How Are Utis Treated
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. After several days of antibiotics, your doctor may repeat the urine tests to be sure that the infection is gone. It’s important to make sure of this because an incompletely treated UTI can come back or spread.
If someone has a lot of pain from a UTI, the doctor may recommend a medicine to help relieve the spasm and pain in the bladder. This will turn pee a bright orange color, but it’s harmless and will usually make a person much more comfortable within hours. In the case of a kidney infection, a doctor may prescribe pain medicine.
If you’ve finished all the medicine or if your symptoms aren’t much better after 2 to 3 days of treatment, contact your doctor.
Drink lots of water during and after treatment because each time you pee, the bladder cleanses itself a little bit more. Cranberry juice may also be helpful. Skip drinks that containe caffeine , such as soda and iced tea.
People who get a doctor’s help for a UTI right away should be clear of symptoms within a week. Someone with a more severe infection may need treatment in a hospital so they can get antibiotics by injection or IV .
A doctor may tell people with UTIs to avoid sex for a week or so, which lets the inflammation clear up completely.
Antibiotics For A Uti
The form of antibiotic used to treat a bacterial UTI usually depends on which part of the tract is involved.
Lower tract UTIs can usually be treated with oral antibiotics. Upper tract UTIs require intravenous antibiotics. These antibiotics are put directly into your veins.
Sometimes, bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics. To reduce your risk of antibiotic resistance, your doctor will likely put you on the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 1 week.
Results from your urine culture can help your doctor select an antibiotic treatment that will work best against the type of bacteria thats causing your infection.
Treatments other than antibiotics for bacterial UTIs are being examined. At some point, UTI treatment without antibiotics may be an option for bacterial UTIs by using cell chemistry to change the interaction between the body and the bacteria.
There are no home remedies that can cure a UTI, but there are some things that you can do that can help your medication work better.
These home remedies for UTIs, like drinking more water, may help your body clear the infection faster.
What Are Causes And Risk Factors For A Urinary Tract Infection
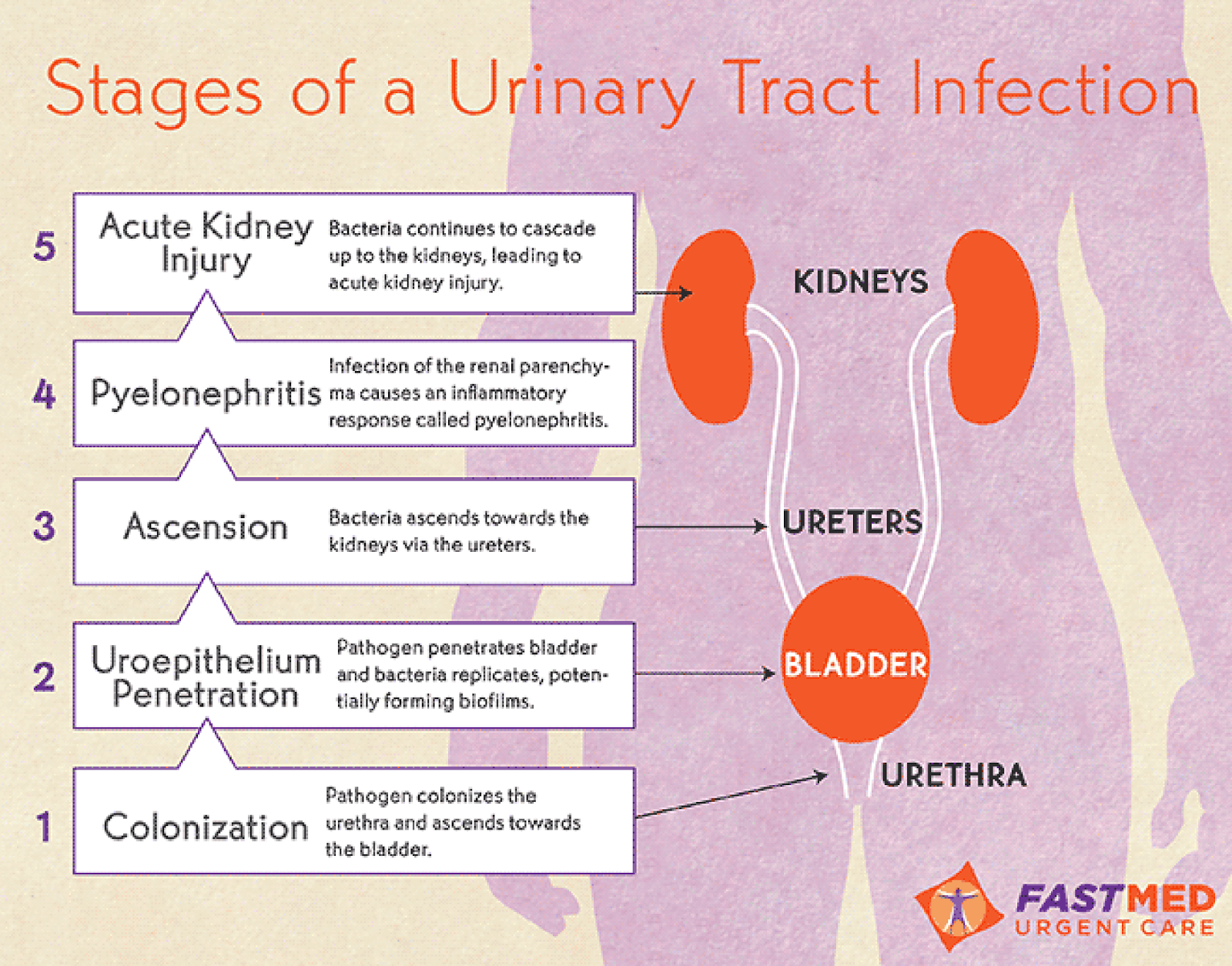
The urine is normally sterile. An infection occurs when bacteria get into the urine and begin to grow. The bacterial infection usually starts at the opening of the urethra where the urine leaves the body and moves upward into the urinary tract.
- The culprit in at least 90% of uncomplicated infections is a type of bacteria called Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli. These bacteria normally live in the bowel and around the anus.
