Uti Diagnosis And Treatment
Think you may have a UTI? The standard way to diagnose one is a urine culture. Most doctors will ask for a clean catch sample, where you pee into a cup midstream after carefully wiping your outer vaginal area.
If you are diagnosed with a UTI, your doctor will likely provide a pregnancy-safe antibiotic for seven to 14 days to get rid of all of the bacteria. Be sure to take the recommended full course, even if you start to feel better midway through treatment, and drink plenty of water.
If the infection has reached your kidneys, your practitioner may suggest staying in the hospital, where you can receive IV antibiotics.
Keep in mind: Some women have a UTI with no symptoms at all. Because an untreated infection can lead to complications including kidney infection and, potentially, an increased risk of fetal growth restriction, preeclampsia and preterm birth notify your provider immediately if you have any UTI-like symptoms.
Likewise, the urine tests at your regular prenatal visits are really important.
Urinary Tract Infection Screening
For pregnant women in intervention clusters, during a home visit at < 19weeks gestation, a clean catch midstream urine specimen was collected for culture. The CHW instructed the mother to spread the labia widely before collecting 20-30mL of the midstream urine into a sterile wide-mouthed container. The urine specimen was immediately placed in a cooler refrigerated with ice-packs and transported to the Sylhet field laboratory, maintaining the cold chain. A random selection of 10% of the control arm women also had urine screened by culture.
Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
ishonest
Anyone can. But they’re more likely when you:
- Are a woman
- Have had UTIs before
- Have a condition that affects your bladder’s nerves
- Have been through menopause
- Are overweight
- Have something that blocks the passage of urine, such as a tumor, kidney stone, or an enlarged prostate
- Use a diaphragm or spermicide for birth control
- Have a catheter, a tube placed into the bladder to drain urine from the bladder into a bag outside the body
- Are a man who has sex with men, has HIV, or hasnt been circumcised
Most of these traits also raise the odds that a simple bladder infection may become a more serious kidney infection or turn into . For pregnant women, a kidney infection can lead to delivering a baby too early.
Also Check: Azithromycin For Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes A Uti During Pregnancy
Several factors can lead to a UTI during pregnancy, including:
- Changes in your body. All women are at risk for UTIs . But pregnant women may be more prone: Changes in hormones may give bacteria an easier opportunity to travel up the urinary tract and cause an infection. Your growing uterus also puts added pressure on your bladder, making it more difficult to completely empty it of urine .
- Bacteria from the bowel. UTI-causing bacteria can come from several places. By far the most common bacterial invader, E. coli, comes from the bowel. Because the urethra is located close to the rectum, these bacteria can be transported up the urethra. Wiping from front to back every time you use the bathroom can help keep bacteria away from this area.
- Intercourse. Sex during pregnancy is perfectly healthy but there is a downside: It also has the potential to lead to a UTI, as bacteria near the vagina may be pushed into the urethra during intercourse. It may not be romantic, but its important to urinate before and after sex to move that bacteria along.
- Group B streptococcus. This type of bacteria, commonly carried in the intestinal tract, can also cause UTIs during pregnancy. Late in your pregnancy, your doctor will test you for this infection and treat you with antibiotics if necessary.
There are also some less avoidable risk factors. If any of these apply to you, be sure to discuss them with your doctor so you can be closely monitored for signs of an infection:
Group B Streptococcal Infection
Group B streptococcal vaginal colonization is known to be a cause of neonatal sepsis and is associated with preterm rupture of membranes, and preterm labor and delivery. GBS is found to be the causative organism in UTIs in approximately 5 percent of patients.31,32 Evidence that GBS bacteriuria increases patient risk of preterm rupture of membranes and premature delivery is mixed.33,34 A randomized, controlled trial35 compared the treatment of GBS bacteriuria with penicillin to treatment with placebo. Results indicated a significant reduction in rates of premature rupture of membranes and preterm delivery in the women who received antibiotics. It is unclear if GBS bacteriuria is equivalent to GBS vaginal colonization, but pregnant women with GBS bacteriuria should be treated as GBS carriers and should receive a prophylactic antibiotic during labor.36
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do For Urinary Incontinence
What Is A Urine Infection And What Are The Symptoms
A urine infection is caused by germs which get into your urine. Usually the germs have come from your skin, and travelled up the tubes of the urinary system. The symptoms may depend on how far up your system the germs have travelled. The germs may cause:
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria. In this situation bacteria are found in your urine but are not causing any symptoms. You will only know you have it if your urine is tested.
