What Happens When A Uti Goes Untreated
Thanks to early diagnosis and proper treatment, the vast majority of lower urinary tract infections result in no complications. However, if left untreated, a UTI can have serious ramifications notes the Mayo Clinic, including:
- Premature birth and low birth weight
- Kidney damage, which can occur is an untreated UTI spreads from the bladder to the kidneys.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
How Long Do I Need To Take Antibiotics To Treat A Uti
How long you take antibiotics for a UTI depends on how severe your UTI is and which antibiotic youre prescribed. Some medications like fosfomycin only require one dose, while a more severe UTI might require 14 days or more of treatment. Most require 3 to 7 days of treatment.
Within the first 1 to 2 days of starting your antibiotics, youll probably notice your UTI symptoms start to fade away. If your UTI is more severe or youve had symptoms for a while before starting antibiotics, it might take a few more days for you to notice improvement.
In any case, its important to take all the antibiotics youre prescribed, even if you start feeling better before finishing them. Stopping antibiotics early can lead to antibiotic resistance, which means the medication might not work as well as it should if you need it to treat an infection in the future. It can also mean your UTI might come back if you havent treated it completely.
Also Check: Otc Urinary Tract Infection Medication
Why A New Antibiotic For Treating Utis Is Needed
, PhD, the department head and a professor in the Fitts Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at North Carolina State University, says its exciting that there may be a new treatment for UTIs because we need more drugs to match with the specific bugs that we have, including for uncomplicated UTIs and for more complicated cases.
Liu adds there currently are limited options to treat the most common UTIs because resistance to one of the antibiotics has been steadily increasing.
Moore points to a 2021 report from the World Health Organization that cautioned there are not enough new antibiotics in development to overcome the increasing risk of antibiotic resistance.
Early and effective treatments are important because otherwise, it can develop into more severe kidney and blood infections that can be life-threatening, explained Liu.
What Does It Mean If You Have Recurring Utis

Recurrent urinary tract infections are widespread. One study found that 44% of women who experience acute uncomplicated cystitis will have a recurrence later that year, usually within three months from the initial episode. Most providers define recurrent UTIs as two or more infections in six months or three episodes or more over a year .
Recurrent UTIs usually do not indicate a failure of the first treatment, though the same strain of germs may have reinfected you. If your last infection happened recently, your healthcare provider might ask for a urine culture to see if the drug was active. A UTI is considered a relapse of the same infection if the recurrence happens within two weeks of a previous episode .
Recommended Reading: Treats For Dogs With Urinary Problems
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
What Should I Do If My Antibiotic Doesnt Work For My Urinary Tract Infection
If your symptoms dont improve within a couple of days or get worse after starting an antibiotic you should contact your healthcare provider. A different antibiotic, a longer course of antibiotics or another treatment may be required. A physical exam or urine sample may be required.
When you have a UTI its important to:
- Only take an antibiotic that has been prescribed for you
- Take the antibiotic exactly as instructed by your healthcare provider and finish the full course of treatment even if you feel better
- Drink plenty of water and other fluids
- Urinate or pee regularly
Recommended Reading: Does Dehydration Cause Urinary Tract Infections
Adverse Effects Of Uti Antibiotics And Specific Patient Factors
If youve ever read the leaflet that comes with your UTI antibiotics, you will know there are many side effects that can occur with antibiotic use. Certain people react to certain antibiotics, and some antibiotics are much more likely to cause side effects than others.
Side Effects Of Common Antibiotics Used To Treat Uncomplicated UTI
| Antimicrobial Agent |
|---|
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections In Children
BRETT WHITE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Feb 15 83:409-415.
Acute urinary tract infections are relatively common in children, with 8 percent of girls and 2 percent of boys having at least one episode by seven years of age. The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli, accounting for approximately 85 percent of urinary tract infections in children. Renal parenchymal defects are present in 3 to 15 percent of children within one to two years of their first diagnosed urinary tract infection. Clinical signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection depend on the age of the child, but all febrile children two to 24 months of age with no obvious cause of infection should be evaluated for urinary tract infection . Evaluation of older children may depend on the clinical presentation and symptoms that point toward a urinary source . Increased rates of E. coli resistance have made amoxicillin a less acceptable choice for treatment, and studies have found higher cure rates with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Other treatment options include amoxicillin/clavulanate and cephalosporins. Prophylactic antibiotics do not reduce the risk of subsequent urinary tract infections, even in children with mild to moderate vesicoureteral reflux. Constipation should be avoided to help prevent urinary tract infections. Ultrasonography, cystography, and a renal cortical scan should be considered in children with urinary tract infections.