- These bacteria can move from the area around the anus to the opening of the urethra. The two most common causes of this are improper wiping and sexual intercourse.
- Usually, the act of emptying the bladder flushes the bacteria out of the urethra. If there are too many bacteria, urinating may not stop their spread.
- The bacteria can travel up the urethra to the bladder, where they can grow and cause an infection.
- The infection can spread further as the bacteria move up from the bladder via the ureters.
- If they reach the kidney, they can cause a kidney infection , which can become a very serious condition if not treated promptly.
The following people are at increased risk of urinary tract infection:
The following special groups may be at increased risk of urinary tract infection:
Read Also: Fastest Way To Cure Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infection: Diagnosis
According to the UK NHS, the diagnosis for UTI involves the following procedure:
-
Your doctor may ask you for a urine sample to check in for any blood, bacteria or white blood cells which might direct towards an urinary tract infection. Make sure to clean your genitals and collect the sample midway.
-
Another urine lab test may involve to check in what type of bacteria may be responsible for the infection to prescribe the best suited medicines.
-
If you might be experiencing frequent UTIs, your doctor may take image tests like MRI or CT scan to check for any abnormalities in the urinary tract.
-
Recurrent UTIs may make your doctor to ask you for a cystoscopic in which a thin, flexible tube shall be inserted in your urethra and bladder to check for abnormalities.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti In A Child
Symptoms can occur a bit differently in each child.
Symptoms in babies can include:
- Fever
Symptoms in children can include:
- Sudden need to urinate
- Loss of control of urine
- Pain while urinating
- Pain above the pubic bone
- Blood in the urine
- Pain in the back or side below the ribs
- Tiredness
The symptoms of a UTI can seem like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop A Urinary Tract Infection Before It Starts
Should I Take Antibiotics To Prevent Uti
Not usually. Antibiotics are medicines used to kill bacteria that cause infection. When you take an antibiotic to kill bacteria, the bacteria can change or adapt in a way that it becomes resistant to the antibiotic being used. This means that the antibiotic can no longer kill the bacteria. It takes a stronger antibiotic to then kill the bacteria in the future. There are a limited number of antibiotics that can kill bacteria, so its best to use antibiotics only when needed to avoid reaching the point when the bacteria are resistant to all antibiotics.
Here are a few recommendations for using antibiotics and better avoiding antibiotic resistance.
- Do not take antibiotics that are not prescribed to you.
- Do not take antibiotics for conditions that do not require them. For example, dont take antibiotics to treat viruses like the cold or flu.
