Can I Prevent Urine Infections
Unfortunately, there are few proven ways to prevent urine infections. No evidence has been found for traditional advice given, such as drinking cranberry juice or the way you wipe yourself.
There are some measures which may help in some cases:
- It makes sense to avoid constipation, by eating plenty of fibre and drinking enough fluid.
- Older women with atrophic vaginitis may wish to consider hormone replacement creams or pessaries. These have been shown to help prevent urine infections.
- If there is an underlying medical problem, treatment for this may stop urine infections occurring.
- For some people with repeated urine infections, a preventative low dose of antibiotic taken continuously may be prescribed.
What Causes Utis In The Elderly
Anything that introduces bacteria into the urinary tract or impedes the flow of urine and causes urine to stay in the bladder is very likely to cause a UTI.
Eighty five percent of all UTI infections are caused by Escherichia coli or E. coli bacteria. Several other types of bacteria make up the other fifteen percent, but E.coli is by far the most prominent, and it can make its way into the urinary tract several different ways.
E. coli is found naturally where digestion occurs in the gastrointestinal tract, so it can sneak into the urinary tract. This commonly happens because the end of the gastrointestinal tract is the anus, and the beginning of the urinary tract is the urethra. The anus and the urethra are close to one another, especially on the female body.
Due to the proximity of the entry and exit of the above two pathways, poor hygiene can cause UTIs. Back-to-front wiping after a bowel movement can transfer bacteria into the urethra. Wearing soiled underwear or disposable undergarments too long can also introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. Bacteria in both cases is an infectious traveler that multiplies.
Myths And Facts Regarding Utis In Older Adults
Myth #1: Confusion alone indicates a UTI.
Fact: Older adults have a tendency to experience delirium and confusion, especially if they have any form of cognitive impairment, depression, malnutrition or functional dependency. Unfortunately, its quite common at nursing facilities to check a urine sample at the first sign of confusion, explains Dr. Lathia. However, delirium could be caused by a variety of factors the most common of which is dehydration.
Myth #2: It doesnt hurt to check a urine sample.
Fact: Problems begin when a doctor checks a urine sample without the patient reporting any other UTI-related symptoms. Many older adults have some bacteria in their urine. Quite often, this indicates a condition known as asymptomatic bacteriuria, which is characterized by an elevated level of urinary bacteria that doesnt cause any symptoms, says Dr. Lathia. According to Aging Health, approximately 6 to 16 percent of women over age 65 and nearly 20 percent of women over age 80 have asymptomatic bacteriuria. For older women living in nursing facilities, the incidence rate ranges from 25 to 50 percent.
Detecting an innocuous level of urinary bacteria may cause doctors to start an antibiotic without confirming the presence of multiple other UTI signs or symptoms, explains Dr. Lathia. This hasty treatment can lead to problems in the future.
Myth #3: Bacteria in the urine always requires medication.
Read Also: How To Treat Urinary Incontinence Naturally
Seniors Dont Need To Be Routinely Screened For Utis
Older adults often provide urine samples during their annual wellness exams. These dont need to be screened for a UTI if a person doesnt have symptoms such as fever, urinary pain and/or urinary frequency, says Fishburne.
Many older adults including up to 16 percent of all women over age 65 and almost 20 percent of women over age 80 have bacteria in their urine with no signs of a UTI at all. If theres no infection, an antibiotic wont do anything and can cause other adverse effects, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or vaginal yeast infections. There is also the possibility it can encourage the growth of drug-resistant bacteria.
Diagnosing A Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults

Vague, uncommon symptoms such as confusion make UTIs challenging to diagnose in many older adults. Once your doctor suspects a UTI, its easily confirmed with a simple urinalysis.
Your doctor may perform a urine culture to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection and the best antibiotic to treat it.
There are home UTI tests that check urine for nitrates and leukocytes. Both are often present in UTIs. Because bacteria are often in the urine of older adults to some degree, these tests arent always accurate. Call your doctor if you take a home test and get a positive result.
Antibiotics are the treatment of choice for UTIs in older adults and younger people. Your doctor may prescribe amoxicillin and nitrofurantoin .
More severe infections may require a broad-spectrum antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin .
You should start antibiotics as soon as possible and take them for the entire duration of treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Stopping treatment early, even if symptoms resolve, increases the risks of recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic overuse also increases your risk for antibiotic resistance. For this reason, your doctor will likely prescribe the shortest treatment course possible. Treatment typically lasts no more than 7 days, and your infection should clear up in a few days.
Its important to drink plenty of water during treatment to help flush out the remaining bacteria.
Also Check: Guys Get Urinary Tract Infections
Epidemiology Of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is rare in younger people, but over the age of 75 years, it is found in 7â10% of men and 17â20% of women. A study among nursing home residents reported up to 25%-50% had ASB at any given time. Prevalence of ASB is 100% in patients with long-term indwelling catheters and about 3%â5% with short-term use.
