Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
What Are The Symptoms Of Utis In The Elderly
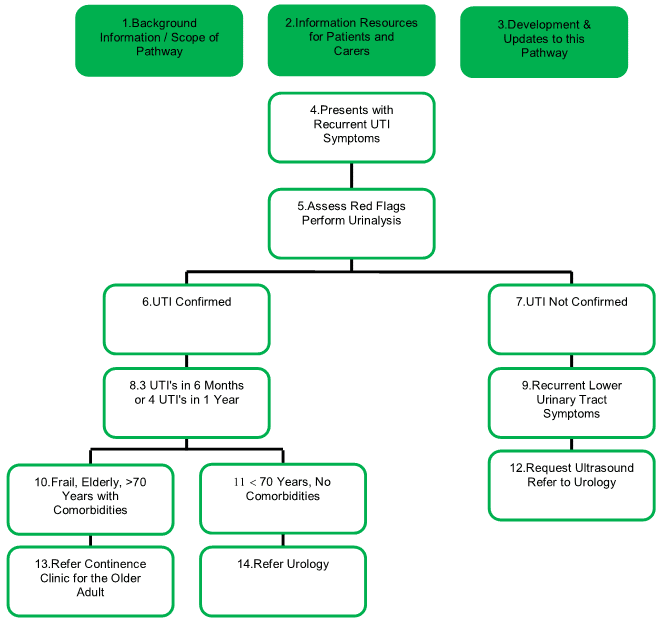
Like anyone with a UTI, older adults may experience typical physical symptoms. Yet they may not notice a mild infection right away. This is because chronic urinary problems common in seniors, such as urinary incontinence or frequency, may have similar symptoms to a UTI, masking an infection.
Common symptoms of a UTI include:
- Burning, painful sensation with urination
- Frequent, intense urge to urinate even when theres little urine to pass
- A feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied
- Blood in the urine
- Inability to perform common daily tasks, such as getting dressed or feeding themselves
Take Showers Instead Of Baths
Switching to showers may reduce your risk of UTIs if you usually take baths. Warm water can encourage bacterial growth, meaning that although relaxing, a long soak could give rise to an infection. For those worried about the chance of a fall, installing grab bars or using a shower seat may make it possible to shower more safely.
Read Also: What Is A Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
One reviewer extracted study characteristics and outcome data from included trials. We contacted two authors for subgroup data on postmenopausal women. One author replied and provided relevant outcome data. Two reviewers independently assessed the risk of bias of the included studies using the Cochrane Collaborations risk of bias tool. Disagreements were resolved through discussion. We used RevMan V.5.3 to meta-analyse the data and generate forest plots.
Empty Your Bladder After Sex
Following sex, be sure to use the bathroom and empty your bladder as soon as possible. You should also drink extra water to flush any bacteria out of the urinary tract.
If you suspect you have a urinary tract infection and need relief from your symptoms, schedule a diagnostic evaluation at Primary Care & Walk-In Medical Clinic online, , or visit the clinic in person.
You Might Also Enjoy
Don’t Miss: What Antibiotics Are Given For Urinary Tract Infections
Simple Ways To Prevent A Uti In Elderly Women
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are more than a painful medical condition. Left untreated, these infections can spread through the body. The leading cause of sepsis, an untreated UTI can ultimately result in death. For caregivers of elderly patients, learning how to recognize a UTI can be tricky as the symptoms are varied. Fortunately, there are three easy ways to avoid the onset of the infection to begin with.
