What Do Urodynamic Test Measure
Urodynamic test results help diagnose the cause and nature of a lower urinary tract problem. These tests can range from simply observing the urinary process to taking precise measurements using sophisticated instruments including ultrasound and x-ray equipment.
Your doctor will decide the type of urodynamic test based on your current health, a physical examination, and your lower urinary tract symptoms .
A simple observation might entail:
- recording the length of time it takes a person to produce a urinary stream
- noting the volume of urine produced
- recording the ability or inability to stop the urine flow in midstream
Imaging equipment that takes pictures of the bladder filling and emptying, pressure monitors that record the pressures inside the bladder, and sensors that record muscle and nerve activity are all used for taking more precise measurements.
Depending on the type of urodynamic test, you may be asked to arrive for testing with a full bladder, however, most urodynamic tests don’t involve any special preparations. Some tests may require you to stop taking certain medications.
Recovery After Urodynamic Testing
You may experience mild discomfort for a few hours when urinating after having urodynamic tests. Your doctor may recommend you drink an 8-ounce glass of water every half-hour for two hours to help reduce the discomfort.
Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic for one to two days to prevent infection. If you show any signs of infection including pain, chills, or fever, you should contact your doctor immediately.
What Can I Expect Before The Procedure
You might be asked to complete a bladder diary for three days, if you have not already done so. This provides an idea about the nature and amount of your fluid intake as well as how much and how often do you pass urine. This enables understanding your bladder function.
If you are taking tablets to improve your bladder function, you need to stop these medications for 2 weeks prior to the test. On the day of the test, it is good to wear clothes that are easy to remove, as you will be asked to remove clothes from your bottom half and wear a gown.
Try to arrive with a comfortably full, or at least half full, bladder, as you will be asked to pass urine at the start of the test.
If you are known to have recurrent urinary tract infection, you will be asked to have a urine test a week or so before the appointment. You might be provided with an antibiotic prescription prior to use prior to the test.
You May Like: How To Reverse Urinary Retention
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract is the body’s drainage system for removing wastes and extra water. The urinary tract includes two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra. Blood flows through the kidneys, and the kidneys filter out wastes and extra water, making urine. The urine travels down two narrow tubes called the ureters. The urine is then stored in a muscular, balloonlike organ called the bladder. The bladder swells into a round shape when it is full and gets smaller as it empties. When the bladder empties, urine flows out of the body through the urethra.
After Urodynamic Diagnostic Test
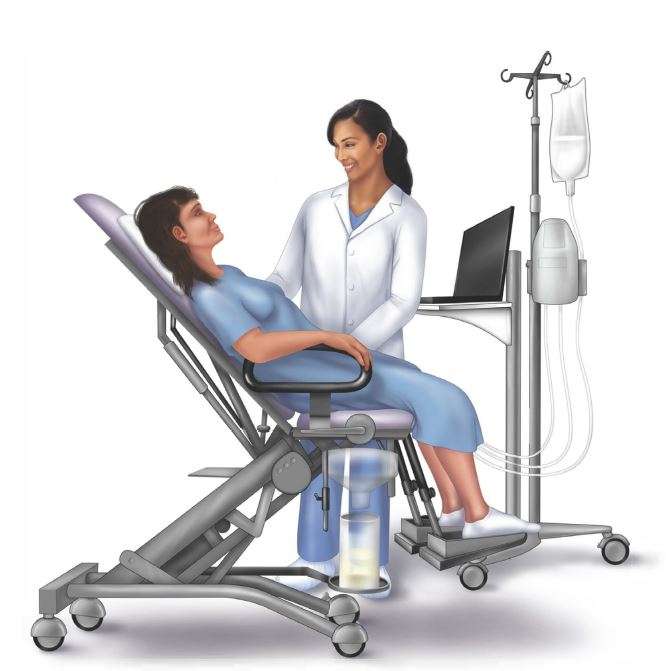
There is no recovery time required after this procedure or any special precautions to be practised.
Patients are free to continue their normal routines and diet without concern. The doctor will advise extra intake of fluids to make it easier to urinate for the first few days.
The doctor may prescribe antibiotics to prevent an infection. Its normal to see blood in the urine after the test, which will lessen with time.
-
Canberra Urology and Gynaecology CentreSuite 3, Level 2, Equinox 170 Kent Street
Read Also: Magnetic Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
What Information Is Gained From A Urodynamic Study
The aim of the urodynamic study is to reproduce the bothersome urinary symptoms so that the underlying problem with the urinary tract is shown.
