Causes Kidney Stones Vs Utis
UTIs occur when bacteria make their way into the urinary tract and begin to multiply, which can lead to symptoms. Women are more likely to develop more UTIs than men because the female urethra is shorter, which means bacteria have a shorter distance to travel to establish an infection. If left untreated, these UTIs can continue to spread upward into the kidneys.
Kidney stones are generally the result of a less severe UTIs progression due to lack of treatment, but they can sometimes occur in other ways as well. When there is not enough water to dilute the uric acid, a component of urine, the urine becomes more acidic. An excessively acidic environment in urine can lead to the formation of kidney stones.
How Do You Know When A Uti Becomes A Kidney Infection
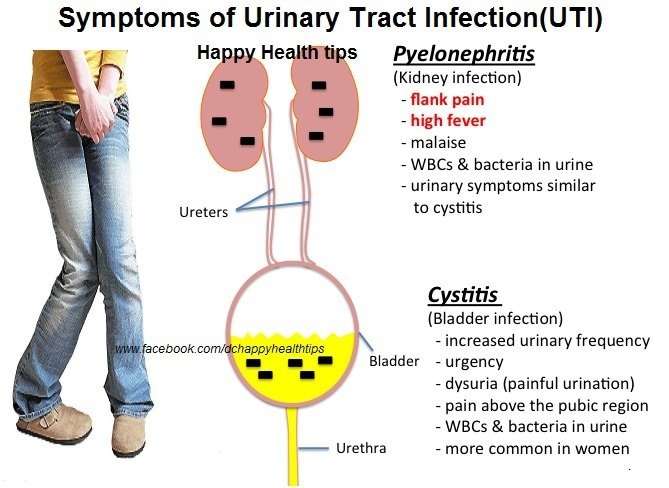
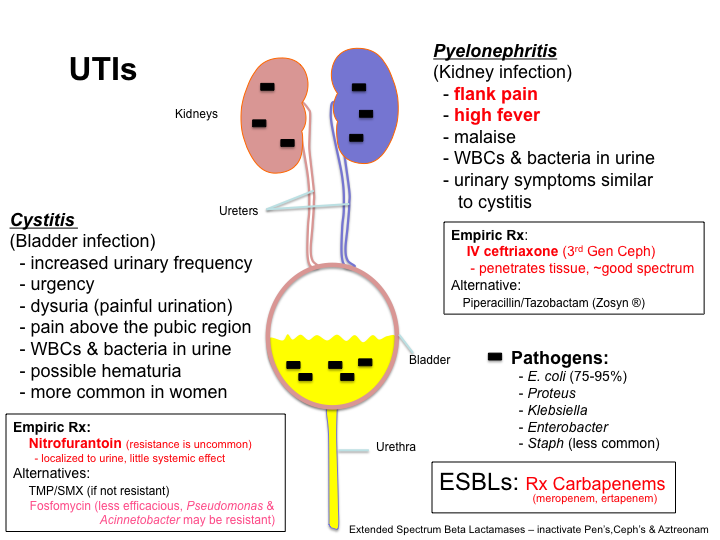
Kidney infections are also termed as pyelonephritis where the viral or bacterial infection can cause infection and is a type of urinary tract infection. The kidneys play an essential role in the human body. They are a part of the urinary tract where it removes waste in the form of urine from the body. The urinary system comprises of the urethra, urinary bladder, ureter, and kidneys. If any part of the urinary system gets infected then the bacteria or virus can travel to the ureters and result in a kidney infection.
Consider watching this video to know more about 5 signs of kidney diseases.
Kidney infections result in an excruciating, painful sensation that usually occurs due to urinary tract infections. Kidney infections are not so serious if treated on time with antibiotics, however, if they are not treated on time they can permanently damage the kidneys. Kidney infections come within a few hours. You feel like having fever, being fatigued, sick with back pain or pain over the sides. Along with the symptoms of kidney infection, patients usually suffer from symptoms of UTI i.e. cystitis where they have frequent urges to pee, burning or painful sensation during peeing, cloudy or smelly pee and urine might have blood. You can also suffer from loss of appetite, stomach pain, vomiting, and nausea.
