voiding are associated with disturbances in brain circuits using specific neurotransmitters, in particular serotonin . Fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndrome are conditions seen more often in patients with IC than the general population,5963 and these conditions are associated with OAB and possibly with depression, which provides a potential link with 5-HT metabolism. Perhaps the strongest evidence for diminished 5-HT function in depressed patients is the remarkable efficacy of selective serotonin uptake inhibitors in this group of patients. In addition, neuropharmacologic evidence indicates that some forms of depression are associated with abnormalities in the promoter for the serotonin transporter gene.64,65
Also Check: How To Treat Stress Urinary Incontinence
What You Need To Know
- Issues with urinating or passing stools are referred to as bladder and bowel dysfunction.
- Bladder and bowel problems often originate with nerve or muscle dysfunction, as these systems control the flow of urine and the release of stool.
- Other health issues may cause bladder and/or bowel dysfunction, including medicinal side effects, stress, neurologic diseases, diabetes, hemorrhoids and pelvic floor disorders.
- Therapy and management for these conditions can range from dietary changes and exercise to electrical stimulation and surgery depending on individual diagnosis.
Bladder or bowel incontinence means a problem holding in urine or stool. You may have unwanted passage of urine or stool that you cant control. These conditions can be stressful to deal with. But dont feel embarrassed about talking to your healthcare provider. They are used to dealing with these issues, and can help you manage the problem.
Precautions And Proper Diagnosis
The main symptoms of OAB can also occur in other health conditions like bladder cancer, urinary tract infection and enlarged prostate. Seeing blood in your urine is not a symptom of OAB.
A sudden and frequent need to urinate is common in both OAB and a UTI. How can you tell the difference between these two urinary health issues? Unlike OAB, a UTI also comes with other symptoms such as discomfort while urinating. In addition, OAB symptoms are continuous while UTI symptoms are sudden and may also include a fever.
Overflow incontinence is characterized by the involuntary release of urine from an overfull urinary bladder, often in the absence of any urge to urinate. This condition is not associated with OAB. It typically occurs in people who have a blockage of the bladder outlet, which can occur with benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer or a narrowing of the urethra. Overflow incontinence can also occur when the muscle responsible for removing urine from the bladder is too weak to empty the bladder in a normal way.
It is very important to see a doctor to ensure a proper diagnosis if you experience any changes in your urine and/or urination habits.
You May Like: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Side Effects
Obstruction In People With A Penis
Possible causes of obstruction in people with a penis
- Cystocele. Cystocele occurs when the bladder lowers and pushes against your vagina.
- Rectocele. This is when the rectum expands and pushes against your vagina.
- Uterineprolapse. Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus lowers and pushes against the bladder.
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional right away if you are unable to urinate or have severe pain in your abdomen. Acute urinary retention can be life threatening.
If you have any of the other symptoms of urinary retention, such as trouble urinating, frequent urination, or leaking urine, talk with your health care professional about your symptoms and possible treatments. Chronic urinary retention can cause serious health problems.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Go Away On Its Own
Does Overactive Bladder Only Happen In Women
More women than men experience overactive bladder, however, around three to 11 percent of men may experience urinary incontinence. The most common type of incontinence in men is urge incontinence, accounting for about 80 percent of cases. In men, stress incontinence can occur and may happen after prostate surgery, trauma or neurologic damage. With both women and men, the incidence increases with age.
What Causes An Overactive Bladder
It is often hard to say what causes an overactive bladder. Doctors recognise several underlying causes and it is important to make sure that there is no other treatable condition causing your symptoms before you assume that your problem is due to an overactive bladder.
We do know that some things can irritate the bladder and make symptoms worse such as:
- Some fluids we drink may cause problems. Caffeine and alcohol may irritate the bladder and cause urgency and frequency. Some fizzy drinks and fruit teas containing hibiscus can also irritate the bladder
- On the other hand, some people do not drink enough fluids, their urine becomes very concentrated and this can also irritate the bladder
- Another common cause of urgency is an infection. Your doctor or practice nurse can do a simple urine dipstick test to see if there is an infection present
You May Like: Tart Cherry Juice For Urinary Tract Infection
Nerve Disease Or Spinal Cord Injury
Many events or conditions can damage nerves and nerve pathways. Some of the most common causes are
- vaginal childbirth
- infections of the brain or spinal cord
- Diabetes
- accidents that injure the brain or spinal cord
- multiple sclerosis
- heavy metal poisoning
- pelvic injury or trauma
In addition, some children are born with nerve problems that can keep the bladder from releasing urine.
What Are The Complications Of A Neurogenic Bladder
The following are often linked to a neurogenic bladder:
- Urine leakage often happens when the muscles holding urine in do not get the right message.
- Urine retention happens if the muscles holding urine in do not get the message that it is time to pass urine.
- Damage to the tiny blood vessels in the kidney may happen if the bladder becomes too full and urine backs up into the kidneys. This causes extra pressure and may lead to blood in the urine.
- Infection of the bladder, ureters, or kidneys often results from urine that is held too long before its passed out of the body.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection In Children
Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
Meeting with a specialist in pelvic floor physical therapy to learn exercises and techniques that are known to improve the pelvic floor muscles. Pelvic floor physical therapy can be used to improve stress urinary incontinence, urge urinary incontinence, urinary frequency, urinary urgency and fecal incontinence.
How Is It Diagnosed
To diagnose urinary retention, a doctor will first ask about the history of your symptoms and perform a physical exam. The physical will include an examination of your genitals and rectum to look for any symptoms affecting those areas that may also affect the urinary tract.
Some other tests that may be used to confirm a diagnosis
likely be inserted to help quickly drain the urine. Local anesthesia will be used to make sure you dont feel pain or discomfort from the catheter.
If a catheter doesnt work or cant be used because of an injury or other condition, a doctor may insert a suprapubic catheter into the skin above your bladder to drain the urine.
Also Check: Best Pads For Male Urinary Incontinence
How Can Neurogenic Bladder Affect Your Life
The symptoms of neurogenic bladder can seriously affect your quality of life. They may make it difficult for you to get through your day without interruptions. You may feel afraid to go out with friends, take vacations or do everyday things. You may be afraid you may not be able to find a bathroom when you need one. Some people begin to cancel activities and withdraw from their lives. Neurogenic bladder may affect your work and your relationships. You may feel tired, depressed, anxious and lonely. If you are experiencing incontinence, the leaking urine can sometimes cause skin problems or infections.
What Is The Outcome
The outcome will depend on the underlying cause of urinary retention and whether the urinary retention has caused any damage to your kidneys:
- Some causes of urinary retention resolve quickly without any long-term problems – eg, urinary retention after a general anaesthetic.
- In other cases, urinary retention will resolve once the underlying cause has been treated – eg, prostate gland enlargement.
- Occasionally the cause of urinary retention cannot be cured and a long-term small, flexible tube is needed. Sometimes this can be done by regularly inserting a catheter into the bladder and then removing the catheter once the bladder is emptied.
Read Also: What Is A Urinary Tract Infection Caused By
What Causes Urinary Retention
Urinary retention can be caused by an obstruction in the urinary tract or by nerve problems that interfere with signals between the brain and the bladder. If the nerves arent working properly, the brain may not get the message that the bladder is full. Even if you know that your bladder is full, the bladder muscle that squeezes urine out may not get the signal that it is time to push, or the sphincter muscles may not get the signal that it is time to relax. A weak bladder muscle can also cause retention.
Bladder Has Two Distinct Roles
Recommended Reading: Women’s Urinary Tract Problems