What Is The Food Can Help To Cure Urine Retention
If you are suffering from chronic urine retention then changing your diet can help to get rid of this problem.
- Drink more coconut water to ease the difficulty in passing urine.
- Increase the intake of water.
- It will help to flush out harmful toxins and prevent infection.
- Avoid acidic and spicy food.
- Do drink sugary soft drinks.
- Avoid drinking too much coffee.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Add cucumber, watermelon, muskmelon to your diet to prevent urine retention.
- Raisins also help to treat urine retention at home.
Who Is At Risk For Urinary Retention
Those at the greatest risk of suffering from urinary retention include:
- Men more than women
- People over the age of 50
- Those who suffer from shy bladder
- Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Men due to prostate issues
- Those who take NSAIDs or drugs with anticholinergic properties
- Those who suffer from substance abuse
- Those who have suffered certain muscle damage
- Those who have suffered neurological damage
- Those who go under general or spinal anesthesia
- Those who are being operated on for longer than 2 hours
- Those with Parkinsons disease
- Those with cancer of any part of the urinary system
Appendix A: Search Strategy
Database: Ovid MEDLINE®< 1946 to November Week 3 2012> Search Strategy:
Read Also: What Can Cause Urinary Retention
Myrbetriq Has Few Side Effects Which Are Mostly Tolerable
Mirabegron has been used for many years in thousands of patients. It is well-tolerated by most patients. In some patients, it may cause increased high blood pressure, and for this reason, blood pressure monitoring is recommended. This drug should not be used in patients who have uncontrolled high blood pressure to start with.
Talk to board-certified urologists at New York Urology Specialists today to see if Myrbetriq may be right for you. We offer treatment for overactive bladder in Manhattan, and we see patients from all New York City boroughs, other cities, and overseas.
What Causes Chronic Urinary Retention
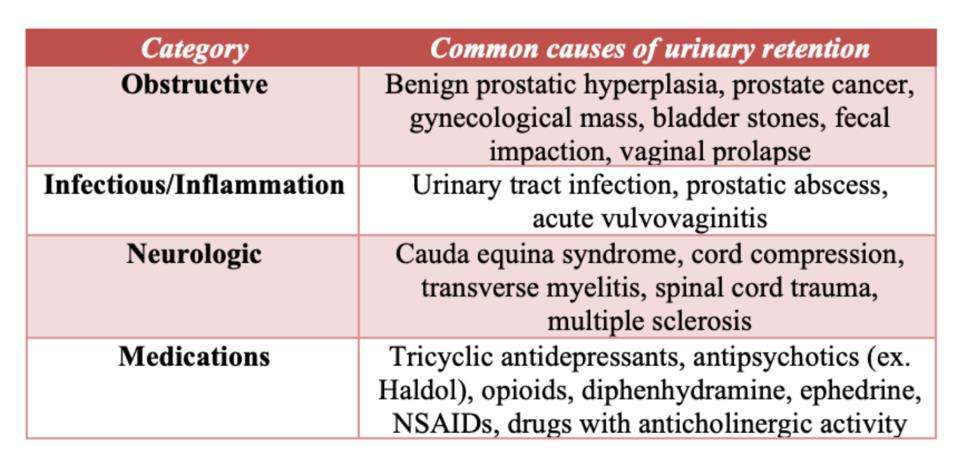
Urinary retention can happen for several different reasons. These causes can include:
- A blockage to the way urine leaves your body.
- Medications youre taking for other conditions.
- Nerve issues that interrupt the way your brain and urinary system communicate.
- Infections and swelling that prevent urine from leaving your body.
- Complications and side effects of medications given to you for a surgical procedure.
Blockage
When something blocks the free flow of urine through the bladder and urethra, you might experience urinary retention. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body. In men, a blockage can be caused when the prostate gland gets so big that it presses on the urethra. This is the most common cause of chronic urinary retention in men. One cause in women is a bladder that sags. This is called cystocele. It can also be caused when the rectum sags into the back wall of the vagina a condition called rectocele. Some causes can happen to both men and women. The urethra can get narrow due to scar tissue. This is called a stricture. Urinary stones can also block the flow of urine out of your body.