The urodynamic study provides information about:
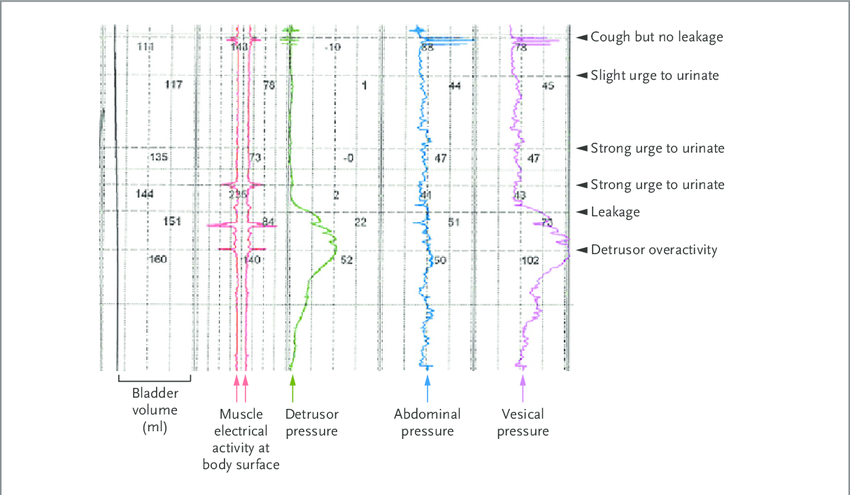
- Bladder overactivity showing evidence of detrusor overactivity or unstable bladder contractions
- Bladder compliance the elasticity of the bladder wall which may be impaired in neurological conditions or with previous pelvic radiation
- Stress urinary incontinence showing the type and severity of stress incontinence which helps guide the choice of surgical treatment
- Obstruction- showing the site and severity of blockage in the urinary tract e.g. due to enlargement of the prostate in men, due to prolapse in women, due to neurological disorders
- Quality of the bladder muscle contraction which can decline with ageing, medical problems such as diabetes and neurological problems
Dr. Karen McKertich
What Happens During Urodynamic Testing
Testing is done in a room in the X-ray department.
For the first part of the test, you will need to empty your bladder into a special toilet called a flowmeter. This measures how much urine you pass and the flow of the urine. You will usually be left alone in the room whilst you are doing this. This is why you need to come to the test with a full bladder.
Once you have been to the toilet you will usually have an ultrasound test performed to see how empty your bladder is. This test is done by having some gel on the skin over your bladder and then an ultrasound probe being moved over this area.
The next part of the test measures the way your bladder works as it fills up. You will be asked to lie down on a special bed. Two very thin tubes are put into your bladder, by inserting them into the tube from your bladder that passes out urine . You may find this a little uncomfortable. One is to fill up your bladder and the other is to measure the pressure in your bladder. Another catheter is put into your vagina or back passage . This allows the pressure inside your bladder to be compared with the pressure outside your bladder.
Once the catheters are in the correct position, fluid runs into your bladder at a controlled rate. This slowly fills your bladder whilst recordings are made. The clinician performing the test will ask you questions – for example, how your bladder feels and when it feels full.
Read Also: Is Azithromycin Good For Urinary Tract Infection
Types Of Urodynamic Studies
The following are urodynamic studies currently used for diagnosis today:
Uroflowmetry is the use of a uroflowmeter to determine the rate of urine flow. The device measures the amount of urine, the rate of release, and how long it takes for the flow rate to reach its peak. The resulting data tells a doctor whether the patient’s bladder muscles are weak or strong. Uroflowmetry also reveals urine-flow obstruction, which can signify other issues.
Multi-Channel Video Urodynamics utilize X-rays or sound waves to produce images of the lower urinary tract during bladder filling and emptying.
Cystometry refers to the use of a cystometrogram to measure bladder pressure when it is full and when the patient needs to void. During this procedure, a catheter empties the bladder then fills it with warm fluid. A second catheter is inserted into the rectum or vagina in order to measure the pressure of the intra-abdomen.
Electromyograms measure the bladder muscle signals. Because bladder muscles need to signal properly for the bladder to function properly, any anomalies may indicate an underlying neurological disorder. This procedure is often required in conjunction with a CMG.
Pressure Studies are often performed along with a CMG and are used to measure pressure at a leakage site. This test is particularly useful for examining stress incontinence, in which leakage occurs in response to abdominal pressure on the bladder.