- Do not take antibiotics simply because your urine has bacteria. It is very common for people with SCI to have bacteria in their urine, so you usually only need to take an antibiotic to treat a UTI when you begin to you have signs and symptoms.
- Antibiotics may be used to prevent infection in some situations. For example, women with SCI are often prescribed antibiotics to prevent UTI during pregnancy.
Urinary Tract Infection In Men
Approved by: Maulik P. Purohit MD, MPH
Urinary Tract Infection is generally caused by a microbe, such as bacteria. Men are at a decreased risk of developing a UTI than women, because of the anatomical structure of the male urinary system. The infection can occur more frequently with increasing age, due to a blockage in the urinary tract, having a bladder catheter, or with a decreased immune system.
Don’t Miss: Amoxicillin For Urinary Tract Infection
What Are Other Possible Causes Of Painful Urination
A painful burning feeling when you urinate is often a sign of a urinary tract infection . However, painful urination can occur even if you dont have an infection. Certain drugs, like some used in cancer chemotherapy, may inflame the bladder. Something pressing against the bladder or a kidney stone stuck near the entrance to the bladder can also cause painful urination.
Painful urination can also be caused by vaginal infection or irritation. You might be sensitive to chemicals in products such as douches, vaginal lubricants, soaps, scented toilet paper, or contraceptive foams or sponges. If it hurts to urinate after youve used these products, youre probably sensitive to them.
Watch For Early Signs Of Infection
You may notice warning signs before you start to experience symptoms of UTI.
- Gritty sediment in the urine.
- Mucus in the urine. This is often a sign of high levels of bacteria in the
- Dark, cloudy or bad smelling urine.
If you notice any of these, you might be able to fend off UTI.
- Cut back on drinking liquids with alcohol, caffeine, and sugar.
- Drink more water to help wash out more of the bacteria.
- If you do intermittent catheterization, do it more often. If you use an indwelling catheter, change it.
Consider changing it again after the early signs of infection have gone away.
Read Also: Hills Urinary Care C D Multicare
When Should I Reach Out To My Doctor About Frequent Urination
Because the conditions behind frequent urination can range wildly from casual to severe, you should speak to your doctor about anything outside of your typical urination patterns. In some cases, frequent urination may be just an annoying symptom that will end when you cut back on the caffeineor have the baby. However, if you are unsure why youre urinating so frequently, it is best to set up an appointment and talk about it. This is a symptom that can often be treated and isnt something that you need to just deal with.
There are a few signs to keep an eye out for and call your doctor immediately if you have them with frequent urination. These include:
- If you have a fever.
- If you are vomiting.
- If you have back pain .
- If you see blood in your urine.
- If you have a discharge coming out of your vagina or penis.
The Most Common Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
Most UTIs are caused by bacteria. But you may be interested to know that while E.coli is the most common, it is certainly not the only culprit.
In fact, new testing methods based on molecular technology are showing that E.coli may be much less prominent in urinary tract infections than we think.
In the USA, it is currently believed the breakdown of what causes UTIs looks like this:*It is generally believed non-bacterial UTIs are more likely to occur in people with compromised immune systems.
This is an estimated breakdown based on various sources and studies. But researchers may have to drastically reassess assumptions, as a recent review of 11,000 urine samples using molecular testing found E.coli DNA in just 40% of the samples.
On top of that, DNA of 1200 individual microbial species was detected. Obviously, thats substantially more than weve shown here.
Now for a quick lesson on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It sounds science-y, and, well, it is, but its also cool.
First, Gram is the last name of a Danish physician who developed a technique of staining bacteria with violet dye to differentiate between two distinct types. It has nothing to do with weight.
Gram-positive bacteria retain a blue or purple colour after the test, while Gram-negative bacteria do not, and are instead red or pink. You can find some really pretty pictures online.
Take another look at that diagram above. Two things should now be clear:
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Tract Infection At Home
When Should People Seek Medical Care For A Uti
Any adult or child who develops any of the symptoms of a urinary tract infection needs to be evaluated by a medical professional, preferably within 24 hours. Most medical offices can test urine for infection by using a quick urine “dipstick” test.
- Someone who has symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection should call a health care professional for an appointment, preferably on the same day that symptoms are recognized.
- Someone who has symptoms of an upper urinary tract infection involving the kidneys should call a health care professional immediately. Depending on the situation, he or she will recommend either a visit to the office or a hospital emergency department.
