Key Points About Urinary Tract Infections
- Urinary tract infections are a common health problem that affects millions of people each year. These infections can affect any part of the urinary tract.
- Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
- The most common symptoms of UTIs include changes in urination such as frequency, pain, or burning urine looks dark, cloudy, or red and smells bad back or side pain nausea/vomiting and fever.
- Antibiotics are used to treat UTIs. Other treatments may include pain relievers, and drinking plenty of water to help wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Other things that can be done may help reduce the likelihood of developing UTIs.
When To Seek Emergency Medical Help
Although unpleasant, UTIs do not require immediate medical attention. Some people make the error of assuming that a kidney infection is the same as a cold.
Kidney infections are dangerous illnesses that need to be treated by a doctor. A kidney infection that is left untreated can soon result in kidney scarring or long-term kidney damage. Additionally, these infections may result in sepsis, which may result in septic shock.
As a result, if a kidney infection worsens, it may be fatal. Its crucial that a medical practitioner treat it right away.
Be aware that kidney stones can obstruct blood flow and induce an infection or sepsis if they are not addressed. A urologist may need to perform a procedure using intravenous antibiotics for this.
Urinate Completely To Avoid Urinary Tract Infections
Women are especially prone to urinary tract infections, which can also involve the bladder. One way to reduce your risk is to make sure that you urinate completely, says Gopal Badlani, MD, of the Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center in Winston-Salem, North Carolina, and a specialist in bladder issues. If you tighten your muscles to stop urinating too soon, the urine that didn’t quite escape will head back to your bladder, which can bring bacteria into your system.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Lower Back Pain
Specimen Collection Transportation And Processing
Specimen collection. Suprapubic aspiration is the best method to avoid contamination of specimens with bacteria in the distal urethra. This collection method is used infrequently because it is not indicated clinically , it is invasive and uncomfortable, and it requires too much time and too many resources to be practical. Collection of urine by use of a single catheter is the next-best technique for obtaining urine specimens with minimal contamination, but, again, it is not indicated clinically for most patients because it is too labor intensive and costly for routine use and it is invasive. It has added disadvantages, because the process of inserting a catheter through the urethra can introduce bacteria into the bladder , and rare complications have been reported.
As discussed below, correct processing and handling of urine specimens, as well as correct interpretation of test results, is dependent on the method used to collect the specimen. It is, therefore, of obvious importance for clinicians to specify the method of collection on the test requisition slip. Other information that should be included on the test requisition slip includes the date and time of specimen collection, patient demographic information, and any clinically relevant information .
Nonculture Methods For The Laboratory Diagnosis Of Uti
Detection of bacteriuria by urine microscopy. Bacteriuria can be detected microscopically using Gram staining of uncentrifuged urine specimens, Gram staining of centrifuged specimens, or direct observation of bacteria in urine specimens. Gram stain of uncentrifuged urine specimens is a simple method. A volume of urine is applied to a glass microscope slide, allowed to air dry, stained with Gram stain, and examined microscopically. The performance characteristics of the test are not well-defined, because different criteria have been used to define a positive test result. In one study, the test was found to be sensitive for the detection of 105 cfu/mL but insensitive for the detection of lower numbers of bacteria . Other investigators have found the test to be of low sensitivity for the detection of UTI .
Performance characteristics of Gram staining for detection of bacteriuria.
Performance characteristics of leukocyte esterase and nitrite tests, alone or in combination, for detection of bacteriuria and/or pyuria.
A number of drugs can change the color of urine abnormal urine color may affect urine tests that are based on the interpretation of color changes. In some cases, this can mask color changes, and in others, it may result in false-positive interpretations .
Also Check: Causes Of Urinary Incontinence In Elderly Males
Prophylaxis Of Recurrent Utis
Recommendations.
Strategies for preventing recurrent UTI include using antibiotics or nonpharmacologic therapies. Whether to use antibiotic prophylaxis, and which agent, should be a shared decision between the physician and patient. Before prescribing antibiotics, clinicians should counsel patients about behavioral strategies to prevent recurrent UTIs given the increasing resistance to antibiotics, adverse effects of antibiotics on normal flora, and potential for serious adverse effects.
In sexually active women, prophylactic antibiotic use reduces the frequency of recurrent UTIs compared to placebo . Intermittent single-dose antibiotic prophylaxis after coitus appears as effective as daily prophylaxis, with fewer adverse effects. Single-dose prophylaxis is the preferred option for women who develop cystitis related to sexual intercourse. The reduction in recurrent UTI only lasts as long as the woman takes the antibiotic. Once antibiotics are discontinued, UTIs occur at the same rate as in placebo-treated sexually active women. Adverse events from antibiotic use are generally mild, although women vary in their evaluation of the impact of various side effects .
