Urinary Tract Infections In Elderly Patients: How Best To Diagnose And Treat
DALE P. MURPHY, MDSeries Editorand MARYJO CLEVELAND, MD
How is urinary tract infection best managed in elderly persons?
Genitourinary infection is the second most common type of infection in community-dwelling adults older than 65 years it occurs only slightly less frequently than upper respiratory tract infection. 1 The presentation of UTI in elderly patients may differ significantly from that in younger ones. Chronic urinary symptoms are common in elderly persons, and the classic triad of UTI-frequency, urgency, and dysuria-occurs routinely in older persons without infection.2 As many as one third of community- dwelling elderly women are incontinent, which can further confuse the presentation. A high index of suspicion is needed first to entertain the diagnosis and then to pursue a thorough evaluation.A variety of risk factors predispose older persons to UTIs . In those between ages 50 and 70 years, the most common are urinary tract surgery, incontinence, cystocele, high postvoid residual volume, and low estrogen levels. Neurogenic conditions of the bladderparticularly those associated with diabetes and with anticholinergic medicationalsopredispose to UTI.3 In patients older than 70 years, risk factors include the use of multiple antibiotics, the presence of an indwelling catheter, and a history of UTI.
Private Duty Nursing Services
Sometimes, seniors need help with more than daily living tasks and require a licensed medical professional. Centric Healthcare offers the services of private duty nurses who attend to your or your loved ones medical needs in your home. Examples of our services that can assist in the treatment and prevention of UTI include assistance with catheter care, medication administration, and a trained eye that can help identify self-care needs and watch for classic and non-classic UTI symptoms.
Preventing Utis In Elderly Women
Also Check: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Side Effects
Complications Of Utis In Seniors
A UTI that goes untreated in anyone can lead to complications. However, elderly individuals have a higher risk of complications from urinary tract infections than any other category of individual.
- Kidney damage. A typical UTI can become more difficult to treat and tolerate if it moves into the kidneys. In addition, it can cause scarring on the kidneys, which leads to potential for hypertension and kidney failure.
- . Because kidney function can be reduced, some of the waste the kidneys would normally filter out and push from the body with urination may flow back into the bloodstream, leading to illness, which is difficult on the seniors immune system.
- . In the same process, the infection may enter the bloodstream, leading to blood poisoning that is a life threatening issue.
- Worsening dementia. While the symptoms of confusion that a UTI causes in the elderly may not directly lead to dementia, if the condition develops in a patient who already has dementia, a urinary tract infection could cause a quicker progression of dementia, leading to worsening overall health for the elderly patient.
Types Of Urinary Incontinence
There are different types of incontinence:
- Stress incontinence occurs when urine leaks as pressure is put on the bladder, such as during exercise, coughing, sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects. Its the most common type of bladder control problem in younger and middle-aged women. It also may begin later, around the time of menopause.
- Urge incontinence happens when people have a sudden need to urinate and cannot hold their urine long enough to get to the toilet. It may be a problem for people who have diabetes, Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease, multiple sclerosis, or stroke.
- Overflow incontinence happens when small amounts of urine leak from a bladder that is always full. A man can have trouble emptying his bladder if an enlarged prostate is blocking the urethra. Diabetes and spinal cord injuries can also cause this type of incontinence.
