Seek Medical Attention For Utis
It is important to seek medical attention if you think you may have a UTI particularly if you think you may have a bladder or kidney infection, both of which are very serious conditions. Early treatment of urinary infection can help to prevent infection spreading to the bladder or kidneys.
Your doctor will test your urine to check which micro-organism is present. Urinary tract infections usually respond quickly and well to antibiotics.
Quality Assessment / Risk Of Bias
Two review authors assessed the risk of bias of included studies independently, with any discrepancies being resolved by consensus, or through discussion with a third reviewer , if necessary. The risk of bias was assessed using a modified version of the assessment checklist developed by Downs and Black . Quality items that pertained to interventions and trial studies were removed as they were not deemed to be appropriate for the studies included in this review. An additional five quality items were added to the quality assessment to determine if studies described the criteria used for confusion, UTI and bacteriuria, and if their criteria for UTI and confusion were valid and reliable. Criteria for confusion were deemed valid and reliable if accepted criteria were utilised, including: the Confusion Assessment Method, the Organic Brain Syndrome Scale or the Diagnosis and Statistical Manual criteria . Similarly, criteria for UTI were deemed valid and reliable if established criteria for UTI were utilised, including: the McGeer Criteria, the revised McGeer Criteria, the Loeb Criteria, or the Revised Loeb Criteria . The modified checklist finally consisted of 14 quality items, grouped into: reporting, internal validity, external validity and criteria . The risk of bias for each quality item was reported as low risk of bias, high risk of bias, unclear risk of bias or not applicable.
Table 2 Quality Assessment Criteria
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Urinating After Sexual Intercourse
Causes And Symptoms Of Utis
Bacteria that enter the urinary tract are responsible for causing UTIs. More than 90 percent of infections of the bladder are the result of E. coli bacteria from the intestines. Improper wiping from back to front following a bowel movement increases the likelihood of bacteria entering the urinary tract. Unfortunately, some strains of E. coli bacteria have become resistant to many antibiotics commonly prescribed to treat UTIs.
Younger patients with urinary tract infections typically have symptoms that include pain or burning when urinating, pain in the lower abdomen, a frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or bloody urine, and strong smelling urine. Fever, chills, and nausea may also be present.
While the elderly may have some of these classic symptoms, they may experience symptoms not generally associated with UTIs. These include a sudden change in behavior, restlessness, agitation, confusion, delirium, and hallucinations. Those with Alzheimers disease or dementia often exhibit more behavioral symptoms. Seniors may also display poor motor skills, a loss of coordination, and a greater tendency to fall.
Why Does Your Risk For Utis Increase With Age

Again, there are a few reasons that the elderly are more susceptible to UTIs. In both men and women over 65 the risk becomes greater because they tend to have more difficulties fully emptying their bladder. This causes bacteria to develop in the urinary system and turn into a UTI. In older men, this often happens because of a common condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia , or an enlarged prostate gland. The enlarged prostate blocks the flow of urine and prevents the bladder from fully emptying. As women age, the bladder muscles weaken and prevent the bladder from emptying completely.
Other risk factors to consider for UTIs in older adults include:
- Having a suppressed immune system
- Exposure to different bacteria in the hospital or care facility
- Poor hygiene by elderly adults or their caregivers
Don’t Miss: Medline Urinary Drainage Bag With Anti Reflux Tower
What To Do If You Think Your Child Has A Uti
If you think your child may have a UTI, call your pediatrician. A simple test can diagnose if your child has a UTI. To get rid of the infection, your child will need to take antibiotics.
Its important to continue giving your child the medicine until your pediatrician says the treatment is finished, even if your child feels better. UTIs can return if not fully treated.
Antibiotic Management Of Urinary Tract Infection In Elderly Patients In Primary Care And Its Association With Bloodstream Infections And All Cause Mortality: Population Based Cohort Study
- Accepted 16 January 2019
Don’t Miss: Will Az Pack Help A Urinary Tract Infection
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease pain:
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day, especially during hot weather
Its important to follow the instructions on the packet so you know how much paracetamol you or your child can take, and how often.
