S To Better Kidney Health For People With Sickle Cell Disease
People with sickle cell disease are at greater risk than the general population for kidney complications. Share your medical history with your healthcare team so it can properly identify and treat any complications of SCD you currently have or may develop. Your healthcare team may include your primary care provider, SCD provider, and any other healthcare specialists. Below are common kidney complications and steps you can take for better kidney health.
How Is Hematuria Treated
If your hematuria is caused by an infection, like a urinary tract infection , hematuria is treated with antibiotics. Your healthcare provider will test your urine after treating you with antibiotics to make sure that your infection has cleared. The goal of your healthcare provider is to find the cause of blood in your urine. If no serious condition is causing hematuria, no treatment is needed.
Also in the A to Z Guide
Is Sickle Cell An Adaptation To Malaria
A gene known as HbS was the center of a medical and evolutionary detective story that began in the middle 1940s in Africa. Doctors noticed that patients who had sickle cell anemia, a serious hereditary blood disease, were more likely to survive malaria, a disease which kills some 1.2 million people every year.
Read Also: Treat Urinary Tract Infection Over The Counter
What Are Possible Complications Of Sickle Cell Disease In Pregnancy
Because sickling affects so many organs and body systems, you are more likely to have complications in pregnancy if you have sickle cell disease. Complications and increased risks may include:
-
Infections, including infection in the urinary tract, kidneys, and lungs
-
Gallbladder problems, including gallstones
-
Heart enlargement and heart failure from anemia
-
Miscarriage
Complications and increased risks for your developing baby may include:
-
Severe anemia
-
Preterm birth
-
Low birth weight
-
Stillbirth and newborn death
How To Utilize Team Care
A multidisciplinary approach in the management of patients with SCD decreases rates of complications and improves clinical outcomes.
Management is by a primary hematologist working in conjunction with multidisciplinary team that would include primary care physician, nephrologist, nurse, social worker, pscychologist, geneticist, dietitian, health educator, and pharmacist.
Patients are usually seen in a multidisciplinary sickle cell clinic that would coordinate comprehensive care with a primary care physician.
A knowlegeable primary care provider or other health professionals, in the setting of limited access to such clinic, would manage patients with periodic referral to SCD specialists for comprehensive evaluation and management of serious complications.
Nurses, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants are key team members in providing longitudinal care focused on health promotion and maintenance in patients with sicke cell disease.
Joint nephrology and hematology SCD clinics provides an ideal environment where âspeedyâ formulation of management plans involving CKD, dialysis and transplantation can be made.
You May Like: Royal Canin Urinary Tract Food
Who Has Sickle Cell Disease
In the UK, about 12,500 people have SCD. It is more common in people whose family origins are African, African-Caribbean or Asian or Mediterranean. It is rare in people of North European origin. On average, 1 in 2,400 babies born in England have SCD, but rates are much higher in some urban areas – about 1 in 300 in some places.
SCD is now one of the most common inherited conditions in babies born in the UK.
Natural History Epidemiology And Genetic Modifiers
In most cases, SCN develops slowly and insidiously over time, starting in the very young with glomerular hyperfiltration and leading to microalbuminuria in late childhood or early adulthood. The majority of patients do not progress further, but a number will gradually develop unselective proteinuria and slowly progressive CKD leading to decreased renal reserve. These patients are at increased risk of AKI-complicating VOCs or other interim illnesses, events that often precipitate a further decline in their baseline renal function following recovery from the acute episode. ESRD is a relatively rare complication, though its incidence is on the rise. A prospective case-control study from the early 1990s demonstrated that 4.2% of HbSS patients and 2.4% of HbSC patients had advanced renal failure with a median age of onset of 23.1 and 49.9 years, respectively. In the follow-up study, the prevalence of chronic renal failure in the HbSS patients increased to 12% in adults, but the mean age of onset had also risen to 37 years. Another study demonstrated that 10.5% of deaths in adult patients with SCD were associated with renal impairment. In keeping with this trend, in 2008, advanced CKD was reported as present in 24% of SCD patients who had survived to 60 years of age or more and was the cause of death in 45% in those who died above this age.