Until Next Time,
Read Also: Are Almonds Bad For Your Kidneys
Urinary Tract Infection Update: Kidney Stones Vs Uti And Risk Factors Prevention And Natural Treatment Of Uti
A urinary tract infection is an infection that occurs anywhere along the urinary system, including the bladder, kidneys, or ureters. Women are more likely to develop UTIs, which can also be a recurring problem for many. To learn more about UTIs including how they differ from kidney stones, how to treat and prevent them, and some factors that cause them, check out the articles below.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Immediate Relief
Prevention Of Future Stones
Once your health care provider finds out why you are forming stones, he or she will give you tips on how to prevent them. This may include changing your diet and taking certain medications. There is no “one-size-fits-all” diet for preventing kidney stones. Everyone is different. Your diet may not be causing your stones to form. But there are dietary changes that you can make to stop stones from continuing to form.
Diet Changes
Drink enough fluids each day.
If you are not producing enough urine, your health care provider will recommend you drink at least 3 liters of liquid each day. This equals about 3 quarts . This is a great way to lower your risk of forming new stones. Remember to drink more to replace fluids lost when you sweat from exercise or in hot weather. All fluids count toward your fluid intake. But it’s best to drink mostly no-calorie or low-calorie drinks. This may mean limiting sugar-sweetened or alcoholic drinks.
Knowing how much you drink during the day can help you understand how much you need to drink to produce 2.5 liters of urine. Use a household measuring cup to measure how much liquid you drink for a day or two. Drink from bottles or cans with the fluid ounces listed on the label. Keep a log, and add up the ounces at the end of the day or 24-hour period. Use this total to be sure you are reaching your daily target urine amount of at least 85 ounces of urine daily.
Reduce the amount of salt in your diet.
Eat the recommended amount of calcium.
Diagnosing And Treating Kidney Stones
Kidney stones should be diagnosed and treated by a urologist or a nephrologist. Diagnosing kidney stones may include blood tests, urine tests, imaging tests, and/or analysis of any stones that may have already been passed. Treatment is dependant on the type of stone, but treatments include medications, antibiotics, lithotripsy , ureteroscopy , and tunnel surgery .
You May Like: Exercises To Help With Urinary Incontinence
Kidney Stones Vs Utis: Us Prevalence And Economic Impact
Prevalence of kidney stones is roughly one in 11 Americans. This prevalence may be on the incline as a result of poor lifestyle choices, including eating habits. Men are more likely to develop kidney stones than women, and the rates are higher among obese and overweight persons than normal weight individuals.
Annually, an estimated 150 million UTIs are diagnosed, amounting to six billion dollars in healthcare costs. In the U.S., there are 8.1 million UTI cases, with women being more prone to the infections than men.
Feeling Faint Dizzy Or Weak
Why this happens:
Anemia related to kidney failure means that your brain is not getting enough oxygen. This can lead to feeling faint, dizzy, or weak.
What patients said:
I was always tired and dizzy.
It got to the point, like, I used to be at work, and all of the sudden Iâd start getting dizzy. So I was thinking maybe it was my blood pressure or else diabetes was going bad. Thatâs what was on my mind.
You May Like: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Kidney Stones
Read Also: How To Stop Urinary Incontinence
Kidney Stones And Utis: Signs And Symptoms
Common symptoms of a urinary tract infection include abdominal pain, burning with urination, increased frequency in urination, and urinary urgency. Other symptoms may accompany a UTI, including fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. Urine may also appear pinkish or light red, and have a strong odor. Pelvic pain may be experienced as well.
Kidney stones symptoms include severe pain, pain that travels across the lower abdomen, pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity, pain in urination, pink, red or brown blood in urine, nausea and vomiting, persistent need to urinate, urinating more frequent than usual, fever and chills with the presence of an infection, and urination in small amounts only.
You should see a doctor if symptoms change to a pain so severe you are unable to stand or move, if pain is accompanied by nausea or vomiting, if fever or chills develop, and if there is blood in urine or difficulty passing urine.
