Urinary Tract Infections And Dementia
Urinary tract infections are a type of infection common among older people. If a person with a memory impairment or dementia has a UTI, this can cause sudden and severe confusion known as delirium.
Urinary tract infections and dementia
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
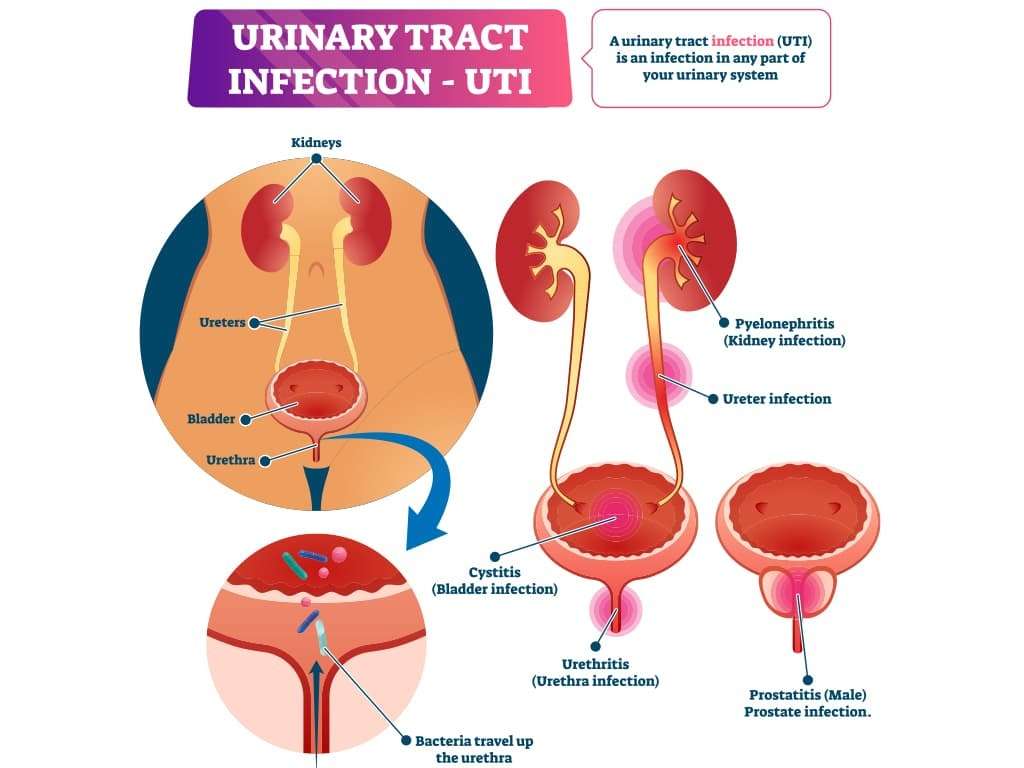
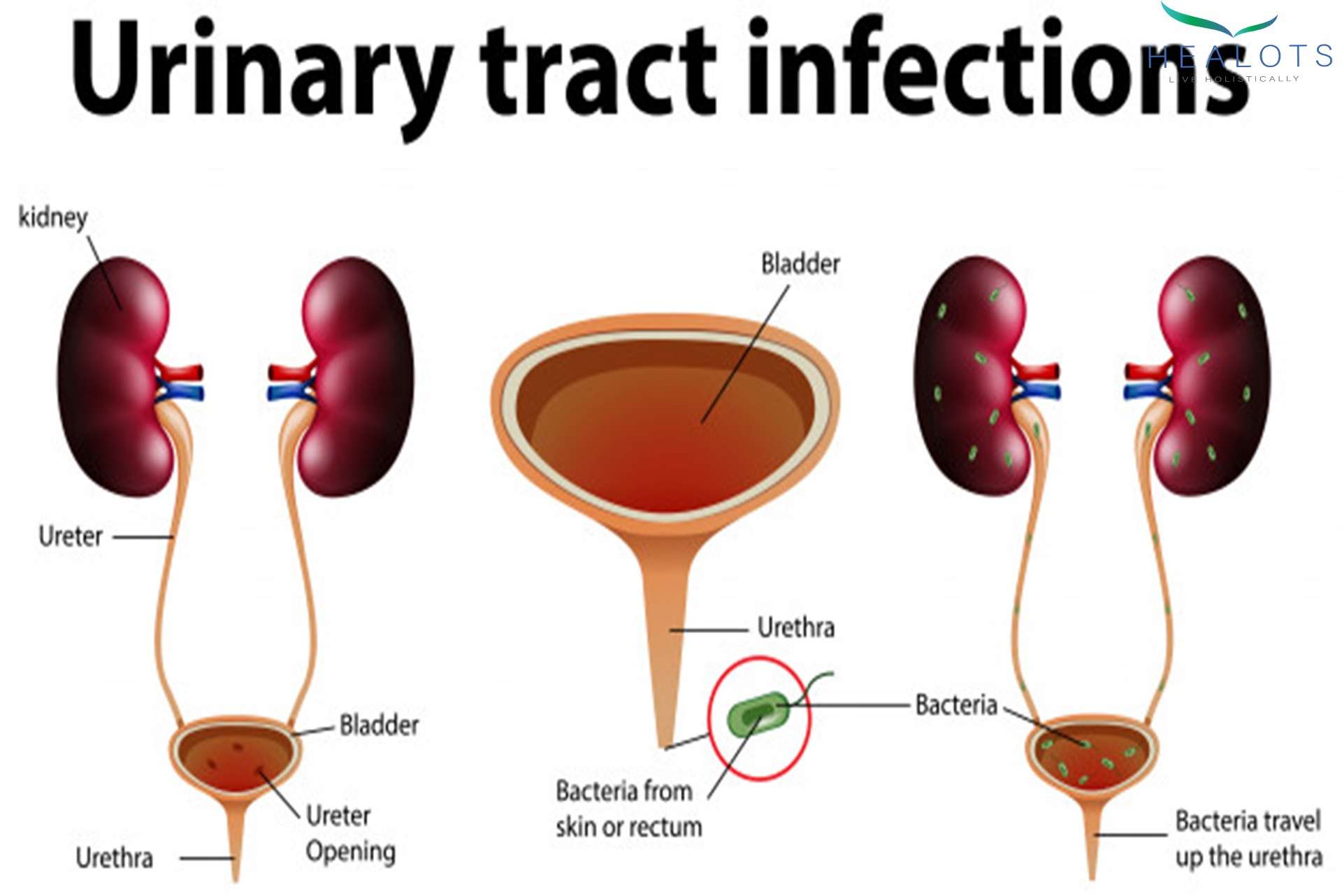
A urinary tract infection is an infection of the urinary system. This type of infection can involve your urethra , kidneys or bladder, .
Your urine typically doesnt contain bacteria . Urine is a byproduct of our filtration systemthe kidneys. When waste products and excess water is removed from your blood by the kidneys, urine is created. Normally, urine moves through your urinary system without any contamination. However, bacteria can get into the urinary system from outside of the body, causing problems like infection and inflammation. This is a urinary tract infection .
Small Molecules Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
Our detailed understanding of pilus assembly and pilusreceptor binding has opened the door to the development of two classes of small, rationally designed synthetic compounds to inhibit pili: mannosides, which inhibit pilus function and pilicides, which inhibit pilus assembly. Targeting CUP pilus function or assembly has therapeutic potential, as it should block UPEC colonization, invasion and biofilm formation, thus preventing disease,,,.
Mannosides, which are FimH receptor analogues, have been developed to bind FimH with high affinity and block FimH binding to mannosylated receptors,,. Mannosides are potent FimH antagonists that offer a promising therapeutic opportunity for the treatment and prevention of UTIs by interrupting key hostpathogen interactions. Studies in mouse models have demonstrated the potential of mannosides as novel therapeutic strategies against UTIs: mannosides are orally bioavailable they are potent and fast-acting therapeutics in treating and preventing UTIs they function by preventing bladder colonization and invasion they are effective against multidrug-resistant UPEC they potentiate antibiotic efficacy and they are effective against established UTIs and CAUTIs,,,.
Also Check: How To Reduce Urinary Incontinence
What Is Icd 10 Code For Urinary Tract Infection
3.9/5Urinary tract infectionICD10code
Keeping this in consideration, what is the CPT code for urinary tract infection?