Read Also: Sacral Nerve Stimulation For Urinary Incontinence
What Tests To Perform
Signs of hematuria
-
Diagnostic work up should exclude other causes of hematuria. This would include urinary tract infections, renal stone disease, tumors, vascular malformations, vasculitis, glomerulonephritis and coagulation disorders.
Renal ultrasound is the initial imaging study to screen for stone, tumor and renal papillary necrosis.
Increased echogenicity in the medullary pyramids in the absence of hypercalciuria is characteristic radiologic finding in patients with SCD disease.
-
Helical CT is helpful in earlier detection of renal papillary necrosis.
-
Cystoscopy can be performed to help in identifying source and location of the bleeding.
Signs of tubular dysfunction
-
Close monitoring of electrolytes and acid base status, particularly in settings of decreased kidney function, dehydration, hemolysis and sickle cell crisis.
-
24-hour creatinine clearance should not be used to estimate GFR since increased creatinine secretion overestimates renal function.
-
Alternative methods for GFR estimation include:
Cystatin-C measurement
-
Partial or total nephrectomy on rare occasion.
Tubular dysfunction
Proteinuria, glomerulopathy and CKD
Anemia of CKD should be treated with oral iron, hydroxyurea and erythrocyte stimulating agents
What Triggers Sickle Cell Pain
Any activity or situation that limits or decreases blood flow, or lowers the amount of oxygen in your blood, can trigger sickle cell pain. Often, you won’t know what triggered a pain crisis. But, there are some known triggers for sickle cell pain.37
- High altitudes , where there is less oxygen in the air
- Low-oxygen activities, such as scuba diving or flying in an unpressurized plane2
- Sudden temperature changes, such as jumping into a cold pool or becoming overheated
- Being in cold weather for longer than a few minutes31
- Dehydration, or not drinking enough water38
- Intense exercise, especially if you become overheated, don’t take breaks, or don’t drink enough water39
- Stress.38 Sometimes stress can cause your blood vessels to narrow, limiting blood flow and causing pain. Having sickle cell disease can be stressful, in addition to everyday stressors. Learn ways to manage stress.
Recommended Reading: Physical Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
How Does Sickle Cell Disease Affect The Menstrual Cycle
Sickle cell disease is different in every person, but women and girls may experience unique complications.
- Delayed puberty. Girls who have sickle cell anemia may get their period about 2 years later than girls who do not have sickle cell anemia, while those with milder types of sickle cell disease may have less of a delay.18
- More pain crises before and during your period. Many women experience more pain crises just before and during their period.42 This may be caused by changes in hormone levels. Hormonal treatment such as progesterone injections may help.18
- Heavy periods. Many women with sickle cell disease do not have heavy periods. But, if you have heavy periods, heavy bleeding may increase your risk of iron-deficiency anemia. Doctors often prescribe birth control pills to lessen heavy menstrual bleeding.18 But not all birth control pills are OK for women with sickle cell disease due to a higher risk of stroke. Talk to your doctor or nurse about progesterone-only birth control. Birth control with progesterone combined with estrogen may increase your risk of stroke.
Tests For Newborn Babies
In the UK, all newborn babies are offered a bloodspot test at 5-8 days after birth. This tests for a number of medical conditions which are considered important because early treatment makes a difference. The test is done by taking a small spot of blood from the baby’s heel. The bloodspot test now includes testing for SCD throughout the UK. You will be given the results about six weeks later.
If the baby has sickle cell trait, no action or treatment is needed. If the baby has SCD, the result will be explained. You will be given a clinic appointment to check the diagnosis and to start treatment. Treatment should begin by the time the baby is 3 months old.
Recommended Reading: Ok Google Urinary Tract Infection
How Is Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed
Along with a complete medical history and physical exam, you may have blood and other tests.
Many states routinely screen newborns for sickle cell so that treatment can begin as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce the risk of complications.