Recommended Reading: Hollister Vented Urinary Leg Bag
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
You May Like: How To Treat Puppy Urinary Tract Infection
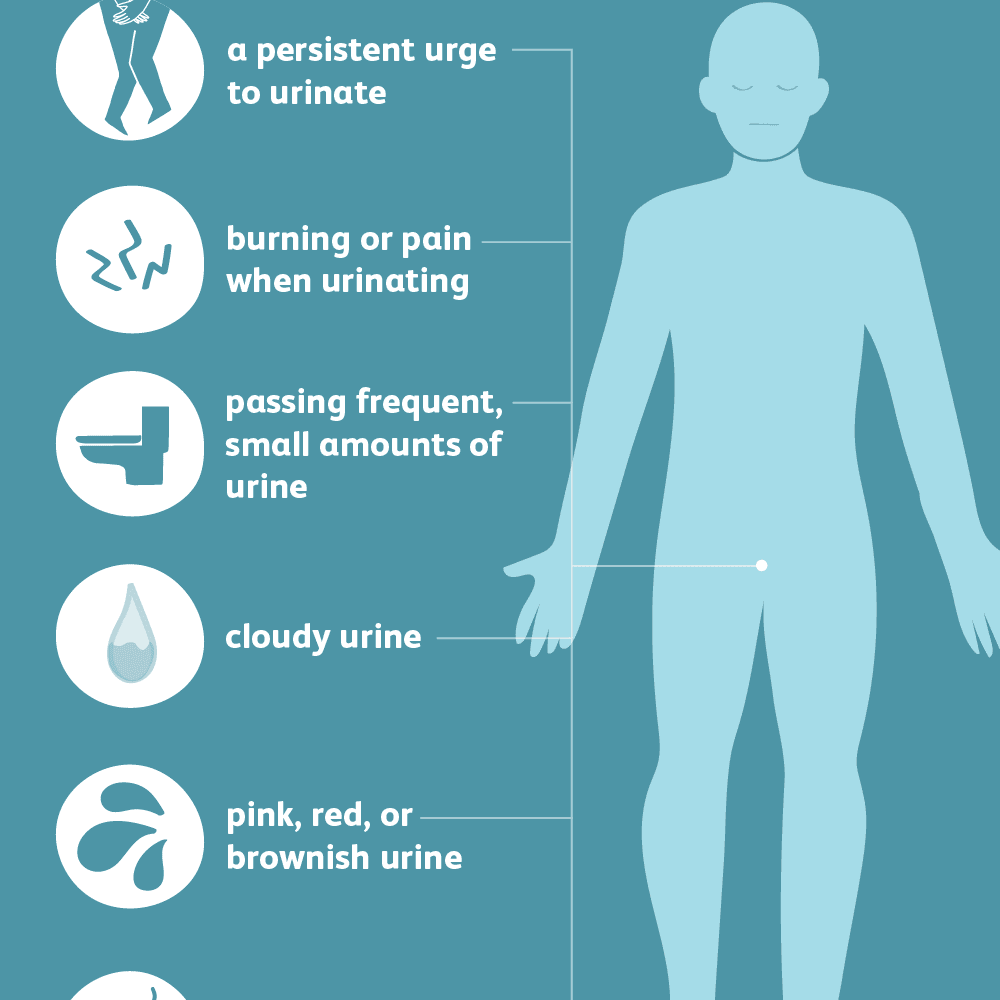
Antimicrobial Treatment For Symptomatic Utis
Antimicrobial treatment is appropriate for symptomatic UTIs but not for asymptomatic bacteriuria.13,25 A meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials involving 328 elderly patients with asymptomatic bacteriuria showed no significant benefit for antimicrobial treatment over placebo in the resolution of bacteriuria .3
The 2018 EAU guidelines on urological infections3 recommend fosfomycin, pivmecillinam, or nitrofurantoin as first-line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis in adult women. Combination antimicrobial therapy with amoxicillin plus an aminoglycoside, or a second-generation cephalosporin plus an aminoglycoside, is recommended for treatment of complicated UTIs. For complicated UTI with systemic symptoms, empirical intravenous treatment with a third-generation cephalosporin is recommended. Although EAU guidelines state that fluoroquinolones may be considered for use in certain circumstances,3 the European Medical Agency has suspended or restricted their use due to disabling and potentially permanent side effects involving muscles, tendons or joints, and the nervous system. The EMA advises special caution if using quinolones or fluoroquinolones in the elderly due to their higher risk of tendon injury.26
The increasing antimicrobial resistance of uropathogens is challenging the paradigm of empirical antibiotic therapy for symptomatic UTIs, underscoring the need for alternative treatment strategies.