Advise patients to increase their daily consumption of water. According to one randomized controlled trial, nonpregnant premenopausal women who drank 1.5 L of additional water per day decreased their risk of recurrent UTI compared to women who consumed their usual fluid intake.
Differential Diagnosis Of Uti In Men
Chronic bacterial prostatitis causes recurrent UTIs, and usually the same bacterial strain is found with each episode. However, only about 10% of men with chronic prostatitis symptoms actually have chronic bacterial prostatitis, with E. coli being the most common organism.
Urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men may cause lower urinary tract symptoms . Urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome encompasses the related diagnosis that occurs in both men and women, called painful bladder syndrome or interstitial cystitis. Typical symptoms include chronic pelvic pain, often with urinary urgency and frequency. If no infection is found, routine use of antibiotics is not recommended.
Kidney stones and bladder stones can cause UTI-like symptoms, usually with gross or microscopic hematuria. If stone disease is suspected, imaging with a renal stone protocol abdominal CT is recommended.
Prostate cancer is typically asymptomatic in its early stages, but can cause lower urinary tract symptoms or urinary retention in some men. A full discussion is beyond the scope of this guideline, but an elevated PSA or abnormal prostate on digital rectal exam are indications for a urology consultation.
Epididymitis, orchitis, and epididymo-orchitis may be due to a bacterial infection or an STI such as Neisseria gonorrhea or Chlamydia trachomatis. Viral causes are also possible, so when orchitis is present, consider testing for mumps using a buccal swab, especially if parotitis is also present.
You May Like: What To Do When Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnosis Of Uti In Men
Recommendations.
Symptoms of cystitis and pyelonephritis are similar in men and women. However, acute UTI in men can also include acute bacterial prostatitis, epididymitis, and urethritis. Suspect urethritis in any sexually active male with dysuria. UTI in men is generally considered to be complicated because of the risk of acute bacterial prostatitis, which can be a severe and potentially life-threatening systemic infection. Chronic bacterial prostatitis presents as recurrent UTI, typically with the same bacterial strain each time.
Symptoms unique to men include slow urinary stream, a sense of incomplete emptying, penile discharge, suprapubic or groin pain, and testicular pain. Signs of acute UTI in men may include an enlarged and tender boggy prostate, or a tender epididymis or testis.
If STI is a consideration, first collect an initial void urine sample , before collecting a clean catch midstream sample. Send the initial void urine sample for gonorrhea and Chlamydia testing in symptomatic males age 14-35 years, as well as in those who have STI exposure risks, a new sexual partner, penile discharge, or signs and symptoms of epididymitis or orchitis. STI testing can also be done on a urethral swab.
Obtain a clean catch urinalysis. The presence of bacteriuria along with symptoms supports a diagnosis of UTI. Pyuria is not diagnostic of UTI, but the absence of pyuria can be used to rule out UTI with a negative predictive value of 95%.
Symptomatic Cystitis In Pregnancy
Recommendation.
The diagnosis of cystitis in pregnancy is made based on the presence of lower urinary tract symptoms and laboratory testing. Unlike in nonpregnant patients, urine culture should be routinely obtained to confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment.
Treat cystitis during pregnancy with nitrofurantoin for 7 days or cephalexin for 7 days. Avoid use of nitrofurantoin after 37 weeks gestation because it may increase neonatal jaundice.
You May Like: What To Do For Urinary Retention
Walk Regularly To Avoid Retaining Fluids
Some people, like those who are sedentary or have heart disease, may develop fluid buildup in their legs during the day. At night, this fluid causes them to need to empty their bladders frequently. If you have fluid retention in your legs that’s causing an active bladder overnight, try walking around more throughout the day. If you can’t walk, flex your calf muscles and raise your legs to waist level.
Acute And Chronic Prostatitis
In the 1800s, prostatitis was thought to be secondary to excessive alcohol consumption or physical or sexual activity. It was often associated with gonorrhea and could be fatal or lead to abscess formation. By the 1920s, most cases were attributed to microorganisms, and antibiotics combined with prostate massage were standard therapy after World War II. Although the role of bacteria was questioned in the 1950s, it was reemphasized in 1968 when Meares and Stamey described their “4-glass test.”