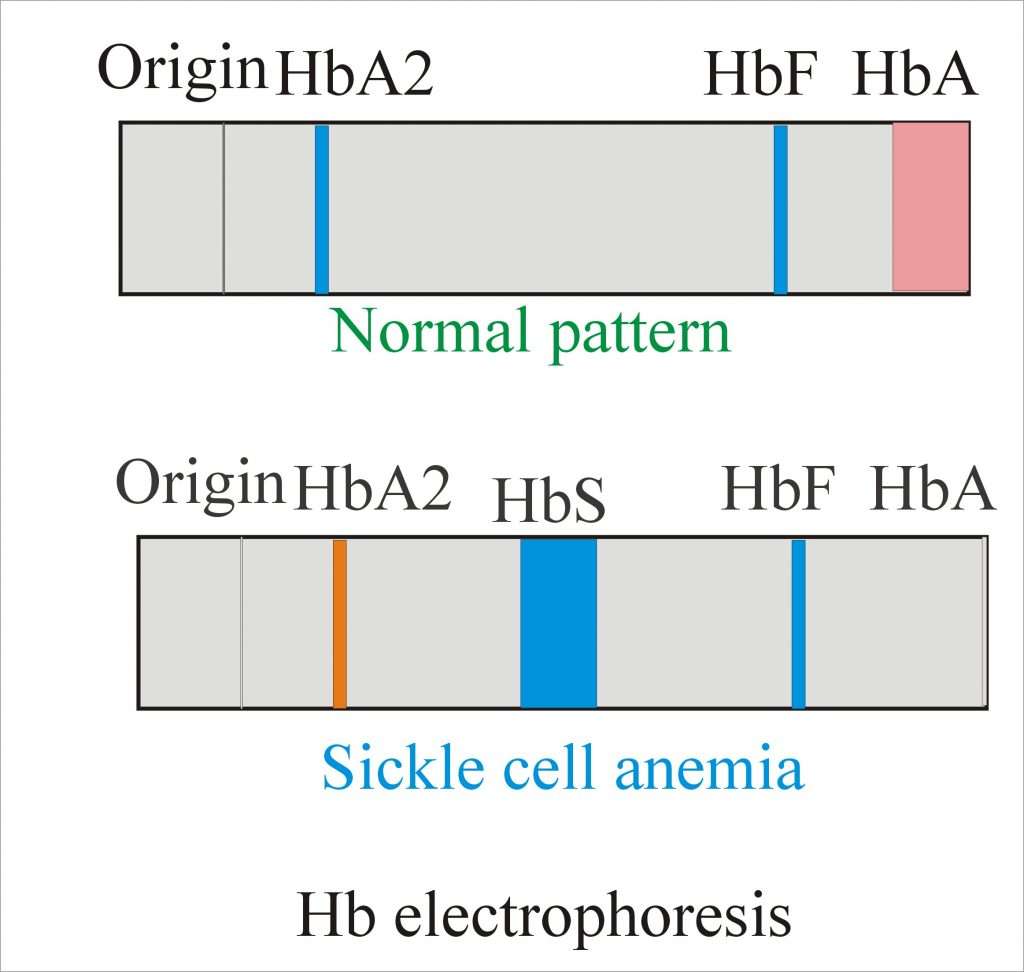
Hemoglobin electrophoresis is a blood test that can determine if a person is a carrier of sickle cell, or has any of the diseases associated with the sickle cell gene.
Hematuria And Renal Papillary Necrosis In Sickle Cell Nephropathy
-
Hematuria may be microscopic or macroscopic.
-
Usually painless, benign and self-limited. It may be hemorrhagic, prolonged and difficult to control resulting in severe blood loss.
-
It can occur at any age and is a common finding in patients with sickle cell trait and disease.
-
Gross hematuria is most often reported in patients with sickle cell trait because of higher frequency of this trait compared to that of sickle cell disease.
-
Bleeding is usually unilateral and occurs more commonly in the left kidney as a result of increased venous congestion in a longer left renal vein that is prone to kinking and compression by adjacent vessels.
-
Hematuria may signal presence of renal papillary necrosis, renal stone disease or renal carcinoma.
Renal papillary necrosis can be asymptomatic and may be an incidental finding in imaging studies.
It may be, but not always, associated with macroscopic hematuria.
Sloughing of renal papillae can occasionally cause acute kidney injury from obstruction.
Urinary tract infection has been associated with renal papillary necrosis and has been suspected to contribute to its development in SCD.