Symptoms Can Be Different
In younger adults, symptoms of a UTI can be pretty dramatic: pain and burning during urination, as well as a frequent, often urgent need to pee. But Fishburne notes that symptoms are often less obvious in older adults.
Its not always easy to separate the signs of an infection like incontinence and the need to go the bathroom more frequently from other underlying conditions such as overactive bladder, which are more common in the older population. Among older adults, UTIs may cause symptoms not seen in younger people, such as confusion or agitation. That doesnt mean your loved one definitely has a UTI if they are just showing signs of delirium, stresses Fishburne. But if they have the symptoms above, lower back pain, blood in their urine or tenderness in their abdomen, they should see a physician immediately.
Some older adults may also present with a fever over 100 degrees, but this does not occur in every situation and would more suggest involvement of the upper urinary tract or the kidneys. Any of these symptoms should prompt a call to your doctor. At-home test kits arent always accurate and may often be unnecessary.
Recommended Reading: Female Urinary Tract Infection Over The Counter Treatment
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
The main cause of UTIs, at any age, is usually bacteria. Escherichia coli is the primary cause, but other organisms can also cause a UTI.
In older adults who use catheters or live in a nursing home or other full-time care facility, bacteria such as Enterococci and Staphylococci are more common causes.
Drink Plenty Of Fluids
Fluid intake is an essential part of urinary health and UTI prevention. Urine plays an important role in overall urinary health. Each time you urinate, it helps flush microbes out of your bladder and urethra. If you don’t urinate frequently enough, bacteria growth is more likely to occur.
Staying hydrated aids in urine production by providing the liquid needed to produce the bodily fluid. Water intake is a major part of hydration, but you can also get water from other drinks and from foods. Your medical provider can advise you on how much water to drink daily to support your urinary health.
Read Also: Home Remedies To Get Rid Of A Urinary Tract Infection
When To See A Doctor
If you suspect you or a loved one has a UTI, its best to see a healthcare provider. Symptoms like painful, urgent or frequent urination shouldnt be ignored, Dr. Slopnick stresses.
Your doctor will ask about symptoms and perform a urine culture and possibly other tests to confirm if a UTI is to blame. If youre experiencing multiple UTIs a year, your doctor may also order other tests to better understand if a prolapsed bladder, enlarged prostate or other condition is causing frequent infection.
How Can Parents Help
At home, these things can help prevent recurrent UTIs in kids:
Drinking Fluids Encourage kids to drink 810 glasses of water and other fluids each day. Cranberry juice and cranberry extract are often suggested because they may prevent E. coli from attaching to the walls of the bladder. Always ask your doctor, though, if your child should drink cranberry juice or cranberry extract, because they can affect some medicines.
Good Bathroom Habits Peeing often and preventing constipation can help to prevent recurrent infections.
No Bubble Baths Kids should avoid bubble baths and perfumed soaps because they can irritate the urethra.
Frequent Diaper Changes Kids in diapers should be changed often. If poop stays in the genital area for a long time, it can lead to bacteria moving up the urethra and into the bladder.
Proper Wiping Girls should wipe from front to back after using the toilet to reduce exposure of the urethra to UTI-causing bacteria in poop.
Cotton Underwear Breathable cotton underwear is less likely to encourage bacterial growth near the urethra than nylon or other fabrics.
