What Impacts The Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. According to the ACS, the five-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%. This is called non-muscle invasive bladder cancer . More than half of people are diagnosed at this stage.
If a tumor is invasive but has not yet spread outside the bladder, the five-year survival rate is 69%. Approximately 33% of bladders cancers are diagnosed at this stage. If the cancer extends through the bladder to the surrounding tissue or has spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, the five-year survival rate is 37%. If the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is 6%. About 4% of people are diagnosed at this stage.
It is important to remember that statistics about the five-year survival rates for people with bladder cancer are estimates only and come from annual data based on the number of people with this cancer. A number of new and promising bladder cancer treatments that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the last five years might not be reflected in a five-year survival rate statistic.
Just like no single treatment is appropriate for all bladder cancer patients, there is not one statistic that applies to everyone either. Talk with your doctor about your own individual situation to gain the best understanding you can.
What Are The 5
In 2020, approximately 17,980 deaths in the United States are predicted to be attributed to bladder cancer1. This represents the eighth most common cause of cancer deaths in men.
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%, while the 10-year survival rate is 70% and the 15-year survival rate is 65%1. Notably, as each patient and cancer are different, it is not possible to definitely know the disease course for an individual patient.
Diagnosis Of Urethral Cancer
-
Cystourethroscopy
Diagnosis is suggested clinically and confirmed by cystourethroscopy and examination under anesthesia . Biopsy may be required to differentiate urethral carcinoma, prolapse, and caruncle. CT Computed Tomography Imaging tests are often used to evaluate patients with renal and urologic disorders. Abdominal x-rays without radiopaque contrast agents may be done to check for positioning of ureteral stents… read more or MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging Imaging tests are often used to evaluate patients with renal and urologic disorders. Abdominal x-rays without radiopaque contrast agents may be done to check for positioning of ureteral stents… read more is used for staging.
Also Check: Chronic Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
Prognosis And Survival For Bladder Cancer
If you have bladder cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for bladder cancer.
You May Like: Antibiotics Used For Bladder Infections
Changes In Bladder Habits Or Symptoms Of Irritation
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as:
- Having to urinate more often than usual
- Pain or burning during urination
- Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full
- Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream
- Having to get up to urinate many times during the night
These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection , bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate . Still, its important to have them checked by a doctor so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Read Also: Royal Canin Urinary Plus Calm
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Kidney Cancer Causes And Risk Factors
Anything that increases your chance of getting kidney cancer is called a risk factor.
The known risk factors for kidney cancer include:
- Smoking: This is the biggest risk factor for kidney cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke are absorbed into the blood, and then pass through the kidneys and collect in the urine. These chemicals can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of developing kidney cancer.
- Age: Most cases occur after age 50
- Gender: Men are more than twice as likely to get kidney cancer as women
Read Also: Clearing Urinary Tract Infection Naturally
Association Of Tumor Architecture With Clinical And Pathologic Characteristics
Table 1 shows the association of tumor architecture with clinical and pathologic characteristics before and after propensity score matching . Of 857 patients, sessile and papillary growth patterns were present in 212 and 645 patients, respectively. The mean follow-up period of sessile group and papillary group was 39.34 ± 35.31 months and 47.10 ± 35.19 months, respectively. Tumor architecture exhibited significant association with bladder cancer history, CKD group, tumor stage, lymph node status, histological grade, LVI, concomitant CIS, and variant type . In total, 32 patients with papillary growth pattern and 36 patients with sessile growth pattern had received either neoadjuvant or adjuvant perioperative chemotherapy. In the propensity score analysis, 424 papillary and sessile tumor architecture were analysed. The baseline characteristics in the weighted groups were well balanced.
Table 1 Association of tumor architecture with clinical and pathologic characteristics in patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma before and after propensity-score analysis.
Original Researchbladder Cancer Survival: Women Better Off In The Long Run
Gender-related risk ratio of bladder cancerrelated death is not stable over time.
-
Female risk rates are significantly higher within the first 2 years after diagnosis.
-
Men experience higher risk for bladder cancerrelated death in the long run.
-
T-Stage at diagnosis explains much of gender-specific survival difference.
Also Check: Can Iud Cause Urinary Incontinence
Ubc Occurrence Is About Threefold Higher In Europe And North America
Although usually not perceived as such by the general population, UBC is among the more commonly occurring cancers. It ranks tenth in worldwide absolute incidence: sixth in men and seventeenth in women . Approximately 550,000 new UBCs were diagnosed worldwide in 2018 . The worldwide Age Standardized Incidence Rate per year is 9.6 per 100,000 for males and 2.4 per 100,000 for females. Figure 1 shows the worldwide ASRs for UBC in both sexes.