Medications
Nerve issues
- Trauma to the spine or pelvis.
- Pressure on the spinal cord from tumors and a herniated disk.
- Vaginal childbirth.
Urinary retention from nerve disease occurs at the same rate in men and women.
Infections and swelling
Surgery
Read Also: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Urinary S O Moderate Calorie
How Is Chronic Urinary Retention Diagnosed
History and physical exam: During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and how long you have had them. He or she will also ask about your medical history and your drug use. A physical exam of the lower abdomen may show the cause or give your provider additional clues. After this, certain tests may be needed. Men may have a rectal exam to check the size of their prostate.
Your urine may be saved and checked to look for infection.
Ultrasound of the bladder: The amount of urine that stays in your bladder after urinating may be measured by doing an ultrasound test of the bladder. This test is called a postvoid residual or bladder scan.
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a test in which a thin tube with a tiny camera on one end is put into your urethra. This lets the doctor look at pictures of the lining of your urethra and bladder. This test may show a stricture of the urethra, blockage caused by a stone, an enlarged prostate or a tumor. It can also be used to remove stones, if found. A computed tomography scan may also help find stones or anything else blocking the flow of urine.
Urodynamic testing: Tests that use a catheter to record pressure within the bladder may be done to tell how well the bladder empties. The rate at which urine flows can also be measured by such tests. This is called urodynamic testing.
Evaluation And Treatment Of Acute And Chronic Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition that makes it difficult, if not impossible, to fully empty your bladder. Even after using the restroom, youll still feel like you need to urinate but youre unable to void more urine. Its a condition that often occurs due to other health or urologic problems and is more common as you get older. While men are 10 times more likely to experience urinary retention, it can and does still occur in women.2 In this article, well discuss the evaluation and treatment of acute and chronic urinary retention.
Don’t Miss: Myasthenia Gravis And Urinary Incontinence
Surgical Treatment Is Necessary For Some Cases These Treatments Might Include:
- Prostate surgery. The most common surgery is transurethral resection of the prostate. In this procedure, the urologist uses a tiny tool, inserted through a catheter, to remove a section of the prostate. This treatment is used frequently for urinary retention caused by BPH.
- Internal urethrotomy. When there is a stricture that cannot be resolved by widening, a urologist can open the stricture with an incision. The procedure is performed via a special catheter inserted into the urethra.
- Cystocele or rectocele repair. Women whose bladder or rectum has fallen may need surgery to return the organs to their normal position. A urologist specializing in female reproductive surgery will repair any defects in the tissue of the vaginal wall. This repaired tissue then will be strong enough to hold the organs in their proper places, restoring normal urinary retention function.
- Removal of tumors or cancer. If the cause of the urinary retention is a tumor or cancerous tissue in the urethra, bladder or prostate, removing those tissues may reduce the problem.
Review Of Key Questions
For all Evidence-based Practice Center reviews, Key Questions were reviewed and refined as needed by the EPC with input from Key Informants and the Technical Expert Panel to assure that the questions are specific and explicit about what information is being reviewed. In addition, the Key Questions were posted for public comment and finalized by the EPC after review of the comments.
Also Check: Urinary Tract Infection Kidney Pain
Urinary Retention In Adults: Evaluation And Initial Management
DAVID C. SERLIN, MD JOEL J. HEIDELBAUGH, MD and JOHN T. STOFFEL, MD, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Am Fam Physician. 2018 Oct 15 98:496-503.
Urinary retention is the inability to voluntarily pass an adequate amount of urine and can be attributable to acute and chronic etiologies. Acute urinary retention is a urologic emergency characterized by the sudden inability to urinate combined with suprapubic pain, bloating, urgency, distress, or, occasionally, mild incontinence.1 Chronic urinary retention is usually associated with non-neurogenic causes, is often asymptomatic, and lacks consensus on defining criteria. The overall incidence of urinary retention is much higher in men than women and increases dramatically as men age. Estimates for men range from 4.5 to 6.8 per 1,000 person-years, increasing up to 300 per 1,000 person-years for men in their 80s, whereas the incidence in women is only seven per 100,000 per year.24
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Initial evaluation of the patient with suspected urinary retention should involve a detailed history, including current use of prescription and over-the-counter medications and herbal supplements.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Initial evaluation of the patient with suspected urinary retention should involve a detailed history, including current use of prescription and over-the-counter medications and herbal supplements.