Regular Bathroom Visits Some kids may not like to use the school bathroom or may become so engrossed in a project that they delay peeing. Kids with UTIs should pee at least every 3 to 4 hours to help flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
Read Also: How Does Cranberry Juice Help Urinary Tract Infections
Other Ways To Prevent Some Utis Coming Back
If you keep getting a bladder infection , there is some evidence it may be helpful to take:
- D-mannose a sugar you can buy as a powder or tablets to take every day
- cranberry products available as juice, tablets or capsules to take every day
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
If you’re taking warfarin, you should avoid cranberry products.
Page last reviewed: 22 March 2022 Next review due: 22 March 2025
Implications For Research And Practice
Based on the data we analysed, a pragmatic approach is required when considering prescribing long-term antibiotics in older patients with recurrent UTI. Although long-term antibiotics may reduce the risk of UTI recurrence in women, this benefit diminishes on cessation of treatment. Little is known about optimal prophylaxis period, long-term effects on health, risk of antibiotic resistant infections, effect in older men, effect in frail care home residents or impact on important patient-centred outcomes. These unknowns must be balanced against benefits and patient preferences.
Future research efforts on recurrent UTI should focus on improving the design and reporting of trials and developing a core set of outcomes to allow better synthesis of trial data. Antibiotic prophylaxis should be compared with non-antibiotic prophylaxis with some evidence of efficacy rather than those with little or poor evidence of efficacy. Researchers should address unanswered questions regarding long-term effects, duration of use, adverse effects and antibiotic resistance.
Don’t Miss: Purina Pro Plan Focus Urinary Tract Health Formula
Role Of Urinary Testing In Diagnosing Symptomatic Utis In Older Adults
The utility of urinary dipstick testing, urinalysis, and urine culture is challenging in the older adult because of the high prevalence of bacteriuria and pyuria that may not be clinically important. As in the case of Mrs M, all urinary studies to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, pyuria, and bacteriuria over a 2-year period were positive.
The urinary dipstick, although easy and convenient, has variable test characteristics.38 Sensitivity and specificity for urinary dipstick testing to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or both vary in older adults by the age of study participants, clinical suspicion of UTI, and laboratory definition for UTI used . The sensitivity and specificity for a positive dipstick test in older patients with was 82% and 71% , respectively.27 Other studies of elderly patients showed the negative predictive value for dipstick testing ranges from 92% to 100%.4,28 Urinary dipstick analysis should be performed in the out-patient setting primarily to rule out and not to establish a diagnosis of UTI. In a patient with a low pretest probability of UTI, if the dipstick is negative for leukocyte esterase and nitrites, it excludes the presence of infection and mitigates the need to obtain urinalysis and urine culture . High false-positive rates limit dipstick testing effectiveness.27 Further urinary studies are warranted for patients with a high pretest probability of UTI.
What Is A Urine Infection And What Causes It
Most urine infections are caused by germs that come from your own bowel. They cause no harm in your bowel but can cause infection if they get into other parts of your body. Some bacteria lie around your back passage after you pass a stool. These bacteria sometimes travel up the tube called the urethra and into your bladder. Some bacteria thrive in urine and multiply quickly to cause infection.
A urine infection is often called a urinary tract infection by healthcare professionals. When the infection is just in the bladder and urethra, this is called a lower UTI. If it travels up to affect one or both kidneys as well then it is called an upper UTI. This can be more serious than lower UTIs, as the kidneys can be damaged by the infection.
You May Like: Royal Canin Urinary Tract Food
How Urinary Tract Infections Affect The Elderly
Elderly patients who need catheters to urinate are at increased risk for urinary tract infections, especially if they recently had surgery for urinary dysfunction.
Older people who have a depressed immune system, like diabetes, may also not be able to naturally protect themselves against the bacteria. This can lead to current urinary tract infections.
Elderly men who have an enlarged prostate can suffer complications that increase their risk for urinary tract infections. The abnormal prostate can trap urine inside the bladder, which leads to recurrent urinary tract infections.