Recommended Reading: Is Urinary Tract Infection A Sexually Transmitted Disease
When To See A Doctor About A Uti
As mentioned, antibiotics are typically needed to treat a UTI, so it’s important to seek prompt care if you notice the signs of one.
Especially if:
- Your symptoms are severe or getting worse
- Your symptoms don’t improve after a few days
- You’re getting recurrent UTIs
“Early and effective UTI treatment helps ensure that the infection is dealt with while it’s easiest to treat and before it progresses to the kidneys,” says Dr. Kannady. “Even a mild kidney infection can come with fairly debilitating symptoms, including fever, vomiting and intense pain. These infections also require a longer course of antibiotics.”
And the more serious the kidney infection, the greater the risk of complications. They can range from hospitalization to even permanent kidney damage or a life-threatening bloodstream infection in some cases.
In men, UTIs also can spread to the prostate and cause prostatitis which also often requires a longer course of antibiotics to treat.
“By initiating antibiotics as soon as a UTI is identified, we can greatly reduce the risk of these more complex and serious outcomes,” says Dr. Kannady.
Lastly, if your UTI symptoms don’t improve after taking antibiotics for a few days, be sure to follow up with your doctor.
Antibiotics For More Complicated Urinary Tract Infections
A different antibiotic may be better for a more severe or stubborn UTI. This may include a UTI that:
- Spreads to the kidneys
- Is not responding to treatment
Additionally, there is a medical category of complicated UTIs that may require a different antibiotic regimen.
Complicated UTIs include UTIs that occur:
- In a person with a childhood history of UTIs
- In a person with a weakened immune system
- In a child or postmenopausal woman
- During pregnancy
- With a medical condition, like diabetes
- With an abnormality of the urinary tract, like a stone, obstruction, catheter or kidney deformity
In these cases, a urine culture may be done to make the choice of antibiotic. A urine culture grows the bacteria from the urine so that it may be identified under a microscope and tested for antibiotic sensitivity. The best antibiotic will be determined by the culture and sensitivity results.
No matter what antibiotic your health care provider prescribes, it is important to take the entire course as directed. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
If your antibiotic doesnt seem to be working and symptoms dont go away or come right back, let your health care provider know.
Don’t Miss: Pomegranate Juice For Urinary Tract Infection
The 5 Best Antibiotics For Uti Take This Not That
