New Solution That Eliminates Staph Aureus Gonorrhea Std Syphilis And Other Infections In Few Weeks
Doctors and other medical institutions, have warned that mere toilet infections, if not properly treated can cause staphylococcus, pelvic inflammatory disease , which is one of the major culprit responsible for infertility.
To make it even worse, staphylococcus, STDs and other urinary tract infections comes with painful symptoms such as
- wormlike movement in the body
- itching of private part
- discharge at the tip of the penis
- vaginal discharge
- burning sensation in the body
- frequent urination
If you are experiencing any of these serious infections, then you are not alone. My husband and I suffered from similar problems for about 3 years. We tested positive to staphylococcus aureus.
So we visited several hospitals, tried expensive antibiotics and used lots of products bought from networking companies just so we could get rid of this staph
But sadly, the stubborn infection remained in ourbody system for 3 years!
At that time, the infection affected my fertility, destroyed our immune system and made us suffer painful symptoms.After several trial and errors, I continued searching for a permanent cure until I came in contact with an old time friend, who was a health expert that has now relocated to Canada.
She recommended a NAFDAC Approved herbal treatment that completely cures Staphylococcus, urinary tract infections, and other STDs like Gonorrhea, Syphillis etc.
3. Take herbal medicines that help flush off infections from your body system.
NADI HERBAL CAPSULES
Eye And Cns Infections
The limited published data suggest that linezolid may be considered for the treatment of patients with meningeal or cerebral infections. Animal data suggest that daptomycin may have some advantages over vancomycin owing to its superior bactericidal activity, but there are no dosing recommendations or human data to support this. The evidence of good penetration into the eye and the relative toxicity of acidic vancomycin in delicate tissues mean that comparative assessment of linezolid in Gram-positive eye infections in animals is overdue to permit formulation of appropriate human trials in deep eye infections.
Recommendation 14: There is insufficient evidence to make a specific recommendation in deep eye and CNS infection. Gentamicin, sodium fusidate or chloramphenicol may be used for superficial eye infections if the strain is susceptible.
Sample Size And Sampling Technique
Since there is no previous study on MRSA among UTI suspected in Ethiopia, we used 50% of population proportion formula, and d was the margin of error and adding 10% of the sample size for non-response rate, the total study sample size was calculated as 422 study subjects.
Systematic sampling was performed by estimating the total number of patients in the register of the same study period and study duration in the previous year. K value was calculated by dividing total population by sample size. Then, the first participant was selected based on the value of K. Since k 1, data collection started from the first participant and continues using every other participant until the total sample size was completely filled.
All adult patients suspected of having a UTI and attended the OPD of AMGH during data collection were included and those patients who had received antibiotics within the last two weeks, aged less than 18 years and study participants who were not capable of responding to the questionnaire were not included in this study.
Also Check: Best Food For Feline Urinary Tract Health
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
CLSM images of biofilm inhibition caused by the drug treatment were taken as visual confirmation of the drug action . The fixed biofilms were stained using FITC dye which fluoresces green on attachment to the peptides on the surface of healthy cells constituting the biofilm, while the stain EtBr intercalates with the extracellular DNA formed as a result of the lysis of cells and fluoresces red. Untreated cells were taken as the negative control to further visualize the healthy biofilm. Drug treatments with SarABIM, o-coumaric acid and UTIQQ showed disruption of biofilm, but not much of cell inhibition. Treatment with gentamicin showed cell growth inhibition. When used in combination with UTIQQ, the activity of gentamicin had been confirmed to increase significantly with an increased levels of dead cells in the biofilm.
Figure 10. Live/dead staining observed using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Biofilm of the mixed bacterial population was developed onto glass cover-slips under various conditions of treatment using SarABIM, o-coumaric acid, hybrid drug UTIQQ and antibiotic gentamicin. Control with no drug treatment, SarABIM treatment at MBIC50, o-coumaric acid treatment at MBIC50 , hybrid drug UTIQQ treatment at MBIC50 , Gentamicin treatment at MIC , Synergetic effects of Gentamicin , and UTIQQ .
