Managing The Elderly With Urinary Incontinence And Dementia
Si Ching LIM
Senior Consultant, Department of Geriatric Medicine, Changi General Hospital, Singapore
*Corresponding author: Si Ching LIM, Senior Consultant, Department of Geriatric Medicine, Changi General Hospital, Singapore, E-mail:
Received: April 14, 2017 | Accepted: June 03, 2017 | Published: June 05, 2017
Citation: Si Ching LIM Managing the Elderly with Urinary Incontinence and Dementia. Int Arch Urol Complic 3:027. doi.org/10.23937/2469-5742/1510027
Medication For Incontinence In The Elderly
Medications are frequently used in combination with behavioral therapies. Here are some commonly prescribed options:
Anticholinergic or antispasmodic drugs
These are usually prescribed for urge incontinence. Examples include Vesicare®, Detrol LA®, Ditropan XL®, Oxytrol skin patch®, and Santura®. The most common side effect is dry mouth. Less common side effects include blurred vision, constipation, and mental confusion.
Antibiotics
These are prescribed when incontinence is caused by a urinary tract infection or an inflamed prostate gland.
H4) Tofranil® and Sudafed® These are used to treat stress urinary incontinence, and they work by tightening muscles around the bladder.
Track How Often You Urinate
To help find the cause of incontinence, for a few days keep a record of how much you drink and how often you pee. Make note of any leaking, along with anything — drinking a lot, heavy lifting — that might have triggered it. Bring the record to your doctor’s appointment. It will help your doctor better understand your symptoms and could give clues about the cause.
10
Don’t Miss: Azo Urinary Pain Relief Maximum Strength Tablets
Bladder Anatomy And Physiology
The anatomy and physiology of the bladder are complex, but a basic understanding of these topics is essential in order to appreciate the various types of UI and their management., illustrates the basic anatomic structures and nervous system wiring involved in bladder function, including the detrusor muscle, the internal and external sphincters , and their neurological components.
Bladder anatomy and physiology.
Reduced activation of the sympathetic nervous system results in relaxation of the detrusor muscle, closure of the sphincter, and bladder filling. When the volume of urine in the bladder reaches 200 to 400 mL, the sensation of urge to void is relayed via the spinal cord to the brain centers. Voluntary voiding involves the parasympathetic nervous system and the voluntary somatic nervous system. Influences from these systems cause contractions of the detrusor muscle and corresponding somatic nervous activity, leading to sphincter relaxation.
How Is Incontinence Diagnosed
Often, the diagnosis process for incontinence will start with a conversation with your healthcare provider about your medical history and bladder control issues. Your provider might ask you questions like:
- How often do you urinate?
- Do you leak urine between trips to the toilet, how often does this happen and how much urine do you leak each time?
- How long have you been experiencing incontinence?
These questions can help your provider figure out a pattern with your leakage, which often points to a specific type of incontinence. When your provider is asking about your medical history, its important to list all of your medications because some medications can cause incontinence. Your provider will also ask about any past pregnancies and the details around each delivery.
There are also several specific tests that your provider might do to diagnose incontinence, including:
While at home, your provider might recommend you keep track of any leakage in a journal for a few days. By writing down how often you experience incontinence issues over the span of a few days, your provider might be able to identify a pattern. This can really help in the diagnosis process. Make sure to write down how often you need to urinate, how much you are able to go each time, if you leak between trips to the bathroom and any activities you might be doing when you leak urine. Youll then bring this journal with you to your appointment and talk about it with your provider.
Don’t Miss: Strep B Urinary Tract Infection
Catheterisation For Detrusor Under
The main treatment strategy for a poorly contractile bladder is clean intermittent catheterisation. Drugs with parasympathetic activities are not widely used because of poor efficacy and poor side effect profile. New treatment modalities like neuromodulation, neurostimulation or reconstruction with muscle transposition have been explored but data is limited for the elderly .