What are the best antibiotics for your urinary tract infection ? When you are sick with a UTI, you need a quick and effective treatment and this will often mean a course of antibiotics.
Sometimes you are so overwhelmed with UTI symptoms, that youll take any antibiotic you can get. However, it is important to be careful and informed about the different treatment options.
When You Need Themand When You Dont
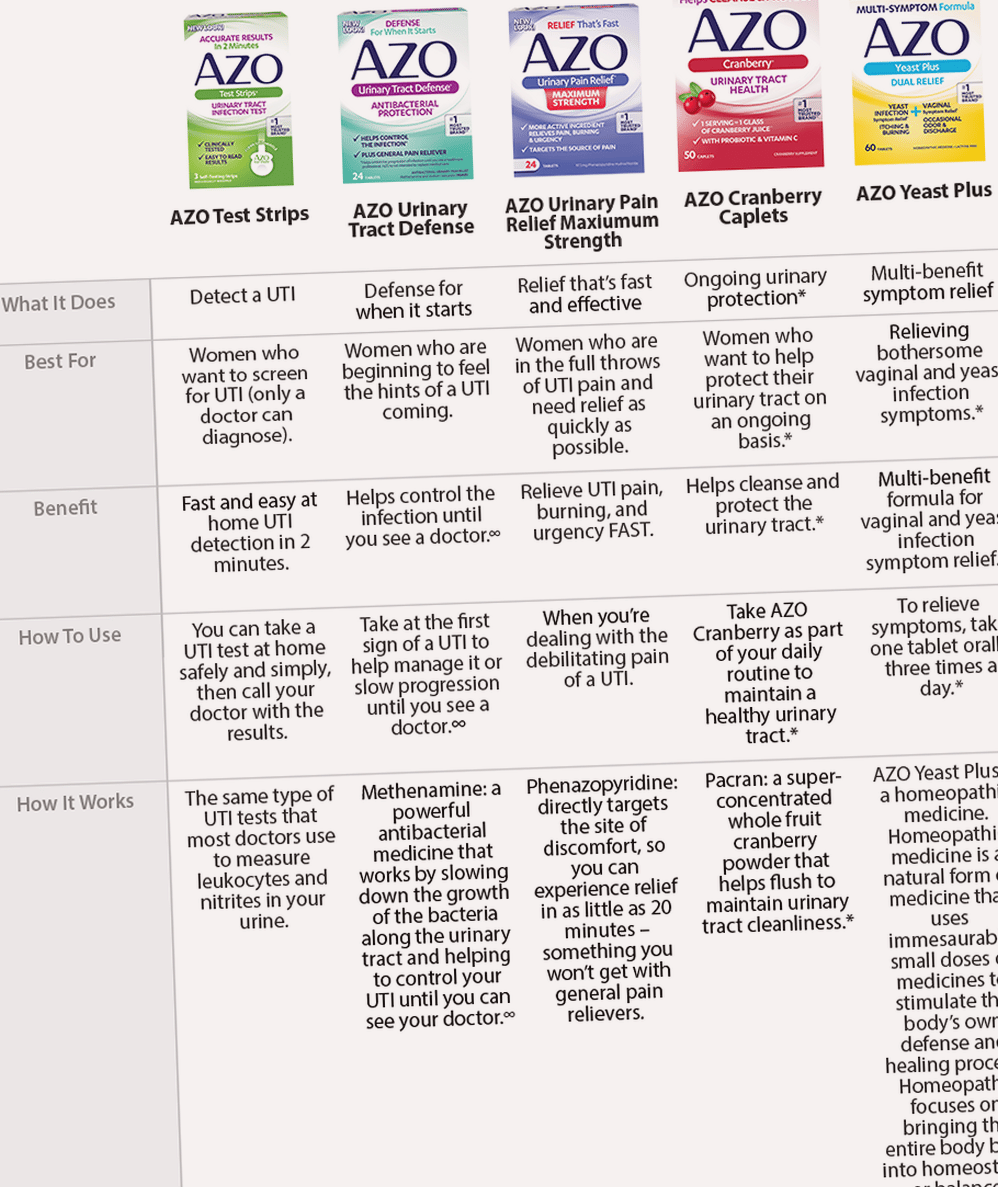
Antibiotics are medicines that can kill bacteria. Doctors often use antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections . The main symptoms of UTIs are:
- A burning feeling when you urinate.
- A strong urge to urinate often.
However, many older people get UTI treatment even though they do not have these symptoms. This can do more harm than good. Heres why:
Antibiotics usually dont help when there are no UTI symptoms.
Older people often have some bacteria in their urine. This does not mean they have a UTI. But doctors may find the bacteria in a routine test and give antibiotics anyway.
The antibiotic does not help these patients.
- It does not prevent UTIs.
- It does not help bladder control.
- It does not help memory problems or balance.
Most older people should not be tested or treated for a UTI unless they have UTI symptoms. And if you do have a UTI and get treated, you usually dont need another test to find out if you are cured. You should only get tested or treated if UTI symptoms come back.
Antibiotics have side effects.
Antibiotics can have side effects, such as fever, rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, tendon ruptures, and nerve damage.
Antibiotics can cause future problems.
Antibiotics can kill friendly germs in the body. This can lead to vaginal yeast infections. It can also lead to other infections, and severe diarrhea, hospitalization, and even death.
Antibiotics can be a waste of money.
When should older people take antibiotics for a UTI?
10/2013
Don’t Miss: Preventing Urinary Tract Infections After Menopause Without Antibiotics
Antibiotics Used For Uncomplicated Utis
If you are a healthy individual whose urinary tract is anatomically and functionally normal and you have no known heightened UTI susceptibility youve got whats dubbed an uncomplicated UTI, according to guidelines published in August 2019 in the Journal of Urology. For these individuals, antibiotics are considered the first-line of treatment.
The type of antibiotics you are prescribed and for how long is contingent on the type of bacteria detected in your urine, your current health status, and whether your UTI is uncomplicated or complicated. Depending on which antibiotic your doctor prescribes, women may need a single dose or up to a five-day course. For men, antibiotics are usually given for a slightly longer period of time, notes UpToDate.