It may also help to avoid having sex until you feel better.
You cannot pass a UTI on to your partner, but sex may be uncomfortable.
Taking cystitis sachets or cranberry products has not been shown to help ease symptoms of UTIs.
What Are The Symptoms Of Utis In The Elderly
Like anyone with a UTI, older adults may experience typical physical symptoms. Yet they may not notice a mild infection right away. This is because chronic urinary problems common in seniors, such as urinary incontinence or frequency, may have similar symptoms to a UTI, masking an infection.
Common symptoms of a UTI include:
- Burning, painful sensation with urination
- Frequent, intense urge to urinate even when theres little urine to pass
- A feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied
- Blood in the urine
- Inability to perform common daily tasks, such as getting dressed or feeding themselves
Don’t Miss: How To Clear Up A Urinary Tract Infection
Why Are Seniors At Risk For Utis
Men and women older than 65 are at greater risk for UTIs. This is because both men and women tend to have more problems emptying their bladder completely as they age, causing bacteria to develop in the urinary system.
In older men, this often happens because of a common condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia , or an enlarged prostate gland. The enlarged prostate blocks the flow of urine and prevents the bladder from fully emptying.
Other risk factors for UTIs in older adults include:
- Using a catheter to empty the bladder
- Having kidney stones, which can block the flow of urine
- Having a suppressed immune system, which lowers the bodys defense against infection
Major Causes Of Hematuria
Below are common causes of hematuria
- Kidney, bladder or prostate cancer
- Enlarged prostate
- Diseases of the ureter such as malignancy, stones, stricture
- Mimics of hematuria
- Vigorous exercise
It is important to remember the following the red colour change in urine does not necessarily reflect the degree of blood loss- so if you see blood in urine, do not panic and assume the patient will bleed to death. hematuria present with signs and symptoms of UTI is fairly common and transient, i.e. short-lasting. However, if you have a patient who presents with hematuria that is not explained by an obvious condition or persists beyond the UTI then you should refer the patient for further investigation.
The above highlights the importance of following up with patients with hematuria or any ailment for that matter- to confirm it has resolved or ensure appropriate referral where necessary.
Don’t Miss: Can Hpv Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
What Are Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
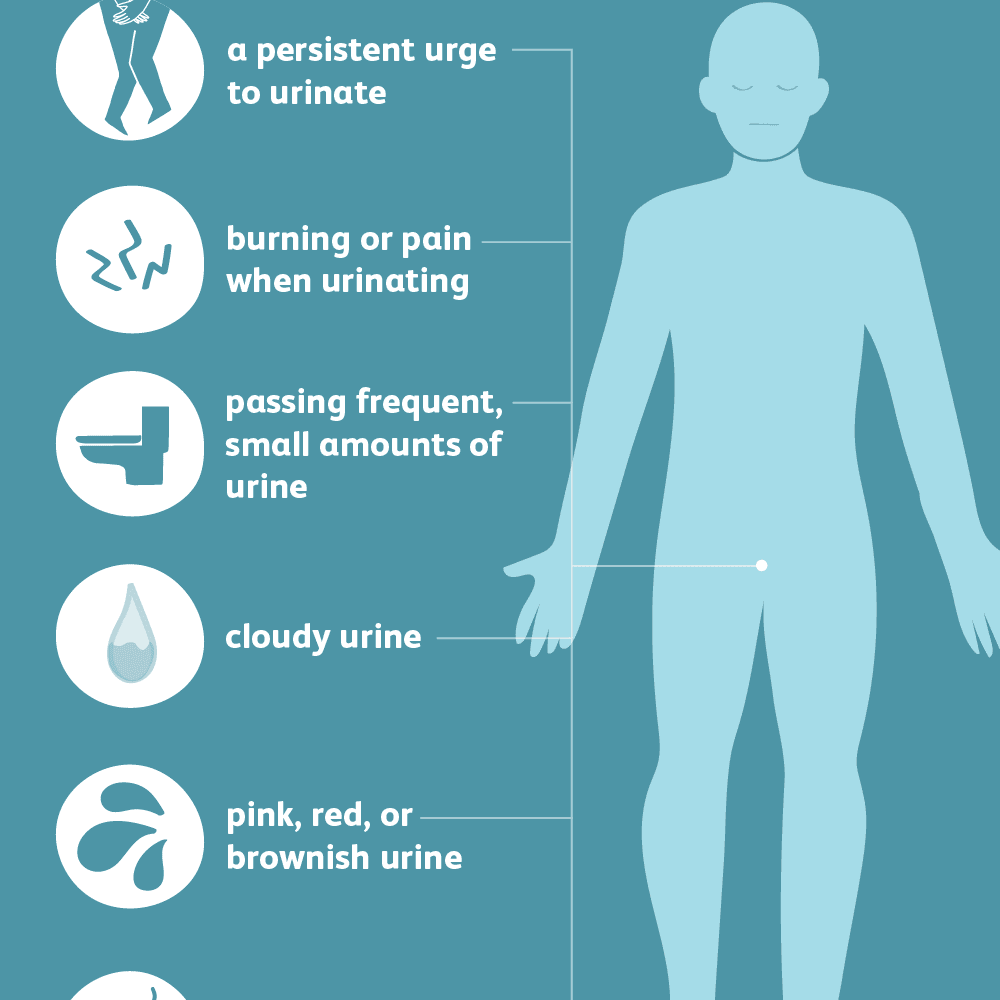
A recurrent urinary tract infection is an infection that comes back after you have been treated for a previous UTI.
The causes of recurrent urinary tract infections are usually due to the bacteria that cause the initial infection not being completely eradicated from the body. This can happen if you do not finish the full course of antibiotics prescribed or if the bacteria are resistant to the antibiotics used.