How Common Are Utis In The Elderly
According to a recent review in the journal Drugs in Context, UTIs are more common in women at any age because they have a shorter urethra, which is the tube that carries urine out of the bladder. This allows bacteria from the rectum to move up the urethra and infect the bladder. The majority if UTIs are caused by bacteria called E. coli. E.coli do not cause infections in the colon or rectum, but they do in other parts of the body like the bladder or kidneys.
UTIs increase with age in both men and women. After age 65, about 10 percent of women will experience a UTI, by age 85 almost 30 percent will get a UTI. For both older men and women, the risk of infection is much higher if they are living in a nursing home or a long-term care facility.
Recommended Reading: How To Take Azo Urinary Tract Defense
Epidemiology Risk Factors And Pathophysiology Of Uti
In the United States of America, UTIs cause 15.5% of hospitalisations and 6.2% of deaths attributable to an infectious disease in patients over the age of 65 years. Although a weak association, increasing age is a risk factor for UTI. Ageing disrupts acquired immunity due to T-cell dysfunction and blunted cytokine-mediated inflammatory response., Normal defence mechanisms include the ability to void completely, acidification of urine from organic acids, and immunoglobulin production. Women are especially prone to UTIs because of their shorter urethral length and frequent vaginal colonisation. Older women could also be more affected due to loss of pelvic floor muscle tone and associated prolapse. Other frequently seen risk factors are anatomical abnormalities, sexual activity at any age, anal intercourse, diabetes, urinary incontinence, and physical limitations, Other risk factors for UTI in older adults are summarised in Table .
| Risk factor |
|---|
|
How To Prevent Utis In Seniors
Older adults can help prevent UTIs by drinking plenty of fluids to flush the bacteria from their systems, Forciea says. She recommends older adults drink four to six 8-ounce glasses of water a day. Forciea further notes that drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry tablets also can make urine less inviting for bacteria.
Use these strategies to help prevent UTIs in elderly women:
- Urinating promptly after the urge arises
- Wiping front to back
- Emptying the bladder shortly after sex
- Taking showers instead of baths
If your loved one has frequent UTIs or other challenges that require help with daily tasks, consider talking to one of our Senior Living Advisors about home care or senior living options that can improve their quality of life.
Read Also: How To Relieve Urinary Tract Pain
Here Are A Few Common Risk Factors Of Urinary Infection:
How Can Utis Be Prevented
Personal hygiene and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce seniors risk of developing a UTI. They include:
- Drinking plenty of fluids
- Limiting or avoiding caffeine and alcohol altogether.
- Not using feminine hygiene products
- Thoroughly wiping after toileting
- Wearing, and changing daily, breathable cotton underwear
- It is better to set timers/reminders for seniors who are memory impaired and try and use the toilet instead of an adult brief.
Read Also: Urinary Incontinence Treatment For Elderly
How Does A Uti Affect The Brain
You may be wondering how an infection in the urinary tract affects the brain? Scientists havent found the exact link between UTIs and delirium, but heres what experts believe is happening.
Any time we have an infection, our immune system kicks into gear to fight it off. During this process, our body releases chemicals that cause inflammation. These chemicals can also lead to many of the symptoms we feel, like fatigue or fevers. In older adults, the brain is more affected by the inflammation and the stress hormones that the body produces to fight the infection. The effects of this inflammation and stress on the brain are what show up as delirium.
So, why dont young, healthy adults get delirium with infections like UTIs? This has to do with the blood-brain barrier, a special protection between the brain and the rest of the body. The blood-brain barrier keeps bacteria, viruses, and fungi that threaten the health of the brain from reaching it. This barrier isnt as strong in older adults, so the inflammation from infection has a higher chance of affecting their brains.
However, not all older adults with UTI get delirium, and not all people with delirium have a UTI.
Why Antibiotics Aren’t Always Prescribed
For younger patients, if bacteria are present in a urine sample, the first treatment is generally antibiotics. However, when it comes to elderly patients, the diagnosis and treatment aren’t always as clear-cut. That’s partly because many elderly patients have bacteria in their urine even if they don’t have a UTI. The scientific name for this is asymptomatic bacteriuria . This presence of bacteria becomes increasingly common with age.
Because ASB doesn’t cause any physical problems, an antibiotic isn’t usually considered to be necessary. That means a physician might not always prescribe antibiotics after a positive urine test.
Physicians are also reluctant to prescribe antibiotics if a patient doesn’t have clear symptoms because of the medical community’s wish to minimize unnecessary antibiotics prescriptions. Overuse of antibiotics has led to an increase in infections that are resistant to antibiotics, so it’s important not to overprescribe them.
How do physicians know whether an elderly patient has a UTI and when to prescribe antibiotics? They typically consider other signs of a UTI, such as frequent or burning urination. But, as discussed above, older patients don’t always have these “typical” UTI symptoms. Elderly dementia patients, in particular, may only have behavioral changes.
Also Check: Treat Urinary Tract Infection Over The Counter
What Are The Symptoms
It may be hard to figure out if a loved one has a UTI or not, because they may not have the classic symptoms. This is because urinary problems, such as incontinence, may have similar symptoms related to another issue, making it more difficult to recognize.