Codes 038.11 and 995.91 are assigned to report the systemic infection, staphylococcus aureus sepsis. Code 599.0 is reported to identify UTI as the localized infection. Code E879.
Subsequently, question is, can you code UTI and pyelonephritis together? In the case of a patient with a UTI diagnosis, if you do not know the cause of the infection, you should use N39. 01 for acute cystitis, or N10 for pyelonephritis. However, while certainly a good practice, using a secondary code to identify the reason for the infection might not be necessary for reimbursement.
Subsequently, one may also ask, is acute cystitis the same as UTI?
Acute cystitis is a sudden inflammation of the urinary bladder. Most of the time, a bacterial infection causes it. This infection is commonly referred to as a urinary tract infection . Irritating hygiene products, a complication of certain diseases, or a reaction to certain drugs can also cause acute cystitis.
What is cystitis?
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder. Inflammation is where part of your body becomes irritated, red, or swollen. In most cases, the cause of cystitis is a urinary tract infection . A UTI happens when bacteria enter the bladder or urethra and begin to multiply.
Dont Miss: Flagyl Pills For Yeast Infection
Should I Be Worried If I Have These Conditions And Frequent Urination
If you ever have a symptom that is outside of whats normal for your body, reach out to your healthcare provider. In some cases, pregnancy, for example, frequent urination is completely normal and nothing to worry about. However, in some conditions, your caregiver may want to know if you are urinating much more than you typically do. Theres a very wide range of conditionswith varying levels of seriousnessthat could cause frequent urination. It is always safe to discuss your symptoms with your healthcare provider.
Read Also: Constipation And Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections
Normal urine is sterile and contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It does not contain bacteria, viruses, or fungi. A UTI occurs when germs, most often bacteria from the digestive tract, get into the opening of the urethra and start to multiply.
Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
Why Was The Uti Program Developed
- It is common to find bacteria in the urine of the elderly but it does not always mean that they have a UTI.
- Older people are often given antibiotics for what health care providers and other caregivers assume to be UTIs.
- It can be harmful to treat somebody with antibiotics when they dont need them.
- Antibiotic use can increase the risk of antibiotic resistance, which can make it more difficult to treat future infections.
For more information on the overuse of antibiotics in long term care homes, see .
Read Also: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Cause An Elevated Psa
Physical Changes Spur Urinary Tract Infections During Menopause
Frequent sexual intercourse is one of the biggest UTI risk factors for younger women. For menopausal women, however, physical changes such as the thinning of vaginal tissue, difficulty fully emptying the bladder, incontinence, and pelvic organ prolapse are the main culprits.
In addition, during menopause, the body produces less estrogen, a hormone that among other functions helps keep the bacteria levels in the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. Vaginal estrogen creams may restore the normal bacterial balance of the vagina, thus helping to stave off recurrent UTIs.
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will use the following tests to diagnose a urinary tract infection:
- Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is used to determine the type of bacteria in your urine. This is an important test because it helps determine the appropriate treatment.
If your infection does not respond to treatment or if you keep getting infections over and over again, your doctor may use the following tests to examine your urinary tract for disease or injury:
- Ultrasound: In this test, sound waves create an image of the internal organs. This test is done on top of your skin, is painless and doesnt typically need any preparation.
- Cystoscopy: This test uses a special instrument fitted with a lens and a light source to see inside the bladder from the urethra.
- CT scan: Another imaging test, a CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes cross sections of the body . This test is much more precise than typical X-rays.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Discharge Male
What Causes Utis In Women
A UTI is caused by bacteria from your skin or rectum entering the urinary tract and causing an infection. Women with typically female genitals are more likely than other people to get UTIs. The urethra is the tube that takes urine out of your body from your bladder. In most women, the urethra is shorter and closer to the rectum. Both of these factors mean that bacteria dont have as far to travel, making it easier for an infection to start. Some women may have different types of genitals. Depending on their anatomy, these women may be more or less likely to get UTIs.
For Those Who Experience Frequent Utis Managing Risk Factors May Help With Prevention
In some people, urinary tract infections come back again and again. Women, especially, are likely to have recurrent UTIs. While recurrences usually develop within three months of the original infection, having more than two within six months is technically considered a recurrence.