- Functional incontinence occurs in many older people who have normal bladder control. They just have a problem getting to the toilet because of arthritis or other disorders that make it hard to move quickly.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Canine Urinary S O
Institutionalized Older Adults & Catheterized Patients
Similar to other populations, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in nursing home residents requires the presence of genitourinary symptoms in the setting of a positive urine culture. In older adults who are cognitively intact, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI is relatively straightforward. However, nursing home residents often suffer from significant cognitive deficits, impairing their ability to communicate, and chronic genitourinary symptoms , which make the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in this group particularly challenging. Furthermore, when infected, nursing home residents are more likely to present with nonspecific symptoms, such as anorexia, confusion and a decline in functional status fever may be absent or diminished . In the setting of atypical symptoms, providers are often faced with the challenge of differentiating a symptomatic UTI from other infections or medical conditions. The high prevalence of bacteriuria plus pyuria in this population often leads to the diagnosis of UTI. Although bacteriuria plus pyuria is necessary for diagnosis of a laboratory-confirmed UTI, alone it is not sufficient for making the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI. To date, universally accepted criteria for diagnosing UTI in this population do not exist, making it difficult for providers to distinguish a symptomatic UTI from other conditions in the presence of new nonspecific symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Urinary Incontinence
Treatment Considerations In Older Adults
Dr N: She told me that her incontinence had definitely gotten worse in the last couple of weeks. I had noticed that another physician had sent a urine culture that had grown more than 105 CFU/mL of E coli that was sensitive to all antibiotics. Assuming that this was asymptomatic bacteriuria, it was not treated with antibiotics. A repeat urine culture again showed more than 105 CFU/mL of E coli, again it was pan sensitive. Given her symptoms, I treated her with a 7-day course of an antibiotic. However the antibiotics didnt really make a difference.
Studies have shown that treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria does eradicate bacteriuria. However, reinfection rates , adverse antimicrobial drug effects, and isolation of increasingly resistant organisms occur more commonly in the therapy vs nontherapy groups. No differences in genitourinary morbidity or mortality were observed between the 2 groups.