- Bladder infection . This is common, both in pregnant and non-pregnant women. Typical symptoms are pain when you pass urine and passing urine more often. You may also have other symptoms such as pain in your lower tummy , blood in your urine, and a high temperature .
- Kidney infection . This is uncommon but may occur as a complication from cystitis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. It is usually a more serious infection, making you feel very unwell. Some or all of the possible symptoms may occur, which include:
- Pain in your side over your kidney.
- Having a high temperature.
- Symptoms of cystitis as above.
- Feeling generally unwell.
What Are The Symptoms Of Utis During Pregnancy
Common symptoms of a UTI during pregnancy are similar to those that you might experience at any other time, and include:
- a burning sensation when you pass urine
- feeling the urge to urinate more often than usual
- urinating before you reach the toilet
- feeling like your bladder is full, even after you have urinated
- urine that looks cloudy, bloody or is very smelly
- pain above the pubic bone
- fever
Sometimes the first sign of an infection is a faint prickly sensation when you pass urine. If the infection is more advanced and has moved up to the kidneys, you may also experience fever with a particularly high temperature, back pain and vomiting.
Also Check: Does Cranberry Juice Clean Urinary Tract
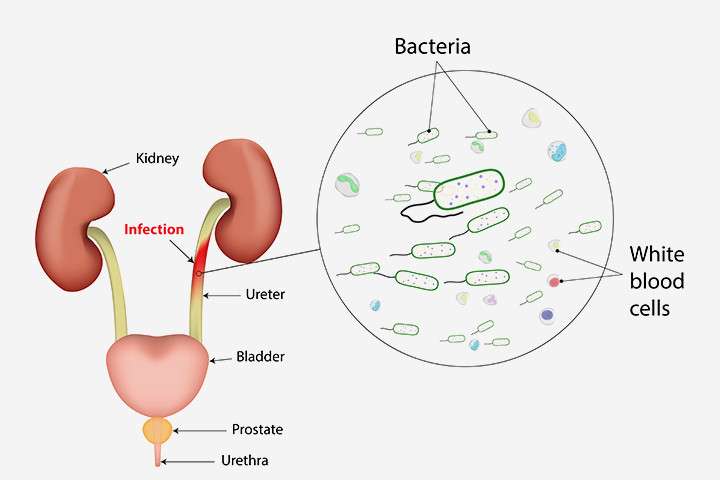
What Is A Uti
A UTI is a bacterial infection of the urinary tract, which includes the bladder , the urethra or, in more serious cases, the kidneys .
The urinary tract removes waste and extra water from the body. It’s made up of two kidneys, where urine is produced, two ureters, which carry urine to your bladder, the bladder itself, which collects and stores the urine, and the urethra, the tube that sends the urine out of your body.
Sometimes, normal bacteria from your skin and other areas can trespass into the urinary tract, where they multiply fast, resulting in infection.
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
For women who suffer from frequent, chronic, and recurrent UTIs, low-dose antibiotic prophylaxis including nitrofurantoin , cephalexin , or trimethoprimâsulfamethoxazole can provide symptomatic relief.
However, as discussed earlier in the section âUTIs in Pregnancy,â the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria limits the effectiveness of our current antibiotic arsenal. For example, individuals who suffer from serious recurrent or chronic UTIs may benefit greatly from carbapenems such as ertapenem, but these antibiotics are considered one of our last lines of defense and so should be used cautiously. The ongoing emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, with the high frequency of rUTIs, highlights the need for a better understanding of these infections and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Recurrent UTIs are thought to arise from the ability of bacteria to attach to and invade the bladder epithelium, where they can form intracellular reservoirs protected from antibiotics and host defenses. Thus, many emerging treatments for UTIs are aimed at blocking adhesion of bacteria to the urothelium.