How To Train Your Bladder
Try using behavioral techniques such as bladder training. Start by going to the bathroom to pee every half hour, whether you feel the urge or not. As you get into the rhythm, gradually — over days or weeks — expand the time between bathroom breaks. Eventually, you may be able to space breaks by 3 to 4 hours and the urges in between may decrease.
9
You May Like: Can I Take Azo Urinary Tract Defense With Antibiotics
Treatment For Urinary Incontinence
Today, there are more treatments for urinary incontinence than ever before. The choice of treatment depends on the type of bladder control problem you have, how serious it is, and what best fits your lifestyle. As a general rule, the simplest and safest treatments should be tried first.
Bladder control training may help you get better control of your bladder. Your doctor may suggest you try the following:
- Pelvic muscle exercises work the muscles that you use to stop urinating. Making these muscles stronger helps you hold urine in your bladder longer. Learn more about pelvic floor exercises and how to do them.
- Biofeedback uses sensors to make you aware of signals from your body. This may help you regain control over the muscles in your bladder and urethra. Biofeedback can be helpful when learning pelvic muscle exercises.
- Timed voiding may help you control your bladder. In timed voiding, you urinate on a set schedule, for example, every hour. You can slowly extend the time between bathroom trips. When timed voiding is combined with biofeedback and pelvic muscle exercises, you may find it easier to control urge and overflow incontinence.
- Lifestyle changes may help with incontinence. Losing weight, quitting smoking, saying no to alcohol, drinking less caffeine , preventing constipation and avoiding lifting heavy objects may help with incontinence. Choosing water instead of other drinks and limiting drinks before bedtime may also help.
Dementia And Changes To The Lower Urinary Tract
Dementia is an umbrella of neurodegenerative disorders which cause degeneration of the CNS. The Alzheimer’s Disease Association estimated that currently, there are 46.8 million people living with dementia worldwide and this number will double every 20 years to 74.7 million in 2030 and 131.5 million in 2050. Much of this increase will be in the developing world.
Central control of detrusor activities includes the frontal cortex, basal ganglia, Pontine Micturition Centre. The central control provides an inhibitory input on the detrusor to reduce contractions during the bladder filling phase. Dementia, particularly vascular dementia, normal pressure hydrocephalus, Frontotemporal lobe dementia, Alzheimer’s Disease present with features of detrusor over-activity where urgency is the main symptom. Among the elderly with Alzheimer’s disease, urge incontinence is the commonest presentation and UI is proportional to the dementia severity and impairment of ADLs .
Diffuse Lewy Body Dementia , Multisystem atrophy, Parkinson’s Disease Dementia and AD have additional component of autonomic dysfunction, in addition to the central causes. The autonomic dysfunction presents with detrusor over-activity as the main type of UI. The synuclein deposition in PDD and DLBD is present in central nervous system and postganglionic sympathetic nerves .
Recommended Reading: What Can Happen If A Urinary Tract Infection Goes Untreated
Treatments For Male Urinary Incontinence
There are a number of treatment approaches for urinary incontinence to improve bladder control for men, depending on how severe it is and its underlying cause. A combination of treatments might be necessary. There are several categories of medications to treat overactive bladder and relax the bladder muscles and medications for men with incontinence caused by an enlarged prostate. Neuromodulation techniques include percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation, Botox injections in the bladder, and Interstim implantation. When indicated, surgical procedures are available to help alleviate incontinence issues.
Treatment For Male Incontinence
Treatment for male incontinence depends on the underlying causes, and treatment plans often involve a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. The common types of medication used to treat male incontinence include:
Alpha-blockers, which are prescribed to those with an enlarged prostate and helps men to empty their bladder more effectively
Anticholinergics, which are used to treat overactive bladders
Mirabegron, which relaxes bladder muscles in order to increase the amount of urine your bladder can hold.