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are more than a painful medical condition. Left untreated, these infections can spread through the body. The leading cause of sepsis, an untreated UTI can ultimately result in death. For caregivers of elderly patients, learning how to recognize a UTI can be tricky as the symptoms are varied. Fortunately, there are three easy ways to avoid the onset of the infection to begin with.
You May Like: Cystex Urinary Pain Relief Side Effects
How Are Utis Treated In Older Adults
Antibiotics are the first choice of treatment for UTIs. Mild UTIs often clear up in only a few days with the right antibiotic.
However, depending on the persons age and health plus the severity of the infection, treatment for a UTI may take several weeks and a longer course of antibiotics. In more severe cases, older adults may need to be hospitalized to receive IV antibiotics.
If your loved one has symptoms of a UTI, its important to make an appointment with their doctor right away. If symptoms are severe, call the doctor immediately to determine whether a trip to the emergency room is necessary.
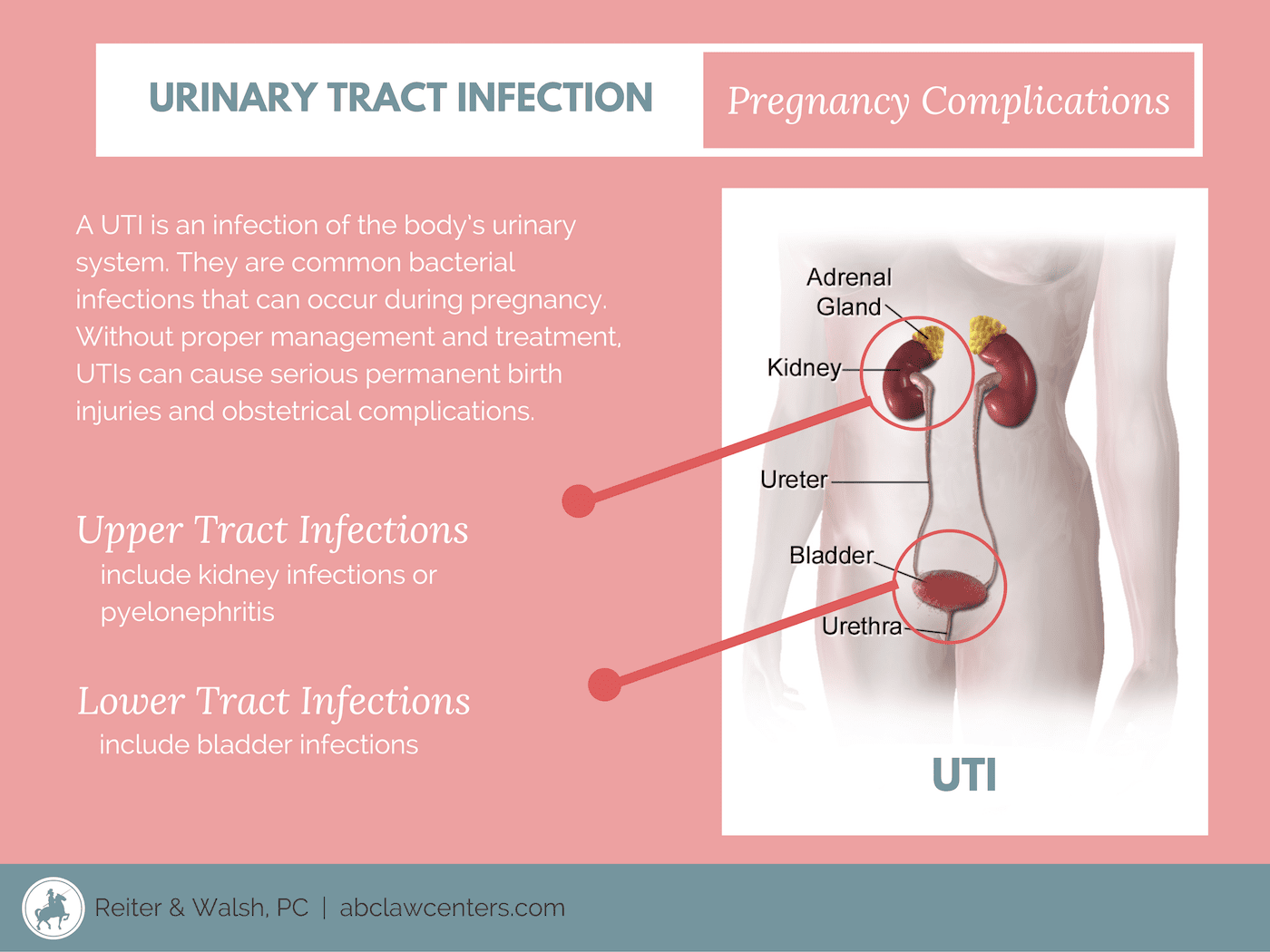
Urinary Tract Infection In The Elderly Patient: Epidemiology Presentation And Treatment
Michelle Blanda, MD, FACEP, Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine, Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine/Summa Health System, Akron, OH.
Peer Reviewer: Rita Kay Cydulka, MD, FACEP, Associate Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, OH.
Elderly patients represent a heterogeneous group, ranging from individuals in the community who are clinically well and fully functional to those who are impaired, non-communicative, immobile nursing home residents. A common cause for emergency presentation in this age group is infection.
Urinary tract infections with respiratory infections are the most common cause of bacteremia in the elderly.1-4 This is true for the community-dwelling elder, as well as for the institutionalized elderly patient. For the emergency department physician, this diagnosis often is a challenge. UTIs in the older population may present in an obscure manner. Patients in this age group tend to have multiple medical problems and can present with multiple somatic complaints. Conversely, physicians must be careful to not prematurely assign the diagnosis of UTI to a patient who actually has a different source of infection or another problem.
The Editor
Also Check: How Urinary Tract Infection Is Transmitted
What Are The Symptoms Of Utis In The Elderly
Like anyone with a UTI, older adults may experience typical physical symptoms. Yet they may not notice a mild infection right away. This is because chronic urinary problems common in seniors, such as urinary incontinence or frequency, may have similar symptoms to a UTI, masking an infection.