Urinary bladder cancer incidence in 2018 in the world, by sex
The incidence varies significantly between geographical regions, with the highest rates observed in Europe and North America, but also in Syrian, Israeli, Egyptian and Turkish males. About threefold lower rates are seen in South-East Asia, except for Japan, and in Latin America and Northern Africa in both sexes . The lowest rates are observed in Sub-Saharan Africa, Mexico and some Middle Eastern and Central Asian countries.
Adenocarcinoma And Small Cell Carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma and small cell carcinoma are rare forms of bladder cancer. Each makes up about one percent of bladder cancers, according to Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
Adenocarcinoma is linked to inflammation and chronic infection as well as bladder defects at birth. Small cell carcinoma begins in the small nerve-like cells in the bladder and is an aggressive cancer.
Recommended Reading: Kidney Stone Vs Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostics And Treatment For Urothelial Cancer
The development of the tumornodemetastasis classification and staging system has been important for the standardization of diagnostics and treatment in cancers since 1958 . Hematuria is the most common sign of UC and leads to cystoscopy . Over the years, the diagnostic arsenal has increased to include ultrasound and computed tomography . A Finnish study defined the diagnostic periods: pre-CT and pre-US era , US era and CT era . Detailed demographic and clinical data from bladder cancer patients recorded by the Swedish National Register of Urinary Bladder Cancer from 1997 to 2014 were reported e.g. 74% of male and 68% of female tumors were non-muscle invasive, and the rest were muscle invasive . According to this Register, there was a stage shift between periods 19972001 and 20072011 in clinical T categorization: Ta from 45% to 48%, T1 from 21.6% to 22.4%, and T2-T4 from 27% to 25% . According to this source, between periods 19972001 and 20072011 intravesical treatment after transurethral resection for T1G2 and T1G3 tumors increased from 15% to 40% and from 30% to 50%, respectively cystectomy for T2-T4 tumors increased from 30% to 40%.
How Can I Prevent Bladder Cancer
You may not be able to prevent bladder cancer, but it may be helpful to know the risk factors that may increase the chance youll develop bladder cancer. Bladder cancer risk factors may include:
- Smoking cigarettes: Cigarette smoking more than doubles the risk of developing bladder cancer. Smoking pipes and cigars or being exposed to second-hand smoke also increases that risk.
- Cancer treatments: Radiation therapy is the second-most common risk factor. People who have certain chemotherapy drugs may also develop an increased risk of bladder cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines , are at an increased risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infections: People who have frequent bladder infections, bladder stones or other urinary tract diseases may have an increased risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Past bladder cancer: People with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Also Check: 24 Hour Urinary Free Cortisol Test
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer occurs when cells within the lining of the bladder wall begin to grow in a disordered, uncontrolled way.
Exactly what prompts this disordered growth is not fully known. However, several factors associated with a higher risk of bladder cancer have been identified, including:
- Age – most people diagnosed with bladder cancer are older than 55 years.
- Sex – compared to women, men are 4 times more likely to develop bladder cancer.
- Smoking – smoking is associated with around half of all bladder cancers in men and women.
- Race – in the United States, White Americans have the highest rate of bladder cancer.
- Previous bladder cancer – people who have had bladder cancer may have a recurrence.
- Workplace exposures – certain chemicals in some workplaces may contribute to higher rates of bladder cancer in workers. For example, painters, hairdressers, and truck drivers are at increased risk.
- Arsenic in drinking water.
- Certain types of medication.