Botox, which is injected into the bladder to help relax muscles
Don’t Miss: Does Zpack Treat Urinary Tract Infections
Measurement Of Potential Confounders
Men were asked whether a doctor or other health care provider had ever told them they had any of a list of 20 medical conditions the number of conditions was summed to give a co-morbidity score. Men were categorised as having an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer based on self-reported diagnosis by a doctor or other health care provider.
Prevalence And Type Of Urinary Incontinence
The prevalence of UI according to age is shown in . The overall prevalence of UI was 14.8%, increasing from 12.0% for the men aged 7074 years old to 26.3% among men 8589 years old but reduced to 16.3% for those aged 90 years old .
Urgency incontinence was the most frequent type of urinary incontinence, with 20% of men reporting leaking urine before getting to the toilet . About 10% of men experienced post-micturition dribbling and 5% of men reported leaking urine for no obvious reason. Three percent of men reported using pads or other incontinence aids.
Analysis of the data from the ICIQ showed that the frequency of urine leakage was strongly correlated with the quantity of urine leaked . Both frequency and quantity of urine leakage were strongly correlated with the self-perceived impact on daily life rating in the ICIQ. Among those defined with UI, 12.6% reported a score over 5 on the self-perceived impact on life scale . The overall ICIQ summed score in all men in CHAMP ranged from 0 to 18 , with a median score of zero, the first quantile was zero and the third quantile was three.
Recommended Reading: Google What Are The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Etiology And Risk Factors
Multiple factors, including age-related physiological changes, may result in or contribute to the various syndromes of UI. Both genitourinary and non-genitourinary factors may contribute to incontinence in aging patients. Age-related functional changes in the urinary tract may contribute to UI. In women, risk factors for these genitourinary changes include multiple or complex vaginal deliveries, high infant birth weight, a history of hysterectomy, and physiological changes related to the transition to postmenopause. Smoking, a high body mass index, and constipation are also associated with an increased risk of UI.
Pathophysiological causes of UI include lesions in higher micturition centers, in the sacral spinal cord, and in other neurological areas as well. UI may also be associated with numerous comorbidities, such as Parkinsons disease, Alzheimers disease, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Functional factors, including mobility and dexterity, along with reaction time and lack of access to a bathroom facility, may also contribute to UI.
Is He Regularly Constipated
Constipation is one of the most common causes of fecal incontinence in men. Chronic constipation could lead to an impacted hard stool in the rectum becoming too large for him to pass. As a result, the rectum muscles and intestines stretch and eventually weaken. Watery stools could also pass around the hard stool and leak out, causing fecal incontinence.
Recommended Reading: Cure For Urinary Tract Infection In Males
Related Conditions And Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Fecal incontinence is light to moderate bowel leakage due to diarrhea, constipation, or muscle or nerve damage.
As described in the section above on causes of urinary incontinence, common conditions may contribute to chronic urinary incontinence, including: urinary tract infection , constipation, interstitial cystitis or other bladder conditions, nerve damage that affects bladder control, side effects from a prior surgery, and neurological disorders.
Are Certain Types Of Incontinence More Common In Men
Certain types of incontinence are more common among men. Urge incontinence, which occurs when UI occurs after a sudden need to urinate, is the most common.