What Causes Urinary Retention
- Blockages, such as a stone, growth, or narrowing of your urethra
- A weak bladder muscle
- Nerve damage from diabetes, stroke, or spinal cord injury
- Bladder diverticula, which are pockets of urine that form in your bladder and do not empty
- Certain medicines, such as narcotics, antihistamines, or antidepressants
Read Also: Urinary Tract Infection Men Home Treatment
What Symptoms Would I Have With A Rectocele
Many women with a rectocele have no symptoms, and the condition is only seen in a pelvic examination. In general, if a rectocele isnt causing you symptoms or discomfort, it can be left alone.
When symptoms are present, you may have:
- Difficulty having bowel movements.
- The need to manually reduce the bulge in your vagina to have a bowel movement.
A rectocele should be treated only if your symptoms interfere with your quality of life.
Legal Approval In The United States

At the present time, there is one temporary prostatic stent that has received approval. The Spannertemporary prostatic stent maintains urine flow and allows natural voluntary urination. The prostatic stent is a completely internal device and can be inserted and removed as easily as a . It permits normal bladder and sphincter functioning and can be worn comfortably by patients. The temporary prostatic stent is typically used to help patients maintain urine flow after procedures that cause prostatic swelling, such as brachytherapy, cryotherapy, TUMT, TURP. It has also become an effective differential diagnostic tool for identifying poor bladder function separate from prostatic obstruction.
Recommended Reading: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Urinary Tract Infections
What Is The Long
The degree of success after rectocele repair depends on a number of factors, including:
- Type of symptoms present.
- Length of time the symptoms have been present.
- Surgical method and approach taken.
Studies show about 75% to 90% of patients have significant improvement but this level of satisfaction decreases over time.
What Is Chronic Urinary Retention
Chronic urinary retention happens over a long period of time and slowly presents itself. Because of this, many people dont even realize they have chronic urinary retention because its unaccompanied by other symptoms at first or they are so minor that you dont notice them. However, over time, chronic urinary retention can also become dangerous and can result in serious complications.
Since chronic urinary retention happens gradually, the symptoms are often less intense and can easily be mistaken for other urologic conditions. Symptoms of chronic urinary retention include:2
- Feeling like you need to urinate frequently, often eight or more times a day
- Difficulty starting your urine stream
- Weak urine stream
- Feeling of fullness in pelvis/lower abdomen
Recommended Reading: Physical Therapy For Urinary Incontinence
What Is Acute Urinary Retention
As we mentioned, urinary retention is when your bladder doesnt fully empty while using the restroom, even if its still full. Although you will still feel the need to urinate, you cant empty your bladder. Urinary retention comes in two forms, acute and chronic.
Acute urinary retention is when it happens suddenly. Youre unable to urinate, even though your bladder is completely full. Acute urinary retention often only lasts a short time, but it can cause severe pain and even be life threatening.1 Due to the severity of acute urinary retention, its considered a urologic emergency and requires immediate medical care. The primary symptom that youll experience with AUR is a feeling like you need to use the bathroom but cant accompanied by high levels of pain or discomfort in your lower abdomen.2
Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
Acute urinary retention requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include:
- A complete inability to pass urine
- A painful urge to urinate
- Pain or swelling in your lower abdomen
Chronic urinary retention symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Trouble starting urination
- Weak or intermittent urination stream
- A feeling of needing to urinate after finishing urination
You May Like: What Can I Do To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
What Are The Possible Complications Of Urinary Retention
The complications of urinary retention and its treatments may include:
UTIs: the normal flow of urine usually prevents germs from infecting the urine. With urinary retention, bacteria may be able to infect the urine because the urine cannot flow out of the bladder.
Bladder damage: if the bladder becomes stretched too far or for long periods, the muscles may become damaged and unable to work properly.