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A UTI happens when bacteria get into the urinary system and multiply, leading to redness, swelling, and pain2. UTIs tend to be more common in women than men because of anatomy, however, they can affect anyone. Symptoms of UTIs can overlap with symptoms of kidney stones. An urgent need to urinate, but with only a few drops of urine to pass is typical for a UTI versus kidney stones. Other symptoms include2:
- A burning feeling during urination
- An aching feeling, pressure, or pain in the lower abdomen
- Cloudy or blood-tinged urine
- Strong odor to the urine
A urine test will be able to determine if you have a UTI. If so, an antibiotic course is typically prescribed. When a UTI isnt caught early, it can spread to the kidneys and turn into a more serious infection.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Kidney Pain
The Association Between Bacteria And Urinary Stones
Andrew L. Schwaderer1,2, Alan J. Wolfe3
1The Research Institute at Nationwide Childrens Hospital, Center for Clinical and Translational Research, Columbus, OH, USA 2Division of Nephrology, Nationwide Childrens Hospital, Columbus, OH, USA 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Loyola University Chicago, Stritch School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA
Contributions: Conception and design: All authors Administrative support: None Provision of study materials or patients: None Collection and assembly of data: A Schwaderer Data analysis and interpretation: All authors Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Urinary tract infection kidney stones microbiome
Submitted Aug 25, 2016. Accepted for publication Sep 21, 2016.
doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.11.73
What Are Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are solid masses made up of minerals and salts that usually form inside your kidneys but can affect any part of your urinary tract. There are different types of kidney stones depending on the specific cause, so there may be uric acid stones, calcium stones , struvite stones, cystine stones, or xanthine stones. Kidney stones are known to be one of the most painful medical conditions, but they usually cause no permanent damage when properly and promptly treated. Unlike UTIs, kidney stones occur more commonly in men than in women. Men have a 13% chance of developing kidney stones in their lifetime, while women have a 7% risk.
Also Check: Urinary Incontinence Devices For Women
What Are Bladder Stones
Bladder stones form when minerals in urine crystalize and clump together in the bladder. The medical term for bladder stones is bladder calculi.
Bladder stones generally develop when some urine stays in the bladder after you pee. Without treatment, stones can cause infections, bleeding and long-term problems in the urinary tract.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider About Bladder Stones
If you have any signs of bladder stones, talk to your provider. Stones continue to grow when they remain in the bladder. Thats why its important to get treated as soon as you notice symptoms.
Without treatment, bladder stones can lead to health problems like frequent urinary tract infections. Repeated UTIs can damage the urinary tract.
A note from Cleveland Clinic If you have signs of bladder stones, be open and honest with your healthcare provider. Effective treatments are available if the stones are too big to pass. Its important to get treated as early as possible and address any health conditions that may be causing bladder stones. Early treatment can relieve symptoms, help you avoid long-term damage and keep bladder stones from developing again.
Don’t Miss: Medicine For Stress Urinary Incontinence
Pressure Or Pain In The Lower Back
In some cases, a stone may become stuck in the ureter. The ureter is the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder. A blockage here causes urine to back up in the kidney, resulting in pressure and pain sensations in the lower back. These symptoms may occur on the left or right side, depending on which kidney is affected.
According to the University of Chicago, pain or pressure are usually the first signs of a kidney stone. In some cases, the symptoms may be very subtle and build up slowly. In other cases, they may come on suddenly, with no early warning signs. This pain can be severe and may lead to nausea or vomiting, or both. People often experience sharp, stabbing pain, and common measures such as rest or lying down do not relieve it.
Differentiating Kidney Stones From A Urinary Tract Infection
It can be concerning to experience pain down there. Many questions of what could be causing the pain and discomfort run circles in your mind. Your first move might be calling your primary care doctor and declaring you have a UTI. Stop right there the symptoms of UTIs and kidney stones can be similar, but treatment is very different. In this article, we will be discussing the similarities and differences between the two and when you should go see a doctor.
You May Like: Botox For Urinary Incontinence Side Effects
Complications Of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can range in size from a grain of sand to that of a pearl or even larger. They can be smooth or jagged, and are usually yellow or brown. A large stone may get stuck in the urinary system. This can block the flow of urine and may cause strong pain.
Kidney stones can cause permanent kidney damage. Stones also increase the risk of urinary and kidney infection, which can result in germs spreading into the bloodstream.
Ok Got It But Then What Is A Kidney Infection
A kidney infection is, in essence, a UTI that has spread into the kidneys. While this type of infection is rare, its also very dangerous and if youre experiencing any of the following signs of a kidney infection, you should see a doctor immediately:
-
Upper back or side pain
-
Fever, shaking or chills
-
Feeling nauseous
-
Vomiting
While most kidney infections can be treated simply with an antibiotic, if left untreated, a kidney infection can cause damage to your kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease. The bacteria could even spread to your bloodstream creating a life-threatening situation.