References
RELATED ARTICLES
Fluoroscopy And Video Urodynamics
Video urodynamic studies have become the investigative technique of choice for incontinence in many referral and research centers. This technique involves the simultaneous display of real-time images of the bladder neck and urethra, as well as cystometric summaries of bladder, intra-abdominal, and, in some cases, urethral pressures.
The precise placement of pressure transducers and a constant understanding of their exact anatomic location is one of the advantages of this technique. Another advantage is the ability to fluoroscopically observe the bladder neck area throughout bladder filling and during stress maneuvers.
Contrast material can be observed entering the proximal urethra just before leakage thus, leak-point pressure findings can potentially be more precise. Cough profiles and pressure transmission ratios can also be determined.
The physical location of the transducer tip can be observed during urethral pressure profilometry and correlated with the pressure findings. Although probably not necessary for the evaluation of straightforward stress incontinence, video urodynamics can be a valuable diagnostic tool in complex cases.
Video urodynamic studies are the criterion standard for the evaluation of an incontinent patient. Video urodynamic studies combine the radiographic findings of a VCUG and multichannel urodynamics. A videourodynamic study is the most sophisticated diagnostic test for an incontinent patient.
Don’t Miss: Best Thing For Urinary Tract Infections
What Should I Do To Prepare For A Urodynamic Test
If you are taking any medication for your bladder then it is likely that you will be asked to stop this for a week before this test.
Your hospital may ask you to arrive for your test with a comfortably full bladder. If this is difficult, some hospitals may ask you to arrive a little early so that you can have a drink to fill your bladder.
The test usually takes around 2-3 hours.
How Advanced Gynecology Can Help
We are always here to help you find the right care. Our patient coordinators can help you schedule an appointment for an exam or for urodynamic testing if your doctor has prescribed it as the next step in your treatment plan.
For more information, schedule an appointment today or call 706-389-9228 to speak with one of our patient coordinators.
You May Like: Male Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Over The Counter
Postvoid Residual Volume Measurement
PRV is the remnant volume of urine in the bladder after active full urination, used with patients with overflow incontinence, it is common in the elder than an adult, or conditions with unobvious cause, to detect the ability of the patient to fully evacuate the bladder or not. After urination, a small flexible catheter inserted in the bladder for a full evacuation and may be measured by the US on the bladder.
PRV 100-200 ml needs attention and considered indeterminate, measurements need to be repeated at another time, while more than 200ml considered overflow rate.
Are There Any Side

Some urodynamic tests involve using X-rays. X-rays should not be used on pregnant women so let your doctor know before the test if you are, or think you could be, pregnant.
Most people have urodynamic tests without experiencing any problems. As mentioned above, there is a small chance of developing a urinary tract infection. Contact your GP if you develop any of the following symptoms:
- A stronger than usual urge to pass urine.
- Your urine smells, is cloudy or has blood in it.
- You want to pass urine more often during the day and night.
- A burning or stinging sensation when you pass urine and feel that you are only passing small amounts at a time.
- Lower backache or pain in your kidneys.
- If you feel hot and develop a high temperature.
Further reading and references
Recommended Reading: How Does Cranberry Juice Help Urinary Tract Infections
How Does The Lower Urinary Tract Usually Work
Your lower urinary tract includes the bladder and the urethra.
The bladder is a balloon-shaped organ that stores urine, which is made in the kidneys. Its held in place by pelvic muscles in the lower part of your belly.
The bladder is relaxed when it isnt full. Nerve signals in your brain let you know that your bladder is getting full. When it is full, you feel the need to release urine. The brain then tells the bladder muscles to squeeze . This forces the urine out of your body through your urethra.
Your urethra has muscles called sphincters. They help keep the urethra closed so you dont leak before its time. These sphincters open up to release urine when the bladder contracts.
What Do Urodynamics Involve
On arrival, you will be taken to a private area. You will be asked to remove the clothes on your bottom half and will be given a robe to wear. You will be asked to pass urine in a commode that will measure the rate and volume of you passing urine.
After that, you might be examined to assess if you have prolapse, if this has not been done before. The area around the urethra is cleaned and a catheter is passed into your bladder, to fill it and record pressure changes. Another catheter will be passed either through the vagina or rectum to get the pressure inside your abdomen. This will be deducted from the pressure inside your bladder to the get the pressure caused by the bladder itself.
The test can be carried out in the sitting, semi sitting, lying down or standing position.