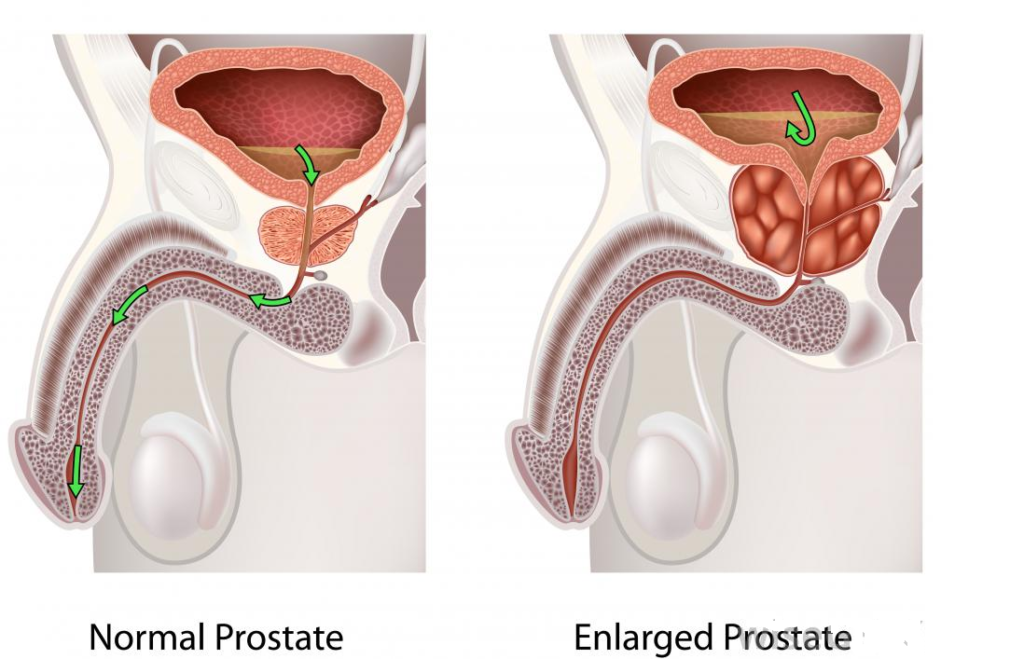
This condition is often associated with an enlarged prostate gland, which can lead to an overactive bladder.
Stress incontinence, which occurs alongside actions and movements that put pressure on the bladder, is also common in men.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Urinary
Urinary Incontinence In Men: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Written byDr. Victor MarchionePublished onAugust 8, 2016
Urinary incontinence or loss of bladder control in men is not uncommon, but it can be treated once the cause is determined.
Uncontrollable urine in men or urinary incontinence occurs in eleven to 34 percent of older men, but it is not just an issue that impacts the aging. Younger men can also experience UI due to health problems. Urinary incontinence also happens to women, but the biggest issue with UI in men is that they are less likely to speak with their doctors about it. This means that the statistics could actually be much higher in men that the current numbers indicate. Discussing the problem is the first step to addressing the symptoms and finding a treatment.
Urinary incontinence often results in the accidental leakage of urine from the body, so it can be uncomfortable and inconvenient. A man can feel a strong, sudden need to urinate just before losing a large amount of urine. Doctors refer to this as urgency incontinence. For some people, this condition keeps them from enjoying certain activities, including sports and exercise. It can also cause a lot of emotional distress.
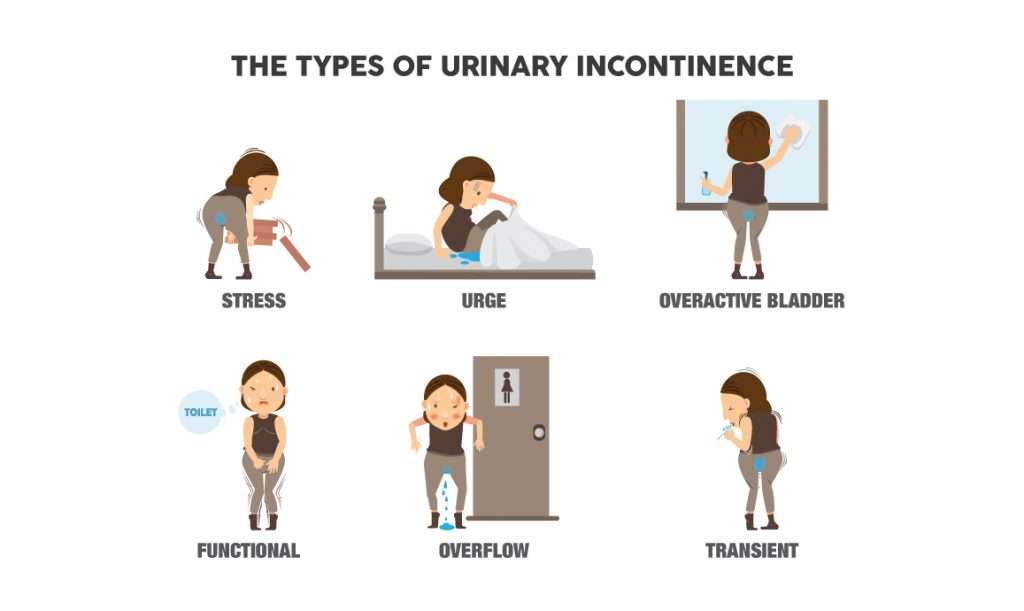
There are different types of urinary incontinence, so it is important to get a proper assessment from a doctor to determine what type you might have and how to go address it. The types of UI men experience include urgency incontinence, stress incontinence, functional incontinence, overflow UI, and transient UI.