Recommended Reading: What Medicine Can I Take For Urinary Tract Infection
Clinical History And Initial Laboratory Data
A 40-year-old Central African woman with homozygous sickle cell disease was referred for evaluation of proteinuria. During the past 5 years, her serum creatinine level ranged from 0.35 mg/dL 0.70 mg/dL was 610 mg/g 2 months ago, it was 7779 mg/g.
At nephrology evaluation, she reported multiple vaso-occlusive pain crises as a child. She had a vaso-occlusive pain crisis and required red cell transfusion following a therapeutic abortion 5 years ago. Six emergency room visits followed for vaso-occlusive pain crises. She has proliferative sickle cell retinopathy and restrictive lung disease. Folic acid was her only medication and she took acetaminophen for a vaso-occlusive pain crisis 2 months ago.
Table 1 Laboratory results at initial nephrology visit
What Research Is Being Done On Sickle Cell Disease
Research and new medicines such as vaccines are helping people with sickle cell disease live decades longer, with fewer health problems, than in the past. Doctors and researchers are working on better ways to treat sickle cell pain and on cures for all people with sickle cell disease.49 Current sickle cell disease research areas include:
- Bone marrow transplants. Many people with sickle cell disease do not have a bone marrow donor who is a good match, so they cannot get a bone marrow transplant. Researchers are studying how more people could donate bone marrow, how to make bone marrow transplants safer for people with sickle cell disease, and how to stop side effects from bone marrow transplants, such as infertility.50
- Gene therapy. Changing the genes of someone with sickle cell disease could cure the disease. Researchers are exploring whether gene therapy can help sickle blood cells make a healthy type of hemoglobin.21
- Clinical trials. Clinical trials or studies are how researchers test new medicines and procedures to treat sickle cell disease. Some medicines work slightly differently in people who have different backgrounds, so it’s helpful to have as many people as possible participate to find new cures. Go to ClinicalTrials.gov to find a study in your area.
Also Check: Can Probiotics Help With Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Outlook
Sickle cell disease is a serious condition which may shorten life. Without treatment, people with SCD may die in childhood, from problems such as infection. Good treatment makes a great difference. Improvements in treatment mean that life expectancy has increased.
Even with modern treatment, SCD can still cause serious or life-threatening problems. Dangerous problems are severe infection, acute chest syndrome and sudden severe anaemia. Awareness of symptoms and early treatment are important.
There is a lot of individual variation in the severity and outlook for SCD. Some people get very few problems from their SCD others have more symptoms or more complications.
The treatment of sickle cell anaemia is a developing area of medicine. New treatments continue to be developed and the information on outlook above is very general. The specialist who knows your case can give more accurate information about the outlook for your particular situation.
Blood And The Immune System
All patients with sickle cell disease will experience chronic anemia. Due to the fact that there is an issue with the shape of red blood cells, they break quickly and get clogged in blood vessels. Severe episodes of anemia can also happen in an individual with sickle cell anemia.
These episodes in some cases require treatment with blood transfusions. In addition, those with SCA might have deteriorated immune systems and be more susceptible to infections. For this reason, individuals with sickle cell anemia must look for treatment right away if they have a fever or become ill.
You May Like: Natural Remedies For Male Urinary Tract Infection
Inflammatory Bowel Disease In A Child With Sickle Cell Anemia
Khaled Alqoaer
1Pediatric Department, Prince Salman North West Armed Forces Hospital, P.O. Box 100, Tabuk 71411, Saudi Arabia
Academic Editor:
Abstract
Sickle cell anemia is a chronic haemoglobinopathy that can affect many organs in the body including gastrointestinal tract. However, colonic involvement is very rare and usually in the form of ischemic colitis. We are reporting an 11-year-old Saudi girl with SCA who presented with persistent diarrhea and was found to have inflammaftory bowel disease.
1. Introduction
Homozygous sickle cell anemia is an autosomal recessive chronic haemoglobinopathy characterized by abnormal globin chain of hemoglobin content of the red blood cells that result in sickle shapes, attraction of RBCs to each other, and polymerization when in a low oxygen environment. The RBC polymerization leads to manifestations such as chronic occlusion of blood vessels , reduced blood flow to vital organs , and alterations of the immune system. The gastrointestinal manifestation of SCA varies . We are reporting a child with SCA who presented with chronic colitis resembling inflammatory bowel disease.