What Is A Staphylococcal Infection
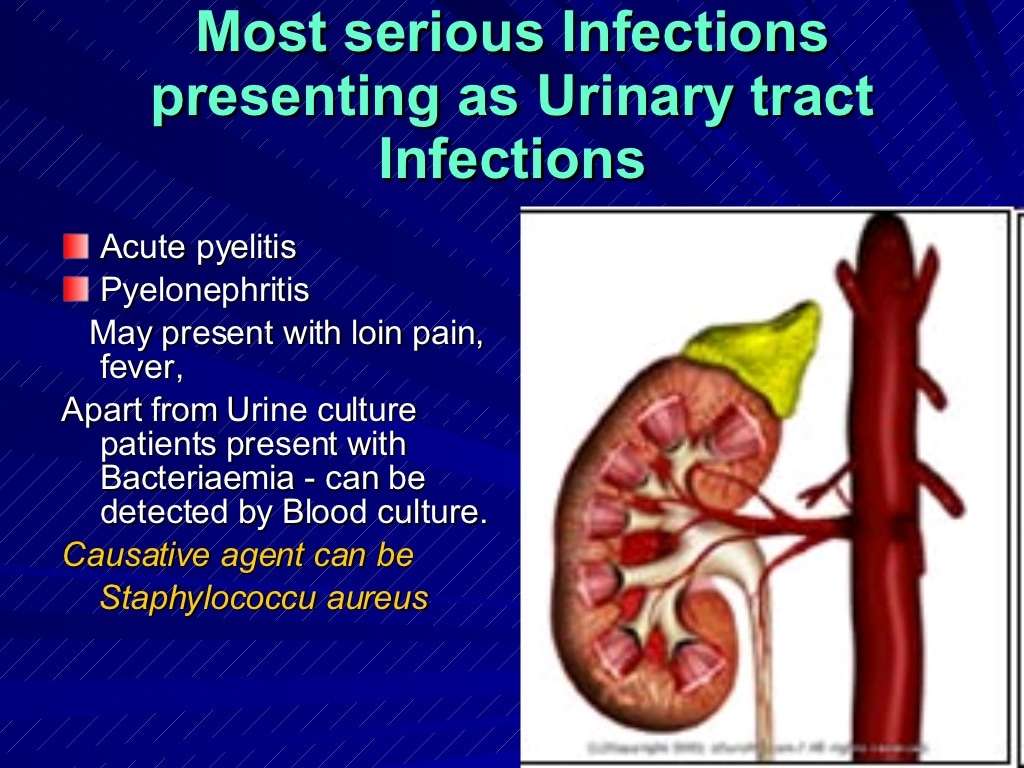
Staphylococcus aureus, or staph, are common bacteria that normally live on the skin. The bacteria also live harmlessly in the nasal passages of roughly 30 percent of the U.S. population. Staph can cause infection when they enter the skin through a cut or sore. Infection can also occur when the bacteria move inside of the body through a catheter or breathing tube.
Staphylococcus aureus, or S. epidermidis, can cause staphylococcal meningitis, an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord caused by it usually develops as a complication of a surgical procedure or a blood-borne infection.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Urinary So Aging Calm
Common Questions About Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women
JAMES J. ARNOLD, DO LAURA E. HEHN, MD and DAVID A. KLEIN, MD, MPH, National Capital Consortium Family Medicine Residency, Fort Belvoir, Virginia
Am Fam Physician. 2016 Apr 1 93:560-569.
Patient information: See related handout on recurrent urinary tract infections, written by the authors of this article.
Urinary tract infections are the most common bacterial infection in women of all ages.1 An estimated 30% to 44% of women will have a second UTI within six months of an initial infection.24 Healthy women with normal urologic anatomy account for most patients who have recurrent UTIs.15
UTI = urinary tract infection.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
Recurrent UTI is typically defined as three or more UTIs in 12 months, or two or more infections in six months.25 Recurrence is thought to occur by ascent of uropathogens in fecal flora along the urogenital tract and by reemergence of bacteria from intracellular bacterial colonies in uroepithelial cells. In either mechanism, the same species that caused the initial infection is typically the reinfecting agent.5
Surgical Site Infection Prophylaxis
Recommendation 16: We see no reason to change our recommendation that patients who require surgery and have a history of MRSA colonization or infection without documented eradication or are at a high risk of MRSA colonization receive glycopeptide prophylaxis alone or in combination with other antibiotics active against other potential pathogens. The use of glycopeptides may also be considered if there is an appreciable risk that patients’ MRSA carriage may have recurred or they come from facilities with a high prevalence of MRSA.
We recommend that the use of aminoglycosides be reassessed for prophylaxis of staphylococcal infections in patients not expected to have MRSA colonization.
Recommended Reading: What Juice Helps Urinary Tract Infections
Determination Of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration And Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
The minimum inhibitory concentration of a compound is the lowest concentration that retards the visible growth of the microorganism, and is a measure of the cell growth parameters. The minimum bactericidal concentration is the lowest concentration of the compound that causes cell viability loss of 99.9%, i.e., only 1 in 1000 cell survives at MBC of a compound. The cell density was measured at 600 nm before the crystal violet biofilm assay to find the effect of the compound on growth. Further the cells were plated after appropriate serial dilutions of upto 108 X fold, in triplicates, onto the Cation-Adjusted Muller-Hinton Agar plates. The observed count of the colony forming units per mL of broth provides a measure of the survival of the cells. Untreated group was taken as negative control. The experiments for in vitro drug response were done twice independently.