Urinary Incontinence In Older Adults
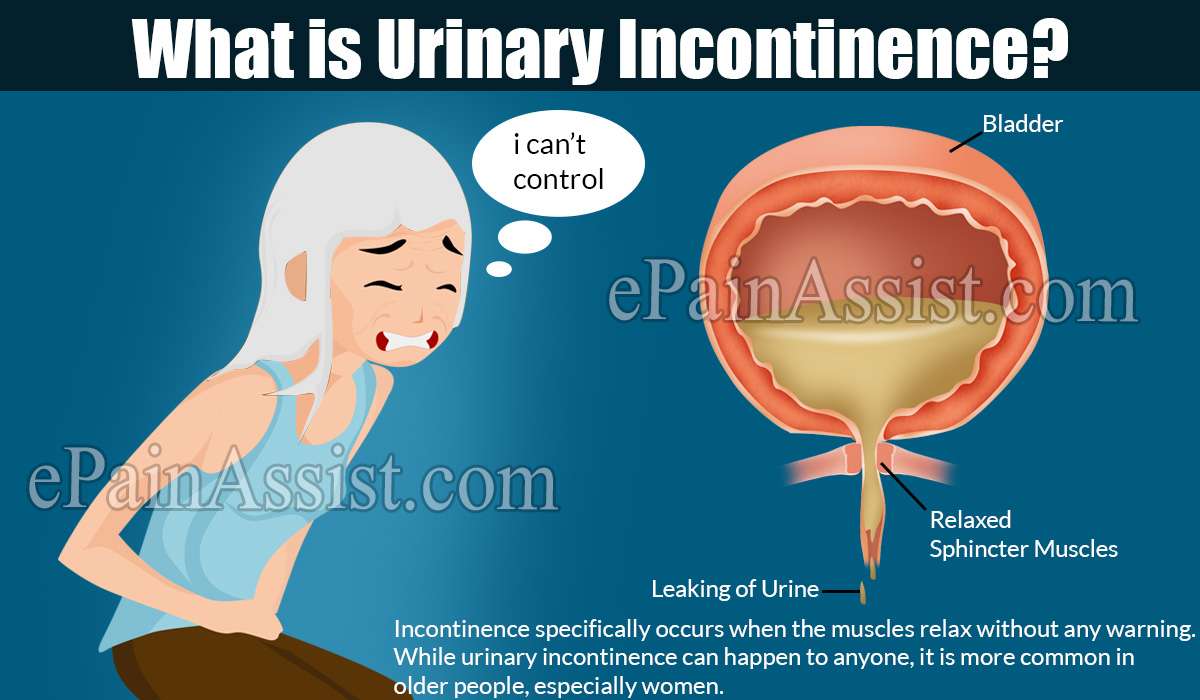
Urinary incontinence means a person leaks urine by accident. While it may happen to anyone, urinary incontinence is more common in older people, especially women. Incontinence can often be cured or controlled. Talk to your healthcare provider about what you can do.
