Specialized Tests To Diagnose Incontinence
Urology Specialists
Sometimes routine testing does not reveal the underlying cause, and further evaluation is required. You may be referred to a urologist or a urogynecologist for more specialized testing if your health concern is accompanied by pain, recurrent UTIs, blood or protein in the urine, neurological symptoms or muscle weakness, or pelvic organ prolapse. Women with this issue who have a history of radiation or surgery to the pelvic region may also be referred to a urologist.
Urodynamic Testing
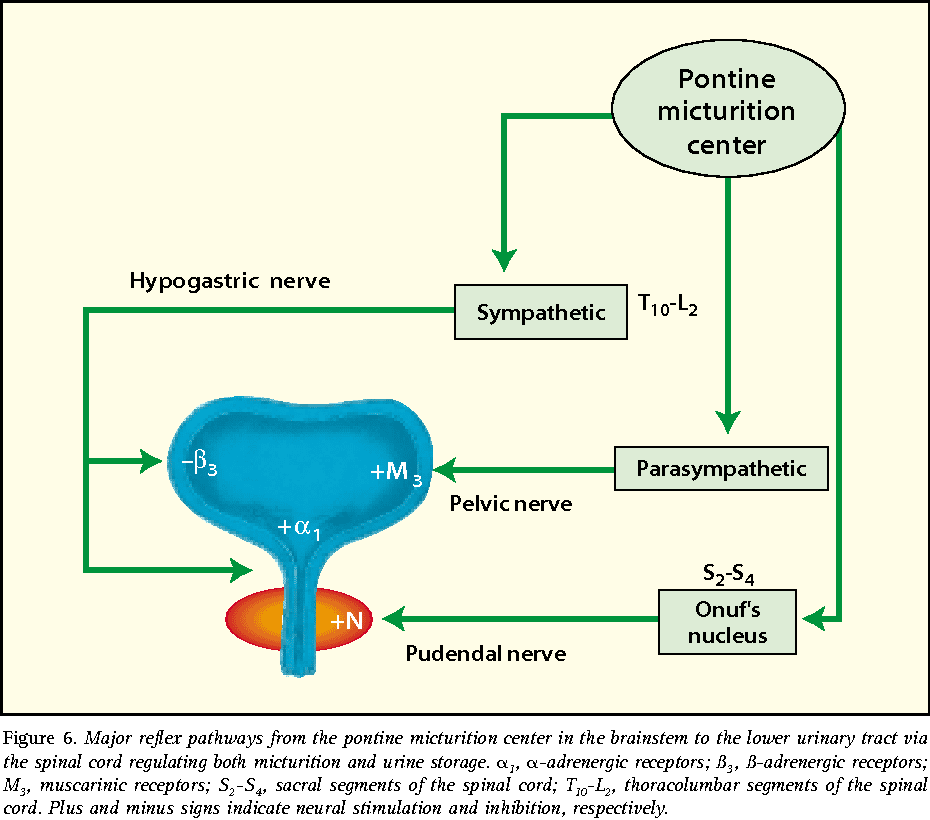
Specialized testing can assess how well the bladder, urethra, and sphincters store and dispose of urine. There are many different types of instruments that can be used for urodynamic testing. Cystometry is a test that is used to help diagnose urge incontinence. It measures bladder pressure. The structures in the pelvis can be visualized with ultrasound. Uroflowometry can measure the volume of urine and flow rate. This test is used to determine the strength of related muscles and helps assess whether urine flow is blocked. There are other tests a urologist may perform depending on your symptoms.
Try Pelvic Floor Therapy
Pelvic floor therapy is a type of specialized physical therapy that strengthens the muscles that support your bladder and bowels. This can be very effective in treating urinary incontinence caused by an overactive bladder.
During pelvic floor therapy, a physical therapist may lead you through exercises that target your pelvic floor, use mild electrical stimulation to help you have more awareness of your pelvic floor muscles, and use other specialized techniques. If youre interested in pelvic floor therapy, talk with a doctor about getting a referral.
Urinary Incontinence In Children
The prevalence of urinary incontinence is 6.39 % in 7-year-olds and 1.14.2 % in children aged 1113 years . General paediatric guidelines distinguish between urinary incontinence related to an overactive bladder, delayed micturitions, bladder sphincter dyssynergia/discoordination, combined forms, giggle incontinence, bladder dysfunction and constipation-related incontinence . Urinary incontinence significantly impairs the quality of life and self-esteem of affected children . In 2015, Maternik et al. published a good review of incontinence as well as the testing and treatment of children.