The rate of bladder filling will be varied to test your bladder. You will be asked to cough from time to time, to ensure the catheters are in place. You will be asked to perform a number of manoeuvres, such as bearing down, washing your hands in water and bouncing your heels, to assess your bladder function.
At the end, you will be asked to pass urine again in the commode, this time with catheters in place.
A scan might be performed to measure how much urine is left in the bladder. If this is significant, it might be emptied by a catheter.
In some instances, the test will be performed under x ray to see the shape and mobility of the bladder. This is called video urodynamics.
Also Check: What Is The Medicine For Urinary Tract Infection
Who Needs A Urodynamic Study
Some of the reasons people need a urodynamic study include:
- To define the type of incontinence, particularly when the history is unclear e.g. in cases of very severe incontinence with continuous leakage
- When invasive or surgical treatments for incontinence are being considered
- When the conservative and initial measures in treating urinary incontinence have not been successful
- In people who have a complex history or medical problems such as:
- A history of previous Urological surgery or Gynaecological surgery including surgery for incontinence or prolapse
- Unsuccessful previous surgery
- Mixed stress and urge incontinence symptoms to help determine the different treatment options
- Neurological disorders e.g. spinal cord injuries, strokes, head injuries, multiple sclerosis, Parkinsons disease
Why Are Urodynamic Tests Performed
Urodynamic tests are used on patients who are experiencing more severe signs and symptoms of incontinence. The urologist will use the results of the test in order to determine the cause of the incontinence as well as develop the right treatment plan for you. Urodynamic tests are also performed on patients who are considering surgical treatment options for their incontinence.
You May Like: Urinary Incontinence Treatment For Elderly
How Do Urodynamic Tests Work
The first part of the tests checks how much urine leaves your bladder over a certain length of time. This is called the flow rate. A special toilet records the flow of your urine. A computer then checks for any abnormalities in flow rate.
A decreased flow rate can indicate problems with bladder emptying. For example, this could be an obstruction to bladder drainage or underactivity of your bladder muscle.
The second part of the tests is called filling cystometry. For this test, thin tubes called catheters are inserted into your bladder and your back passage or your vagina. These can measure the pressure in your bladder and tummy as your bladder fills with fluid. Using these measurements, doctors compare the different pressure readings.
If urine leaks with no change in pressure in your bladder muscle, you may have stress incontinence. Leaking is brought on by an increase in pressure inside your abdomen – for example, when coughing.
If involuntary bladder muscle activity causes an increase of pressure in your bladder and leads to leaking, you may have urge incontinence.
What Results Can I Expect After This Type Of Testing Is Complete
Patients will receive one of two results either normal or abnormal. A normal result means that the bladder is functioning as it should be. An abnormal result indicates that the bladder cannot relieve itself all the way and too much urine is left behind, the bladder does not contain enough fluid before having the urge to urinate or the bladder cannot retain urine for a significant amount of time. Once the doctor analyzes the results of the test, an incontinence treatment plan can be developed.
Urinary incontinence can make people feel both uncomfortable and embarrassed, but it is important to know that it is a relatively common condition especially as people age. The best thing you can do for yourself is to talk with a urology expert about your symptoms and about your concerns.
Know that urodynamic tests can be performed in order to help diagnose your particular issue and provide you with the relief you need. Treating your incontinence will allow you to live a comfortable and confident life once again.
Recommended Reading: Goat Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
What Can I Expect After A Urodynamic Test
After the tests some people feel a slight stinging or burning sensation when they pass urine. If you drink plenty of fluids these symptoms should quickly settle. If discomfort lasts more than 24 hours, you should take a sample of your urine to your GP for testing because it may be a sign of infection.
Some people find a small amount of blood in their urine when they go to the toilet. If this lasts more than 24 hours, you should also see your GP because it may be a sign of infection.
After having urodynamic tests there is a small possibility that you may develop a urinary tract infection. This is caused by putting the very thin tubes into your bladder during the test. To help reduce the likelihood of developing an infection after the test, your hospital may advise you to:
- Drink extra fluids for 48 hours after the test. This will help you to ‘flush’ your system through. Aim to drink about two and a half litres a day for the 48 hours after the test .
- Cut down on your tea and coffee intake for 48 hours after the test. This will reduce bladder irritation until your bladder returns to normal. Drink water, herbal and fruit teas, juices and squash.
- When you go to the toilet to pass urine, take a bit longer to make sure that your bladder is fully empty. When you have finished passing urine, wait for a couple of seconds and then try again.