Surgery As A Consolidation Therapy
Patients who respond to primary chemotherapy may benefit from surgical consolidation if the disease is limited and located in the regional lymph nodes or metastatic site/sites amenable to surgical removal . The concept of metastasectomy in urothelial carcinoma was first described in the early 1980s, when Cowles et al. reported long-term survival for six patients who underwent wedge resection for solitary pulmonary metastasis. After more than one decade, multiple reports started to demonstrate the suggested benefits of surgical excision of metastatic lesions as part of a multimodality approach . In the age of immunotherapeutics, reduction of tumor burden may become even more important.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For A Urinary Tract Infection
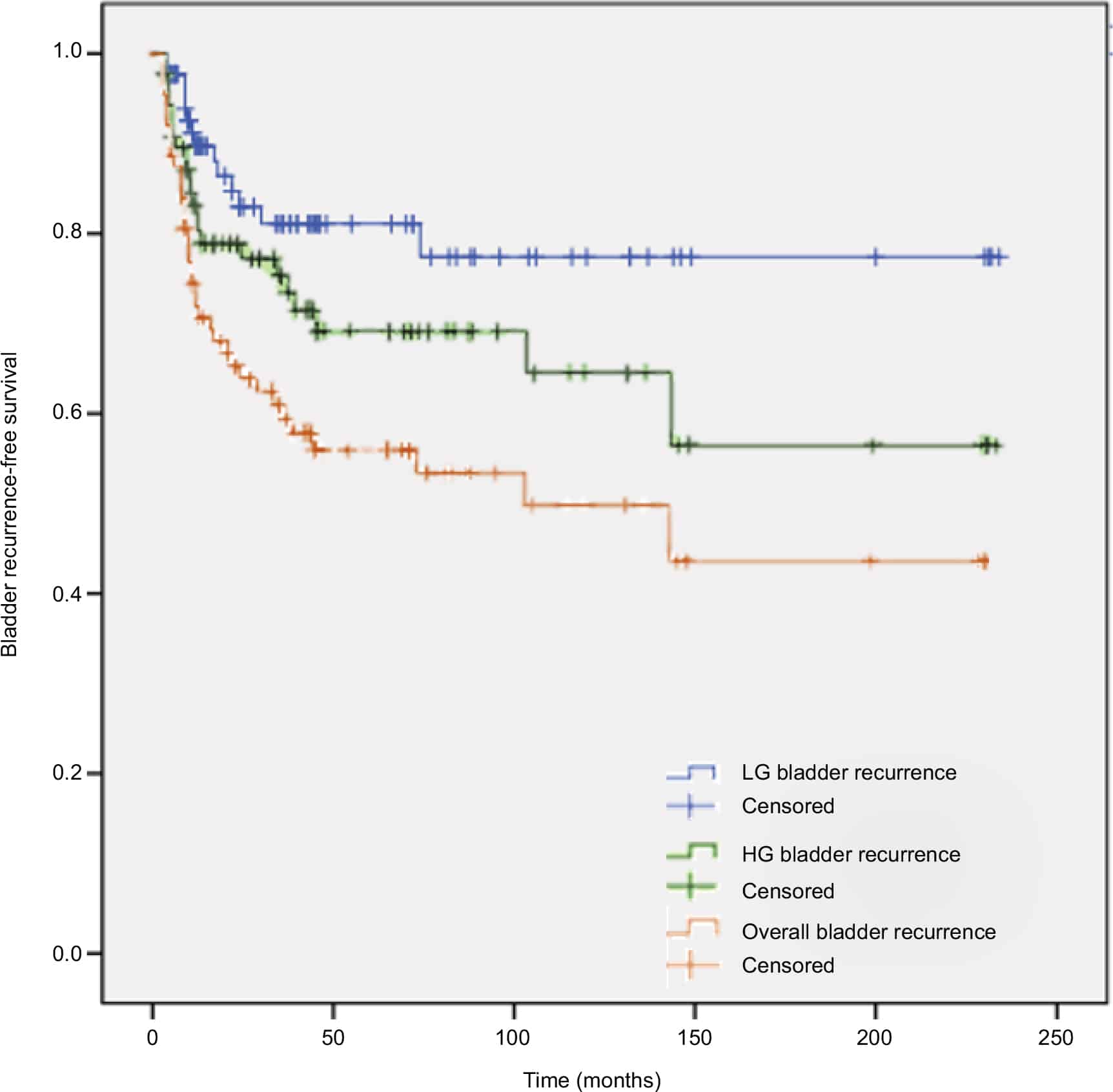
How Does Recurrence Of Bladder Cancer Affect Survival Rate
Recurrent bladder cancer is cancer that has returned after initial treatment. Recurrence rates for bladder cancer depend on the stage of the original tumor, with 5-year recurrence rates of approximately 65% in patients with non-invasive or in situ tumors and 73% in patients with slightly more advanced disease at first diagnosis.16
Many patients with non-invasive bladder cancer have recurrences that are typically not life threatening however, the prognosis is generally worse if the disease has spread into deeper layers of the bladder wall or beyond to the lymph nodes or other organs.