Besides precautions and at-home strategies to help prevent UTIs, sometimes antibiotics are used as a preventive measure for those with frequent UTI recurrences.
Managing risk factors by maintaining good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back for women and avoiding spermicides can lower your likelihood of repeat UTIs.
Read Also: Pain In Urinary Tract Male
Prevent Your Bladder From Getting Too Full
Empty your bladder when needed. Empty it completely each time. This will help to reduce your chances of developing two common problems that increase your risk for UTI.
Who Experiences Frequent Urination
The need to urinate is something that everyone feels. This shared experience isnt always consistent though. Sometimes you may need to urinate much more often than what is typical for you. This can happen to anyone. Men, women, and children can all have this symptom. However, its more common at certain times in your life or when you have other conditions. Youre more likely to frequently urinate if youre:
- A middle-age or old adult.
- Pregnant.
Read Also: Urinary So Morsels In Gravy
Is Uti Common After Spinal Cord Injury
Yes. Here are 3 of the more common reasons people with SCI develop UTIs.
1. Most people lose normal urinary function after SCI. They need a bladder management option to empty the urine from their bladder to keep their bladder and kidneys healthy. Most bladder management options make it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder through the urethra.
- Please read Bladder Management Options Following Spinal Cord Injury” to learn more about normal urinary function, how it changes after SCI, and bladder management options.
2. Most people lose normal bowel function after SCI, and contact with stool is common during bowel management. Stool has bacteria that can cause a UTI. UTIs are often caused when bacteria from stool gets into the bladder when the bladder is being emptied.
- Please read Bowel Function after Spinal Cord Injury to learn more about normal bowel function, how it changes after SCI, and bowel management options.
3. Once in the bladder, bacteria are hard to get rid of. People with normal bladder function can usually get rid of most bacteria by fully emptying their bladder when they urinate. However, many people with SCI cant fully empty their bladder, even with good bladder management. This allows bacteria to stay in the bladder almost all of the time, making it easier for a UTI to develop.
Seek Medical Attention For Utis
It is important to seek medical attention if you think you may have a UTI particularly if you think you may have a bladder or kidney infection, both of which are very serious conditions. Early treatment of urinary infection can help to prevent infection spreading to the bladder or kidneys.
Your doctor will test your urine to check which micro-organism is present. Urinary tract infections usually respond quickly and well to antibiotics.
Also Check: Does Apple Cider Vinegar Help Urinary Tract Infections
Watch For Early Signs Of Infection
You may notice warning signs before you start to experience symptoms of UTI.
- Gritty sediment in the urine.
- Mucus in the urine. This is often a sign of high levels of bacteria in the
- Dark, cloudy or bad smelling urine.
If you notice any of these, you might be able to fend off UTI.
- Cut back on drinking liquids with alcohol, caffeine, and sugar.
- Drink more water to help wash out more of the bacteria.
- If you do intermittent catheterization, do it more often. If you use an indwelling catheter, change it.
Consider changing it again after the early signs of infection have gone away.
How Do You Get Urinary Tract Infections
The design of the human body makes it so it isnt hard to get a bacterial UTI, because the infection comes from outside, through the urethra. Bacteria in the genital area can enter the urethra and the urinary tract, either because wiping after going to the bathroom, sexual activity, or unsanitary conditions. Once the bacteria have entered the urethra, the body tries fight them off, but sometimes the bacteria multiply and cause an infection.
In the case of a fungal infection, usually the fungus gets to the urinary tract through the blood stream. Those who develop this type of infection are usually ill with a disease that has compromised their immune system, such as AIDS.
In general, women get more UTIs than do men and this increases with age. Statistics show that many women get more than one. Almost 20% of women who have had one UTI will go on to have a second. Of this 20%, 30% of those will have a third, and in turn, 80% of these women will have more.
Read Also: What Antibiotics Are Given For Urinary Tract Infections
Implementing The Uti Program
The three phases of the UTI Program are designed to help LTCHs adopt and sustain best practices for managing and treating UTIs. Each phase is supported by tools and resources that have been developed based on current evidence in infection prevention and control, antimicrobial stewardship and clinical practice. The resources are listed in the pages that follow.