Jack D. Sobel, Donald Kaye, in, 2015
Don’t Miss: Azo Urinary Tract Defense Antibacterial Protection
Deterrence And Patient Education
After 2 to 4 weeks following completion of treatment, urine culture should be obtained to assure that reinfection has not occurred.
Suppressive antibiotic therapy, usually with nitrofurantoin once daily, is commonly recommended especially in cases where patients have had prior UTI. This is typically continued thru pregnancy and the early postpartum period.
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors Of Uti During Pregnancy
Other than hormonal changes, here are some of the causes and risk factors of UTI during pregnancy are
Also Check: What Is Best Treatment For Urinary Tract Infection
Pregnancy And Urinary Tract Infections
During pregnancy, there are normal changes in the function and anatomy of the urinary tract. These include kidney enlargement, and compression of the ureters and bladder by the growing uterus. During pregnancy, the bladder does not empty as well. The urine is not as acidic and it contains more sugars, protein, and hormones. All of these factors can contribute to an increased susceptibility to UTI.
Types of UTI in pregnancy include the following:
-
Asymptomatic bacteriuria. A silent infection often caused by bacteria present in the woman’s system before pregnancy. This type of infection occurs in about 5 to 10 percent of pregnant women. Asymptomatic bacteriuria may lead to acute bladder infection or kidney infection if left untreated.
-
Acute urethritis or cystitis. A urethral or bladder infection that causes symptoms including pain or burning with urination, frequent urination, feeling of needing to urinate, and fever.
-
Pyelonephritis. A kidney infection. Symptoms of pyelonephritis may include those of acute cystitis plus flank pain. Pyelonephritis may lead to preterm labor, severe infection, and adult respiratory distress syndrome.
The most common organism that causes UTI is Escherichia coli , a normal organism of the vagina and rectal area. Other organisms may also cause UTI, including group B streptococcus, and sexually transmitted gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Why Are Utis Common During Pregnancy
UTIs are common during pregnancy. Thats because the growing fetus can put pressure on the bladder and urinary tract. This traps bacteria or causes urine to leak.
There are also physical changes to consider. As early as six weeks gestation, almost all pregnant women experience ureteral dilation, when the urethra expands and continues to expand until delivery.
The larger urinary tract, along with increased bladder volume and decreased bladder tone, all cause the urine to become more still in the urethra. This allows bacteria to grow.
To make matters worse, a pregnant womans urine gets more concentrated. It also has certain types of hormones and sugar. These can encourage bacterial growth and lower your bodys ability to fight off bad bacteria trying to get in.
2 and 10 percent of pregnant women experience a UTI. Even more worrisome, UTIs tend to reoccur frequently during pregnancy.
Women whove had UTIs before are more prone to get them during pregnancy. The same goes for women whove had several children.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Health Cranberry Pills
Is A Uti Dangerous During Pregnancy
Any infection during pregnancy can be extremely dangerous for you and your baby. Thats because infections increase the risk of premature labor.
I found out the hard way that an untreated UTI during pregnancy can also wreak havoc after you deliver. After I had my first daughter, I woke up a mere 24 hours after coming home with a fever approaching 105F .
I landed back in the hospital with a raging infection from an undiagnosed UTI, a condition called pyelonephritis. Pyelonephritis can be a life-threatening illness for both mother and baby. It had spread to my kidneys, and they suffered permanent damage as a result.
Moral of the story? Let your doctor know if you have any symptoms of a UTI during pregnancy. If youre prescribed antibiotics, be sure to take every last pill to knock out that infection.