Typically, if you are diagnosed with an uncomplicated UTI, one of the following will be prescribed as first-line treatment:
The following antibiotics are considered second-line treatments for UTI. They are generally chosen because of resistance patterns or allergy considerations:
RELATED: The Connection Between E. Coli and UTIs
Treating A Uti From Other Causes
In some patients, recurrent infections occur without a clearly identifiable cause and then patients may be put on prophylactic antibiotics which are a low, daily dose, to help prevent infection. This is rare as our Guidance® UTI Test more accurately identifies not only the more common bacteria, but also the uncommon bacteria that other available tests would not detect including fungi and viruses.
Also Check: How To Fix Stress Urinary Incontinence
Are There Any Over
Over-the-counter antibiotics for a UTI are not available. You should see your doctor to have your symptoms evaluated.
Your provider may recommend an OTC product called Uristat to numb your bladder and urethra to ease the burning pain during urination. Uristat can be bought without a prescription at the pharmacy. A similar phenazopyridine product called Pyridium is also available.
Take phenazopyridine for only 48 hours, and be aware it may cause your urine to turn a brown, orange or red color which may stain fabrics or contact lenses. It may be best to not wear contact lenses while being treated with phenazopyridine.
Phenazopyridine is not an antibiotic and will not cure a UTI.
See also: Ratings of Urinary Anti-Infectives
What Are The Warning Signs Of A Bladder Infection
Alice Sparrow
Read Also: Burning Sensation In Anus And Urinary Tract
Can Vitamins Or Supplements Help With A Uti
Probiotics, cranberries, vitamin C and D-mannose are all supplements that have been studied for their potential to prevent urinary tract infections. There is a plausible mechanism for each of them however, studies have not consistently shown marked benefit. More evidence is needed to make a final recommendation for or against their use or efficacy.
Cranberry Pills vs. Cranberry Juice for UTI
Cranberry extract pills are more likely to be helpful than cranberry juice, since cranberry pills do not have the sugar that juice contains. Cranberry can contribute to heartburn and gastrointestinal upset.
Read Also: How To Diagnose Viral Infection
How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infection: 8 Helpful Remedies
How to prevent urinary tract infection? Any infection in any part of your urinary system, bladder infections, kidney, urethra, and ureters can be termed a urinary tract infection. The most frequent form of urinary tract infection is a bladder infection urinary tract infections always involve the lower urinary tract.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and other components of the National Institutes of Health points out that bladder infection is more likely depending on age, health conditions, and habits. Womens infection normally happens when the bowel bacteria reach the bladder and urethra. In the case of men, bladder infection occurs when you have an enlarged prostate, and the normal urine flow is restricted.
A bladder infection is usually recognized after a physical examination and medical tests. If you have recurrent UTIs, then your doctor might recommend additional tests. Detection of white blood cells during urine culture also indicates urinary tract infection UTI. All this makes you wonder how to prevent urinary tract infection and stay healthy.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Water Retention
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms usually bacteria that enter the urethra and bladder, causing inflammation and infection. Though a UTI most commonly happens in the urethra and bladder, bacteria can also travel up the ureters and infect your kidneys.
More than 90% of bladder infection cases are caused by E. coli, a bacterium normally found in the intestines.
Can A Uti Go Away On Its Own

While most patients with a UTI will be prescribed antibiotics, the truth is, uncomplicated urinary tract infections are often self-limiting, meaning they can potentially run their course sans antibiotic treatment, noted a 2018 report in PLoS Medicine.
In fact, that same report found that more than one-half of the women studied experienced a UTI resolution without the use antibiotics. However, since kidney infections occurred in 7 out of 181 women using ibuprofen, the researchers concluded that, at this time, they cannot recommend ibuprofen alone as initial treatment to women with uncomplicated UTIs.
A better idea, for now: Simply wait until a positive urine culture comes back before treating with antibiotics.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Without Antibiotics
What Are The Symptoms Of A Uti
Symptoms of a UTI can differ depending on what part of the urinary tract is infected.
A bladder infection usually causes symptoms that include the following:
- Burning when urinating
- The feeling that you need to pee frequently, but when you go to the toilet very little urine comes out
- Pain in the pelvic area just above the pubic bone.
Bladder infections are usually considered a simple UTI and treatment is usually with antibiotics for three to five days. Symptoms usually resolve in a couple of days.
People with an infection of the urethra may experience symptoms similar to a bladder infection in addition to itching or irritation at the end of the urethra where the pee comes out.
Symptoms of a kidney infection are usually more widespread and more severe than those of a bladder infection and may include:
- Fever or chills
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Read Also: Antibiotic For H Pylori Bacteria
You May Like: How Do I Get Rid Of Urinary Retention