How Do Utis Affect People With Dementia
If someone with dementia develops a UTI, they may quickly become more confused or agitated, or you might notice a sudden change in their behaviour. This sudden confusion is also known as delirium.
The person with dementia may not be able to communicate how they feel, so if you notice a sudden or drastic change in them, seek medical advice. Infections can speed up the progression of dementia, so it’s important to get help quickly if you suspect someone has a UTI.
How Utis Are Diagnosed
In most cases, if you think you have a UTI, you should visit a health care provider and give a urine sample for testing. A urinalysis is a test that looks for white blood cells, red blood cells, bacteria, and or other chemicals such as nitrites in your urine. A proper urinalysis can pinpoint an infection and a urine culture can help your health care provider choose the best antibiotic for treatment. It is vital to get a urinalysis and culture performed to make sure you have an infection and require care. Use of antibiotics when not needed, can be tricky, and can lead to greater rates of bacterial antibiotic resistance.
It should be noted that some individuals get a urinalysis result that shows bacteria, but the individuals are not having any symptoms of a UTI. This event is common in older adults. If the individual has bacteria in their urine, but has no symptoms, treatment is not right. Treatment should be given to individuls who have bacteria and associated UTI symptoms.
In closing, it should be noted that studies on cranberry juice and linked supplements are mixed. Some studies show that cranberry supplements can be helpful and other studies show that they don’t help stop UTIs before they happen. Be sure to read about the pros and cons of cranberry products, and decide if they’re right for you. For now, practice these tips to lower your risk of getting a UTI.
Role Of Urinary Testing In Diagnosing Symptomatic Utis In Older Adults
The utility of urinary dipstick testing, urinalysis, and urine culture is challenging in the older adult because of the high prevalence of bacteriuria and pyuria that may not be clinically important. As in the case of Mrs M, all urinary studies to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, pyuria, and bacteriuria over a 2-year period were positive.
The urinary dipstick, although easy and convenient, has variable test characteristics. Sensitivity and specificity for urinary dipstick testing to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or both vary in older adults by the age of study participants, clinical suspicion of UTI, and laboratory definition for UTI used . The sensitivity and specificity for a positive dipstick test in older patients with was 82% and 71% , respectively. Other studies of elderly patients showed the negative predictive value for dipstick testing ranges from 92% to 100%., Urinary dipstick analysis should be performed in the out-patient setting primarily to rule out and not to establish a diagnosis of UTI. In a patient with a low pretest probability of UTI, if the dipstick is negative for leukocyte esterase and nitrites, it excludes the presence of infection and mitigates the need to obtain urinalysis and urine culture . High false-positive rates limit dipstick testing effectiveness. Further urinary studies are warranted for patients with a high pretest probability of UTI.
Read Also: Diabetes And Urinary Tract Infections
Why Do The Elderly Get Urinary Tract Infections
By | Submitted On January 18, 2009
Urinary tract infection is the most common infection in elderly people and is the most common cause of bacteremia. The pervasiveness of bacteremia is very much related with age.
Factors that mystify the diagnosis of urinary tract infection in older people include existing underlying pathological condition, drug regimen or drug exposure, manifold appearances of symptoms, and the widespread existence of urinary symptoms not related to UTI.
Those who are concerned in the care of the elderly people with urinary tract infection must consider predisposing factors, safe and effective preventions, optimal assessment approaches, and therapeutic antimicrobial therapies at this time on hand for safe and effective use in the midst of this tolerant populace.
Studies in different countries have shown that urinary tract infection among the elderly is out of control, both in their own home and in institutional care centers are at risk for this pathologic condition.
More than a few learning have found out that many nursing home inhabitants have an insufficient intake of calories, proteins, vitamins and minerals.