Acute prostatitis is caused by an acute infection of the entire prostate gland, resulting in fever and localized pain. Microscopically, neutrophilic infiltrates, diffuse edema, and microabscesses may be seen, which may coalesce into larger collections.
Chronic prostatitis may be caused by inflammatory or noninflammatory diseases. This condition may arise via dysfunctional voiding, intraprostatic reflux, chronic exposure to microorganisms, autoimmune mechanisms, irritative urinary metabolites, and as a variant of neuropathic pain. Chronic bacterial prostatitis often produces few or no symptoms related to the prostate, but it is probably the most common cause of relapsing UTI in men.
Chronic prostatitis has been subdivided by the National Institutes of Health into the following categories:
Don’t Miss: Quick Cure For Urinary Tract Infection
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Treated
You will need to treat a urinary tract infection. Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria and fight an infection. Antibiotics are typically used to treat urinary tract infections. Your healthcare provider will pick a drug that best treats the particular bacteria thats causing your infection. Some commonly used antibiotics can include:
- Nitrofurantoin.
Its very important that you follow your healthcare providers directions for taking the medicine. Dont stop taking the antibiotic because your symptoms go away and you start feeling better. If the infection is not treated completely with the full course of antibiotics, it can return.
If you have a history of frequent urinary tract infections, you may be given a prescription for antibiotics that you would take at the first onset of symptoms. Other patients may be given antibiotics to take every day, every other day, or after sexual intercourse to prevent the infection. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment option for you if you have a history of frequent UTIs.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection

These are the most common symptoms of a UTI:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Urine looks dark, cloudy, or reddish in color
- Urine smells bad
- Feeling pain even when not urinating
- Pain in the back or side, below the ribs
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Despite an strong urge to urinate, only a small amount of urine is passed
- Women may feel an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone
The symptoms of UTI may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always see a health care provider for a diagnosis.
You May Like: Can Alcohol Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Natural Remedies For Uti From Medical Medium
We found very interesting information from the ‘Medical Medium, Liver Cleanse‘ book by Anthony Williams. He is well known for finding natural solutions to treat UTIs, Yeast Infections, and Bacterial vaginosis
- Aloe vera: 2 or more inches of fresh gel daily
- Amla berry: 2 teaspoons twice a day
- Cats claw: 2 dropperfuls twice a day
- Chaga mushroom: 2 teaspoons daily
- D-mannose: 1 teaspoon powder four times a day
- Goldenseal: 4 dropperfuls twice a day
- Hibiscus: 2 cups of tea daily
- Lemon balm: 4 dropperfuls twice a day
- Mullein leaf: 3 dropperfuls twice a day
- Olive leaf: 2 dropperfuls twice a day
- Oregon grape root: 1 dropperful twice a day
- Rose hips: 2 cups of tea daily
- Vitamin C: 6 500-milligram capsules Ester-C or 1 tablespoon liquid liposomal twice a day
- Zinc : up to 2 dropperfuls twice a day
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
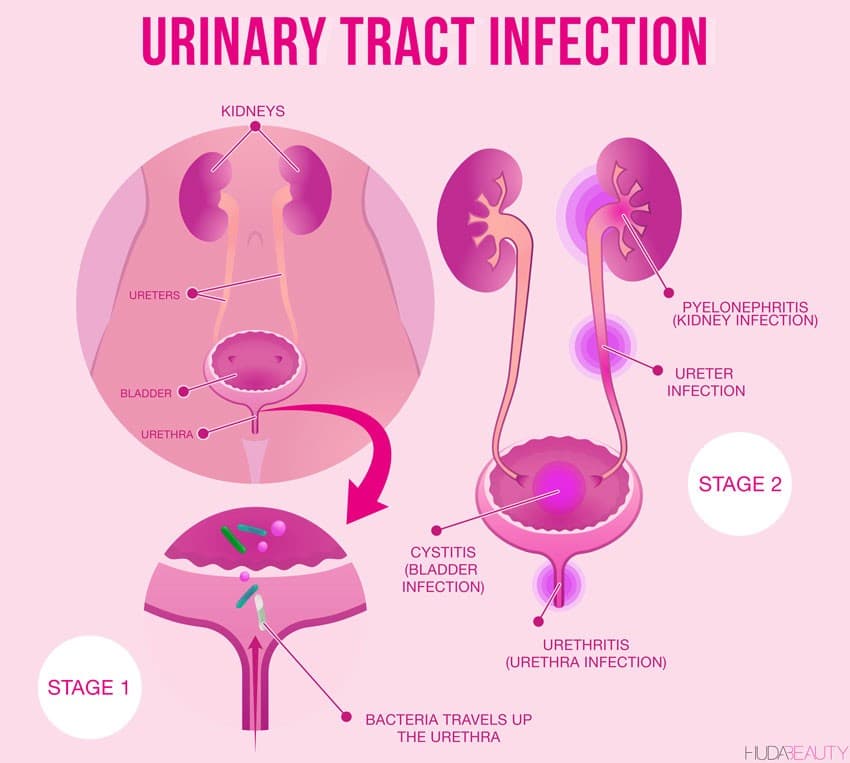
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms usually bacteria that enter the urethra and bladder, causing inflammation and infection. Though a UTI most commonly happens in the urethra and bladder, bacteria can also travel up the ureters and infect your kidneys.