You can help prevent UTIs during your pregnancy by:
- emptying your bladder frequently, especially before and after sex
- wearing only cotton underwear
- avoiding douches, perfumes, or sprays
- drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
- avoiding any harsh soaps or body wash in the genital area
Most UTIs during pregnancy are treated with a course of antibiotics. Your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic that is pregnancy-safe but still effective in killing off bacteria in your body.
If your UTI has progressed to a kidney infection, you may need to take a stronger antibiotic or have an intravenous version administered.
When Is My Urine Checked During Pregnancy
- You should usually have your urine tested early in pregnancy. Your midwife may ask you to bring a sample in a container or sample bottle. Treatment is advised if any germs are found – even if you have no symptoms. If bacteria are found, you should have regular routine urine tests throughout the pregnancy.
- You will normally be asked to bring a urine sample at each of your antenatal checks. How often this is depends on how your pregnancy is progressing and whether you have any problems or complications.
- You should also have your urine tested if you develop symptoms of bladder infection or kidney infection at any stage during pregnancy.
Also Check: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
What Is The Treatment For Utis In Pregnancy
UTIs in pregnancy are treated with antibiotics, even if you have no symptoms. If left untreated, UTIs can progress to cause a serious kidney infection known as pyelonephritis. They have also been linked with higher rates of low birth weight of the baby and premature birth .
| When you see a health provider, always tell them you are pregnant as not all antibiotics or medicines are safe in pregnancy. |
|---|
- Your doctor will choose an antibiotic that is safe to use during your stage of pregnancy. The most commonly recommended antibiotic is nitrofurantoin. Usually, a 7-day course of antibiotics is prescribed. You should finish the whole course to completely treat the infection and reduce the chance of it coming back.
- Your symptoms should begin to improve within a few days, if you had any. If you still have symptoms for more than 2 days after starting treatment, or you get worse, see your doctor as soon as possible.
- After finishing the antibiotics, you will need a further urine check 1 week later to check the infection has been treated properly.
- You will then have urine tests each month while pregnant to make sure the UTI doesn’t come back.
Uti Symptoms And Prevention
A urinary tract infection , also called bladder infection, is a bacterial inflammation in the urinary tract. Pregnant women are at increased risk for UTIs starting in week 6 through week 24 because of changes in the urinary tract. The uterus sits directly on top of the bladder. As the uterus grows, its increased weight can block the drainage of urine from the bladder, causing a urinary tract infection during pregnancy.
Read Also: Kidney Stone In Urinary Tract
What Are The Common Causes Of Utis
Your urinary tract is normally free of bacteria. If bacteria enter the tract and multiply, they can cause a UTI. There are several factors that increase the risk of developing an infection:
- Infection with common bacteria in your gut, usually from faeces can contaminate your urinary tract
- Being sexually active increases the risk of bacteria moving around the genital area and entering the urinary tract
- If you have weak pelvic floor muscles your bladder might not empty completely, which can lead to an infection
- Women with diabetes are at increased risk of developing a UTI since the sugar in their urine may cause bacteria to multiply
What Causes A Urine Infection
Most urine infections are caused by bacteria which come from your own bowel. They cause no harm in your bowel but can cause infection if they get into other parts of your body. Some bacteria lie around your back passage after you pass a stool . These bacteria can sometimes travel to your urethra and into your bladder. Some bacteria thrive in urine and multiply quickly to cause infection.
Women are more prone than men to urine infections, as their urethra is shorter and opens nearer the anus. Pregnant women are also more prone than non-pregnant women to urine infections. This is partly due to the hormonal changes of pregnancy which affect the urinary tract and tend to slow down the flow of urine. It also may be that the enlarged womb presses on the bladder and prevents it draining as well. If urine does not drain quickly from the bladder, germs are more able to multiply and cause an infection.
Less commonly there may be other causes of a urine infection. If you have to have a tube passed into your bladder, it is easier for germs to directly reach your bladder, and this may make urine infection more likely. Occasionally for people whose immune systems are not working well, the infection may spread through the bloodstream rather than up the urinary tubes.
Recommended Reading: What Do You Do For A Urinary Tract Infection