Chronic kidney disease: for some people, urinary retention causes urine to flow backwards into the kidneys. This backward flow is called reflux and it may damage or scar the kidneys.
Urinary incontinence: this may occur together with chronic urinary retention or after surgery .
Prostate gland surgery may cause urinary incontinence in some men. This problem is often temporary and gets better quite quickly. Most men recover their bladder control in a few weeks or months after surgery.
Urinary Retention In Young Women: Fowlers Syndrome
Fowlers syndrome is a fairly rare type of non-obstructive urinary retention that affects young women. It is thought that the problem is related to dysfunction of the urinary sphincter that does not work in sync with the bladder muscle. Interstim neuromodulation has been shown to be a benefit to women with Fowlers syndrome as having Botox injections in the sphincter muscles.
We offer effective treatment options for non-obstructive urinary retention. Treatments such as urinary catheterization, urethral Foley catheters, and suprapubic catheters can help the bladder to empty.
If you have any questions, to schedule a consultation or if you need a second opinion, pleasecontact us or call:
Dr. Alex Shteynshlyuger is a board-certified urologist in NYC who specializes in treating men and women with urinary problems including retention of urine, frequent urination, difficulty emptying the bladder, urinary urgency and incontinence.
We see patients from all parts of New York City , Long Island, Westchester and New Jersey as well as other parts of the USA. We also see from Canada, Japan, South America, Russia, Asia, Europe, Middle East, Africa, the Caribbean and other parts of the world.
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Male Urinary Tract Infection
How Is A Cystocele Diagnosed
A Grade 2 or Grade 3 cystocele can be diagnosed from a description of symptoms and from an examination of the vagina.
The doctor may also perform certain tests, including the following:
- Urodynamics: Measures the bladders ability to hold and release urine.
- Cystoscopy : A long tube-like instrument is passed through the urethra to examine the bladder and urinary tract for malformations, blockages, tumors, or stones.
Urinary Retention Without Blockage: Interstim To The Rescue

Urinary retention without blockage as its underlying cause is difficult to treat. Men and women regardless of age have typically been married to urinary catheterization for life. Fortunately, for many men and women regardless of age who cannot empty their bladder without a catheter, Interstim for treatment of non-obstructive urinary retention offers hope of living the life catheter-free. The remarkable success of Interstim in helping men and women with urinary retention live fuller lives is appreciated by many men and women who have been successfully treated with Interstim. Many patients are able to stop catheterizing completely some may only need to catheterize occasionally.
You May Like: Artificial Urinary Sphincter Surgery Recovery
Does Length Of Catheterization Affect Success Of Interstim Treatment For Non
Surprisingly, the duration of catheterization does not affect the success of Interstim sacral neuromodulation in making people urinate on their own. Many patients who have been using a suprapubic catheter, Foley catheter or doing CIC for many years have the potential to benefit from the Interstim procedure.
When To See A Doctor After Urine Retention
Normally urine retention problem occurs in old people or people with some kind of disease. If the cause for urine retention is some kind of underlying disease or obstruction in the bladder then visit a doctor immediately. For chronic urine retention treatment you donât need to visit the hospital this can be a cure at home with the help of home remedies.
Urine retention can be a very painful and fatal health issue. So if you feel too much pain and sudden blockage of urine then visit a doctor. If you cannot visit a doctor immediately then use natural home remedies for urine retention problems. Leave your question, suggestion, and feedback in the comment box.
Read Also: Kidney Stone In Urinary Tract
When Should Someone Seek Medical Care For An Inability To Urinate
- This condition requires urgent bladder drainage to prevent damage to the bladder, kidneys, and ureter.
- Your doctor may advise you to go to a hospital emergency department without delay.
- If you have symptoms of chronic urinary retention, you should also let your health care provider know, since chronic urinary retention may lead to urinary tract infections, incontinence, further bladder damage, and damage to your kidneys.
Urologists are most often involved in the care of patients with urinary retention. However, women are also often treated by urogynecologists. Internists, family physicians, and emergency-room physicians also frequently treat urinary retention.