In general practice, assessment is limited to the medical history, clinical examination and evaluation of drinking/diuresis diaries. In addition, the urine can be tested with urine dipsticks and bacterial cultures if appropriate. General practitioners can also request ultrasound of the kidneys/urinary tract, but if a non-functional cause of incontinence is suspected, the child should be referred to a paediatrician. The Norwegian Enuresis Forum has useful information and micturition diaries available for download from its website .
Read Also: Candida Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
What Is Overactive Bladder
OAB Basics
The condition known as overactive bladder may or may not be associated with urge incontinence. OAB refers to sudden, uncontrollable bladder contractions. When these contractions are associated with leaks, urge incontinence is also present. OAB is disruptive because strong, frequent bladder contractions prompt numerous trips to the bathroom throughout the day and sometimes also at night. OAB can interfere with work, fitness, and social life. If you get up multiple times at night to urinate, OAB can also keep you from getting a good night’s sleep.
A Common Problem
OAB is an extremely common disorder. Approximately 33% of people in the United States have OAB. An estimated 40% of women in the U.S. have the condition. Despite the fact that millions of people and a large percentage of women have OAB, it is not normal and you don’t have to live with uncomfortable, limiting symptoms. There are treatments that can help.
History And Physical Examination
A preliminary diagnosis of urinary incontinence can be made on the basis of a history, physical examination and a few simple office and laboratory tests. Initial therapy may be based on these findings. If complex conditions are present or if initial treatments are unsuccessful, definitive specialized studies are required. Because urinary incontinence is a common condition, patients being examined for another problem may mention episodes of urinary incontinence. For instance, patients presenting with cold symptoms may remark that every time they cough, they âleakâ urine. Rather than attempt a complete evaluation for urinary incontinence during that visit, the physician can ask a few simple screening questions.
Table 1 lists a few key questions that can provide information on the severity of urinary incontinence and help distinguish the major subtypes. If the patient answers affirmatively to these screening questions, a 24-hour âbladder diaryâ can be given to the patient to complete . The diary entries can then be reviewed at a subsequent office visit. An algorithm for the evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence is provided in Figure 2.
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infection In Elderly
What Causes Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable result of aging, but it is particularly common in older people. It is often caused by specific changes in body function that may result from diseases, use of medications and/or the onset of an illness. Sometimes it is the first and only symptom of a urinary tract infection. Women are most likely to develop urinary incontinence during pregnancy and after childbirth, or after the hormonal changes of menopause.
Lack Of Continuity Or Deformity
The most common cause of incontinence in this category is a fistula. In developed countries, vesicovaginal or ureterovaginal fistulas typically arise as complications of hysterectomy or other pelvic surgery.6 Patients with other abnormalities such as ectopic ureters and diverticulae can also present with incontinence.
Don’t Miss: Can Urinary Tract Infection Go Away Without Antibiotics
Types Of Female Incontinence
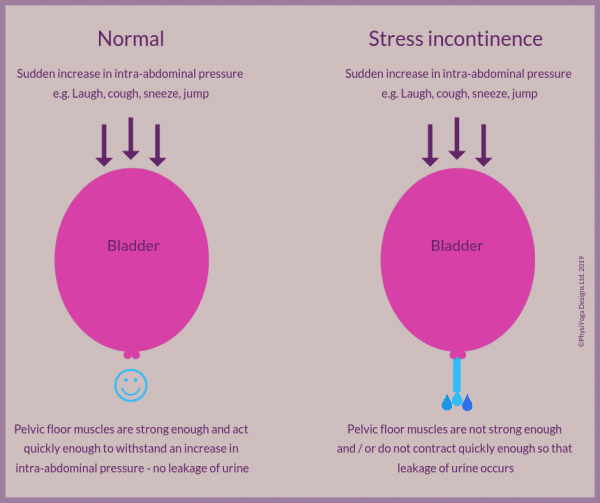
Knowing what type of incontinence you have, is the first important step to finding the right treatment. Once diagnosed, your GP can then advise you what treatment options are available for your specific type of incontinence. While there are several types, the three most common types of female incontinence are stress, urge and overflow incontinence.
Stress incontinence is physical stress or pressure on your internal organs such as a cough, a sneeze or even a laugh when your bladder is full. Read more about stress incontinence.
Urge incontinence is the inability to hold on for more than a few minutes once you have a sudden overwhelming need to urinate. Read more about urge incontinence.
Overflow incontinence is characterised by leaking with no warning or urge to urinate. Read more about overflow incontinence.
What Increases Your Risk
Sometimes several things combine to cause urinary incontinence. For example, a woman may have had multiple childbirths, be older, and have a severe cough because of chronic bronchitis or smoking. All of these might contribute to her incontinence problem.