Symptoms of recurrent urinary tract infections can vary depending on the individual but may include frequent urination, burning sensation when urinating, cloudy or bloody urine, and pelvic pain.
Treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections usually involves re-treatment with the same antibiotics that were used to treat the initial infection. However, if the bacteria are resistant to the first line of antibiotics, your healthcare provider may prescribe a different antibiotic.
Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections can be achieved by taking measures to reduce your risk of developing an infection in the first place. This includes drinking plenty of fluids, urinating regularly, and wiping from front to back after using the toilet. You may also be prescribed a prophylactic antibiotic to take after you have been treated for a UTI.
Recommended Reading: Male Urinary Tract Infection How To Treat
How Are Utis Treated In Older Adults
UTIs can be treated the same for all ages with antibiotics. However, depending on the persons age, health, and severity of the infection, it may take several weeks and a longer course of antibiotics. In more severe cases, seniors may need to be hospitalized to receive IV antibiotics. Look for the signs for early detection in treating a UTI in the elderly so that it doesnt get more severe.
Of course, the best way to treat a UTI is to prevent them. Here are some tips to prevent UTIs, which include the obvious, drinking more water, wiping front to back, and peeing after sex. Yes, older adults have sex too. Those prone to recurrent UTIs, may want to consult with their doctor on taking supplements to keep them at bay. Evidence shows that D-mannose and cranberry powder help prevent bacteria from sticking to your vaginal parts. Checkable Urinary Tract Balance provides all of the nutrients needed to keep UTIs away.
What Happens If A Uti Goes Untreated For An Older Person
UTI infections that go untreated can spread from your bladder to your kidneys and beyond. Especially in older adults or anyone with a lowered immune system, treating an infection earlier can keep it from spreading and overwhelming your system.
An infection that goes untreated can lead to , a serious form of infection. Dr. Slopnick says fear of sepsis is what causes some people to worry about asymptomatic bacteriuria. If you have a UTI, youll almost certainly show symptoms long before the infection spreads or sepsis sets in.
Read Also: To Treat Urinary Tract Infection
How Is A Uti Diagnosed
Your doctor or nurse will discuss your symptoms and if its unclear whether you have a UTI they will use a dipstick urine test to check for infection. In some cases, youll be treated without needing a sample but in other cases, a sample will need to be sent to a lab for urine culture testing that looks for bacteria that cause a UTI. This happens if you:
- have blood in your pee
- have recurrent UTIs
- have an underlying problem with your urinary tract
- have a catheter
- are over 65 years old
Urinary Tract Infections And Dementia
UTIs can cause sudden confusion in older people and people with dementia. If the person has a sudden and unexplained change in their behaviour, such as increased confusion, agitation, or withdrawal, this may be because of a UTI.