If someone has symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection and any of the following applies, he or she may be at risk for complications of the urinary tract infection.
- Vomiting and inability to keep down clear fluids or medication
- Not better after taking antibiotics for two days
- Pregnant
- Having diabetes or another disease that affects the immune system
- Taking medication that suppresses the immune system such as cancer chemotherapy
Infants, children, and elderly people with any of the signs and symptoms of UTI should see their health care professional as soon as possible or go to an emergency department for evaluation.
- People who have blood in the urine
Key Points About Urinary Tract Infections
- Urinary tract infections are a common health problem that affects millions of people each year. These infections can affect any part of the urinary tract.
- Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
- The most common symptoms of UTIs include changes in urination such as frequency, pain, or burning urine looks dark, cloudy, or red and smells bad back or side pain nausea/vomiting and fever.
- Antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Other treatments may include pain relievers, and drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Other things that can be done may help reduce the likelihood of developing UTIs.
You May Like: How To Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection After Intercourse
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
What Kinds Of Doctors Treat Urinary Tract Infections
Most urinary tract infections can be treated by your primary care doctor or your child’s pediatrician. They are usually the best provider to treat you as they are most familiar with your medical history, medications you are taking, and other factors that might affect your treatment. If you seek treatment in an urgent care facility, a specialist in emergency medicine may be involved in your care.
If there are frequent reoccurrences of UTIs or if complicating circumstances are present, your primary care doctor might refer you to a urologist, a physician who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to the urinary system.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Urinary Tract Infection Medicine
Can I Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
You can usually prevent a urinary tract infection with lifestyle changes. These tips can include:
In some post-menopausal women, a healthcare provider may suggest an estrogen-containing vaginal cream. This may reduce the risk of developing a UTI by changing the pH of the vagina. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have recurrent UTIs and have already gone through menopause.
Over-the-counter supplements are also available for UTIs. These are sometimes recommended for people who have frequent UTIs as another way to prevent them. Talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplements and ask if these could be a good choice for you.
What Not To Do When You Get A Uti
As weve mentioned, symptoms can be an indication of something more serious disguised as a simple UTI.
For this reason alone, its best to see a doctor and get tested, particularly if youve experienced multiple UTIs within a year, or have other reasons for concern.
If you do suffer from recurrent UTIs, you need to arm yourself with more information before jumping straight back onto another course of antibiotics or dabbling in home remedies.
| People often tell us that when they get a UTI they treat themselves with medications they were prescribed for a different illness. Not only does this mean its likely the wrong antibiotic, if you only have some of the course leftover, theres an even higher chance it will not treat a UTI effectively. Its best to avoid this practice. |
If you dont know which pathogen is causing your UTI, you are very unlikely to be able to guess the best treatment, let alone choose one that will work at all.
Why?
There is no single treatment that will kill all pathogens that can cause a urinary tract infection.
At best, if you choose or are given the wrong treatment, youll be right back where you started in a month or so. At worst, your UTI will continue to escalate.
UTI research is ongoing, and it can take some time for new findings to make their way into mainstream medicine. We had a chat with Alan Wolfe, who leads the urinary research team at Loyola University.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Use For Urinary Tract Infection
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
As adherence has a key role at nearly every step of UTI pathogenesis, one attractive strategy for the development of antivirulence therapies, including vaccines, has been to target CUP pili. As a general rule, vaccination with whole pili has been ineffective at generating an antibody response that can protect against UTIs. However, adhesin-based vaccines have been shown to be effective at blocking hostpathogen interactions, thus preventing the establishment of disease. Experiments using mouse and cynomolgus monkey models of UTIs determined that immunization with PapDPapG or FimCFimH chaperoneadhesin complexes protected against UTIs. The effectiveness of the FimCFimH vaccine was shown to be due, in large part, to antibodies that block the function of FimH in bladder colonization. Furthermore, the anti-FimH antibodies did not seem to alter the E. coli niche in the gut microbiota. Modifications of this vaccine are currently under development, with the aim of inducing greater immune stimulation,. For example, one approach has been to fuse FimH to the flagellin FliC in order to induce a more substantial acute inflammatory response, which functions through TLR4 signalling via the MYD88 pathway. A Phase I clinical trial began in January 2014 to evaluate the efficacy of a FimCFimH vaccine using a synthetic analogue of monophosphoryl lipid A as the adjuvant.