Physical conditions that make urinary incontinence more likely include:
- Pregnancy and vaginal delivery.
Medicines and foods that may make urinary incontinence worse include:
- Caffeinated and carbonated drinks, such as coffee, tea, and soda pop.
- Alcohol drinks.
- Prescription medicines that increase urine production or relax the bladder .
Read Also: Royal Canin Vet Diet Urinary S O
What Are The Symptoms
The main symptom is the accidental release of urine.
- If you have stress incontinence, you may leak a small to medium amount of urine when you cough, sneeze, laugh, exercise, or do similar things.
- If you have urge incontinence, you may feel a sudden urge to urinate and the need to urinate often. With this type of bladder control problem, you may leak a larger amount of urine that can soak your clothes or run down your legs.
- If you have mixed incontinence, you may have symptoms of both problems.
What Is Female Incontinence
For many women, female incontinence means losing just a few drops of urine when they laugh, sneeze, cough, jog, make love, or even hear running water, when washing the dishes or walking past a fountain.
Female incontinence is widespread and affects women of all ages, including young adults and sometimes even children. Incontinence can be caused by everyday habits, underlying medical conditions, and minor and serious physical problems that can affect both young and old, healthy and ailing.
Some women learn to quickly bring mild incontinence under control by sitting down or crossing their legs tightly. While for others, female incontinence may be a sudden urge to go to the toilet, followed by significant amount of liquid loss.
If youre finding youre experiencing an episode of leakage, take heart that you are not alone. Youll probably discover some of your friends are going through the same thing, as 1 in 3 women experience light bladder leakage. The other thing youll discover is that female incontinence is also entirely treatable.
Don’t Miss: How To Clean Out Urinary Tract
Number Of Deliveries In Younger Women With And Without Ui
See Table 2. UI was more common among younger women who had given birth to one child compared with women who had not given birth , and also when we compared women who had given birth to two children with women who had not given birth . However, UI was reported by 23% of younger, nulliparous women and most frequently in the UI group.
Clues From Young Women
Davis’ study has made her consider doing her own research in younger women who’ve never been pregnant, Buchsbaum says.
“We are in some ways so focused on childbirth being the main risk factor for urinary incontinence that we neglect women who have not given birth,” says Buchsbaum, who has shown that older nuns who’ve never been pregnant deal with incontinence. “We know so little about the pathophysiology . Looking at really young women might help us to understand things a little bit further.”
Emerging evidence shows that incontinence before conception predisposes women to pregnancy-related urinary incontinence, Davis and the other researchers write.
Buchsbaum says she has seen patients as young as 14 and 15 who are dealing with stress incontinence, which older women know is what sometimes happens when they cough or sneeze. Her youngest patients are usually involved in sports or cheerleading, Buchsbaum says. “They leak quite a bit.”
An ideal study of urinary incontinence would begin with teenagers and follow them to age 50 or 60, she says. That’s not possible with the young women Davis studied, because although they provided demographic information, they were not asked to put their names on the questionnaires.
Davis’ study is published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Show Sources
You May Like: Can Cranberry Juice Cure A Urinary Tract Infection
Keeping A Bathroom Journal
You may be asked to keep a bathroom journal before or after your appointment. In your journal, youll log all your bathroom trips and bladder leakage or issues. It can also be helpful to record what you eat and drink in your bladder journal. This record will help your doctor get a more accurate idea of your symptoms and how often they occur. Keeping a journal can also determine what triggers your need to pee or any accidents.
A Condition That Affects All Ages
When you think of Urinary Incontinence, you generally associate it with middle to old age. While many older people do experience Urinary Incontinence, it is also quite prevalent in young adults. There are so many reasons for young adults to acquire this condition, its more common than you would think.
According to the National Association for Continence, an estimated one third of Americans have experienced loss of bladder control at some point in their life. Apparently, 17% of those people are ages 30 39. Another Survey taken by the National Association for Continence reveals 24% of women ages 25 44 have experienced Urinary Incontinence. Researchers have found in a study of 1,000 women aged 16 to 30, who had never been pregnant, found one in eight had incontinence. The most common type of Urinary Incontinence found in women is Stress Urinary Incontinence.
While the statistics provided above discuss Urinary Incontinence in women, it greatly affects men as well. It is said that women experience bladder leakage twice as much as men. This may be due to the fact that men are less likely to report bladder leakage. Studies show that many young men would rather admit to impotence than incontinence. The most common type of Urinary Incontinence in young men is Overactive Bladder. It is very common. Almost more so than diabetes.
Also Check: How To Clean My Urinary Tract
What Are The Symptoms Of Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence is the unwanted loss of urine that is associated with a variety of activities such as:
- Changing positions.