What happens in the body to cause bladder control problems? The body stores urine in the bladder. During urination, muscles in the bladder tighten to move urine into a tube called the urethra. At the same time, the muscles around the urethra relax and let the urine pass out of the body. When the muscles in and around the bladder dont work the way they should, urine can leak. Incontinence typically occurs if the muscles relax without warning.
You May Like: Azo Maximum Strength Urinary Pain Relief Reviews
Incontinence And Alzheimers Disease
People in the later stages of Alzheimers disease often have problems with urinary incontinence. This can be a result of not realizing they need to urinate, forgetting to go to the bathroom, or not being able to find the toilet. To minimize the chance of accidents, the caregiver can:
- Avoid giving drinks like caffeinated coffee, tea, and sodas, which may increase urination. But dont limit water.
- Keep pathways clear and the bathroom clutter-free, with a light on at all times.
- Make sure you provide regular bathroom breaks.
- Supply underwear that is easy to get on and off.
- Use absorbent underclothes for trips away from home.
For more ways to deal with incontinence and other common medical problems in someone with Alzheimers, visit Alzheimers Disease: Common Medical Problems.
Other Types Of Urinary Incontinence
- Overflow incontinence This occurs when a person is unable to empty their bladder completely and it overflows as new urine is produced. It’s often found in people with diabetes or spinal cord injuries.
- Mixed incontinence You show evidence of more than one type.
- Functional incontinence This type of incontinence has less to do with a bladder disorder and more to do with the logistics of getting to a bathroom in time. It’s usually found in elderly or disabled people who have normal or near normal bladder control but cannot get to the toilet in time because of mobility limitations or confusion.
- Nocturia The need to urinate twice or more during the night, usually affecting men and women over the age of 60. In men, nocturia can be a symptom of an enlarged prostate.
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Self Care
How To Deal With Elderly Incontinence
Your loved one may feel embarrassed by their accidents and avoid scheduling a doctors appointment. They may be using absorbent pads or protective underwear to help, but urinary incontinence is very treatable with medical assistance.
They may also hold off because theyre unsure what kind of doctor to see. A primary care doctor, geriatrician, nurse practitioner, or urinary specialist are viable options. If your loved one feels comfortable with their primary care doctor, its generally good to start there.
Women can also find a urogynecologist, while men can visit a urologist.
Behavioral Therapy: The First Treatment For Urinary Incontinence In The Elderly
After a diagnosis is made, behavioral therapy is often the first urinary incontinence treatment for the elderly. This may involve:
Learning to delay urination
You can do this by gradually lengthening the time between bathroom trips. One can also practice double voiding, which is when a person urinates, waits for a few minutes, and then urinates again. This teaches the person to drain their bladder more thoroughly.
Scheduled bathroom visits
This is often effective for people with mobility issues or neurological disorders, even if this means someone else is in charge of taking you to the restroom.
Don’t Miss: Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotic Medicine
How Is Urinary Incontinence Diagnosed
Urinary incontinence is easy to recognize. The primary symptom most people experience is an involuntary release of urine. But the type and cause of the incontinence can be more difficult to determine and may require a variety of exams and tests. Most physicians will use the following:
A bladder diary Your doctor may have you track your fluid intake and output over several days. This may include any episodes of incontinence or urgency issues. To help you measure the amount of urine you pass during an episode of incontinence, you may be asked to use a calibrated container that fits over your toilet to collect the urine.
Urinalysis A urine sample can be checked for infections, traces of blood, or other abnormalities, such as the presence of cancer cells. A urine culture can assess for infection urine cytology looks for cancer cells.
Blood tests Blood tests can look for chemicals and substances that may relate to conditions causing the incontinence.
Pelvic ultrasound In this imaging test, an ultrasound device is used to create an image of the bladder or other parts of the urinary tract to check for problems.
Postvoid residual measurement In this procedure, the patient empties the bladder completely and the physician uses a device to measure how much urine, if any, remains in the bladder. A large amount of residual urine in the bladder suggests overflow incontinence.
UI is usually curable, and if not, then controllable.
Editor’s Picks