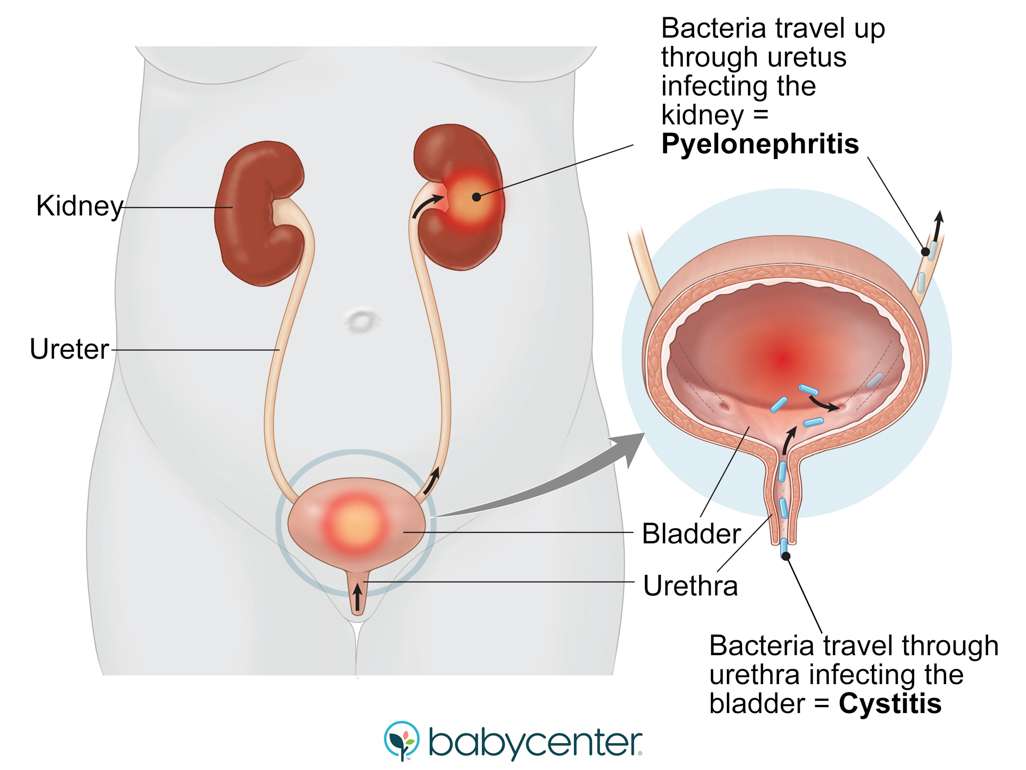
That thereby lead to conditions like urinary tract infection, including cystitis, pyelonephritis and catheter-related infections are amongst the most ordinary nursing home acquired infections.
Late detection of urinary tract infection in the elderly is highly related to the often asymptomatic presence of bacteriuria.
What Is The Treatment For A Urine Infection In Older People
- A course of anantibiotic medicine will usually clear the infection quickly. You should see a doctor if your symptoms are not gone, or nearly gone, after a few days.
- Paracetamol or ibuprofen will usually ease any pain, discomfort, or high temperature .
- An underlying cause such as an enlarged prostate gland or constipation may be found and need treatment.
Note: if you have an infection of your bladder then having plenty to drink is traditional advice to flush out the bladder. However, there is no proof that this is helpful when you have cystitis. Some doctors feel that it does not help and that drinking lots may just cause more toilet trips, giving you more unnecessary pain. Therefore, it is difficult to give confident advice on whether to drink lots or just to drink normally when you have mild symptoms of cystitis. However, if you have a high temperature and/or feel unwell, having plenty to drink helps to prevent having a lack of fluid in your body .
Read Also: How To Get Relief From A Urinary Tract Infection
Role Of Urine Dipstick Testing
Dipstick testing of urine is often used as a fast method for ruling out UTI as the cause of symptoms. This test detects the presence of leucocyte esterase and nitrites . However, Gram-positive bacteria and other organisms such as Enterococci and Pseudomonas species account for larger proportion of UTI in older adults and these microorganisms do not reduce urinary nitrates to nitrites. This may mean that urine dipstick nitrite test will not test positive for these organisms.
Results from a study conducted by Juthani-Mehta et al. in nursing home residents suggests that a dipstick test result that is negative for both leukocyte esterase and nitrite can effectively exclude the diagnosis of UTI. This study, however, observed a positive predictive value of only 45% suggesting that dipstick test is not useful for identifying patients who meet laboratory criteria for UTI. Another study conducted amongst nursing home residents with asymptomatic bacteriuria also observed a very high negative predictive value of urine dipstick testing.
Cortes-Penfield et al. provide a great analogy of urine dipstick testing interpretation. They note that the clinical utility of the urinalysis for diagnosing UTI is similar to that of the D-dimer for the diagnosis of a pulmonary embolism a negative result is of great value for ruling out embolism in patients with all but the highest pre-test probabilities of disease, while a positive result is not sufficient to establish the diagnosis.
Urine Infection In Older People
In this series
If you have a urine infection, you have germs in your bladder, kidneys or the tubes of your urinary system. Urine infections are more common in older people, and there is more likely to be an underlying cause.
In this article
Urine Infection in Older People
In this article
Read Also: Can Smoking Weed Cause Urinary Problems
How Long Does Uti Induced Dementia Last
You may notice some of the following symptoms start to display in your loved one, signaling a change in mental state. The most important thing to remember about the link between UTI and dementia is that the behavior change is significant and happens fairly quickly, usually over a period of one to two days.