The includes additional background information and details about the UTI Programs activities and implementation strategies. We recommend downloading and/or printing the Implementation Guide for reference as you work through each of the implementation phases.
How Is Dysuria Diagnosed
See your healthcare provider if you feel pain or burning when you pee. Dysuria can be a symptom of medical condition that may need to be treated. To diagnose your pain, first your healthcare provider will review your complete medical history, including asking you questions about your current and past medical conditions, such as diabetes mellitus or immunodeficiency disorders. He or she may also ask about your sexual history to determine if an STI could be the cause of the pain. Tests to screen for STIs may also be needed, especially if men have a discharge from their penis or women have discharge from their vagina. If you are a woman of childbearing age, a pregnancy test may be done.
Your provider will also ask about your current prescriptions and over-the-counter medication use and any tried home remedies to manage the dysuria.
Your healthcare provider will also ask you about your current symptoms and obtain a clean catch sample of your urine. Your urine sample will be analyzed for white blood cells, red blood cells or foreign chemicals. The presence of white blood cells tells your provider you have inflammation in your urinary tract. A urine culture reveals if you have a urinary tract infection and if so, the bacteria that are causing it. This information allows your provider to select the antibiotic that will work best in treating the bacteria.
Don’t Miss: How Does Cranberry Juice Help Urinary Tract Infections
What Can Happen If A Uti Is Not Treated
If treated right away, a UTI is not likely to damage your urinary tract. But if your UTI is not treated, the infection can spread to the kidneys and other parts of your body. The most common symptoms of kidney infection are fever and pain in the back where the kidneys are located. Antibiotics can also treat kidney infections.
Sometimes the infection can get in the bloodstream. This is rare but life-threatening.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
While mild UTIs in healthy adukts will often go away on their own without treatment, you shouldn’t avoid seeing a healthcare provider to get a urine test or start treatment.
If you develop signs of a kidney infection, including flank pain, nausea, or vomiting, you need to see a healthcare provider immediately.
If you are pregnant, you should never take a chance with UTIs, especially if you have diabetes, HIV, or have had previous infections. Even mild symptoms should be looked at, treated, and monitored to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Without exception, any symptoms of suggestive of sepsis should be treated as a medical emergency. This is especially true in babies or the elderly.
Don’t Miss: Over The Counter Urinary Tract Infection Pain Relief
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Toxins And Proteases
The UPEC pore-forming toxin HlyA has also received attention as a potential vaccine target and was evaluated in a mouse model of pyelonephritis to assess protection against renal damage,. Vaccination with HlyA reduced the incidence of renal scaring compared with controls however, it did not protect against UPEC colonization of the kidneys. In addition, in a mouse model of UTI, vaccination with the P. mirabilis haemolysin, HpmA, did not provide protection against bacterial colonization. However, vaccination with Pta, an alkaline protease with toxic effects towards epithelial cells, displayed promising results in a mouse model of UTI, protecting against upper UTI, although bacterial burdens in the bladder remained unaffected. Thus, although haemolysins and proteases might provide effective vaccine targets for preventing upper UTIs, additional studies are needed to determine the effectiveness of these enzymes as targets for vaccines.
Should I Take Antibiotics To Prevent Uti
Not usually. Antibiotics are medicines used to kill bacteria that cause infection. When you take an antibiotic to kill bacteria, the bacteria can change or adapt in a way that it becomes resistant to the antibiotic being used. This means that the antibiotic can no longer kill the bacteria. It takes a stronger antibiotic to then kill the bacteria in the future. There are a limited number of antibiotics that can kill bacteria, so its best to use antibiotics only when needed to avoid reaching the point when the bacteria are resistant to all antibiotics.
Here are a few recommendations for using antibiotics and better avoiding antibiotic resistance.
- Do not take antibiotics that are not prescribed to you.
- Do not take antibiotics for conditions that do not require them. For example, dont take antibiotics to treat viruses like the cold or flu.
- Do not take antibiotics simply because your urine has bacteria. It is very common for people with SCI to have bacteria in their urine, so you usually only need to take an antibiotic to treat a UTI when you begin to you have signs and symptoms.
- Antibiotics may be used to prevent infection in some situations. For example, women with SCI are often prescribed antibiotics to prevent UTI during pregnancy.
You May Like: How To Ease Urinary Pain