Catheterization Alters Bladder Ecology To Potentiate Staphylococcus Aureus Infection Of The Urinary Tract
Staphylococcus aureusS. aureus S. aureus S. aureus E. coli5-7. S. aureus S. aureus S. aureus Enterococcus faecalisS. aureus S. aureus S. aureus Enterococcus sps, Candida spsClostridium difficile S. aureus S. aureus S. aureus S. aureusS. aureus S. aureus References:Clin Infect Dis 48, Infect Dis Clin North Am 26, Oman Med J 27, Indian J Med Sci 66, J Med Microbiol 58, J Assoc Physicians India 61, J Urol 181, Scand J Infect Dis 45, Clin Infect Dis 42, Sci Transl Med 6, Mol Med 17, J UrolJ Leukoc Biol 98,
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection No Symptoms
What Is The Role Of Combination Therapy
The role of combination therapy, particularly with rifampicin or fosfomycin, in addition to a ß-lactam antibiotic, in MSSA, or vancomycin, in MRSA, SA-BSI, is a matter of debate. Theoretically, combination therapy could lead to a higher bactericidal activity compared to antibiotic monotherapy and synergistic effects could occur. Combination therapy may be superior in the eradication of intracellular staphylococci and biofilms on foreign materials and thus reduce the risk of secondary late infection and recurrence .
However, disadvantages of combination therapy, such as drug-related side effects and interactions need to be considered in the benefit-risk assessment. Clinical studies have not shown a benefit of routine combination therapy for all patients with SA-BSI . The multicenter randomized ARREST trial by Thwaites et al. found no significant effect of additional rifampicin on treatment failure, disease recurrence, or death.
Symptoms Of Staph Infections
Skin infections due to Staphylococcus aureus can include the following:
If a doctor suspects osteomyelitis, x-rays, computed tomography , magnetic resonance imaging , radionuclide bone scanning Radionuclide Scanning In radionuclide scanning, radionuclides are used to produce images. A radionuclide is a radioactive form of an element, which means it is an unstable atom that becomes more stable by releasing… read more , or a combination is also done. These tests can show where the damage is and help determine how severe it is. Bone biopsy is done to obtain a sample for testing. The sample may be removed with a needle or during surgery.
Read Also: Urinary Incontinence Devices For Women
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Imaging
Biofilm of mixed bacterial population was developed onto glass cover-slips in a six-well cell culture plate, under various conditions of treatment using SarABIM, o-coumaric acid, hybrid molecule UTIQQ and antibiotic gentamicin. This was performed to assess qualitatively the effects of the UTIQQ on the biofilm of the mixed population. After the biofilms were grown for 24 h, the suspension was aspirated and removed carefully. The biofilm was rinsed delicately in 0.9% NaCl solution. Stock solutions of the fluorescein isothiocyanate and ethidium bromide were prepared beforehand. Five microliter each of the dyes were mixed with 1 mL of cold 0.9% NaCl solution to obtain a working solution. The biofilm was stained with 5 L of the working solution of the dyes for 10 min, and then the excess dye was removed by washing with 0.9% NaCl. The cover-slip was then dried for 2 min in an ambient temperature and then fixed using 50 L of toluene. Confocal imaging was performed using Olympus Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope to obtain the live/dead imaging . MIC of gentamicin at 2 g/mL concentration was used along with the UTIQQ to understand the combinatorial effects.
The Role Of Computerized Decision Systems And Phone Consultations

A structured management in diagnostic and treatment is crucial for an optimal outcome. Several studies have shown that an adherence to treatment guidelines and particularly infectious disease bedside-consultation can lead to a reduction of mortality by up to 50% . Given the limited availability of infectious diseases physicians, who are usually based in larger hospitals and the standardized management outlined above, novel approaches are currently under investigation, such as computerized decision support systems and phone consultations, to improve outcome by providing respective expertise also in smaller hospitals . However, it has yet to be proven whether these approaches are as effective as bedside-consultations by infectious diseases physicians.
Read Also: Silent Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
Clearance Of Enteric Carriage
There are studies that examine the use of enteral vancomycin to prevent MRSA infection in ICU., Lower airway infection and oropharyngeal carriage were reduced in the treatment groups compared with controls. In addition, enteral vancomycin has been used to control an MRSA outbreak in ICU. Despite multiple trials on its use, we remain concerned regarding the potential selection for resistant Gram-positive organisms including enterococci and staphylococci and do not support its regular use.