Institutionalized Older Adults & Catheterized Patients
Similar to other populations, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in nursing home residents requires the presence of genitourinary symptoms in the setting of a positive urine culture. In older adults who are cognitively intact, the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI is relatively straightforward. However, nursing home residents often suffer from significant cognitive deficits, impairing their ability to communicate, and chronic genitourinary symptoms , which make the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI in this group particularly challenging. Furthermore, when infected, nursing home residents are more likely to present with nonspecific symptoms, such as anorexia, confusion and a decline in functional status fever may be absent or diminished . In the setting of atypical symptoms, providers are often faced with the challenge of differentiating a symptomatic UTI from other infections or medical conditions. The high prevalence of bacteriuria plus pyuria in this population often leads to the diagnosis of UTI. Although bacteriuria plus pyuria is necessary for diagnosis of a laboratory-confirmed UTI, alone it is not sufficient for making the diagnosis of symptomatic UTI. To date, universally accepted criteria for diagnosing UTI in this population do not exist, making it difficult for providers to distinguish a symptomatic UTI from other conditions in the presence of new nonspecific symptoms.
Also Check: Urinary Incontinence Devices For Women
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
A major strength of this study is the use of individual patient level data for adults older than 65 years extracted from a large nationwide general practice records database and linked to hospital and mortality records. This provided the opportunity to track the care pathways of a vulnerable population with a diagnosis of UTI in the community with a 60 day follow-up. The linkage with mortality data from the Office for National Statistics minimised possible bias in the risk estimates of all cause mortality among older adults treated in a routine care setting.
The large sample size of about 160000 patients with more than 300000 distinct UTI episodes substantially increased the power of the analyses, especially for rare severe adverse events in older adults . As the base population is representative of the English general population, our results are generalisable to the entire English population of elderly patients.
The main limitations of our study are common to observational studies using routinely collected electronic health record data, and include unmeasured and residual confounders, missing data and potential biases, such as confounding by indication, misclassification biases, or inconsistencies in coding within and between practices and over time.
Why Do Utis Return Despite Treatment
There are about a half-dozen oral antibiotics that treat UTIs. Sometimes a doctor will prescribe one drug, then switch to another after a urine culture identifies which bacteria is at work. Adjusting the medication can take time, and recurrent infections may occur in the meantime.
Sometimes a person starts to feel better and decides to stops taking the antibiotic contrary to the doctors instructions and another infection soon follows. Its never a good idea to stop taking antibiotics before your dosage is complete.
But even people who take medication as the doctor prescribes may get recurrent infections, Dr. Vasavada says.
If youre a younger woman who is sexually active, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic to take before and after sexual activity. For post-menopausal women, a vaginal estrogen cream may help reduce infections.
If infections persist, your doctor may test for other health problems in the kidney, bladder or other parts of the urinary system.
Recommended Reading: Tea Tree Oil Urinary Tract Infection
Ways To Prevent A Uti
Antibiotics and natural medicines are available to help clear up UTIs, but there are preventative measures you can take to help ensure your body is able to stave off infections that tend to occur through the normal course of life. Read on to see three ways weve discovered through careful research to help prevent urinary tract infections in older women.
Future Research In Laboratory Confirmation
There is emerging interest in the use of biomarkers, particularly in nursing home settings. Interleukins 8 and 6, lactoferrin and procalcitonin are used in children and postoperative young adults to identify UTI. However, the evidence supporting accuracy of these markers is moderate and further research in older adults is needed.
In 2018, Public Health England published a guideline on âDiagnosis of urinary tract infections: quick reference tool for primary care for consultation and local adaptationâ. It provides a practical and empirical approach to diagnose UTI, minimise antibiotic misuse and reduce emerging resistance.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Signs Of A Urinary Tract Infection
What Are The Symptoms Of Utis In The Elderly
Like anyone with a UTI, older adults may experience typical physical symptoms. Yet they may not notice a mild infection right away. This is because chronic urinary problems common in seniors, such as urinary incontinence or frequency, may have similar symptoms to a UTI, masking an infection.
Common symptoms of a UTI include:
- Burning, painful sensation with urination
- Frequent, intense urge to urinate even when theres little urine to pass
- A feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied
- Blood in the urine
Symptoms of a more severe UTI may include:
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain in the lower abdomen or back
When accompanied by other common UTI symptoms, these changes in behavior can also be key signs of a UTI in elderly adults:
- Confusion or delirium
- Inability to perform common daily tasks, such as getting dressed or feeding themselves
Risk Factors For Utis In The Elderly
The elderly are sometimes already at greater risk for UTIs because they are often not as active as younger individuals. Extended immobility can lead to a UTI because the person isnt able to expel urine as frequently, allowing for the bacteria to cultivate in the urine inside the bladder. Other risk factors may be similar to those in younger people, though significantly amplified, such as:
- Diabetes
- Use of a catheter
Recommended Reading: Help For Female Urinary Incontinence
How Is It Diagnosed
If doctors suspect that a UTI is present, they will test a urine sample in the office or send it to a laboratory for a urinalysis.