Common symptoms of a UTI include:
- Burning, painful sensation with urination
- Frequent, intense urge to urinate even when theres little urine to pass
- A feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied
- Blood in the urine
Symptoms of a more severe UTI may include:
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain in the lower abdomen or back
When accompanied by other common UTI symptoms, these changes in behavior can also be key signs of a UTI in elderly adults:
- Confusion or delirium
- Inability to perform common daily tasks, such as getting dressed or feeding themselves
Uti Diagnosis In The Geriatric Population
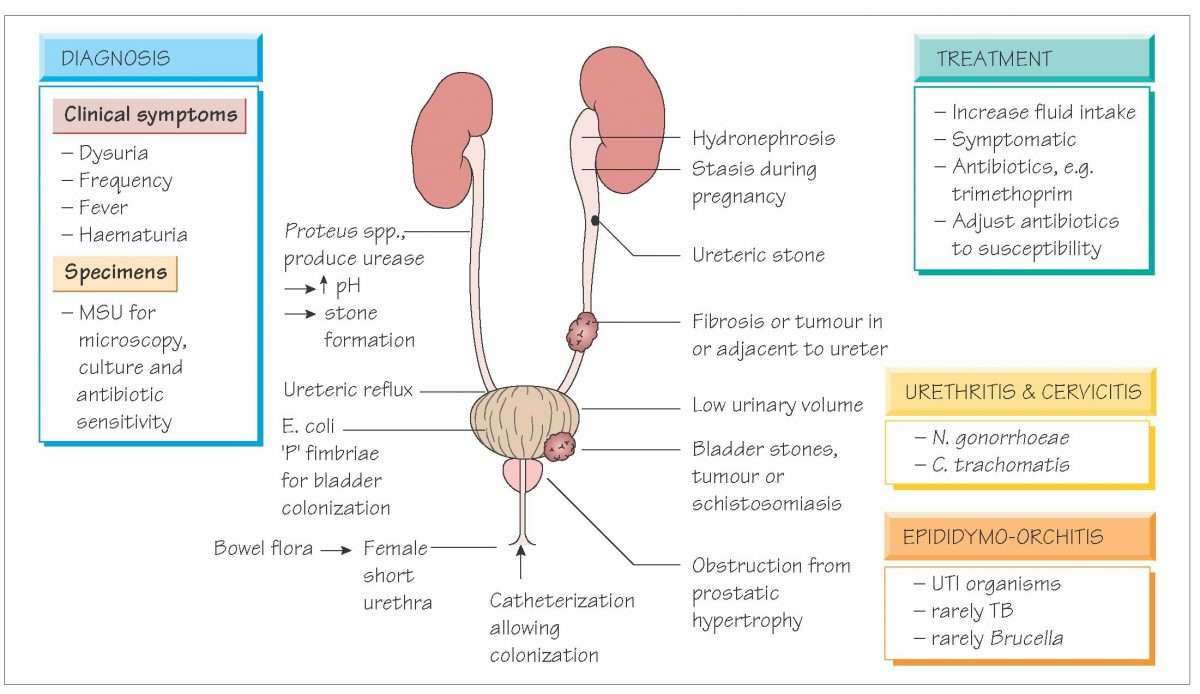
Symptoms in the elderly may differ from those in the general population. General criteria for diagnosing a UTI are presented in TABLES 2 and3.34-37 Also important for diagnosis is a history of recent or multiple sexual contacts or ethanol or drug abuse resulting in syncope and poor hygiene.7,14
Physical Characteristics: A patient with clinically significant UTI appears ill and in distress. Physical findings, while variable, generally include fever . Abdominal examination usually demonstrates tenderness over the suprapubic area, usually without rebound tenderness. Further evaluation may reveal CVA tenderness, which may be considered a hallmark of pyelonephritis or stones. Both males and females may present with urethral discharge. Females may demonstrate evidence of organ prolapse upon gynecologic examination, while in males examination may reveal an enlarged, tender prostate with discharge upon massage and manipulation.37
Laboratory Findings: Laboratory findings in clinically significant UTI will vary depending on the area of the system that is involved. Typically, urinalysis shows proteinuria and red blood cells , and tests are nitrite positive . White blood cells are present, but indicate clinical infection only in excess of 10 per high-power field.31 CBC may show leukocytosis, often with a larger-than-normal number of immature WBCs present .38
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of A Severe Urinary Tract Infection
Empty Your Bladder After Sex
Following sex, be sure to use the bathroom and empty your bladder as soon as possible. You should also drink extra water to flush any bacteria out of the urinary tract.
If you suspect you have a urinary tract infection and need relief from your symptoms, schedule a diagnostic evaluation at Primary Care & Walk-In Medical Clinic online, , or visit the clinic in person.
You Might Also Enjoy
Treating Utis In The Elderly
If you think your loved one might have a urinary tract infection, see a doctor right away to avoid further complications. An urgent care clinic is a viable alternative if you cannot get an appointment with their primary care physician soon enough. Urinalysis and/or a urine culture are typically required to diagnose a UTI, determine what kind of bacteria are present in the urine and select the most appropriate antibiotic for treatment. If caught early on, a course of antibiotics typically clears the infection in no time.