What Are The Symptoms Of Urologic Cancers
Most of the time, symptoms dont occur until the cancer has become more advanced. Then, they depend on the type of cancer. Blood in the urine is a symptom of bladder, kidney and prostate cancerat later stages, pelvic and back pain can also develop.
Patients with prostate cancer may also have other changes in urination and sexual function. Those with testicular or penile cancer may notice a visible lesion on the skin, along with other skin changes or swelling. Any cancer patient can experience weight loss and fatigue.
More often, these cancers are detected during a routine physical exam of the abdomen or genitals.
Read Also: What Will Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
About half of all people with bladder cancer have early-stage cancer thats relatively easy to treat. But bladder cancer often comes back . People whove had bladder cancer will need regular checkups after treatment. Being vigilant about follow-up care is one thing you can do to take care of yourself. Here are some other suggestions from the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network include:
- Follow a heart-healthy diet: Plan menus that include skinless poultry and fish, low-fat dairy products, nuts and legumes, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Focus on high-fiber foods: Bladder cancer treatment may cause digestive issues and a fiber-rich diet may help.
- Get some exercise: Gentle exercise may help manage stress.
- Connect with others: Bladder cancer often comes back. Its not easy to have a rare disease thats likely to return. Connecting with people who understand what youre going through may help.
Urinary diversion
Some people with bladder cancer need surgery that removes their bladder and their bodies natural reservoir for pee. There are three types of urinary diversion surgeries. All three types involve surgically converting part of your intestine to become a passage tube for pee or a reservoir for storing pee.
Urinary diversion may be a challenging lifestyle change. If youll need urinary diversion surgery, ask your healthcare provider to explain each surgery types advantages and disadvantages. That way, youll know what to expect and how to take care of yourself.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
Bladder cancer is relatively rare, so you may not know as much as youd like about the condition. Here are some questions that may be helpful:
- What stage of bladder cancer do I have?
- What are possible treatments?
- What are treatment side effects?
- Will I need surgery?
- How will surgery affect my daily life?
- How often does bladder cancer come back?
- How do you treat recurrent bladder cancer?
- Are there any cutting-edge clinical trials available?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have bladder cancer, it may help to know about half of all people with the condition receive treatment when their tumors are limited to the inner layer of their bladder wall. For them, surgery to remove tumors means theyre cancer-free. But bladder cancer often comes back . If youre worried about recurring cancer, talk to your healthcare provider. Theyre your best resource for information on risk factors that increase the chance youll have another bout of bladder cancer. Theyll help you stay vigilant about symptoms that may be signs of recurring bladder cancer and be there for you if you need more bladder cancer treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/26/2022.
References
Don’t Miss: How To Clean My Urinary Tract
Other Types Of Bladder Cancer
Approximately 2% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. Nonurothelial primary bladder tumors are extremely rare and may include small cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, primary lymphoma, and sarcoma . Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder accounts for only 0.3-0.7% of all bladder tumors. High-grade urothelial carcinomas can also show divergent histologic differentiation, such as squamous, glandular, neuroendocrine, and sarcomatous features.
What Is Unique About Our Approach To Treating These Cancers
Yale Medicines approach to treating urologic cancers is patient-driven, says Dr. Leapman. Not all cancers are the same, and the urologic oncologists at Yale are focused on using all available resources to understand the multiple forces that impact how an individual should be treated.
Our approach is team-driven, he says, allowing experts from multiple disciplines to collaborate and offer world-class, personalized care.
Also Check: Urinary Incontinence Causes In Females
What Is The Survival Rates For Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is one of the most common cancers, with a lifetime risk of 2.02% for men and 1.03% for women.¹ However, the typical 5-year survival rate is fairly high. Most people diagnosed with kidney cancer are between 65 and 74 years old, and it is very uncommon in people under 45.
Early diagnosis significantly improves the survival rate, so it’s important to be aware of risk factors and symptoms.
Have you considered clinical trials for Kidney disease?
We make it easy for you to participate in a clinical trial for Kidney disease, and get access to the latest treatments not yet widely available – and be a part of finding a cure.
Palliative Or Supportive Care
If your cancer is at an advanced stage and can’t be cured, your medical team should discuss how the cancer will progress and which treatments are available to ease the symptoms.
You can be referred to a palliative care team, who can provide support and practical help, including pain relief.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2021 Next review due: 01 July 2024
Recommended Reading: D Mannose For Urinary Frequency