More than 90% of bladder infection cases are caused by E. coli, a bacterium normally found in the intestines.
Recommended Reading: What Do You Treat A Urinary Tract Infection With
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
Cultures And The Laboratory Diagnosis Of Utis
Routine bacterial urine cultures. Urine culture may not be necessary as part of the evaluation of outpatients with uncomplicated UTIs . However, urine cultures are necessary for outpatients who have recurrent UTIs, experience treatment failures, or have complicated UTIs. Urine cultures are also necessary for inpatients who develop UTIs. The bacterial culture remains an important test in the diagnosis of UTI, not only because it helps to document infection, but also because it is necessary for determination of the identity of the infecting microorganism and for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. This is particularly true because of the increased incidence of antimicrobial resistance.
Catheterized patients and many patients with infections of the lower urinary tract have colony counts much lower than 105 cfu/mL if the specimens are obtained via suprapubic aspirate or catheterization . Accordingly, the most appropriate diagnostic criterion for urine culture specimens obtained via suprapubic aspirate or catheterization is a bacterial concentration of 102 cfu/mL .
Interpreting culture results for urine specimens yielding common urinary tract pathogens.
Read Also: Can Sugar Cause Urinary Tract Infections
Additional File : Table S1
Primers used in polymerase chain reaction. Figure S1. Electrophoretogram of PCR identified Enterococcus faecalis. On the right side of the figure, two sets of primers are used for PCR amplification. Urine represents the patients first urine sample. PTC represents positive template control. NTC represents negative template control. L100 represents DNA ladder.
Availability Of Data And Materials
The data supporting the conclusions discussed in this article are included within the article. The datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study are available in NCBI with the accession number SRR11624506, SRR11624507 and SRR11624508. SRR11624507 and SRR11624508 are the sequencing data of urine and blood samples detected for the first time, and SRR11624506 is the urine sample sequencing data during the second follow-up.
Also Check: How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections In Females
Urinary Tract Infection May Damage Your Kidneys
Your kidneys filter waste from your blood into your urine and regulate the amount of water and electrolytes in your blood. These are both important body functions that routinely keep happening right from our birth till our last breath.
But did you know that renal disease can be fatal, frequently with quite serious consequences, and put you incapable of doing your daily chores? If you are not aware of the effects, reading this post may be very beneficial for you to comprehend the infections that your kidneys might get affected with and the natural treatments you may take to prevent if there is an infection.
Typically, kidney infections are brought on by bacteria that got into your kidneys or bladder through your urinary tract. Infections in other parts of your body, surgery on the kidneys or bladder, or obstacles to the flow of urine like kidney stones, tumours, or enlarged prostates can also cause them.
One or both of your kidneys may eventually get infected with pyelonephritis, also referred to as a kidney infection, as a result of a urinary tract infection. They may come on suddenly or gradually, but they almost always feel awful. They could also be severe and even fatal if untreated.
- Being susceptible to urethral infections
- Experiencing issues with a weaker immune system frequently urinating while totally emptying your bladder
Drink Plenty Of Fluids To Flush Out Bacteria But Dont Overdo It
Drinking plenty of water six to eight glasses daily can flush bacteria out of your urinary tract and help prevent bladder infections. But many people drink more than that these days, having heard that drinking water frequently is healthy, Dr. Badlani says. If you’re bothered by a constant need to empty your bladder and you’re drinking fluids throughout the day, cut back on your intake. Also, avoid caffeinated sodas and coffee theyll only make you urinate more.
Sponsored Advertising Content
Also Check: Do Urinary Tract Infections Make You Pee A Lot