Keep in mind that older individuals are also prone to a related condition called asymptomatic bacteriuria, which is characterized by the presence of bacteria in the urine but the absence of any signs or symptoms of a urinary tract infection. The estimated incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria is 15 percent or greater in women and men between 65 and 80 years of age and continues to climb after age 80 to as high as 40 to 50 percent of long-term care residents.
Research shows that most patients with asymptomatic bacteriuria do not develop symptomatic UTIs, therefore antibiotic treatment is not beneficial. In fact, antibiotic use can result in adverse side effects, such as Clostridium difficileinfection, and contribute to the development of resistant bacteria. A seniors physician will consider their symptoms and test results to differentiate between a UTI and asymptomatic bacteriuria and determine whether treatment is necessary.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotic Medicine
Urgent Advice: Ask For An Urgent Gp Appointment Or Get Help From Nhs 111 If:
You think you, your child or someone you care for may have a urinary tract infection and:
- a very high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
- are confused, drowsy or have difficulty speaking
- have not been for a pee all day
- have pain in the lower tummy or in the back, just under the ribs
- can see blood in their pee
These symptoms could mean you have a kidney infection, which can be serious if it’s not treated as it could cause .
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
Diagnosing A Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults
Vague, uncommon symptoms such as confusion make UTIs challenging to diagnose in many older adults. Once your doctor suspects a UTI, its easily confirmed with a simple urinalysis.
Your doctor may perform a urine culture to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection and the best antibiotic to treat it.
There are home UTI tests that check urine for nitrates and leukocytes. Both are often present in UTIs. Because bacteria are often in the urine of older adults to some degree, these tests arent always accurate. Call your doctor if you take a home test and get a positive result.
Antibiotics are the treatment of choice for UTIs in older adults and younger people. Your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin and nitrofurantoin .
More severe infections may require a broad-spectrum antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin .
You should start antibiotics as soon as possible and take them for the entire duration of treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Stopping treatment early, even if symptoms resolve, increases the risks of recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic overuse also increases your risk for antibiotic resistance. For this reason, your doctor will likely prescribe the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 7 days, and your infection should clear up in a few days.
Its important to drink plenty of water during treatment to help flush out the remaining bacteria.
Also Check: What Are The Different Types Of Urinary Incontinence
How Is A Uti Treated
The treatment for your uti will depend on what type of infection it is. If it is a bacterial infection, it will be treated with an antibiotic. If it is determined that it is a fungal infection, it will be treated with a different medication which targets fungal infections.
The first step your doctor will take will be to obtain a urine sample this urine sample will determine if you have an infection. If so, the urine is then also cultured to determine which antibiotic it is sensitive to, in other words, which antibiotic will effectively treat and kill the bacteria. This will take a few days because the bacteria has to grow in a petri dish. See, there really are reasons some of these tests take time!
In the meantime, your physician will immediately start you on a broad spectrum antibiotic this is an antibiotic that effectively treats many types of bacteria. If when the tests come back it is determined that you need a different antibiotic, your doctor will notify you and prescribe a different antibiotic which will treat your specific infection.
Sometimes the pain of a urinary tract infection is so great you may require a medication to alleviate the pain. Your doctor can prescribe a special medication which targets the pain associated with UTIs.
Follow-up is essential to determine if the infection has cleared, so if your physician asks you to come back, please do so!
Prevention Of Utis In The Elderly
Its important to address the issue in advance in the attempt to prevent UTIs in seniors. Several urinary tract infection prevention methods exist, including:
- Reminding the individual to drink plenty of water , as proper hydration keeps the urinary tract in good health
- Avoiding consumption of alcohol and caffeine as much as possible
- Encouraging the senior to use the restroom frequently, at least every three hours
- Promptly caring for soiled materials due to incontinence
- Wiping from front to back when using the restroom
- Promoting good hygiene, such as daily showers, and avoiding baths and special care should be taken if the senior citizen uses a urinary catheter
You May Like: Discomfort In Urinary Tract Male