Recommendation 15: We do not recommend the use of oral vancomycin as prophylaxis or part of clearance regimens for MRSA. In soft tissue lesions, clearance of MRSA should include a systemically active oral or parenteral agent as well as an active nasal cream such as mupirocin. With increased use of mupirocin, mupirocin resistance may become a problem and resistance should be carefully monitored at a local level.
Sample Collection And Processing
During patient urination time, mid-stream urine samples were collected using wide mouthed glass bottles. On the urine sample bottles the patients code, age, and time of urine collection were labeled. Study participants were well advised to sanitise their hands and their genital area with water before collection of 510 mL of clean catch mid-stream urine samples. Urine samples were transported to the microbiology laboratory, department of Medical Laboratory Science, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Arba Minch University. Urine samples were processed, not longer than 2 hours after collection, if there was a delay to process within the 2 hours, samples were kept refrigerated at 4 °C until they were processed.23
You May Like: Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infection In Pregnancy
How To Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections can be very uncomfortable, but there are some measures you can take to prevent them. After urinating or defecating, wipe front to back to prevent bacteria from entering the urethra. Also drink plenty of fluids including cranberry juice, and avoid products such as douches and feminine sprays.
References
Management Of Staphylococcus Aureus Bloodstream Infections
- 1Institute for Infectious Diseases and Infection Control, Jena University Hospital, Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena, Jena, Germany
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine, Jena University Hospital, Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena, Jena, Germany
- 3Center for Sepsis Control and Care, Jena University Hospital, Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena, Jena, Germany
- 4Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine, Department of Medicine I, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
- 5Institute of Medical Microbiology, Jena University Hospital, Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena, Jena, Germany
Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections are associated with a high morbidity and mortality. Nevertheless, significance of a positive blood culture with this pathogen is often underestimated or findings are misinterpreted as contamination, which can result in inadequate diagnostic and therapeutic consequences. We here review and discuss current diagnostic and therapeutic key elements and open questions for the management of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections.
Read Also: Tips For Urinary Tract Infection
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
GC-MS analysis was carried out for the root ethanolic extract of M. dubia using a PerkinElmer Clarus 500 GC-MS system. The program was set at a temperature of 50°C for a duration of 1 min and raised at 10°C/min to 150°C , at 8°C/min to 250°C , at 15°C/min to 300°C . Helium was used as carrier gas. The injector temperature was maintained at 280°C and the mass range was 40450 amu. One microliter of sample dissolved in ethanol was injected into the system. The identification of the compounds was made by comparing their spectra with the National Institute of Standard and Technology spectral library.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Urinary Tract Infections: A Case
Eiyu Matsumoto, MB, and Jennifer R. Carlson, PA-C
Eiyu Matsumoto, MB, and Jennifer R. Carlson, PA-C
Citation:Matsumoto E, Carlson JR. Diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections: a case-based mini-review. Consultant. 2017 57:464-467.
ABSTRACT: Urinary tract infection remains one of the most common indications for prescribing antimicrobial medications in the outpatient setting. Despite the extensive need for treatment of UTIs, the antimicrobial resistance rate has been rising, which has limited the therapeutic options. Application of basic knowledge can not only cure UTIs, but also prevent Clostridium difficile colitis and the development of multidrug-resistant organisms. For these reasons, primary care providers need to be knowledgeable and proficient in the diagnosis and management of UTIs. Three clinical cases, each with their own teaching points, are presented in this review.
KEYWORDS: Urinary tract infection, cystitis, pyelonephritis, asymptomatic bacteriuria, antibiotics
Urinary tract infection is the most common bacterial infection encountered in the ambulatory care setting in the United States, accounting for 8.6 million visits in 2007.1 Acute cystitis is more common than acute pyelonephritis, with an estimated ratio of 28 cases of cystitis to 1 case of pyelonephritis.2
Case 1
Don’t Miss: What Can Cause A Urinary Tract Infection In Males
Determination Of Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration
Briefly, 100 l inoculum of S. aureus ATCC 25923 was plated onto polystyrene microtiter plates in the proportion 1:200 from an overnight culture. Culturing was done in artificial urine media . Varying concentrations of UTIQQ ranging from 1 to 100 g/mL were added, in triplicates. After 24 h, the planktonic cells were removed. PBS wash was done thrice and the cells were fixed using 100 L of 99% methanol. Then 150 L of 0.2% crystal violet was used for 20 min to stain the biofilm cells. Excess stains were removed by washing under slow-flowing cold tap water and the plates were air dried. Again, 33% acetic acid was used to elute the bound crystal violet and the optical reading was read in an ELISA plate reader at 595 nm . The lowest concentration of the compound that inhibits the biofilm by 50% compared to untreated culture control is the minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration and that by 90% is MBIC90.