A urine culture can confirm which bacteria are causing the infection. Knowing the specific type of bacteria allows the doctor to determine a suitable treatment plan.
A condition called asymptomatic bacteriuria is also common in older adults. ASB occurs when there are bacteria in the urine, but they do not cause any signs or symptoms of infection.
Although ASB is common in older adults, it does not typically require treatment, unless it causes other clinical symptoms.
The standard treatment for a UTI is antibiotics, which kill the bacteria causing the infection. Doctors will prescribe an antifungal medication instead if a fungus is causing the UTI.
It is essential that people take the antibiotic or antifungal medication precisely according to the prescription, even if they begin to feel better. Completing the entire prescription will help to destroy all of the infectious bacteria.
What Causes Uti In Elderly Men
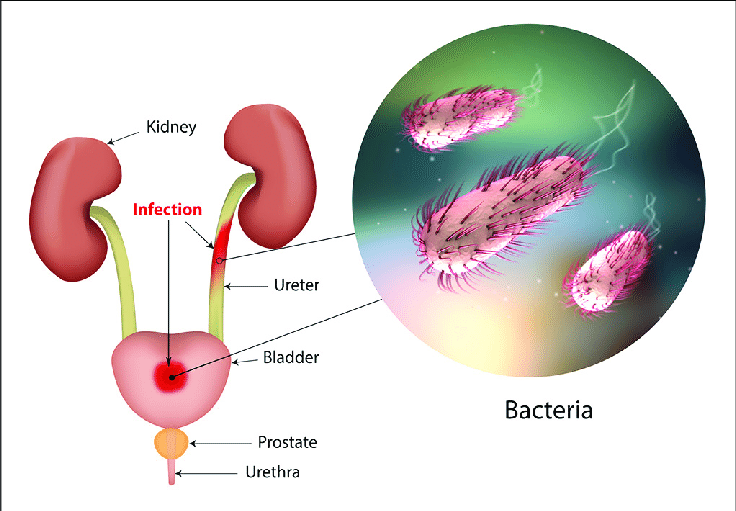
The main cause of UTIs, at any age, is usually bacteria. Escherichia coli is the primary cause, but other organisms can also cause a UTI. In older adults who use catheters or live in a nursing home or other full-time care facility, bacteria such as Enterococci and Staphylococci are more common causes.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Urinary Incontinence Naturally
Why Are Urinary Tract Infections Such A Big Deal For The Elderly
For many young women, urinary tract infections are an occasional annoyance. They cause a few painful hours and many trips to the bathroom, but are soon dispatched with medication.
For many young women, urinary tract infections are an occasional annoyance. They cause a few painful hours and many trips to the bathroom, but are soon dispatched with medication.
But they are something else again for the elderly. They send millions of women – and men – to the hospital every year and can kill if infection spreads to the kidneys or blood.
“Pneumonia and urinary tract infections are the biggest infectious reasons for admission to the hospital for older adults,” said John Bruza, a geriatrician at Penn Medicine.
UTIs are feared enough that many hospitals are working harder to keep infections from starting on their watch by restricting use of urinary catheters. Infections acquired through catheters tend to be worse than those that patients get at home.
Because overuse of antibiotics can lead to tougher bugs, there is also a campaign to make sure doctors don’t assume that vague symptoms in an older person started in the urinary tract.
“It’s just more complicated for older adults,” Bruza said.
Relatively common
Rare in young men, the infections are more common in older men – though still not as frequent as in older women.
“It speaks to just how medically fragile some of these folks can be,” Khelil said.
Weakness, confusion
Hormonal changes
Bladder Health For Older Adults
Everyone uses their bladder many times each day, but they may not know what to do to keep their bladder healthy.
Located in the lower abdomen, the bladder is a hollow organ, much like a balloon, that stores urine. It is part of the urinary system, which also includes the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. Urine contains wastes and extra fluid left over after the body takes what it needs from what we eat and drink.
As you get older, the bladder changes. The elastic bladder tissue may toughen and become less stretchy. A less stretchy bladder cannot hold as much urine as before and might make you go to the bathroom more often. The bladder wall and pelvic floor muscles may weaken, making it harder to empty the bladder fully and causing urine to leak.
You May Like: Home Remedies For Urinary Tract Infection In Females