The classic, or common, symptoms of a UTI can include:
- Burning while urinating
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- A feeling the bladder is not completely empty
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
More severe symptoms of a complicated UTI can include:
Tips For Preventing Utis In The Elderly
The following lifestyle and personal hygiene changes can significantly reduce a seniors risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Drink cranberry juice or use cranberry tablets, but NOT if the elder has a personal or family history of kidney stones.
- Avoid or limit caffeine and alcohol, which irritate the bladder.
- Do not douche or use other feminine hygiene products.
- After toileting, always wipe from front to back .
- If incontinence is not an issue, wear breathable cotton underwear and change them at least once a day.
- Change soiled incontinence briefs promptly and frequently.
- Keep the genital area clean and dry.
- Set reminders/timers for seniors who are memory impaired to try to use the bathroom instead of an adult brief.
Read Also: A Urinary Tract Infection Uti
Other Symptoms Of Utis
If the person has a sudden and unexplained change in their behaviour, such as increased confusion, agitation, or withdrawal, this may be because of a UTI.
These pages explain what a UTI is, the different types of UTIs, their symptoms and treatments, and gives tips on how they may be prevented.
Preventing Utis In The Elderly
Here are steps you can take to protect yourself or your loved ones from UTIs.
- Stay hydrated.
- Use the bathroom when needed . Encourage a bathroom break every two to three hours.
- Practice good hygiene of the genital area and change adult incontinence briefs frequently.
- Be aware of unusual behavioral changes.
- Get routine health exams, especially if you have an existing condition like diabetes or enlarged prostate.
If you notice a sudden change in your loved ones behavior and suspect a UTI, call your health care provider right away.
You May Like: Azo Urinary Tract Pain Relief
Summary Of The Evidence
Following this review, it is evident that all of the studies which have explored the association between suspected UTI and confusion are methodologically flawed, due to poor case definition for UTI or confusion, or inadequate control of confounding factors introducing significant bias. Subsequently, no accurate conclusions about the association between UTI and confusion can be drawn. One study of acceptable quality shows an association between confusion and bacteriuria. However, this sample of patients in whom they tested bacteriuria and pyuria were patients already suspected of having a UTI, introducing a bias into their calculation . In summary, none of the 22 publications had sufficient methodological quality to enable valid conclusions.
Risk Factors For Urinary Tract Infection In Older Adults
Certain factors may increase the risk of UTIs in older people.
Conditions common in older adults may lead to urinary retention or neurogenic bladder. This increases the risk of UTIs. These conditions include Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease, and diabetes.
They often require people to wear incontinence briefs. If the briefs arent changed regularly, an infection may occur.
Several other things put older adults at risk for developing a UTI:
- a history of UTIs
Recommended Reading: How Does A Urinary Tract Infection Feel
Urinary Tract Infections In The Elderly
Anyone who has ever had urinary tract infections knows what an inconvenience they are. But, theyre more than just that for seniors because they often lead to serious health problems.
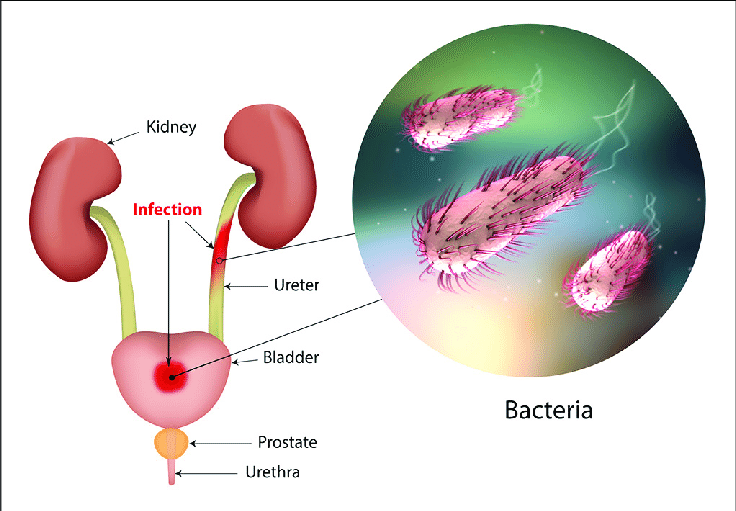
A UTI occurs when bacteria in the bladder, urethra, or kidneys multiply in the urine. If left untreated, a UTI can lead to chronic kidney infections, so often damaging the kidneys permanently and potentially leading to kidney failure.
UTIs are also a leading cause of sepsis, which is a potentially life-threatening response to an infection.
Complications Of Uti In The Elderly: What You Need To Know
Urinary Tract Infection is one of the most common infections affecting older adults. When promptly and properly treated, UTI is easily managed and rarely develops complications. But, when left untreated, UTI can lead to serious health consequences which can include permanent kidney damage. In rare instances, an infection can enter the bloodstream through the kidneys and lead to a life-threatening condition called . Therefore, early recognition of symptoms, testing, diagnosis, and treatment of UTI is important.
Also Check: How To Stop Urinary Incontinence