Also Check: How Accurate Are Home Urinary Tract Infection Tests
Bacteria Can Be Cultured From Urinary Stones
In addition to the aforementioned association between culture-positive urine and USD, bacteria can be cultured from the stones themselves. Studies from 1973 to the present in both Asia and North America have demonstrated that bacteria can be isolated from approximately 1570% of stones following clinical culture . When limited to CaOx stones, 13% to 44% of cultures were positive. E. coli and Pseudomonas spp. were the most common bacteria isolated from stone cultures, followed by the urease-splitting bacteria typically involved in struvite stone formation . However, the reported results may under-represent the bacteria in urinary stones because the standard urine culture protocols used by clinical microbiologists are designed to identify clinical infections by known uropathogens. These protocols are not conducive to growth by slow growing, fastidious or anaerobic bacteria, which comprise the vast majority of bacteria found in urine .
Frequency of bacterial isolates from urinary stone cultures.
When To See A Gp
See a GP if you feel feverish and have pain that will not go away in your tummy, lower back or genitals.
You should also see a GP if you have symptoms of a UTI that have not improved after a few days, or if you have blood in your pee.
Contact a GP immediately if you think your child may have a kidney infection.
If you cannot get a GP appointment and need urgent medical attention, go to your nearest urgent care centre .
If you do not have a local UCC, go to your nearest A& E.
Also Check: Does Cranberry Juice Help With Urinary Tract Infections
What Is A Uti Anyway
A UTI, or urinary tract infection, happens when bacteria enters into any part of your urinary system, which includes the urethra, the bladder, the kidneys or the uterus. If not flushed out of the system, the bacteria can lead to an infection, or a UTI.
If youve ever had a UTI , you probably havent forgotten the symptoms. UTIs are very unpleasant, to say the least, and are often accompanied with one or more of the following:
-
A burning sensation when urinating
-
A strong urge to urinate often, usually passing only small amounts of urine at a time.
-
Cloudy and/or strong smelling urine
-
Pelvic pain
Sequencing And New Culture Techniques Expand Our Knowledge Of The Urinary Tract Microbiota

To expand detection and identification of bacteria in low biomass samples such as urine, we developed enhanced quantitative urine culture . EQUC incorporates more urine volume and a longer incubation period, along with multiple media types and atmospheric conditions . In addition to enhanced culture techniques such as EQUC, 16S rRNA gene sequencing of bacterial DNA has resulted in a paradigm shift in our ability to study the microbiome . 16S rRNA gene sequencing and enhanced culture are complementary, as the sequencing identifies bacteria that cannot be cultured but generally cannot classify below the genus level, while enhanced culture actually isolates the bacteria. These isolates can then be identified more precisely and, most importantly, can be used to study biological relevance.
Recommended Reading: Interstim Implant For Urinary Incontinence
What Is A Uti
A UTI is an infection that can affect anywhere in the urinary tract, including the bladder, ureters, urethra, and kidneys. The urinary tract is responsible for passing urine and eliminating waste from the body. UTIs most commonly affect the lower tract, which includes the urethra and bladder. UTIs can also affect the upper tract, which includes the ureters and kidneys, however, infections affecting the upper tract are typically more severe and are accompanied with worsened symptoms and complications. UTIs are caused by bacteria in the urinary tract. Women are more likely to get UTIs than men, in fact, about 20% of women will get at least once in their lifetime.
Why You Get Stones
Part of preventing stones is finding out why you get them. Your health care provider will perform tests to find out what is causing this. After finding out why you get stones, your health care provider will give you tips to help stop them from coming back.
Some of the tests he or she may do are listed below.
Medical and Dietary History
Your health care provider will ask questions about your personal and family medical history. He or she may ask if:
- Have you had more than one stone before?
- Has anyone in your family had stones?
- Do you have a medical condition that may increase your chance of having stones, like frequent diarrhea, gout or diabetes?
Knowing your eating habits is also helpful. You may be eating foods that are known to raise the risk of stones. You may also be eating too few foods that protect against stones or not drinking enough fluids.
Understanding your medical, family and dietary history helps your health care provider find out how likely you are to form more stones.
Blood and Urine Tests
Imaging Tests
When a health care provider sees you for the first time and you have had stones before, he or she may want to see recent X-rays or order a new X-ray. They will do this to see if there are any stones in your urinary tract. Imaging tests may be repeated over time to check for stone growth. You may also need this test if you are having pain, hematuria or recurrent infections.
Stone Analysis
Recommended Reading: Itching In Urinary Tract Male