The person may not be able to communicate how they feel, therefore it is helpful to be familiar with the symptoms of UTIs and seek medical help to ensure they get the correct treatment.
It is also important to be aware that any infection could speed up the progression of dementia and so all infections should be identified and treated quickly.
UTIs and delirium
Recommended Reading: Coconut Oil For Urinary Tract Infection
The Evidence: Diagnosis Management And Prevention
We searched Ovid for English-language human studies conducted among adults aged 65 years and older and published in peer-reviewed journals from 1946 to November 20, 2013. We focused on community-dwelling older adults. Search terms included UTI, asymptomatic bacteriuria, risk factors and UTI, community-onset UTI, functional decline and UTI, delirium and UTI, dehydration and UTI, diagnosis and UTI, diet and drug therapy and UTI, prevention and UTI, and urine tests and UTI. We also searched for recently published Cochrane reviews regarding treatment and prevention of UTI in community-dwelling older adults. The recommendations that follow are based on evaluation of the existing evidence.
The Role Of Urinalysis And Uncomplicated Uti Diagnosis
Findings on a dipstick suggestive of UTI include either of the following leukocyte esterase or nitrites .
Other findings which may be present but not specific to UTI include hematuria- more common in the setting of UTI but not in urethritis or vaginitis. This can be helpful when differentiating between likely causes of symptoms cloudy urine may be evidence of infection foul urine odour- suggestive of bacteria in the urine.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Strip Test
Tips For Preventing Utis In The Elderly
The following lifestyle and personal hygiene changes can significantly reduce a seniors risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Drink cranberry juice or use cranberry tablets, but NOT if the elder has a personal or family history of kidney stones.
- Avoid or limit caffeine and alcohol, which irritate the bladder.
- After toileting, always wipe from front to back .
- If incontinence is not an issue, wear breathable cotton underwear and change them at least once a day.
- Change soiled incontinence briefs promptly and frequently.
- Keep the genital area clean and dry.
- Set reminders/timers for seniors who are memory impaired to try to use the bathroom instead of an adult brief.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti In The Elderly

Urinary tract infections are pretty common infections especially in women and older adults. In fact, over 1 in 3 infections in seniors living in nursing homes are UTIs. While they may be uncomfortable and annoying for younger adults, they can actually pose serious health threats to seniors. And the symptoms and side effects of a UTI may be different for seniors than younger generations, making the infection difficult to identify. In this post, we will explore the symptoms of a UTI and the health risks they can pose for seniors.
Don’t Miss: Best Thing For Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary Tract Infections And Dementia Urinary Tract Infections And Dementia
Urinary tract infections are a type of infection common among older people. If a person with a memory impairment or dementia has a UTI, this can cause sudden and severe confusion known as delirium.
Urinary tract infections and dementiaUrinary tract infections and dementia .
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
A major strength of this study is the use of individual patient level data for adults older than 65 years extracted from a large nationwide general practice records database and linked to hospital and mortality records. This provided the opportunity to track the care pathways of a vulnerable population with a diagnosis of UTI in the community with a 60 day follow-up. The linkage with mortality data from the Office for National Statistics minimised possible bias in the risk estimates of all cause mortality among older adults treated in a routine care setting.
The large sample size of about 160000 patients with more than 300000 distinct UTI episodes substantially increased the power of the analyses, especially for rare severe adverse events in older adults . As the base population is representative of the English general population, our results are generalisable to the entire English population of elderly patients.
The main limitations of our study are common to observational studies using routinely collected electronic health record data, and include unmeasured and residual confounders, missing data and potential biases, such as confounding by indication, misclassification biases, or inconsistencies in coding within and between practices and over time.
Also Check: Reasons For Urinary Tract Infection In Females