2. The Case
What Are The Complications Of Sickle Cell Disease
Any and all major organs are affected by sickle cell disease. The liver, heart, kidneys, gallbladder, eyes, bones, and joints can suffer damage from the abnormal function of the sickle cells and their inability to flow through the small blood vessels correctly. Problems may include the following:
- Increased infections
- Kidney damage and loss of body water in the urine
- Eye damage
- Multiple organ failure
Recommended Reading: Medicine To Stop Urinary Burning
Out Of Balance: Gut Bacterial Makeup May Exacerbate Pain In Sickle Cell Disease
- Date:
- American Physiological Society
- Summary:
- An overabundance of the bacteria Veillonella in the digestive tract may increase pain in patients with sickle cell disease .
An overabundance of the bacteria Veillonella in the digestive tract may increase pain in patients with sickle cell disease . Researchers from Howard University will present their findings today at the American Physiological Society’s Physiological and Pathophysiological Consequences of Sickle Cell Disease conference in Washington, D.C.
Previous studies have reported that Veillonella, a bacterium that normally lives in the mouth and gut, forms a film in the gastrointestinal tract. Streptococcus bacteria may attach themselves to this film, making them stronger and more virulent. Streptococcus is responsible for diseases such as strep throat, meningitis and bacterial pneumonia.
Story Source:
Concentration Response Curves To Extracellular Cacl2
To evaluate the receptor-independent, direct effects of extracellular Ca2+ influx on bladder contraction, cumulative concentration response curves to CaCl2 under depolarizing conditions were obtained. Bladder strips were prepared and mounted in 10mL organ baths containing KrebsHenseleit Ca2+-free solution containing 1mM EGTA to sequester Ca2+ ions, and cyclopiazonic acid to deplete sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ stores. Bath solution was removed and replaced by KrebsHenseleit Ca2+-free solution containing KCl and CPA . After an equilibration period of 15 min, the cumulative curve to CaCl2 was obtained .
You May Like: Bard Urinary Drainage Bag With Anti Reflux Dome
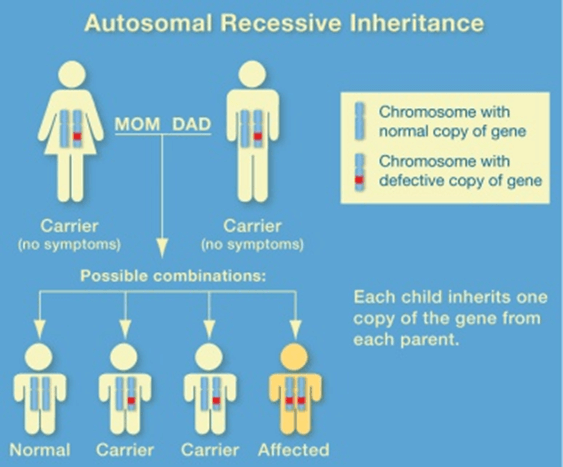
Is Sickle Cell Anemia Dominant Or Recessive
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern , which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
Ex Vivo Functional Studies
The urinary bladder and urethra were surgically removed and placed in chilled Krebs-Henseleit buffer . After removal of the trigone, the DSM was cleaned of connective and adventitial tissues, and two strips of bladder were obtained from each animal. The strips had intact urothelium, and the urethra was removed and cut into rings . The DSM strips were mounted in a 10mL organ system and the urethra rings were mounted in 5mL organ baths, both containing Krebs solution at 37°C, that was continuously bubbled with a mixture of 95% O2 and 5% CO2. DSM strips were vertically suspended between two metal hooks. One hook was connected to a force transducer and the other acted as a fixed attachment point. Tissues were allowed to equilibrate for 60 min under a resting tension of 5 mN. For the urethra rings, the resting tension was adjusted to 2 mN at the beginning of the experiments. The equilibration period was 45 minutes, and the bathing medium was changed every 15 minutes until the start of the experiment. Changes in isometric force were recorded using a Power Lab v.7.2 system .
Don’t Miss: Foods For Healthy Urinary Tract