Take A Probiotic + Other Supplements To Support Urinary Health
The right dietary supplements may play a role in overall urinary health and potentially reduce the risk of infection. Some supplements to consider include:
- Probiotics: Probiotics are good bacteria that are a natural part of the urinary, digestive, and immune systems. Part of their job is to help fight bad bacteria like E. coli. A probiotic supplement can help support the beneficial bacteria in the urinary tract.
- Cranberry: Pure cranberry juice, raw cranberries, and cranberry supplements may make it more difficult for bacteria to stick to the lining of the urinary tract. Studies show that cranberry may reduce the risk of a UTI byup to one-third.
- D-mannose: D-mannose is a type of sugar found in cranberries that are believed to give the fruit its bacteria-reducing benefits. Some supplements contain isolated D-mannose or cranberry standardized to contain a certain percentage of the active compound.
- Hibiscus: Also known as roselle, hibiscus is a flowering plant native to tropical and subtropical biomes. The results of animal studies indicate that it mayreduce inflammation in the urinary tract.
- Dandelion: This flowering plant grows throughout North America and has been used as a natural remedy for centuries. Research shows that the herb hasantibacterial benefits, which could make it beneficial for reducing inflammation in the urinary tract.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Over The Counter Pills
What Is A Uti
A urinary tract infection is the most common type of infection in older adults, and it occurs when bacteria are able to get into the urethra and travel to the bladder. Anywhere along this path, bacteria can grow and cause a series of health issues, including pain and possibly dementia symptoms. An infection can occur in any part of the urinary tract, and is detectable by testing urine for trace amounts of protein and blood that could be harboring bacteria. UTIs are very common- it is estimated that 60% of adult women will have a UTI at some point. Unfortunately, up to a third of these women will have more UTIs in the future. Luckily, there are steps one can take to help our bodies fight and prevent UTIs.
How Are Recurrent Utis Treated
Treatment for recurrent UTIs depends on what’s causing them. Sometimes the answer is as simple as teaching a child to empty their bladder as soon as they have the urge to go.
If a condition like VUR is causing the infections, the solution is a bit more complicated. Kids with VUR must be watched closely, because it can lead to kidney infection and kidney damage. Most kids outgrow the condition. Some might need surgery to correct the reflux.
Some kids with VUR benefit from daily treatment with a small amount of antibiotics, which can also make surgery unnecessary. Kids with VUR should see a pediatric urologist, who can decide if antibiotic treatment is the best option.
In some cases, surgery is needed to correct VUR. The most common procedure is ureteral reimplantation, in which one or both of the ureters are repositioned to correct the backflow of urine from the bladder. This procedure requires only a small incision and, in some children, can be done using robotic-assisted laparoscopy. When surgery is necessary, the success rate is high, but not everyone is a good candidate for it.
Kids may be candidates for ureteral reimplantation if they:
- have an intolerance to antibiotics
- get recurrent infections while on antibiotic treatment
- have severe, or “high-grade,” reflux
- are older kids and teens with reflux
You May Like: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Walgreens
Diagnosing A Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults
Vague, uncommon symptoms such as confusion make UTIs challenging to diagnose in many older adults. Once your doctor suspects a UTI, its easily confirmed with a simple urinalysis.
Your doctor may perform a urine culture to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection and the best antibiotic to treat it.
There are home UTI tests that check urine for nitrates and leukocytes. Both are often present in UTIs. Because bacteria are often in the urine of older adults to some degree, these tests arent always accurate. Call your doctor if you take a home test and get a positive result.
Antibiotics are the treatment of choice for UTIs in older adults and younger people. Your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin and nitrofurantoin .
More severe infections may require a broad-spectrum antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin .
You should start antibiotics as soon as possible and take them for the entire duration of treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Stopping treatment early, even if symptoms resolve, increases the risks of recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic overuse also increases your risk for antibiotic resistance. For this reason, your doctor will likely prescribe the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 7 days, and your infection should clear up in a few days.
Its important to drink plenty of water during treatment to help flush out the remaining bacteria.