The severity of leakage can vary greatly. For some women it can require a severe stress such as running a marathon or a powerful sneeze. In others, the simple motion of rolling over in bed can cause the loss of urine. There is no specific amount of leakage that is considered a cutoff for treatment. The problem is severe enough to be treated when you want it treated, whether it is 20 times daily or 20 times yearly.
Data Collection Questionnaire And Procedure
A questionnaire was tested in a pilot study, which included 20 consecutive women who visited a primary health care centre during one day. The pilot study took place 2 months before the final questionnaire was mailed. The questionnaire contained nine dichotomous questions concerning age, number of deliveries, employment status, use of contraceptives or oestrogen substitutions , physical exercise, smoking habits, UTIs and UI.
The question on UI was defined in the questionnaire as For the present time do you have a problem with involuntary loss of urine ? After 3 and 6 weeks, a postal reminder was sent to the non-responders, accompanied by the questionnaire.
Read Also: Urinary Incontinence In Child Treatment
Amping Up Your Treatment: Medications And Surgery
When more conservative measures have failed, medications – then surgery – are the alternatives, says Galloway.
Medications: No drug helps with stress incontinence, but a class called anticholinergics does help with urge incontinence.
These drugs include Detrol, Oxytrol, Ditropan, and Sanctura — all with similar effectiveness and similar side effects, like dry mouth and constipation, says Galloway.
Medications like Enablexand Vesicare are more effective in controlling the bladder, but don’t cause constipation, he adds.
A transdermal patch called Oxytrol has also been effective, says Galloway, who adds that skin irritation at the patch site does occur in some patients.
Surgery: There are 300 surgical options to treat incontinence, says Brubaker.
“The hard part is picking the surgery that has the best chance of working well for that woman long-term,” he says. “Surgery can create problems. It can cause difficulty in urinating, worsen an urge incontinence problem, or it can do nothing to solve the problem.”
“It helps the urethral sphincter remain closed when abdominal pressure tries to open it. At least, we think that’s how it works,” he says. “We have only five-year outcomes on one group of these devices. But they look promising.”
“Before having any surgery, ask your doctor for names of other patients who have had the procedure in question,” says Galloway.
“Talk to them, find out how it worked. You’ll be in a much better position to decide what to do.”
Show Sources
Other Types Of Incontinence
The main symptom of urinary incontinence is a problem controlling urination.
- Symptoms of stress incontinence:
- Involuntary release of urine, especially when you cough, sneeze, or laugh
- Leaking a small to moderate amount of urine
It is common for a woman to have symptoms of both types of incontinence. This is called mixed incontinence.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Pain Relief For Males
How Is Incontinence Evaluated
The first step toward relief is to see a doctor who has experience treating incontinence to learn what type you have. A urologist specializes in the urinary tract, and some urologists further specialize in the female urinary tract. Gynecologists and obstetricians specialize in the female reproductive tract and childbirth. A urogynecologist focuses on urinary and associated pelvic problems in women. Family practitioners and internists see patients for all kinds of health conditions. Any of these doctors may be able to help you. In addition, some nurses and other health care providers often provide rehabilitation services and teach behavioral therapies such as fluid management and pelvic floor strengthening.
To diagnose the problem, your doctor will first ask about symptoms and medical history. Your pattern of voiding and urine leakage may suggest the type of incontinence you have. Thus, many specialists begin with having you fill out a bladder diary over several days. These diaries can reveal obvious factors that can help define the problem — including straining and discomfort, fluid intake, use of drugs, recent surgery, and illness. Often you can begin treatment at the first medical visit.
If your diary and medical history do not define the problem, they will at least suggest which tests you need.
Behavioral Remedies: Bladder Retraining and Kegel Exercises
How do you do Kegel exercises?
Medicines for Overactive Bladder
Biofeedback
Neuromodulation
Catheterization
Urinary Incontinence In Women: What You Need To Know
-
Urinary incontinence is the accidental loss of urine.
-
Over 25 million adult Americans experience temporary or chronic urinary incontinence.
-
This condition can occur at any age, but it is more common in women over the age of 50.
-
There are four types of urinary incontinence: urgency, stress, functional and overflow incontinence.
-
Behavioral therapies, medications, nerve stimulation and surgery are some of the treatments available for managing urinary incontinence.
You May Like: How Does A Urinary Tract Infection
Types Of Urinary Incontinence
The key to accurate diagnosis of urinary incontinence is consideration of all possible causes during the initial assessment. Most cases of urinary incontinence fall under one of the following six major subtypes: stress incontinence, overactive bladder, mixed incontinence, overflow incontinence, lack of continuity or deformity, or functional incontinence.